前言:
以下都是nefu暑假集训的训练题,我在此把我的模板和写的一些练习题汇总一下并分享出来,希望在能满足我复习的情况下能帮助到你。
正文:
模板:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=mod;
typedef struct{
ll m[n][n];//一个n*n的矩阵,注意矩阵不能太大,若太大则不能给他写成结构
};
matrix P={
//内部填写自己经过推导构造出来的矩阵
};
matrix I={
//内部填写自相应大小的单位矩阵
};
matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){//对两个大小为n*n的矩阵进行相乘并取模操作
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<n;k++){
a.m[i][k]=(a.m[i][k]%mod+mod)%mod;
b.m[k][j]=(b.m[k][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%mod;
}
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix quickpow(ll n){//对矩阵进行快速幂操作
matrix m=P,b=I;
while(n){
if(n&1)b=mul(b,m);
n>>=1;
m=mul(m,m);
}
return b;
}这是矩阵连乘的基础模板
习题:
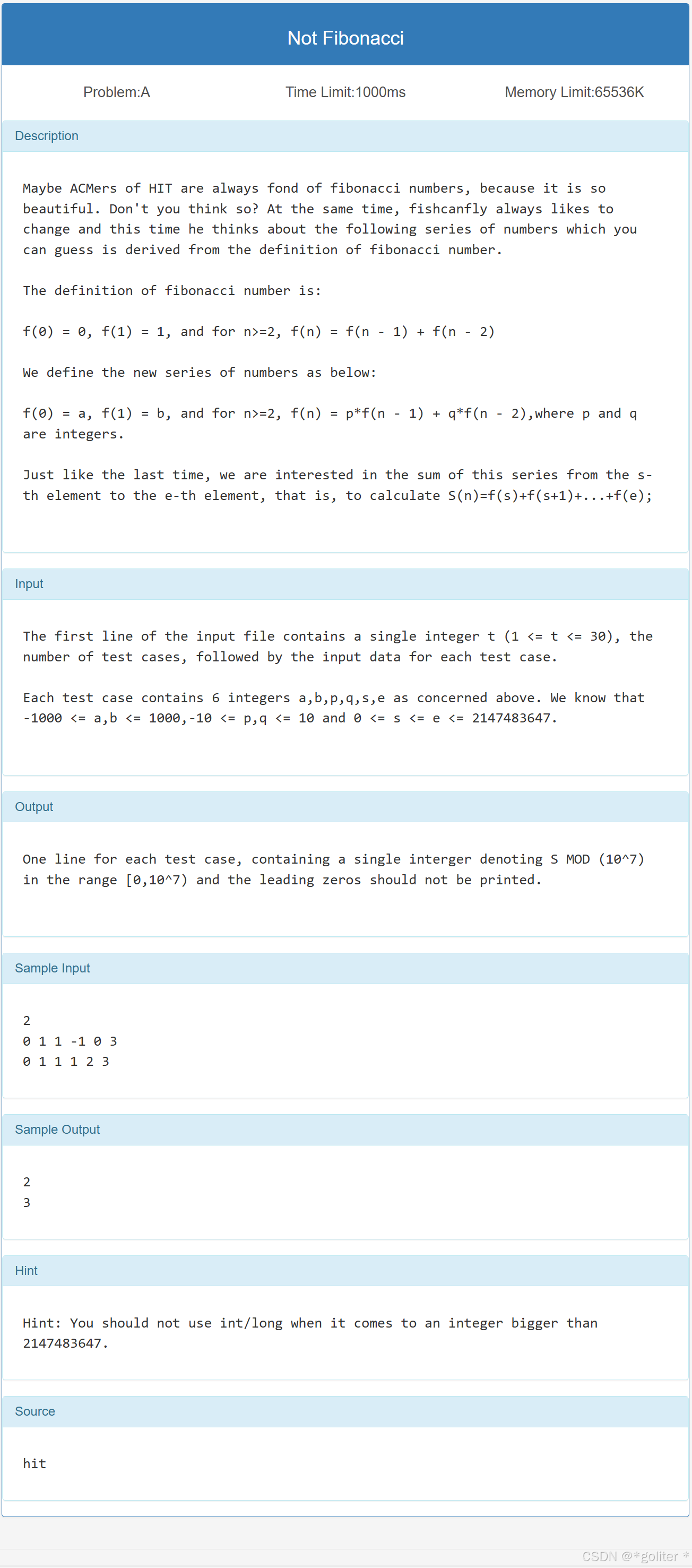
1、Not Fibonacci:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e7;
typedef struct{
ll m[3][3];
}matrix;
matrix P={
0,0,0,
1,0,0,
0,0,1
};
matrix I={
1,0,0,
0,1,0,
0,0,1
};
matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
a.m[i][k]=(a.m[i][k]%mod+mod)%mod;
b.m[k][j]=(b.m[k][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%mod;
}
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix quickpow(ll n){
matrix m=P,b=I;
while(n){
if(n&1)b=mul(b,m);
n>>=1;
m=mul(m,m);
}
return b;
}
ll a,b,p,q,s,e;
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll l,r;
matrix tmp;
cin>>a>>b>>p>>q>>s>>e;
P.m[0][0]=p;P.m[0][1]=q;
P.m[2][0]=p;P.m[2][1]=q;
if(e==0)r=(a%mod+mod)%mod;
else if(e==1)r=((a+b)%mod+mod)%mod;
else{
tmp=quickpow(e-1);
r=(tmp.m[2][0]*b)%mod+(tmp.m[2][1]*a)%mod+(tmp.m[2][2]*(a+b))%mod;
r=(r%mod+mod)%mod;
}
if(s==0)l=0;
else if(s==1)l=a;
else if(s==2)l=((a+b)%mod+mod)%mod;
else{
tmp=quickpow(s-2);
l=(tmp.m[2][0]*b)%mod+(tmp.m[2][1]*a)%mod+(tmp.m[2][2]*(a+b))%mod;
l=(l%mod+mod)%mod;
}
cout<<((r-l)%mod+mod)%mod<<endl;
}
return 0;
}构造出相应的p矩阵为,初始矩阵为
,在根据s,e分别计算即可。
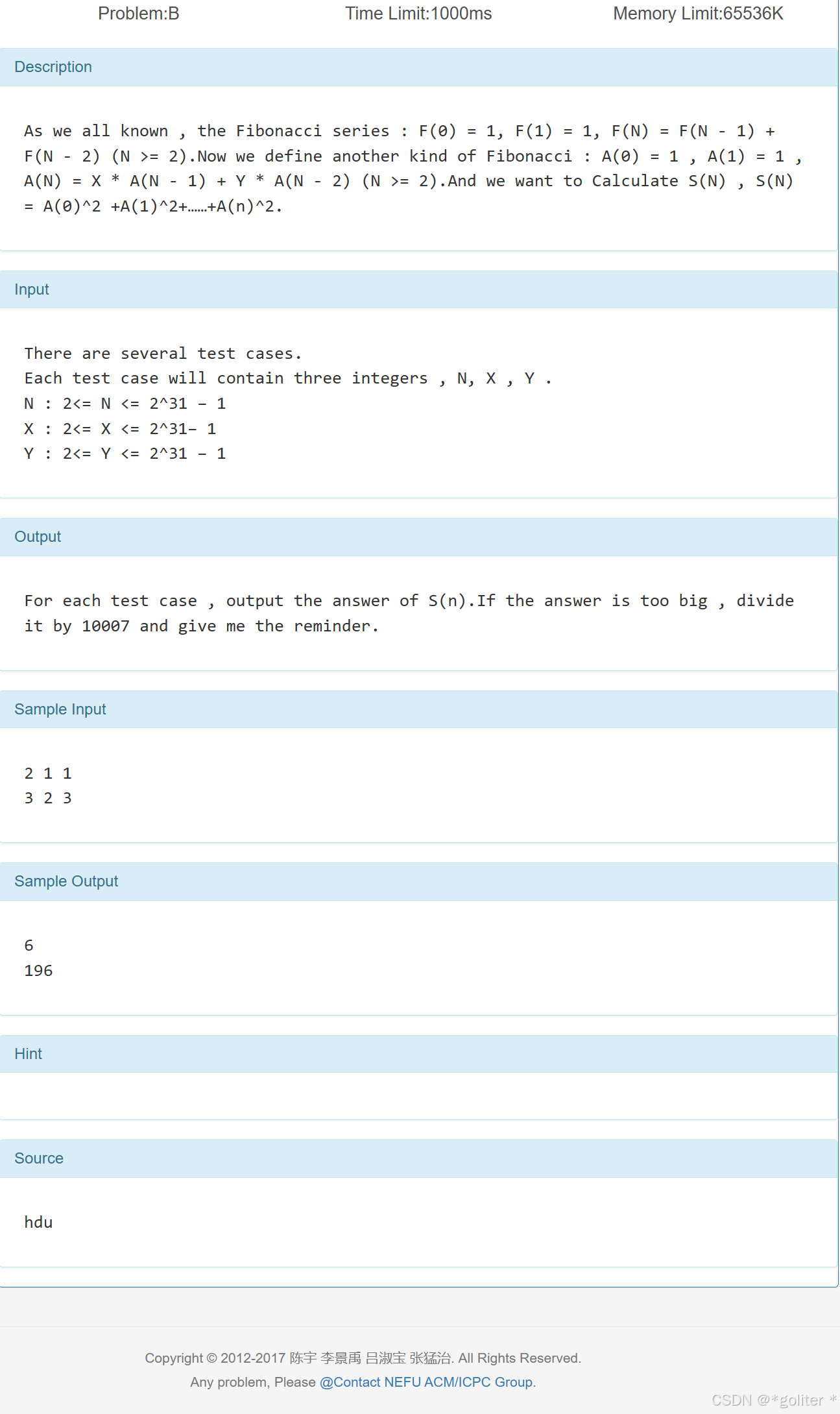
2、Another kind of Fibonacci
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=10007;
typedef struct{
ll m[4][4];
}matrix;
matrix P={
1,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0
};
matrix I={
1,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0,
0,0,1,0,
0,0,0,1
};
matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
a.m[i][k]=(a.m[i][k]%mod+mod)%mod;
b.m[k][j]=(b.m[k][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%mod;
}
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix quickpow(ll n){
matrix m=P,b=I;
while(n){
if(n&1)b=mul(b,m);
n>>=1;
m=mul(m,m);
}
return b;
}
ll n,x,y;
int main(){
while(cin>>n>>x>>y){
ll sum;
P.m[0][1]=x*x%mod;P.m[0][2]=2*x*y%mod;P.m[0][3]=y*y%mod;
P.m[1][1]=x*x%mod;P.m[1][2]=2*x*y%mod;P.m[1][3]=y*y%mod;
P.m[2][1]=x%mod;P.m[2][2]=y%mod;
if(n==0)sum=1;
else if(n==1)sum=2;
else{
matrix tmp=quickpow(n-1);
sum=(tmp.m[0][0]*2%mod)+(tmp.m[0][1]%mod)+(tmp.m[0][2]%mod)+(tmp.m[0][3]%mod);
sum=(sum%mod+mod)%mod;
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}上题的稍难版,不过核心还是推矩阵p和初始矩阵,得出来便可以直接代入模板。
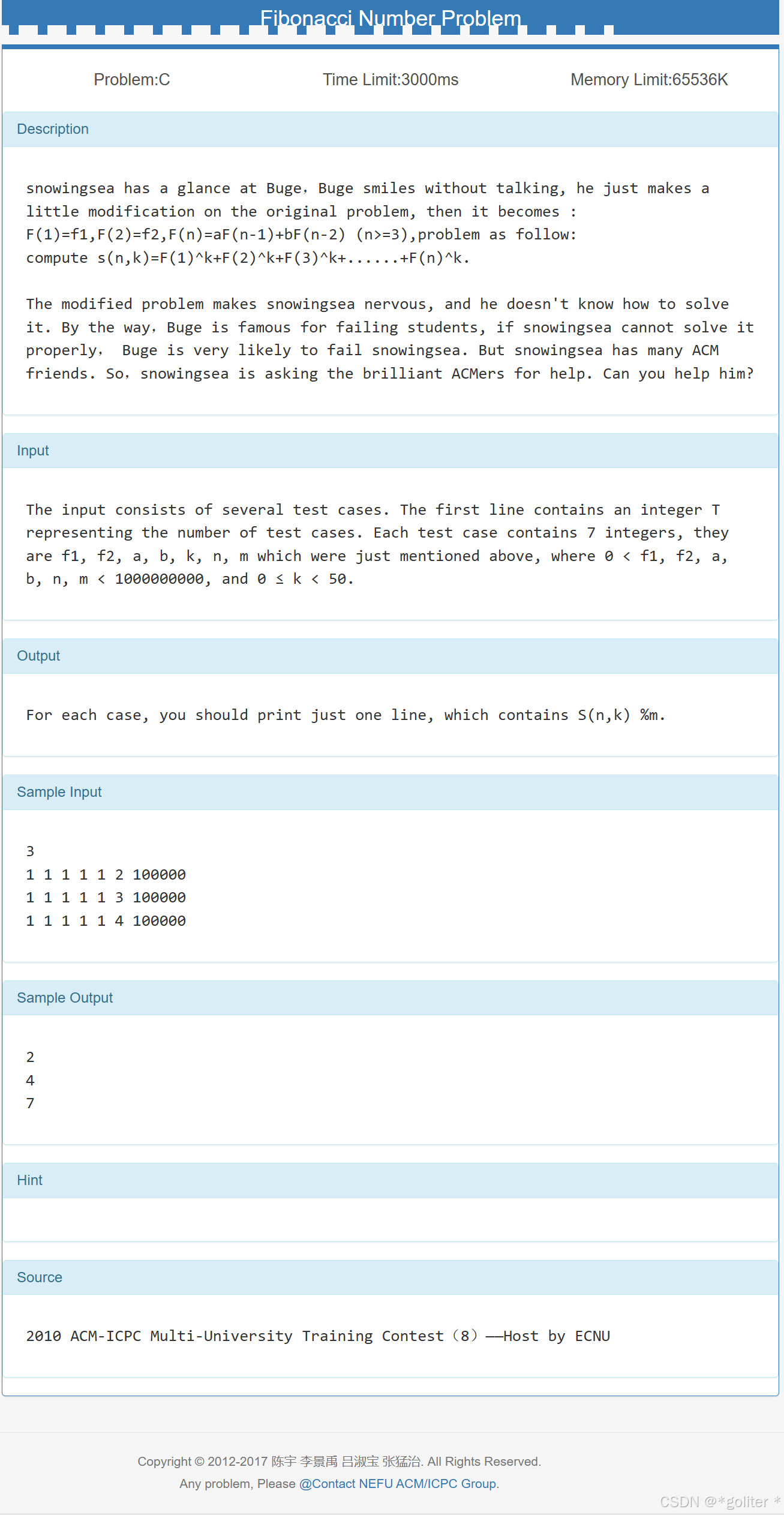
3、Fibonacci Number Problem
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 54;
LL mod, size;//size = 矩阵大小
typedef struct
{
LL m[maxn][maxn];
} Matrix;
Matrix P;
Matrix I;
//正常快速幂
LL quick_mod(LL a, LL b, LL c)
{
LL ans = 1;
if(b == 0)
return 1;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
ans = (ans*a)%c;
b >>= 1;
a = (a*a)%c;
}
return ans;
}
//矩阵乘法
Matrix matrix_mul(Matrix a, Matrix b)
{
int i, j, k;
Matrix c;
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<size; j++)
{
c.m[i][j] = 0;
for(k=0; k<size; k++)
{
c.m[i][j] += ((a.m[i][k]%mod)*(b.m[k][j]%mod))%mod;
}
c.m[i][j] %= mod;
}
}
return c;
}
//矩阵的快速幂
Matrix quick_pow(LL m)
{
Matrix b=P, ans=I;
while(m)
{
if(m & 1)
ans = matrix_mul(ans, b);
m >>= 1;
b = matrix_mul(b, b);
}
return ans;
}
//组合数。。。
LL c[50][50];
int main()
{
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
for(int i=0; i<50; i++)
{
c[i][0] = 1;
c[i][i] = 1;
}
for(int i=1; i<50; i++)
for(int j=1; j<i; j++)
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j] + c[i-1][j-1];
int t;
Matrix tmp;
LL f1, f2, a, b, k, n, m ;
LL sum, ans1, ans2;
//scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
sum = 0;
cin>>f1>>f2>>a>>b>>k>>n>>mod;
//scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld",&f1,&f2,&a,&b,&k,&n,&mod);
memset(P.m, 0, sizeof(P.m));
memset(I.m, 0, sizeof(I.m));
if(k == 0)
printf("%lld\n",n%mod);
else
{
if(n == 1)
cout<<quick_mod(f1, k, mod)<<endl;
else if(n == 2)
cout<<(quick_mod(f1,k,mod) + quick_mod(f2,k,mod))%mod<<endl;
else
{
size = k+2;
//矩阵赋值
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
I.m[i][i] = 1;
P.m[0][0] = 1;
P.m[0][size-1] = 1;
for(int i=1; i<size-1; i++)
P.m[0][i] = 0;
for(int i=1; i<size; i++)
for(int j=size-i,w=0; j<size; j++,w++)
{
P.m[i][j]=(((c[i-1][w]%mod)*quick_mod(a,w,mod))%mod)*quick_mod(b,i-1-w,mod);
P.m[i][j] %= mod;
}
tmp = quick_pow(n-1);
sum = (sum+(tmp.m[0][0]%mod)*(quick_mod(f1,k,mod)))%mod;
for(int i=1; i<size; i++)
{
ans1 = (quick_mod(f1,size-1-i,mod)*quick_mod(f2,i-1,mod))%mod;
ans2 = (ans1*(tmp.m[0][i]%mod))%mod;
sum = (sum+ans2)%mod;
}
cout<<sum%mod<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}首先一个难题就是怎么判断矩阵的维数(矩阵的维数是个变量),解决方法:开一个比较大的数组,然后再用一个公有变量记一下就行了,具体详见代码;
矩阵k次方是啥,找规律来求解;
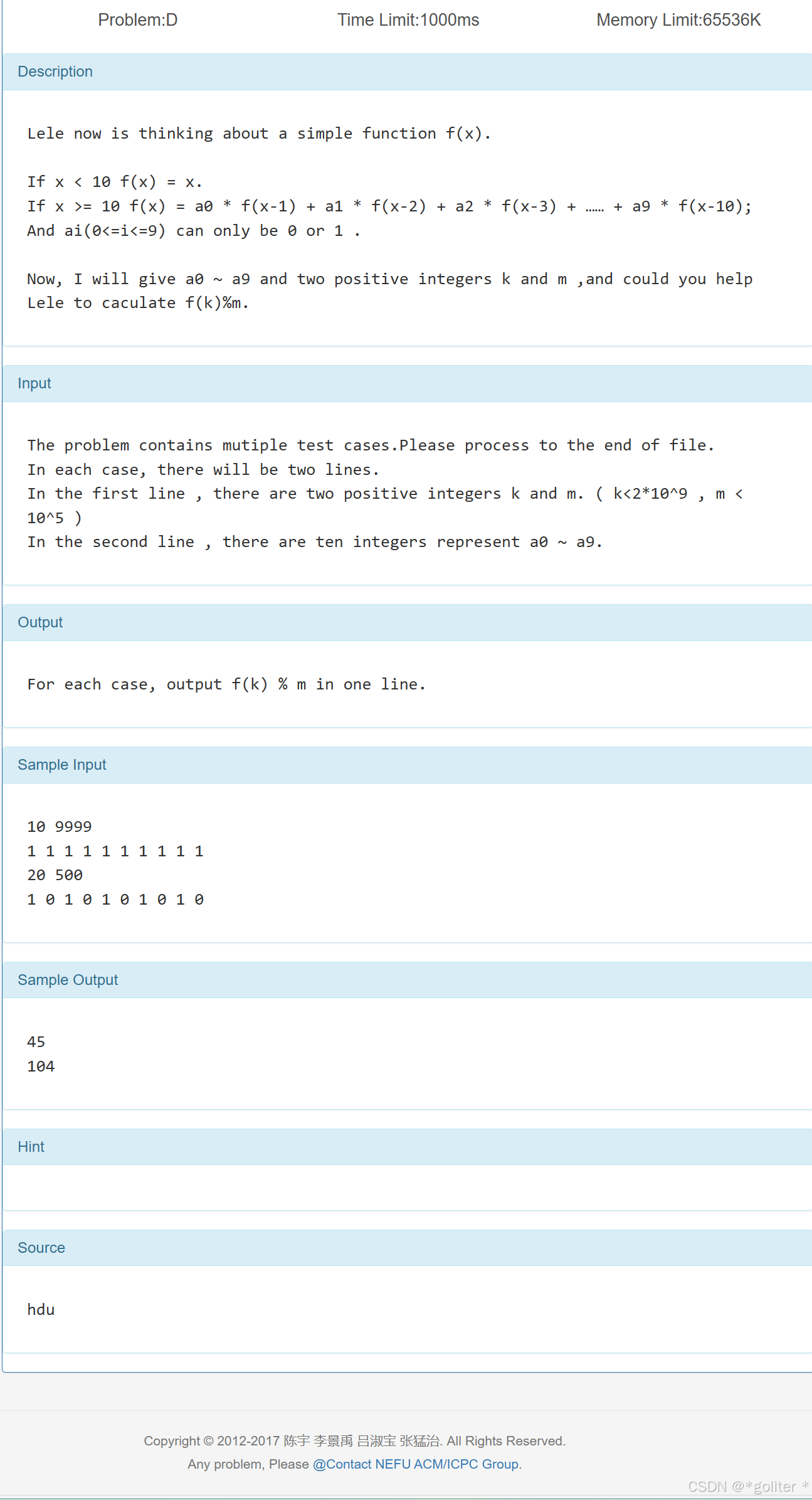
4、A Simple Math Problem
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef struct{
ll m[10][10];
}matrix;
matrix P={
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0
};
matrix I={
1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1
};
int k,m;
matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<10;k++){
a.m[i][k]=(a.m[i][k]%m+m)%m;
b.m[k][j]=(b.m[k][j]%m+m)%m;
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%m;
}
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j]%m+m)%m;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix quickpow(ll n){
matrix m=P,b=I;
while(n){
if(n&1)b=mul(b,m);
n>>=1;
m=mul(m,m);
}
return b;
}
int main(){
while(cin>>k>>m){
cin>>P.m[0][0]>>P.m[0][1]>>P.m[0][2]>>P.m[0][3]>>P.m[0][4]>>P.m[0][5]>>P.m[0][6]>>P.m[0][7]>>P.m[0][8]>>P.m[0][9];
ll sum;
if(k<10){
sum=k%m;
}
else{
matrix tmp=quickpow(k-9);
sum=(tmp.m[0][0]*9)%m+(tmp.m[0][1]*8)%m+(tmp.m[0][2]*7)%m+(tmp.m[0][3]*6)%m+(tmp.m[0][4]*5)%m+(tmp.m[0][5]*4)%m+(tmp.m[0][6]*3)%m+(tmp.m[0][7]*2)%m+(tmp.m[0][8])%m;
sum=(sum%m+m)%m;
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}矩阵稍大稍微有点麻烦,不过还是可以直接写出来的。
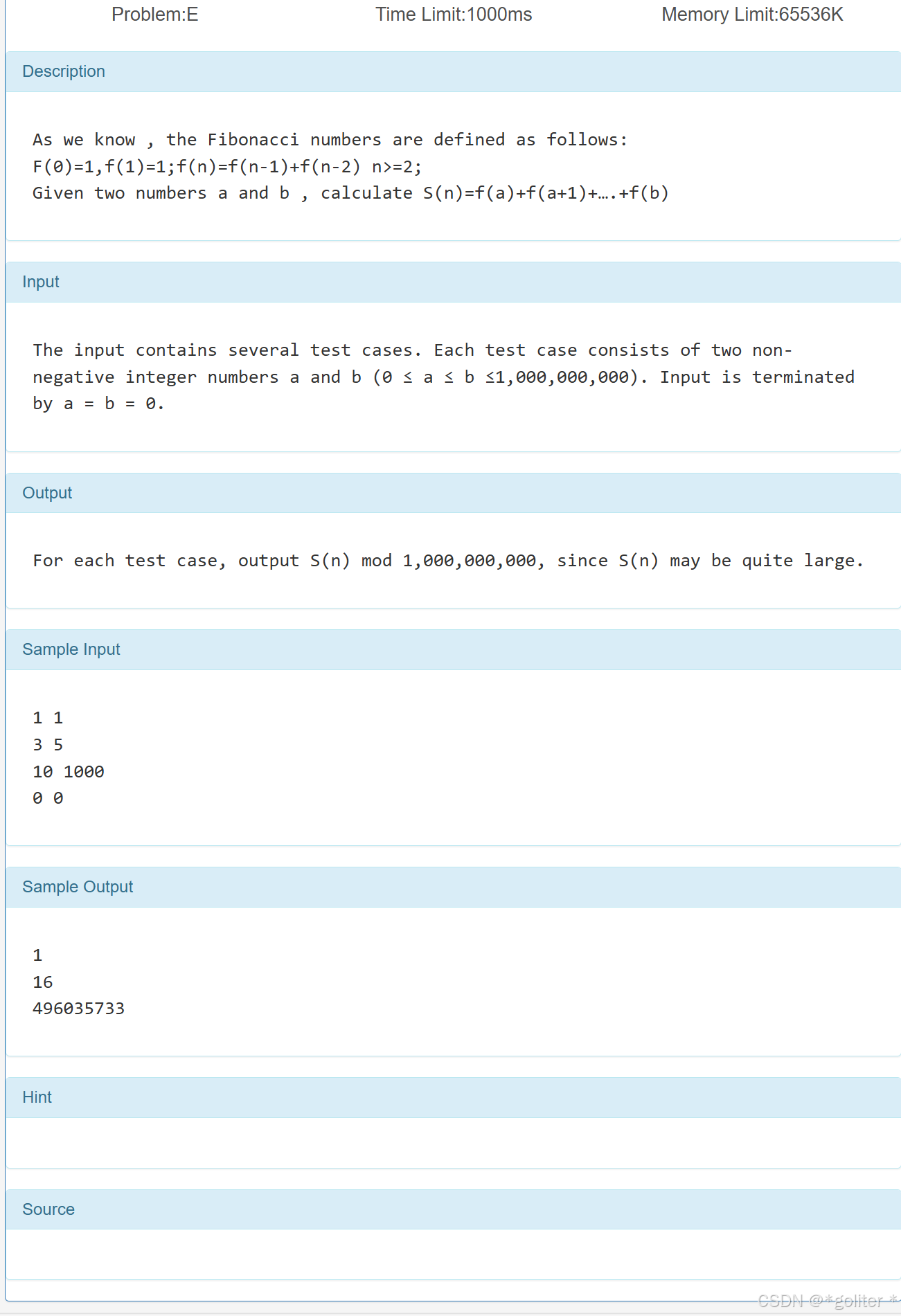
5、Fibs之和
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9;
typedef struct{
ll m[3][3];
}matrix;
matrix P={
0,0,0,
1,0,0,
0,0,1
};
matrix I={
1,0,0,
0,1,0,
0,0,1
};
matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
a.m[i][k]=(a.m[i][k]%mod+mod)%mod;
b.m[k][j]=(b.m[k][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%mod;
}
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix quickpow(ll n){
matrix m=P,b=I;
while(n){
if(n&1)b=mul(b,m);
n>>=1;
m=mul(m,m);
}
return b;
}
ll a,b,p,q,s,e;
int main(){
while(cin>>s>>e){
if(s==0&&e==0)break;
ll l,r;
matrix tmp;
P.m[0][0]=1;P.m[0][1]=1;
P.m[2][0]=1;P.m[2][1]=1;
if(e==0)r=1;
else if(e==1)r=2;
else{
tmp=quickpow(e-1);
r=(tmp.m[2][0])%mod+(tmp.m[2][1])%mod+(tmp.m[2][2])%mod;
r=(r%mod+mod)%mod;
}
if(s==0)l=0;
else if(s==1)l=1;
else if(s==2)l=2;
else{
tmp=quickpow(s-2);
l=(tmp.m[2][0])%mod+(tmp.m[2][1])%mod+(tmp.m[2][2])%mod;
l=(l%mod+mod)%mod;
}
cout<<((r-l)%mod+mod)%mod<<endl;
}
return 0;
}和1一摸一样
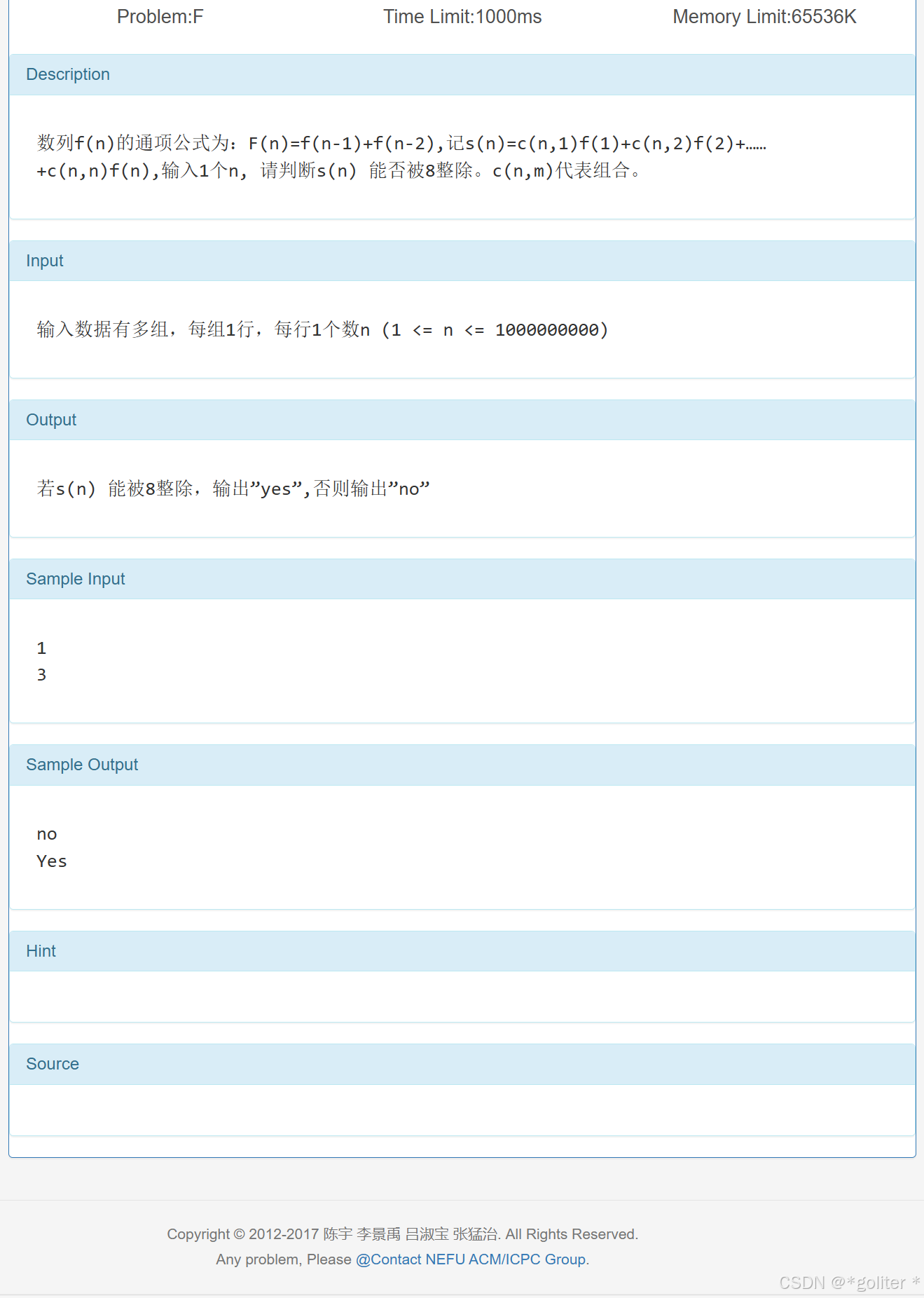
6、fibs的组合
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin>>n){
if(n%3==0){
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
}
else{
cout<<"no"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}找规律
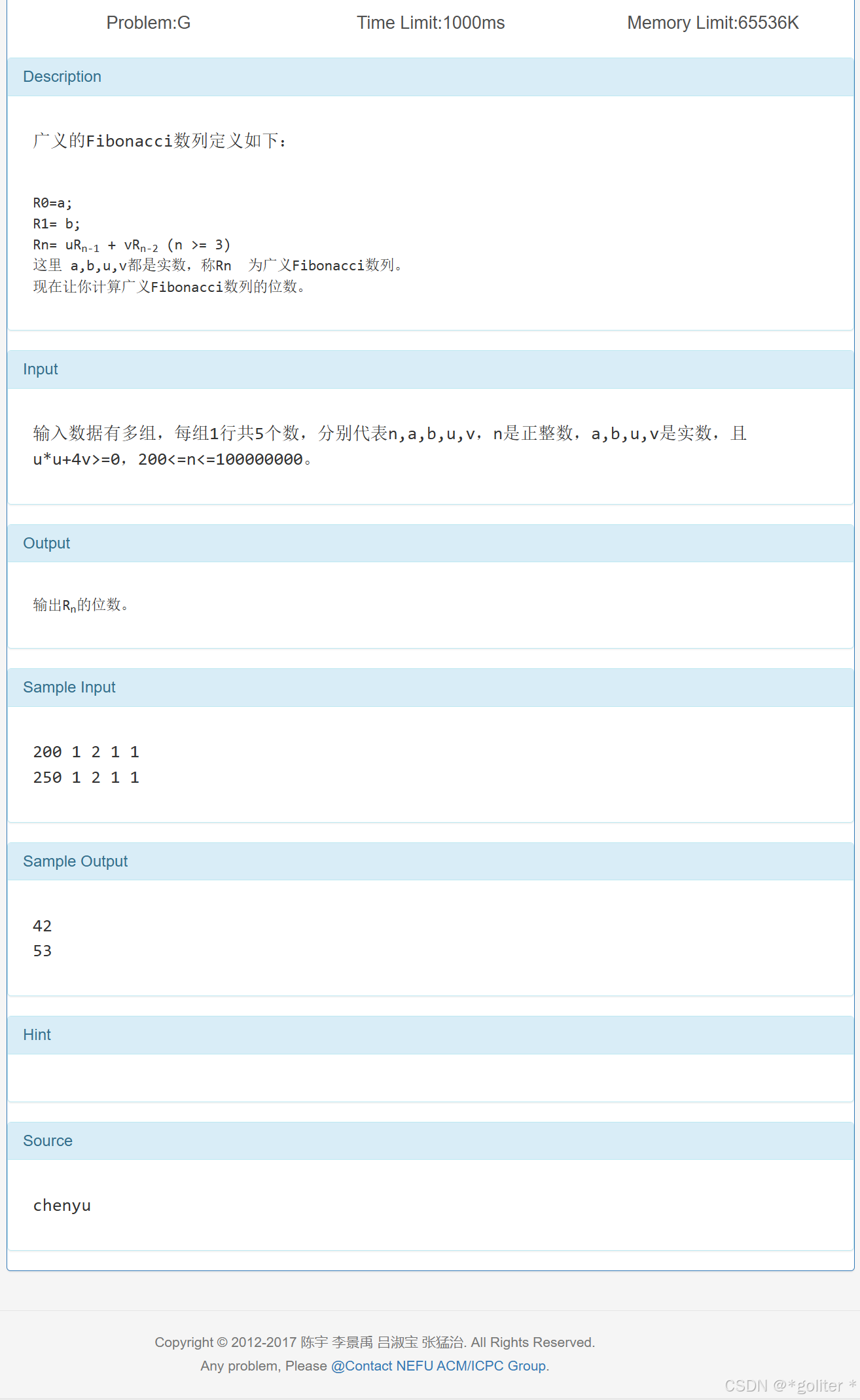
7、fibs的位数
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long n,a,b,u,v;
while(scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld",&n,&a,&b,&u,&v)!=EOF)
{
double c=sqrt(u*u+4*v);
double x=(u+c)/2.0;
double y=(u-c)/2.0;
double len=n*log10(x)+log10(b-a*y)-log10(c);
printf("%lld\n",(long long)len+1);
}
return 0;
}这个是纯概念(而且挺偏的),我感觉比赛不会有这种内容,想了解可以看看这个NEFU 461 fibs的位数()_现在让你计算广义fibonacci数列的位数。-CSDN博客
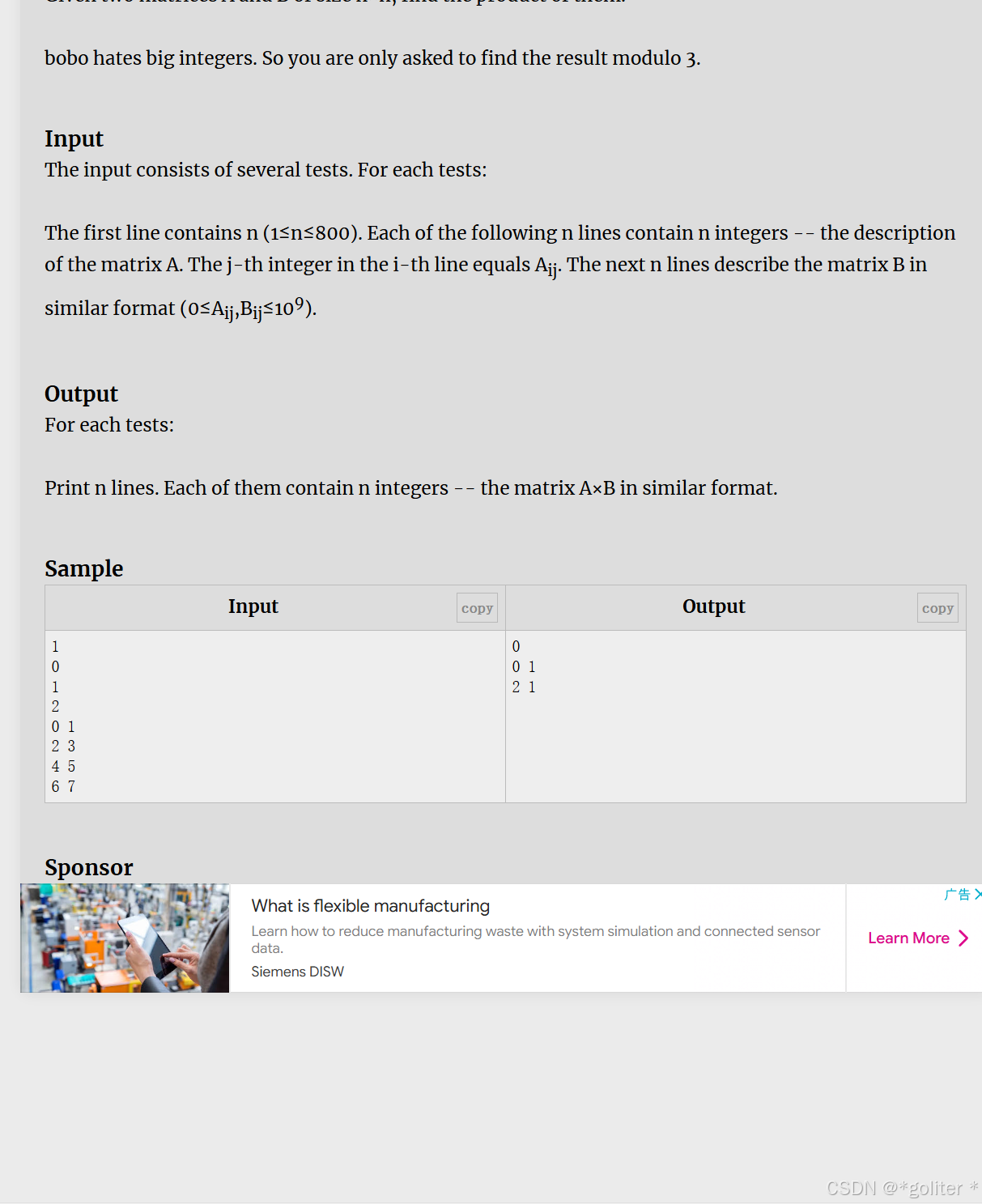
8、Matrix multiplication
cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 817;
const int mod = 3;
int A[MAXN][MAXN], B[MAXN][MAXN];
int C[MAXN][MAXN];
int n;
int Scan()
{
int res = 0, ch;
ch=getchar();
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
res = ch - '0';
while((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9' )
res = res * 10 + ch - '0';
return res;
}
void input()
{
int i, j;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
//scanf("%d",&A[i][j]);
//A[i][j] %= mod;
A[i][j]=Scan()%3;
}
}
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
//scanf("%d",&B[i][j]);
//B[i][j] %= mod;
B[i][j]=Scan()%3;
}
}
}
void multi()
{//两个相等矩阵的乘法,对于稀疏矩阵,有在0处不用运算的优化
memset(C,0,sizeof(C));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(A[i][j] == 0)//稀疏矩阵优化
continue;
for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
{
C[i][k] += A[i][j]*B[j][k];//i行k列第j项
// C[i][k] %= mod;
}
}
}
}
void print()//输出矩阵信息
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(j == 1)
printf("%d",C[i][j]%mod);
else
printf(" %d",C[i][j]%mod);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
input();
multi();
print();
}
return 0;
}这题题目不难,但卡时间有一点刻意了,十分恶心。
9、Number Sequence
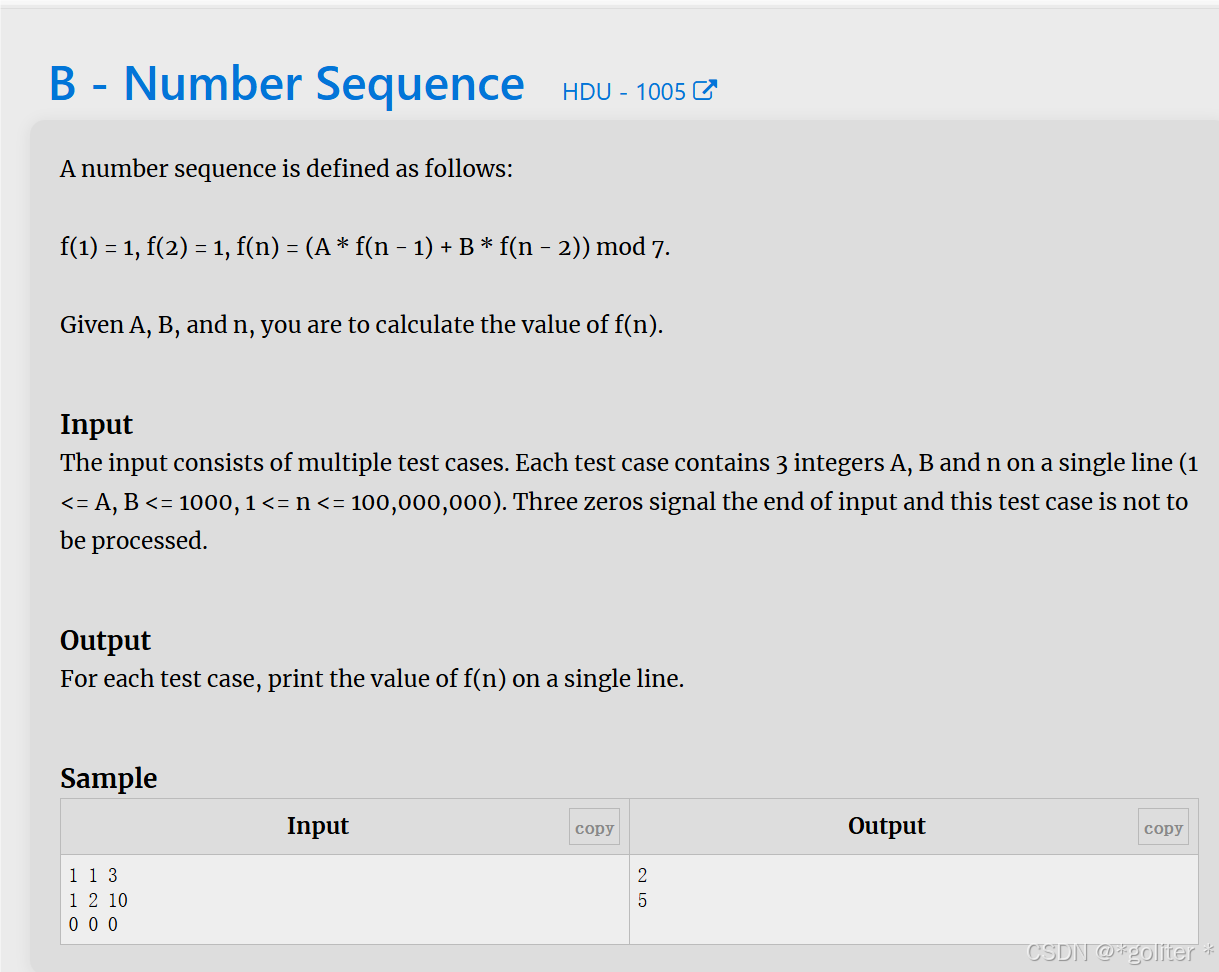
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=7;
typedef struct{
ll m[2][2];
}matrix;
matrix P={
1,1,
1,0
};
matrix I={
1,0,
0,1
};
matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++){
a.m[i][k]=(a.m[i][k]%mod+mod)%mod;
b.m[k][j]=(b.m[k][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%mod;
}
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix quickpow(ll n){
matrix m=P,b=I;
while(n){
if(n&1)b=mul(b,m);
n>>=1;
m=mul(m,m);
}
return b;
}
int main(){
ll a,b,n;
while(cin>>a>>b>>n){
if(a==0&&b==0&&n==0)break;
P.m[0][0]=a;P.m[0][1]=b;
ll sum=0;
if(n==-1)break;
if(n==0){
cout<<0<<endl;
continue;
}
if(n==1){
cout<<1<<endl;
continue;
}
matrix tmp=quickpow(n-2);
sum=(tmp.m[0][0])%mod+(tmp.m[0][1])%mod;
sum=(sum%mod+mod)%mod;
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}模板
10、Fibonacci

cpp
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=10000;
typedef struct{
ll m[2][2];
}matrix;
matrix P={
1,1,
1,0
};
matrix I={
1,0,
0,1
};
matrix mul(matrix a,matrix b){
matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++){
a.m[i][k]=(a.m[i][k]%mod+mod)%mod;
b.m[k][j]=(b.m[k][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%mod;
}
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j]%mod+mod)%mod;
}
}
return c;
}
matrix quickpow(ll n){
matrix m=P,b=I;
while(n){
if(n&1)b=mul(b,m);
n>>=1;
m=mul(m,m);
}
return b;
}
int main(){
ll n;
while(cin>>n){
ll sum=0;
if(n==-1)break;
if(n==0){
cout<<0<<endl;
continue;
}
if(n==1){
cout<<1<<endl;
continue;
}
matrix tmp=quickpow(n-2);
sum=(tmp.m[0][0])%mod+(tmp.m[0][1])%mod;
sum=(sum%mod+mod)%mod;
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}求最后四位就是%10000
11、Gauss Fibonacci
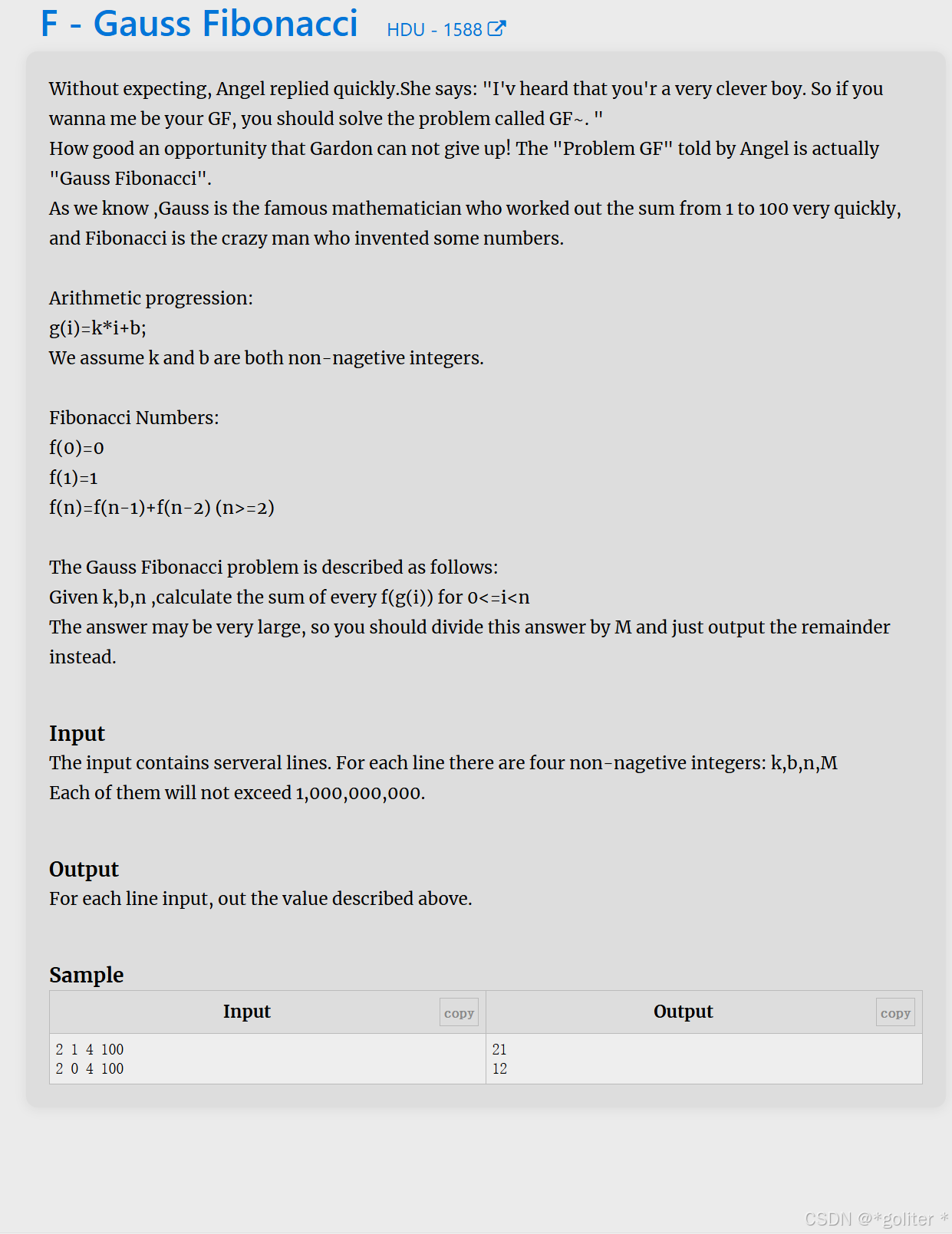
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct matrie{
ll m[10][10];
};
int k,b,n,mod;
matrie A,B,T,C,D,E;
matrie multi(matrie a,matrie b){
matrie c;
memset(c.m,0,sizeof(c.m));
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
for(int k=0;k<10;k++){
c.m[i][j]=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j]+c.m[i][j])%mod;
}
}
}
return c;
}
matrie fast_power(matrie a, ll b) {
matrie res;
memset(res.m,0,sizeof(res.m));
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)res.m[i][i] = 1;
while(b>0){
if(b&1){
res=multi(res,a);
}
b>>=1;
a=multi(a, a);
}
return res;
}
void init(){
T.m[0][0]=0;T.m[0][1]=1;T.m[1][0]=1;T.m[1][1]=1;
A.m[0][0]=0;A.m[0][1]=1;
C=multi(A,fast_power(T,b));
E=fast_power(T,k);
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
D.m[i][i]=1;
B.m[i][i]=B.m[i][i+2]=1;
}
for(int i=2;i<4;i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
D.m[i][j]=D.m[i][j+2]=E.m[i-2][j];
}
}
}
int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d",&k,&b,&n,&mod)!=EOF){
init();
matrie tmp=multi(B,fast_power(D,n-1));
matrie sum;
memset(sum.m, 0, sizeof(sum.m));
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
sum.m[i][j]=tmp.m[i][j];
}
}
matrie ans=multi(C,sum);
printf("%lld\n", ans.m[0][0]);
}
return 0;
}详解可以看看这篇博客HDU 1588 Gauss Fibonacci(分块矩阵优化)-CSDN博客
12、Fast Matrix Calculation

cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long int
const int MOD=6;
int n,m;
struct node{
LL m[10][10];
node()
{
memset(m,0,sizeof(m));
}
};
int a[1005][10],b[10][1005],c[1005][10],d[1005][1005];
node cla(node A,node B)
{
node C;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)//A对应的行
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)//B对应的列
for(int k=0;k<m;k++)
if(A.m[i][k]&&B.m[k][j])//剪枝(添条件,设门槛),提高效率,有一个是0,相乘肯定是0
{
C.m[i][j]+=A.m[i][k]*B.m[k][j];
C.m[i][j]%=MOD;
}
return C;
}
node POW(int k,node ans)
{
node e;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) e.m[i][i]=1;
while(k)
{
if(k%2) e=cla(e,ans);
ans=cla(ans,ans);
k/=2;
}
return e;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
if(n==0&&m==0)
break;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
node ans;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)//A对应的行
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)//B对应的列
for(int k=0;k<n;k++)
if(b[i][k]&&a[k][j])//剪枝(添条件,设门槛),提高效率,有一个是0,相乘肯定是0
{
ans.m[i][j]+=b[i][k]*a[k][j];
ans.m[i][j]%=MOD;
}
ans=POW(n*n-1,ans);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//A对应的行
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)//B对应的列
for(int k=0;k<m;k++)
if(a[i][k]&&ans.m[k][j])//剪枝(添条件,设门槛),提高效率,有一个是0,相乘肯定是0
{
c[i][j]+=a[i][k]*ans.m[k][j];
c[i][j]%=MOD;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//A对应的行
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)//B对应的列
for(int k=0;k<m;k++)
if(c[i][k]&&b[k][j])//剪枝(添条件,设门槛),提高效率,有一个是0,相乘肯定是0
{
d[i][j]+=c[i][k]*b[k][j];
d[i][j]%=MOD;
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//A对应的行
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)//B对应的列
sum+=d[i][j];
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
} 因为n实在太大了,开不了1000*1000的矩阵,但是可以利用矩阵相乘的结合律将(A*B)^n转换为A*(B*A)^(n-1)*B, 这样B和A相乘得到的是一个6*6(最多)矩阵, 将这个矩阵用快速幂计算(n*n-1)次幂,在乘上一开始的A和最后的B即可。
后记:
之后的一些训练题我也会慢慢写出来发表的。