欢迎来到博主的专栏:c++编程
博主ID:代码小豪
文章目录
unordered_map是STL中的关联式容器之一,与常规的map有两点不同
(1)unordered是无序的意思,之所以取这名字,是因为与常规map迭代器前进的方向是有序的,而unordered_map的迭代器前进方向是无序的。
cpp
void test1()
{
int a[] = { 11,25,21,1,6,9,16 };
unordered_map<int, int> op;
map<int, int> m;
for (auto e : a)
{
op.insert(make_pair(e, e));
m.insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
for (auto e : m)//遍历map容器
{
cout << e.first << ' ';//1 6 9 11 16 21 25
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : op)//遍历unordered_map
{
cout << e.first << ' ';//11 9 1 25 21 6 16
}
}(2)之所以造成这种差异,是因为unordered_map的底层用的是哈希表,而map的底层是红黑树。这是底层而造成的差异。
unorder_map的底层
关于哈希表的介绍,博主放在了数据结构专栏中,因此不再赘述。
由于STL标准库中的set和map共用一个hashtable底层(SGI版stl),因此博主将hashtable做了些许修改:
cpp
template<class key,class T,class keyofT>
class hash_tab
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef hash_Node<value_type> Node;
hash_tab()
{
_tab.resize(10);
}
~hash_tab()
{
for (size_t i=0;i<_tab.size();i++)
{
Node* cur = _tab[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tab[i] = nullptr;
_n = 0;
}
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tab;
size_t _n;
keyofT kot;
};由于map和set的数据不一样,set的数据是key类型的,而map的数据是pair<key,value>型的,因此需要一个key值提取器------keyofT。关于keyofT怎么用,博主在会在后续文章提到。
insert
unordered_map类被博主设计成这样,其成员为底层哈希表.
cpp
template<class key,class value>
class unordered_map
{
public:
typedef pair<key, value> value_type;
template<class key,class value>
class unordered_mapkeyofT
{
const key& operator()(const value_type& data)const
{
return data.first;
}
};
private:
myhash::hash_tab<key, value_type, unordered_mapkeyofT<key, value>> _hashtab;//底层哈希表
};如果使用了底层哈希表,那么insert可以直接复用_hashtab的insert函数。
cpp
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& data)
{
return _hashtab.insert(data);
}而unordered_map的erase,find操作都可以这样做,因此模拟实现unordered_map最重要的一步是设计出hashtab使用的迭代器。
迭代器
关于哈希的迭代器,博主是这样构思的,迭代器有两个成员,分别是指向当前哈希表的指针,以及一个指向该表的有效数据的指针。
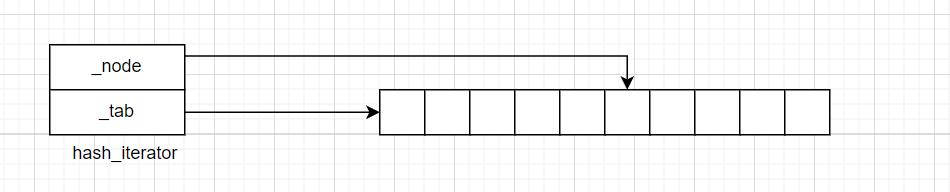
cpp
template<class key,class T,class ref,class ptr,class keyofT>
struct hash_iterator
{
typedef hash_Node<T> Node;
typedef hash_tab<key, T, keyofT> hash;
typedef hash_iterator self;
hash_iterfator(Node* node,hash* tab)
{
_node = node;
_tab = tab;
}
keyofT kot;
Node* _node;//指向节点
hash* _tab;//指向当前哈希表
};begin()函数返回指向哈希表第一个有效数据的节点

cpp
Iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < _tab.size(); i++)
{
cur = _tab[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
return Iterator(cur, this);
}
return Iterator(cur, this);
}end函数则返回nullptr作为结束标志。
cpp
Iterator end()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, this);
}最后加上const版本的begin和end。
cpp
const_Iterator begin() const
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < _tab.size(); i++)
{
cur = _tab[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
return Iterator(cur, this);
}
return Iterator(cur, this);
}
const_Iterator end()const
{
return Iterator(nullptr, this);
}成员访问函数
迭代器的成员访问函数也就是operator*和operator->.这很简单。
cpp
ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
ptr operator->()
{
return &operator*();
}operator++
operator++让迭代器前进到下一个有效数据。做法如下:
(1)有限前进到同一个桶中的下一个有效数据的节点
(2)如果桶中不存在有效节点,就去找下一个有数据的哈希桶。
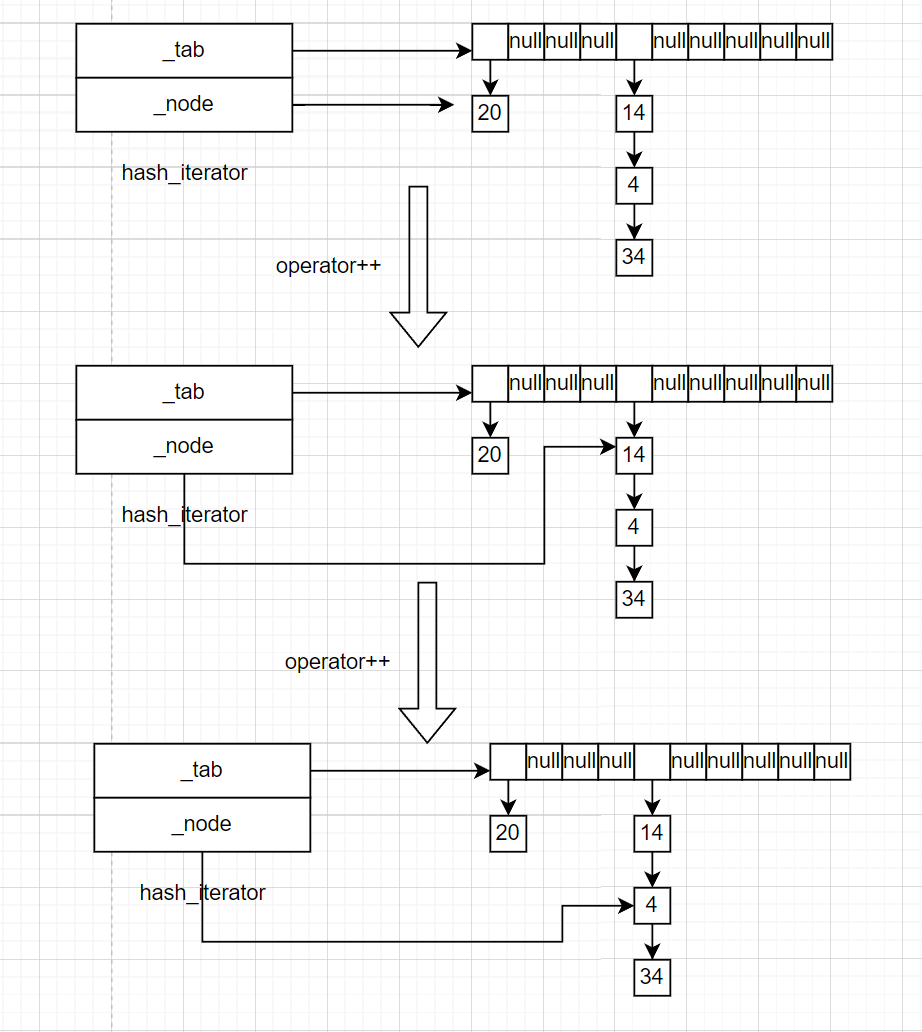
代码如下:
cpp
self operator++()
{
if (_node->_next != nullptr)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
size_t hashnum = kot(_node->_data) % _tab->_tab.size();
hashnum++;
while (hashnum < _tab->_tab.size())
{
Node* cur = _tab->_tab[hashnum];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
_node = cur;
return *this;
}
hashnum++;
}
_node = nullptr;//如果没找到,就返回end()标志
return *this;
}
}operator--
operator--的操作如下:
(1)首先找到当前节点的映射地址
(2)判断该节点是否是该桶的第一个节点
若为否,则迭代器指向该节点的上一个节点
若为真,则迭代器指向上一个桶的最后一个节点

代码如下:
cpp
self operator--()
{
int hashnum = kot(_node) % _tab->_tab.size();
Node* cur = _tab->_tab[hashnum];
if (cur != _node)
{
while (cur->_next != _node)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
_node = cur;
return *this;
}
else//cur==_node
{
for (int i = hashnum-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
cur = _tab->_tab[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
while (cur->_next != nullptr)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
_node = cur;
return *this;
}
}
}
}