目录
- 1、环境准备
- [2、引入 Shiro](#2、引入 Shiro)
- 3、实现认证、退出
-
- 3.1、使用死数据实现
- 3.2、引入数据库,添加注册功能
- [3.3、MD5、Salt 的认证流程](#3.3、MD5、Salt 的认证流程)
- 4.、实现授权
- 5、引入缓存
-
- [5.1、EhCache 实现缓存](#5.1、EhCache 实现缓存)
- [5.2、集成 Redis 实现 Shiro 缓存](#5.2、集成 Redis 实现 Shiro 缓存)
1、环境准备
新建一个 SpringBoot 工程,引入依赖:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3</version>
</dependency>在 resources/static 目录下新建 pages,再新建两个 html 文件
index.html:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
</body>
</html>login.html:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录页</h1>
</body>
</html>添加路由控制器 RoutingController:
java
@Controller
public class RoutingController {
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "pages/index.html";
}
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "pages/login.html";
}
}访问:http://localhost:8080/index、http://localhost:8080/login 正常访问 index.html、login.html 页面。
2、引入 Shiro
①:添加一个自定义 Realm:
java
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
// 授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
// 认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
return null;
}
}暂不实现这两个方法
②:添加 Shiro 配置类 ShiroConfiguration:
java
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfiguration {
// 1.创建 shiroFilter,负责拦截所有请求
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//给filter设置安全管理器
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//配置系统受限资源
//配置系统公共资源
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
// authc 请求这个资源需要认证和授权
map.put("/index", "authc");
//默认认证界面路径
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login");
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return shiroFilterFactoryBean;
}
//2.创建安全管理器
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(Realm realm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//给安全管理器设置
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(realm);
return defaultWebSecurityManager;
}
//3.创建自定义realm
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
return new UserRealm();
}
}看下面代码:
java
// authc 请求这个资源需要认证和授权
map.put("/index", "authc");表示:访问 /index 路径,需要认证、授权;否则,无法访问
③:路由控制器 RoutingController:
java
@Controller
public class RoutingController {
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "pages/index.html";
}
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "pages/login.html";
}
}启动项目再次访问 http://localhost:8080/index,发现页面跳转到登录页面。
这就说明我们的项目中成功的引入了 Shiro
3、实现认证、退出
3.1、使用死数据实现
修改 login.html:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录页</h1>
<form action="/user/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" > <br/>
密码 : <input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>index.html:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<a href="/user/logout">退出用户</a>
</body>
</html>UserController:
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password) {
try {
// 执行登录操作
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 认证通过后直接跳转到 index.html
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password));
return "redirect:/index";
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果认证失败仍然回到登录页面
return "redirect:/login";
}
}
@GetMapping("/logout")
public String logout(){
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.logout();
// 退出后仍然会到登录页面
return "redirect:/login";
}
}UserRealm:实现认证
java
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
// 授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
// 认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
String principal = (String)authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
// TODO 模拟数据库返回的数据
if("christy".equals(principal)){
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,"123456", this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}输入的用户名是 christy,密码 123456,就可以认证通过进入到主页
3.2、引入数据库,添加注册功能
pom.xml 引入依赖:
xml
<!-- mybatis plus -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Druid数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Mysql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>yml 添加配置:
yml
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sb_shiro?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
# 监控统计拦截的filters
filters: stat,wall,slf4j,config
# 配置初始化大小/最小/最大
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 5
max-active: 20
# 获取连接等待超时时间
max-wait: 60000
# 间隔多久进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
# 一个连接在池中最小生存的时间
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
validation-query: SELECT 'x'
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
# 打开PSCache,并指定每个连接上PSCache的大小。oracle设为true,mysql设为false。分库分表较多推荐设置为false
pool-prepared-statements: false
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
mybatis-plus:
type-aliases-package: com.zzc.entity
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: truesql 文件:
sql
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`salt` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(32) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;后端代码
UserController:添加一个注册接口
java
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping("/register")
public String register(User user) {
try {
userService.register(user);
return "redirect:/login";
} catch (Exception e) {
return "redirect:/register";
}
}UserServiceImpl:未写接口
java
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService {
@Override
public void register(User user) {
// 生成随机盐
String salt = SaltUtil.getSalt(8);
// 保存随机盐
user.setSalt(salt);
// 生成密码
Md5Hash password = new Md5Hash(user.getPassword(), salt, 1024);
// 保存密码
user.setPassword(password.toHex());
save(user);
}
}UserMapper:
java
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}User:
java
@Data
@TableName("t_user")
public class User {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
// 用户名
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private String username;
// 密码
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private String password;
// 盐
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private String salt;
// 年龄
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Integer age;
// 邮箱
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private String email;
// 地址
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private String address;
}RoutingController:路由
java
@GetMapping("/register")
public String register() {
return "pages/register.html";
}ShiroConfiguration:过滤掉部分接口
java
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
// authc 请求这个资源需要认证和授权
map.put("/login", "anon");
map.put("/register", "anon");
map.put("/user/register", "anon");
map.put("/user/login", "anon");
map.put("/index", "authc");前端代码
添加一个注册页面 register.html:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>注册页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/user/register" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" > <br/>
密码 : <input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="立即注册">
</form>
</body>
</html>启动项目,在注册页面进行注册
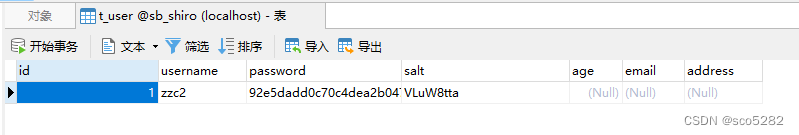
可以看到我们注册的用户已经顺利保存到数据库,而且密码是经过加密的
3.3、MD5、Salt 的认证流程
上面我们完成了基于 MD5+Salt 的注册流程,保存到数据库的密码都是经过加密处理的,这时候再用最初的简单密码匹配器进行 equals() 方法进行登录显然是不行的了,我们下面来改造一下认证的流程
UserRealm:修改认证(从数据库中获取)
java
// 认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
String principal = (String)authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
// 由于 UserRealm 并没有交由工厂管理,故不能注入 UserService
UserService userService = ApplicationContextUtil.getBean(UserService.class);
// 数据库返回的数据
User user = userService.findByUsername(principal);
if (Objects.nonNull(user)) {
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), new CustomerByteSource(user.getSalt()), this.getName());
}
return null;
}ShiroConfiguration:修改 Reaml 配置(添加密码配置器)
java
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
UserRealm userRealm = new UserRealm();
// 设置密码匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
// 设置加密方式
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
// 设置散列次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
userRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
return userRealm;
}ApplicationContextUtil:获取 Spring 的 bean
java
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
public static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
context = applicationContext;
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz){
return context.getBean(clazz);
}
}CustomerByteSource
java
public class CustomerByteSource implements ByteSource, Serializable {
private byte[] bytes;
private String cachedHex;
private String cachedBase64;
public CustomerByteSource() {
}
public CustomerByteSource(byte[] bytes) {
this.bytes = bytes;
}
public CustomerByteSource(char[] chars) {
this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(chars);
}
public CustomerByteSource(String string) {
this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(string);
}
public CustomerByteSource(ByteSource source) {
this.bytes = source.getBytes();
}
public CustomerByteSource(File file) {
this.bytes = (new CustomerByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(file);
}
public CustomerByteSource(InputStream stream) {
this.bytes = (new CustomerByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(stream);
}
public static boolean isCompatible(Object o) {
return o instanceof byte[] || o instanceof char[] || o instanceof String || o instanceof ByteSource || o instanceof File || o instanceof InputStream;
}
@Override
public byte[] getBytes() {
return this.bytes;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.bytes == null || this.bytes.length == 0;
}
@Override
public String toHex() {
if (this.cachedHex == null) {
this.cachedHex = Hex.encodeToString(this.getBytes());
}
return this.cachedHex;
}
@Override
public String toBase64() {
if (this.cachedBase64 == null) {
this.cachedBase64 = Base64.encodeToString(this.getBytes());
}
return this.cachedBase64;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.toBase64();
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.bytes != null && this.bytes.length != 0 ? Arrays.hashCode(this.bytes) : 0;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (o instanceof ByteSource) {
ByteSource bs = (ByteSource) o;
return Arrays.equals(this.getBytes(), bs.getBytes());
} else {
return false;
}
}
private static final class BytesHelper extends CodecSupport {
private BytesHelper() {
}
public byte[] getBytes(File file) {
return this.toBytes(file);
}
public byte[] getBytes(InputStream stream) {
return this.toBytes(stream);
}
}
}重启项目进行测试
4.、实现授权
4.1、基于角色授权
sql 文件:
sql
CREATE TABLE `t_role` (
`id` int NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(200) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `t_role` VALUES (1, 'admin');
INSERT INTO `t_role` VALUES (2, 'user');
CREATE TABLE `t_user_role_ref` (
`id` int NOT NULL,
`user_id` int NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`role_id` int NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `t_user_role_ref` VALUES (1, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO `t_user_role_ref` VALUES (2, 2, 2);Role:
java
@Data
@TableName("t_role")
public class Role {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
// 角色名
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private String name;
}UserRoleRef:
java
@Data
@TableName("t_user_role_ref")
public class UserRoleRef {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
// 用户Id
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Integer userId;
// 角色id
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Integer roleId;
}UserMapper:
java
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}UserRoleRefMapper:
java
public interface UserRoleRefMapper extends BaseMapper<UserRoleRef> {
}RoleServiceImpl:
java
@Service
public class RoleServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<RoleMapper, Role> implements RoleService {
@Autowired
private UserRoleRefMapper userRoleRefMapper;
@Override
public List<Role> listByUserId(Integer userId) {
QueryWrapper<UserRoleRef> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("user_id", userId);
List<UserRoleRef> userRoleRefs = userRoleRefMapper.selectList(wrapper);
List<Role> roles = new ArrayList<>();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(userRoleRefs)) {
List<Integer> roleIds = userRoleRefs.stream().map(UserRoleRef::getRoleId).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
QueryWrapper<Role> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.in("id", roleIds);
roles = baseMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
}
return roles;
}
}UserRealm:实现授权
java
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
// 授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
UserService userService = ApplicationContextUtil.getBean(UserService.class);
RoleService roleService = ApplicationContextUtil.getBean(RoleService.class);
String principal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
User user = userService.findByUsername(principal);
if (Objects.nonNull(user)) {
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
List<Role> roles = roleService.listByUserId(user.getId());
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(roles)) {
roles.forEach(role -> simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole(role.getName()));
}
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
return null;
}
}UserController:当前登录用户是什么角色就打印什么角色
java
@PostMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password) {
try {
// 执行登录操作
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 认证通过后直接跳转到 index.html
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password));
// 授权
if (subject.hasRole("admin")) {
System.out.println("admin");
} else if (subject.hasRole("user")) {
System.out.println("user");
}
return "redirect:/index";
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果认证失败仍然回到登录页面
return "redirect:/login";
}
}4.2、基于资源授权
sql 文件:
sql
CREATE TABLE `t_permission` (
`id` int NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(200) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`url` varchar(200) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (1, 'user:*:*', NULL);
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (2, 'order:*:*', NULL);
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (3, 'order:query:*', NULL);
CREATE TABLE `t_role_permission_ref` (
`id` int NOT NULL,
`role_id` int NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`permission_id` int NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission_ref` VALUES (1, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission_ref` VALUES (2, 1, 2);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission_ref` VALUES (3, 2, 3);Permission:
java
@Data
@TableName("t_permission")
public class Permission {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String url;
}RolePermissionRef:
java
@Data
@TableName("t_role_permission_ref")
public class RolePermissionRef {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private Integer roleId;
private Integer permissionId;
}PermissionMapper:
java
public interface PermissionMapper extends BaseMapper<Permission> {
}RolePermissionRefMapper:
java
public interface RolePermissionRefMapper extends BaseMapper<RolePermissionRef> {
}PermissionServiceImpl:
java
@Service
public class PermissionServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<PermissionMapper, Permission> implements PermissionService {
@Autowired
private RolePermissionRefMapper rolePermissionRefMapper;
@Override
public List<Permission> listByRoleIds(List<Integer> roleIds) {
QueryWrapper<RolePermissionRef> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.in("role_id", roleIds);
List<RolePermissionRef> rolePermissionRefs = rolePermissionRefMapper.selectList(wrapper);
List<Permission> permissions = new ArrayList<>();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(rolePermissionRefs)) {
List<Integer> permissionIds = rolePermissionRefs.stream().map(RolePermissionRef::getPermissionId).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
QueryWrapper<Permission> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.in("id", permissionIds);
permissions = baseMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
}
return permissions;
}
}UserRealm:
java
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
// 授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
UserService userService = ApplicationContextUtil.getBean(UserService.class);
RoleService roleService = ApplicationContextUtil.getBean(RoleService.class);
PermissionService permissionService = ApplicationContextUtil.getBean(PermissionService.class);
String principal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
User user = userService.findByUsername(principal);
if (Objects.nonNull(user)) {
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
// 角色
List<Role> roles = roleService.listByUserId(user.getId());
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(roles)) {
roles.forEach(role -> simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole(role.getName()));
}
// 资源
List<Integer> roleIds = roles.stream().map(Role::getId).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
List<Permission> permissions = permissionService.listByRoleIds(roleIds);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(permissions)) {
permissions.forEach(permission -> simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission(permission.getName()));
}
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
return null;
}
}UserController:
java
@PostMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password) {
try {
// 执行登录操作
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 认证通过后直接跳转到 index.html
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password));
// 角色-授权
if (subject.hasRole("admin")) {
System.out.println("admin");
} else if (subject.hasRole("user")) {
System.out.println("user");
}
// 资源-授权
if (subject.isPermitted("order:*:*")) {
System.out.println("order:*:*");
} else if (subject.isPermitted("user:*:*")) {
System.out.println("user:*:*");
}
return "redirect:/index";
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果认证失败仍然回到登录页面
return "redirect:/login";
}
}重启项目测试
5、引入缓存
5.1、EhCache 实现缓存
Shiro 提供了缓存管理器,这样在用户第一次认证授权后访问其受限资源的时候就不用每次查询数据库从而达到减轻数据压力的作用,使用 Shiro 的缓存管理器也很简单
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3</version>
</dependency>ShiroConfiguration:
java
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
UserRealm userRealm = new UserRealm();
// 设置密码匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
// 设置加密方式
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
// 设置散列次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
userRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
// 设置缓存管理器
userRealm.setCacheManager(new EhCacheManager());
// 开启全局缓存
userRealm.setCachingEnabled(true);
// 开启认证缓存并指定缓存名称
userRealm.setAuthenticationCachingEnabled(true);
userRealm.setAuthenticationCacheName("authenticationCache");
// 开启授权缓存并指定缓存名称
userRealm.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true);
userRealm.setAuthorizationCacheName("authorizationCache");
return userRealm;
}这样就将 EhCache 集成进来了,但是 shiro 的这个缓存是本地缓存,也就是说当程序宕机重启后仍然需要从数据库加载数据,不能实现分布式缓存的功能
5.2、集成 Redis 实现 Shiro 缓存
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>RedisCache:
java
public class RedisCache<K,V> implements Cache<K,V> {
private String cacheName;
public RedisCache() {
}
public RedisCache(String cacheName) {
this.cacheName = cacheName;
}
@Override
public V get(K k) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("获取缓存:"+ k);
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().get(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("设置缓存key: "+k+" value:"+v);
getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().put(this.cacheName,k.toString(),v);
return null;
}
@Override
public V remove(K k) throws CacheException {
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().delete(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public void clear() throws CacheException {
getRedisTemplate().delete(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().size(this.cacheName).intValue();
}
@Override
public Set<K> keys() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().keys(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public Collection<V> values() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().values(this.cacheName);
}
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate)ApplicationContextUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
}RedisCacheManager:
java
public class RedisCacheManager implements CacheManager {
@Override
public <K, V> Cache<K, V> getCache(String s) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("缓存名称: "+ s);
return new RedisCache<K,V>(s);
}
}ShiroConfiguration:
java
// 设置缓存管理器
//userRealm.setCacheManager(new EhCacheManager());
userRealm.setCacheManager(new RedisCacheManager());重启测试项目