文章目录
python
!nvidia-smiWed Sep 11 07:23:53 2024
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 550.90.07 Driver Version: 550.90.07 CUDA Version: 12.4 |
|-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+========================+======================|
| 0 Tesla T4 Off | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 36C P8 9W / 70W | 1MiB / 15360MiB | 0% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
| 1 Tesla T4 Off | 00000000:00:05.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 36C P8 10W / 70W | 1MiB / 15360MiB | 0% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=========================================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
python
!pip install d2l序列模型
python
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
T = 1000 # 总共产生1000个点
time = torch.arange(1, T + 1, dtype=torch.float32)
x = torch.sin(0.01 * time) + torch.normal(0, 0.2, (T,))
d2l.plot(time, [x], 'time', 'x', xlim=[1, 1000], figsize=(6, 3))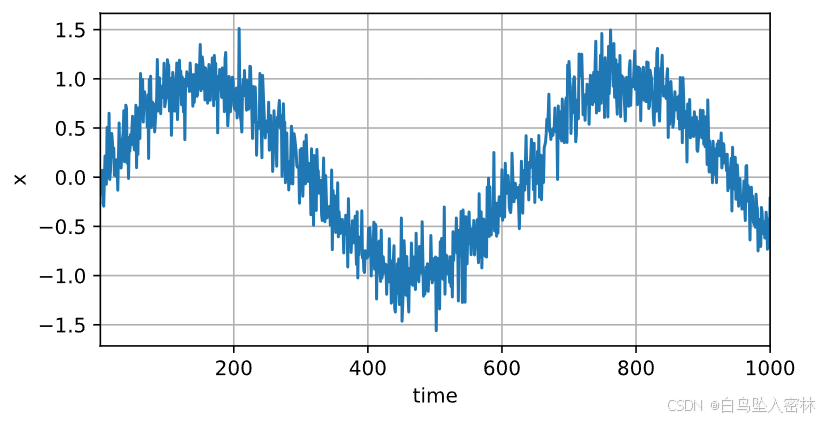
python
tau = 4
features = torch.zeros((T - tau, tau))
for i in range(tau):
features[:, i] = x[i: T - tau + i]
labels = x[tau:].reshape((-1, 1))
batch_size, n_train = 16, 600
# 只有前n_train个样本用于训练
train_iter = d2l.load_array((features[:n_train], labels[:n_train]),
batch_size, is_train=True)
python
# 初始化网络权重的函数
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
# 一个简单的多层感知机
def get_net():
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4, 10),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(10, 1))
net.apply(init_weights)
return net
# 平方损失。注意:MSELoss计算平方误差时不带系数1/2
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none') # reduction='none' 表示计算损失时不对结果进行任何归约(reduction),即不对损失值求和或取平均值。它会返回每个输入数据点对应的损失值,而不是一个标量结果。
python
def train(net, train_iter, loss, epochs, lr):
trainer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
trainer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(X), y)
l.sum().backward()
trainer.step()
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, '
f'loss: {d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss):f}')
net = get_net()
train(net, train_iter, loss, 5, 0.01)epoch 1, loss: 0.082473
epoch 2, loss: 0.065913
epoch 3, loss: 0.060240
epoch 4, loss: 0.058487
epoch 5, loss: 0.058331
python
onestep_preds = net(features)
d2l.plot([time, time[tau:]],
[x.detach().numpy(), onestep_preds.detach().numpy()], 'time',
'x', legend=['data', '1-step preds'], xlim=[1, 1000],
figsize=(6, 3))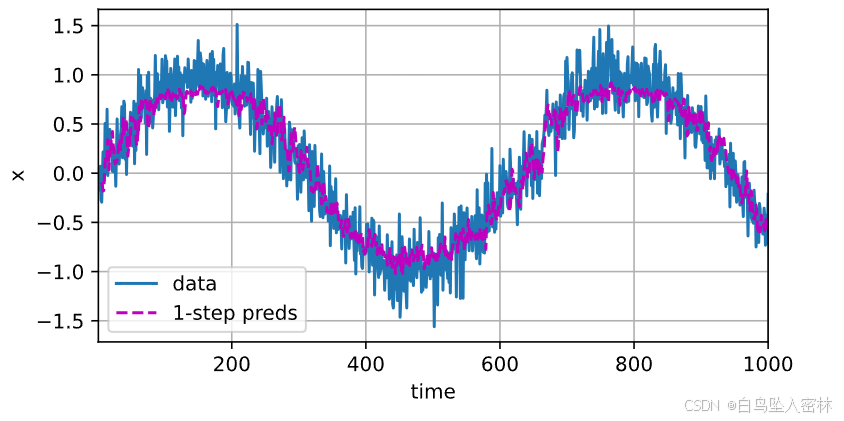
python
multistep_preds = torch.zeros(T)
multistep_preds[: n_train + tau] = x[: n_train + tau]
for i in range(n_train + tau, T):
multistep_preds[i] = net(
multistep_preds[i - tau:i].reshape((1, -1)))
d2l.plot([time, time[tau:], time[n_train + tau:]],
[x.detach().numpy(), onestep_preds.detach().numpy(),
multistep_preds[n_train + tau:].detach().numpy()], 'time',
'x', legend=['data', '1-step preds', 'multistep preds'],
xlim=[1, 1000], figsize=(6, 3))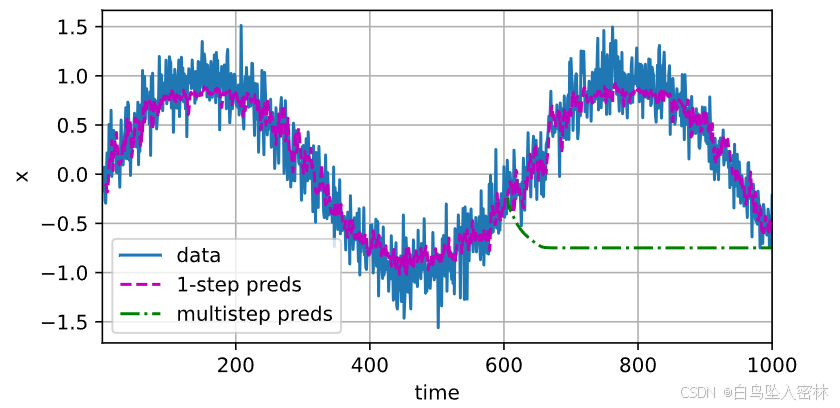
python
max_steps = 64
features = torch.zeros((T - tau - max_steps + 1, tau + max_steps))
# 列i(i<tau)是来自x的观测,其时间步从(i)到(i+T-tau-max_steps+1)
for i in range(tau):
features[:, i] = x[i: i + T - tau - max_steps + 1]
# 列i(i>=tau)是来自(i-tau+1)步的预测,其时间步从(i)到(i+T-tau-max_steps+1)
for i in range(tau, tau + max_steps):
features[:, i] = net(features[:, i - tau:i]).reshape(-1)
steps = (1, 4, 16, 64)
d2l.plot([time[tau + i - 1: T - max_steps + i] for i in steps],
[features[:, (tau + i - 1)].detach().numpy() for i in steps], 'time', 'x',
legend=[f'{i}-step preds' for i in steps], xlim=[5, 1000],
figsize=(6, 3))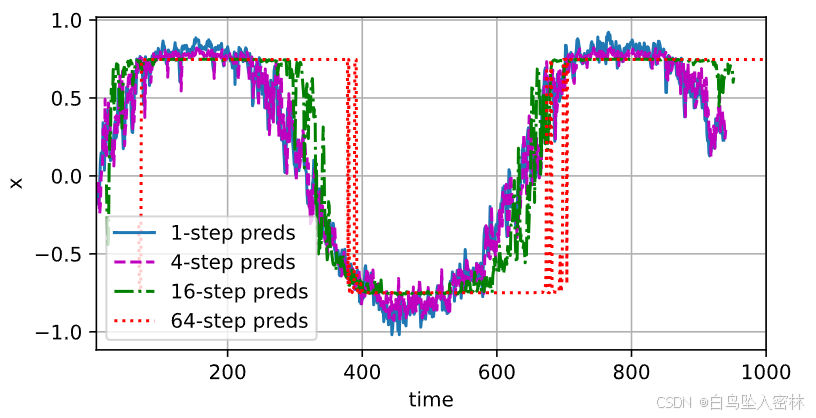
文本预处理
python
import collections
import re
from d2l import torch as d2l
python
d2l.DATA_HUB['time_machine'] = (d2l.DATA_URL + 'timemachine.txt',
'090b5e7e70c295757f55df93cb0a180b9691891a')
def read_time_machine():
"""将时间机器数据集加载到文本行的列表中"""
with open(d2l.download('time_machine'), 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
return [re.sub('[^A-Za-z]+', ' ', line).strip().lower() for line in lines]
lines = read_time_machine()
print(f'# 文本总行数: {len(lines)}')
print(lines[0])
print(lines[10])Downloading ../data/timemachine.txt from http://d2l-data.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.com/timemachine.txt...
# 文本总行数: 3221
the time machine by h g wells
twinkled and his usually pale face was flushed and animated the
python
def tokenize(lines, token='word'):
"""将文本行拆分为单词或字符词元"""
if token == 'word':
return [line.split() for line in lines]
elif token == 'char':
return [list(line) for line in lines]
else:
print('错误:未知词元类型:' + token)
tokens = tokenize(lines)
for i in range(11):
print(tokens[i])['the', 'time', 'machine', 'by', 'h', 'g', 'wells']
[]
[]
[]
[]
['i']
[]
[]
['the', 'time', 'traveller', 'for', 'so', 'it', 'will', 'be', 'convenient', 'to', 'speak', 'of', 'him']
['was', 'expounding', 'a', 'recondite', 'matter', 'to', 'us', 'his', 'grey', 'eyes', 'shone', 'and']
['twinkled', 'and', 'his', 'usually', 'pale', 'face', 'was', 'flushed', 'and', 'animated', 'the']
python
class Vocab:
"""文本词表"""
def __init__(self, tokens=None, min_freq=0, reserved_tokens=None):
if tokens is None:
tokens = []
if reserved_tokens is None:
reserved_tokens = []
# 按出现频率排序
counter = count_corpus(tokens)
self._token_freqs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: x[1],
reverse=True)
# 未知词元的索引为0
self.idx_to_token = ['<unk>'] + reserved_tokens
self.token_to_idx = {token: idx
for idx, token in enumerate(self.idx_to_token)}
for token, freq in self._token_freqs:
if freq < min_freq:
break
if token not in self.token_to_idx:
self.idx_to_token.append(token)
self.token_to_idx[token] = len(self.idx_to_token) - 1
def __len__(self):
return len(self.idx_to_token)
def __getitem__(self, tokens):
if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)):
return self.token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk)
return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens]
def to_tokens(self, indices):
if not isinstance(indices, (list, tuple)):
return self.idx_to_token[indices]
return [self.idx_to_token[index] for index in indices]
@property
def unk(self): # 未知词元的索引为0
return 0
@property
def token_freqs(self):
return self._token_freqs
def count_corpus(tokens):
"""统计词元的频率"""
# 这里的tokens是1D列表或2D列表
if len(tokens) == 0 or isinstance(tokens[0], list):
# 将词元列表展平成一维列表
tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
return collections.Counter(tokens)
python
vocab = Vocab(tokens)
print(list(vocab.token_to_idx.items())[:10])[('<unk>', 0), ('the', 1), ('i', 2), ('and', 3), ('of', 4), ('a', 5), ('to', 6), ('was', 7), ('in', 8), ('that', 9)]
python
for i in [0, 10]:
print('文本:', tokens[i])
print('索引:', vocab[tokens[i]])文本: ['the', 'time', 'machine', 'by', 'h', 'g', 'wells']
索引: [1, 19, 50, 40, 2183, 2184, 400]
文本: ['twinkled', 'and', 'his', 'usually', 'pale', 'face', 'was', 'flushed', 'and', 'animated', 'the']
索引: [2186, 3, 25, 1044, 362, 113, 7, 1421, 3, 1045, 1]
python
def load_corpus_time_machine(max_tokens=-1): #@save
"""返回时光机器数据集的词元索引列表和词表"""
lines = read_time_machine()
tokens = tokenize(lines, 'char')
vocab = Vocab(tokens)
# 因为时光机器数据集中的每个文本行不一定是一个句子或一个段落,
# 所以将所有文本行展平到一个列表中
corpus = [vocab[token] for line in tokens for token in line]
if max_tokens > 0:
corpus = corpus[:max_tokens]
return corpus, vocab
corpus, vocab = load_corpus_time_machine()
len(corpus), len(vocab)(170580, 28)语言模型和数据集
python
import random
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
tokens = d2l.tokenize(read_time_machine())
# 因为每个文本行不一定是一个句子或一个段落,因此我们把所有文本行拼接到一起
corpus = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
vocab = d2l.Vocab(corpus)
vocab.token_freqs[:10][('the', 2261),
('i', 1267),
('and', 1245),
('of', 1155),
('a', 816),
('to', 695),
('was', 552),
('in', 541),
('that', 443),
('my', 440)]
python
freqs = [freq for token, freq in vocab.token_freqs]
d2l.plot(freqs, xlabel='token: x', ylabel='frequency: n(x)',
xscale='log', yscale='log')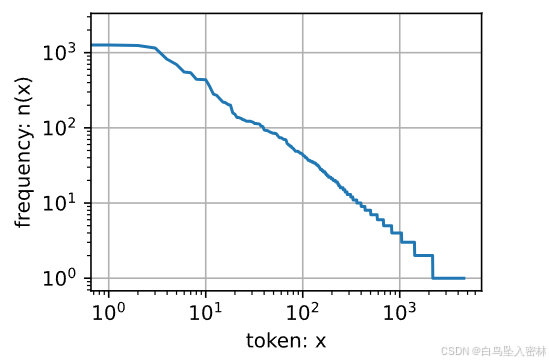
python
bigram_tokens = [pair for pair in zip(corpus[:-1], corpus[1:])]
bigram_vocab = Vocab(bigram_tokens)
bigram_vocab.token_freqs[:10][(('of', 'the'), 309),
(('in', 'the'), 169),
(('i', 'had'), 130),
(('i', 'was'), 112),
(('and', 'the'), 109),
(('the', 'time'), 102),
(('it', 'was'), 99),
(('to', 'the'), 85),
(('as', 'i'), 78),
(('of', 'a'), 73)]
python
trigram_tokens = [triple for triple in zip(
corpus[:-2], corpus[1:-1], corpus[2:])]
trigram_vocab = Vocab(trigram_tokens)
trigram_vocab.token_freqs[:10][(('the', 'time', 'traveller'), 59),
(('the', 'time', 'machine'), 30),
(('the', 'medical', 'man'), 24),
(('it', 'seemed', 'to'), 16),
(('it', 'was', 'a'), 15),
(('here', 'and', 'there'), 15),
(('seemed', 'to', 'me'), 14),
(('i', 'did', 'not'), 14),
(('i', 'saw', 'the'), 13),
(('i', 'began', 'to'), 13)]
python
bigram_freqs = [freq for token, freq in bigram_vocab.token_freqs]
trigram_freqs = [freq for token, freq in trigram_vocab.token_freqs]
d2l.plot([freqs, bigram_freqs, trigram_freqs], xlabel='token: x',
ylabel='frequency: n(x)', xscale='log', yscale='log',
legend=['unigram', 'bigram', 'trigram'])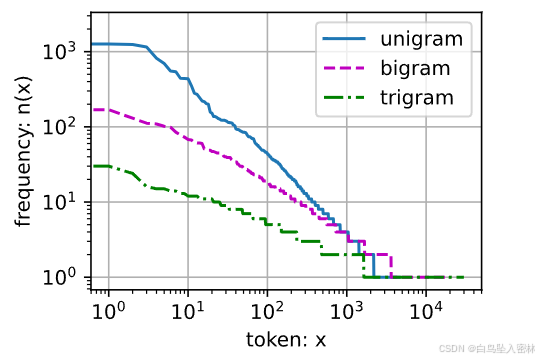
python
def seq_data_iter_random(corpus, batch_size, num_steps): #@save
"""使用随机抽样生成一个小批量子序列"""
# 从随机偏移量开始对序列进行分区,随机范围包括num_steps-1
corpus = corpus[random.randint(0, num_steps - 1):]
# 减去1,是因为我们需要考虑标签
num_subseqs = (len(corpus) - 1) // num_steps
# 长度为num_steps的子序列的起始索引
initial_indices = list(range(0, num_subseqs * num_steps, num_steps))
# 在随机抽样的迭代过程中,
# 来自两个相邻的、随机的、小批量中的子序列不一定在原始序列上相邻
random.shuffle(initial_indices)
def data(pos):
# 返回从pos位置开始的长度为num_steps的序列
return corpus[pos: pos + num_steps]
num_batches = num_subseqs // batch_size
for i in range(0, batch_size * num_batches, batch_size):
# 在这里,initial_indices包含子序列的随机起始索引
initial_indices_per_batch = initial_indices[i: i + batch_size]
X = [data(j) for j in initial_indices_per_batch]
Y = [data(j + 1) for j in initial_indices_per_batch]
yield torch.tensor(X), torch.tensor(Y)
python
my_seq = list(range(35))
for X, Y in seq_data_iter_random(my_seq, batch_size=2, num_steps=5):
print('X: ', X, '\nY:', Y)X: tensor([[ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13],
[14, 15, 16, 17, 18]])
Y: tensor([[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]])
X: tensor([[29, 30, 31, 32, 33],
[19, 20, 21, 22, 23]])
Y: tensor([[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
X: tensor([[24, 25, 26, 27, 28],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]])
Y: tensor([[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])
python
def seq_data_iter_sequential(corpus, batch_size, num_steps): #@save
"""使用顺序分区生成一个小批量子序列"""
# 从随机偏移量开始划分序列
offset = random.randint(0, num_steps)
num_tokens = ((len(corpus) - offset - 1) // batch_size) * batch_size
Xs = torch.tensor(corpus[offset: offset + num_tokens])
Ys = torch.tensor(corpus[offset + 1: offset + 1 + num_tokens])
Xs, Ys = Xs.reshape(batch_size, -1), Ys.reshape(batch_size, -1)
num_batches = Xs.shape[1] // num_steps
for i in range(0, num_steps * num_batches, num_steps):
X = Xs[:, i: i + num_steps]
Y = Ys[:, i: i + num_steps]
yield X, Y
python
for X, Y in seq_data_iter_sequential(my_seq, batch_size=2, num_steps=4):
print('X: ', X, '\nY:', Y)X: tensor([[ 3, 4, 5, 6],
[18, 19, 20, 21]])
Y: tensor([[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[19, 20, 21, 22]])
X: tensor([[ 7, 8, 9, 10],
[22, 23, 24, 25]])
Y: tensor([[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
[23, 24, 25, 26]])
X: tensor([[11, 12, 13, 14],
[26, 27, 28, 29]])
Y: tensor([[12, 13, 14, 15],
[27, 28, 29, 30]])
python
class SeqDataLoader:
"""加载序列数据的迭代器"""
def __init__(self, batch_size, num_steps, use_random_iter, max_tokens):
if use_random_iter:
self.data_iter_fn = seq_data_iter_random
else:
self.data_iter_fn = seq_data_iter_sequential
self.corpus, self.vocab = load_corpus_time_machine(max_tokens)
self.batch_size, self.num_steps = batch_size, num_steps
def __iter__(self):
return self.data_iter_fn(self.corpus, self.batch_size, self.num_steps)
python
def load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps, #@save
use_random_iter=False, max_tokens=10000):
"""返回时光机器数据集的迭代器和词表"""
data_iter = SeqDataLoader(
batch_size, num_steps, use_random_iter, max_tokens)
return data_iter, data_iter.vocab循环神经网络
python
import torch
X, W_xh = torch.randn(3, 1), torch.randn(1, 4)
H, W_hh = torch.randn(3, 4), torch.randn(4, 4)
torch.matmul(X, W_xh) + torch.matmul(H, W_hh)tensor([[ 1.5182, 1.9115, -0.0618, 0.0826],
[-0.3502, 4.0483, 0.9087, -0.2270],
[ 0.7328, -0.7081, 0.9375, -1.7978]])
python
torch.matmul(torch.cat((X, H), dim=1), torch.cat((W_xh, W_hh), dim=0))tensor([[ 1.5182, 1.9115, -0.0618, 0.0826],
[-0.3502, 4.0483, 0.9087, -0.2270],
[ 0.7328, -0.7081, 0.9375, -1.7978]])从0实现
python
%matplotlib inline
import math
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size, num_steps = 32, 35
train_iter, vocab = load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps)
python
F.one_hot(torch.tensor([0, 2]), len(vocab))tensor([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0]])
python
X = torch.arange(10).reshape((2, 5))
F.one_hot(X.T, 28).shapetorch.Size([5, 2, 28])
python
def get_params(vocab_size, num_hiddens, device):
num_inputs = num_outputs = vocab_size
def normal(shape):
return torch.randn(size=shape, device=device) * 0.01
# 隐藏层参数
W_xh = normal((num_inputs, num_hiddens))
W_hh = normal((num_hiddens, num_hiddens))
b_h = torch.zeros(num_hiddens, device=device)
# 输出层参数
W_hq = normal((num_hiddens, num_outputs))
b_q = torch.zeros(num_outputs, device=device)
# 附加梯度
params = [W_xh, W_hh, b_h, W_hq, b_q]
for param in params:
param.requires_grad_(True)
return params
python
def init_rnn_state(batch_size, num_hiddens, device):
return (torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device), )
python
def rnn(inputs, state, params):
# inputs的形状:(时间步数量,批量大小,词表大小)
W_xh, W_hh, b_h, W_hq, b_q = params
H, = state
outputs = []
# X的形状:(批量大小,词表大小)
for X in inputs:
H = torch.tanh(torch.mm(X, W_xh) + torch.mm(H, W_hh) + b_h)
Y = torch.mm(H, W_hq) + b_q
outputs.append(Y)
return torch.cat(outputs, dim=0), (H,)
# 第一个返回值是模型在所有时间步上的输出序列,形状为(时间步数 × 批量大小, 输出维度)。
# 第二个返回值是最终的隐藏状态H,以便后续使用。
python
class RNNModelScratch: #@save
"""从零开始实现的循环神经网络模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, num_hiddens, device,
get_params, init_state, forward_fn):
self.vocab_size, self.num_hiddens = vocab_size, num_hiddens
self.params = get_params(vocab_size, num_hiddens, device)
self.init_state, self.forward_fn = init_state, forward_fn
def __call__(self, X, state):
X = F.one_hot(X.T, self.vocab_size).type(torch.float32)
return self.forward_fn(X, state, self.params)
def begin_state(self, batch_size, device):
return self.init_state(batch_size, self.num_hiddens, device)
python
num_hiddens = 512
net = RNNModelScratch(len(vocab), num_hiddens, d2l.try_gpu(), get_params,
init_rnn_state, rnn)
state = net.begin_state(X.shape[0], d2l.try_gpu())
Y, new_state = net(X.to(d2l.try_gpu()), state)
Y.shape, len(new_state), new_state[0].shape(torch.Size([10, 28]), 1, torch.Size([2, 512]))
python
def predict_ch8(prefix, num_preds, net, vocab, device): #@save
"""在prefix后面生成新字符"""
state = net.begin_state(batch_size=1, device=device)
outputs = [vocab[prefix[0]]]
get_input = lambda: torch.tensor([outputs[-1]], device=device).reshape((1, 1))
for y in prefix[1:]: # 预热期
_, state = net(get_input(), state)
outputs.append(vocab[y])
for _ in range(num_preds): # 预测num_preds步
y, state = net(get_input(), state)
outputs.append(int(y.argmax(dim=1).reshape(1)))
return ''.join([vocab.idx_to_token[i] for i in outputs])
python
predict_ch8('time traveller ', 10, net, vocab, d2l.try_gpu())'time traveller avavavavav'
python
def grad_clipping(net, theta): #@save
"""裁剪梯度"""
if isinstance(net, nn.Module):
params = [p for p in net.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
else:
params = net.params
norm = torch.sqrt(sum(torch.sum((p.grad ** 2)) for p in params))
if norm > theta:
for param in params:
param.grad[:] *= theta / norm
python
#@save
def train_epoch_ch8(net, train_iter, loss, updater, device, use_random_iter):
"""训练网络一个迭代周期(定义见第8章)"""
state, timer = None, d2l.Timer()
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # 训练损失之和,词元数量
for X, Y in train_iter:
if state is None or use_random_iter:
# 在第一次迭代或使用随机抽样时初始化state
state = net.begin_state(batch_size=X.shape[0], device=device)
else:
if isinstance(net, nn.Module) and not isinstance(state, tuple):
# state对于nn.GRU是个张量
state.detach_()
else:
# state对于nn.LSTM或对于我们从零开始实现的模型是个张量
for s in state:
s.detach_()
y = Y.T.reshape(-1)
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat, state = net(X, state)
l = loss(y_hat, y.long()).mean()
if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer):
updater.zero_grad()
l.backward()
grad_clipping(net, 1)
updater.step()
else:
l.backward()
grad_clipping(net, 1)
# 因为已经调用了mean函数
updater(batch_size=1)
metric.add(l * y.numel(), y.numel())
return math.exp(metric[0] / metric[1]), metric[1] / timer.stop()
python
#@save
def train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device,
use_random_iter=False):
"""训练模型(定义见第8章)"""
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='perplexity',
legend=['train'], xlim=[10, num_epochs])
# 初始化
if isinstance(net, nn.Module):
updater = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr)
else:
updater = lambda batch_size: d2l.sgd(net.params, lr, batch_size)
predict = lambda prefix: predict_ch8(prefix, 50, net, vocab, device)
# 训练和预测
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
ppl, speed = train_epoch_ch8(
net, train_iter, loss, updater, device, use_random_iter)
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
print(predict('time traveller'))
animator.add(epoch + 1, [ppl])
print(f'困惑度 {ppl:.1f}, {speed:.1f} 词元/秒 {str(device)}')
print(predict('time traveller'))
print(predict('traveller'))
python
# num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
# train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, d2l.try_gpu())
python
# net = RNNModelScratch(len(vocab), num_hiddens, d2l.try_gpu(), get_params,
# init_rnn_state, rnn)
# train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, d2l.try_gpu(),
# use_random_iter=True)简洁实现
python
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size, num_steps = 32, 35
train_iter, vocab = load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps)
python
num_hiddens = 256
rnn_layer = nn.RNN(len(vocab), num_hiddens)
python
state = torch.zeros((1, batch_size, num_hiddens))
state.shapetorch.Size([1, 32, 256])
python
X = torch.rand(size=(num_steps, batch_size, len(vocab)))
Y, state_new = rnn_layer(X, state)
Y.shape, state_new.shape(torch.Size([35, 32, 256]), torch.Size([1, 32, 256]))
python
class RNNModel(nn.Module):
"""循环神经网络模型"""
def __init__(self, rnn_layer, vocab_size, **kwargs):
super(RNNModel, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.rnn = rnn_layer
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.num_hiddens = self.rnn.hidden_size
# 如果RNN是双向的(之后将介绍),num_directions应该是2,否则应该是1
if not self.rnn.bidirectional:
self.num_directions = 1
self.linear = nn.Linear(self.num_hiddens, self.vocab_size)
else:
self.num_directions = 2
self.linear = nn.Linear(self.num_hiddens * 2, self.vocab_size)
def forward(self, inputs, state):
X = F.one_hot(inputs.T.long(), self.vocab_size)
X = X.to(torch.float32)
Y, state = self.rnn(X, state)
# 全连接层首先将Y的形状改为(时间步数*批量大小,隐藏单元数)
# 它的输出形状是(时间步数*批量大小,词表大小)。
output = self.linear(Y.reshape((-1, Y.shape[-1])))
return output, state
def begin_state(self, device, batch_size=1):
if not isinstance(self.rnn, nn.LSTM):
# nn.GRU以张量作为隐状态
return torch.zeros((self.num_directions * self.rnn.num_layers,
batch_size, self.num_hiddens),
device=device)
else:
# nn.LSTM以元组作为隐状态
return (torch.zeros((
self.num_directions * self.rnn.num_layers,
batch_size, self.num_hiddens), device=device),
torch.zeros((
self.num_directions * self.rnn.num_layers,
batch_size, self.num_hiddens), device=device))
python
# device = d2l.try_gpu()
# net = RNNModel(rnn_layer, vocab_size=len(vocab))
# net = net.to(device)
# num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
# # predict_ch8('time traveller', 10, net, vocab, device)
# train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device)GRU
从0开始实现
python
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size, num_steps = 32, 35
train_iter, vocab = load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps)
python
def get_params(vocab_size, num_hiddens, device):
num_inputs = num_outputs = vocab_size
def normal(shape):
return torch.randn(size=shape, device=device)*0.01
def three():
return (normal((num_inputs, num_hiddens)),
normal((num_hiddens, num_hiddens)),
torch.zeros(num_hiddens, device=device))
W_xz, W_hz, b_z = three() # 更新门参数
W_xr, W_hr, b_r = three() # 重置门参数
W_xh, W_hh, b_h = three() # 候选隐状态参数
# 输出层参数
W_hq = normal((num_hiddens, num_outputs))
b_q = torch.zeros(num_outputs, device=device)
# 附加梯度
params = [W_xz, W_hz, b_z, W_xr, W_hr, b_r, W_xh, W_hh, b_h, W_hq, b_q]
for param in params:
param.requires_grad_(True)
return params
python
def init_gru_state(batch_size, num_hiddens, device):
return (torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device), )
python
def gru(inputs, state, params):
W_xz, W_hz, b_z, W_xr, W_hr, b_r, W_xh, W_hh, b_h, W_hq, b_q = params
H, = state
outputs = []
for X in inputs:
Z = torch.sigmoid((X @ W_xz) + (H @ W_hz) + b_z)
R = torch.sigmoid((X @ W_xr) + (H @ W_hr) + b_r)
H_tilda = torch.tanh((X @ W_xh) + ((R * H) @ W_hh) + b_h)
H = Z * H + (1 - Z) * H_tilda
Y = H @ W_hq + b_q
outputs.append(Y)
return torch.cat(outputs, dim=0), (H,)
python
# 运行较久,不运行了
# vocab_size, num_hiddens, device = len(vocab), 256, d2l.try_gpu()
# num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
# model = RNNModelScratch(len(vocab), num_hiddens, device, get_params,
# init_gru_state, gru)
# train_ch8(model, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device)简洁实现
python
# num_inputs = vocab_size
# gru_layer = nn.GRU(num_inputs, num_hiddens)
# model = RNNModel(gru_layer, len(vocab))
# model = model.to(device)
# train_ch8(model, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device)一个例子
python
import torch
# 1、确定参数
seq_len = 5
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
batch_size = 1
# 2、准备数据
index2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o'] #字典
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3] #用字典中的索引(数字)表示来表示hello
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] #标签:ohlol
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0], # 用来将x_data转换为one-hot向量的参照表
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data] #将x_data转换为one-hot向量
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(seq_len, batch_size,
input_size) #(𝒔𝒆𝒒𝑳𝒆𝒏,𝒃𝒂𝒕𝒄𝒉𝑺𝒊𝒛𝒆,𝒊𝒏𝒑𝒖𝒕𝑺𝒊𝒛𝒆)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
inputs,labels(tensor([[[0., 1., 0., 0.]],
[[1., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 1., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 1., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0., 1.]]]),
tensor([3, 1, 2, 3, 2]))
python
# 3、构建模型
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size, num_layers=1):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=self.input_size, hidden_size=self.hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers)
def forward(self, input):
hidden = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, self.batch_size, self.hidden_size)
out, _ = self.rnn(input, hidden) # out: tensor of shape (seq_len, batch, hidden_size)
return out.view(-1, self.hidden_size) # 将输出的三维张量转换为二维张量,(𝒔𝒆𝒒𝑳𝒆𝒏×𝒃𝒂𝒕𝒄𝒉𝑺𝒊𝒛𝒆,𝒉𝒊𝒅𝒅𝒆𝒏𝑺𝒊𝒛𝒆)
def init_hidden(self): #初始化隐藏层,需要batch_size
return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size)
net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size)
# 4、损失和优化器
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05) # Adam优化器
# 5、训练
for epoch in range(100):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted string: ', ''.join([index2char[x] for x in idx]), end='')
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss: %.4f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))Predicted string: hohhl, Epoch [1/15] loss: 1.2648
Predicted string: oolll, Epoch [2/15] loss: 1.1561
Predicted string: oolll, Epoch [3/15] loss: 1.0815
Predicted string: ollll, Epoch [4/15] loss: 1.0268
Predicted string: ollll, Epoch [5/15] loss: 0.9794
Predicted string: oolll, Epoch [6/15] loss: 0.9351
Predicted string: ohlll, Epoch [7/15] loss: 0.8946
Predicted string: ohlll, Epoch [8/15] loss: 0.8583
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss: 0.8252
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss: 0.7928
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss: 0.7594
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss: 0.7247
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [97/15] loss: 0.3466
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [98/15] loss: 0.3465
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [99/15] loss: 0.3465
Predicted string: ohlol, Epoch [100/15] loss: 0.3464LSTM
从0实现
python
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size, num_steps = 32, 35
train_iter, vocab = load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps)
python
def get_lstm_params(vocab_size, num_hiddens, device):
num_inputs = num_outputs = vocab_size
def normal(shape):
return torch.randn(size=shape, device=device)*0.01
def three():
return (normal((num_inputs, num_hiddens)),
normal((num_hiddens, num_hiddens)),
torch.zeros(num_hiddens, device=device))
W_xi, W_hi, b_i = three() # 输入门参数
W_xf, W_hf, b_f = three() # 遗忘门参数
W_xo, W_ho, b_o = three() # 输出门参数
W_xc, W_hc, b_c = three() # 候选记忆元参数
# 输出层参数
W_hq = normal((num_hiddens, num_outputs))
b_q = torch.zeros(num_outputs, device=device)
# 附加梯度
params = [W_xi, W_hi, b_i, W_xf, W_hf, b_f, W_xo, W_ho, b_o, W_xc, W_hc,
b_c, W_hq, b_q]
for param in params:
param.requires_grad_(True)
return params
python
def init_lstm_state(batch_size, num_hiddens, device):
return (torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device),
torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device))
python
def lstm(inputs, state, params):
# 将参数 params 分解为各个权重和偏置矩阵
[W_xi, W_hi, b_i, # 输入门的权重和偏置
W_xf, W_hf, b_f, # 遗忘门的权重和偏置
W_xo, W_ho, b_o, # 输出门的权重和偏置
W_xc, W_hc, b_c, # 记忆单元的权重和偏置
W_hq, b_q] = params # 最后的输出层权重和偏置
(H, C) = state # 当前的隐藏状态 (H) 和记忆状态 (C)
outputs = [] # 用于存储输出
# 遍历每一个时间步的输入
for X in inputs:
# 输入门计算,决定是否更新记忆单元
I = torch.sigmoid((X @ W_xi) + (H @ W_hi) + b_i)
# 遗忘门计算,决定是否忘记之前的记忆
F = torch.sigmoid((X @ W_xf) + (H @ W_hf) + b_f)
# 输出门计算,决定从记忆单元输出多少
O = torch.sigmoid((X @ W_xo) + (H @ W_ho) + b_o)
# 候选记忆单元 C_tilda,使用 tanh 激活函数生成新的记忆
C_tilda = torch.tanh((X @ W_xc) + (H @ W_hc) + b_c)
# 更新记忆单元 C,结合遗忘门的输出 F 和输入门的输出 I 及 C_tilda
C = F * C + I * C_tilda
# 更新隐藏状态 H,结合输出门 O 和当前记忆单元 C
H = O * torch.tanh(C)
# 输出层的计算,H 投影到输出 Y
Y = (H @ W_hq) + b_q
# 保存当前时间步的输出 Y
outputs.append(Y)
# 返回所有时间步的输出,拼接成一个完整的输出序列,以及最后的隐藏状态和记忆状态
return torch.cat(outputs, dim=0), (H, C)
python
# vocab_size, num_hiddens, device = len(vocab), 256, d2l.try_gpu()
# num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
# model = RNNModelScratch(len(vocab), num_hiddens, device, get_lstm_params,
# init_lstm_state, lstm)
# train_ch8(model, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device)简洁实现
python
# num_inputs = vocab_size
# lstm_layer = nn.LSTM(num_inputs, num_hiddens)
# model = RNNModel(lstm_layer, len(vocab))
# model = model.to(device)
# train_ch8(model, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device)深度循环神经网络
python
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size, num_steps = 32, 35
train_iter, vocab = load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps)
python
vocab_size, num_hiddens, num_layers = len(vocab), 256, 2
num_inputs = vocab_size
device = d2l.try_gpu()
lstm_layer = nn.LSTM(num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_layers)
model = RNNModel(lstm_layer, len(vocab))
model = model.to(device)
python
# num_epochs, lr = 500, 2
# train_ch8(model, train_iter, vocab, lr*1.0, num_epochs, device)双向循环神经网络
python
# import torch
# from torch import nn
# from d2l import torch as d2l
# # 加载数据
# batch_size, num_steps, device = 32, 35, d2l.try_gpu()
# train_iter, vocab = load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps)
# # 通过设置"bidirective=True"来定义双向LSTM模型
# vocab_size, num_hiddens, num_layers = len(vocab), 256, 2
# num_inputs = vocab_size
# lstm_layer = nn.LSTM(num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_layers, bidirectional=True)
# model = RNNModel(lstm_layer, len(vocab))
# model = model.to(device)
# # 训练模型
# num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
# train_ch8(model, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device)机器翻译与数据集
python
import os
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
python
#@save
d2l.DATA_HUB['fra-eng'] = (d2l.DATA_URL + 'fra-eng.zip',
'94646ad1522d915e7b0f9296181140edcf86a4f5')
#@save
def read_data_nmt():
"""载入"英语-法语"数据集"""
data_dir = d2l.download_extract('fra-eng')
with open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'fra.txt'), 'r',
encoding='utf-8') as f:
return f.read()
raw_text = read_data_nmt()
print(raw_text[:75])Downloading ../data/fra-eng.zip from http://d2l-data.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.com/fra-eng.zip...
Go. Va !
Hi. Salut !
Run! Cours !
Run! Courez !
Who? Qui ?
Wow! Ça alors !
python
#@save
def preprocess_nmt(text):
"""预处理"英语-法语"数据集"""
def no_space(char, prev_char):
return char in set(',.!?') and prev_char != ' '
# 使用普通空格替换不间断空格:为了确保文本的一致性、简化处理流程,并减少潜在的兼容性和显示问题
text = text.replace('\u202f', ' ').replace('\xa0', ' ').lower()
# 在单词和标点符号之间插入空格
out = [' ' + char if i > 0 and no_space(char, text[i - 1]) else char
for i, char in enumerate(text)]
return ''.join(out)
text = preprocess_nmt(raw_text)
print(text[:80])go . va !
hi . salut !
run ! cours !
run ! courez !
who ? qui ?
wow ! ça alors !
python
type(text)str
python
#@save
def tokenize_nmt(text, num_examples=None):
"""词元化"英语-法语"数据数据集"""
source, target = [], []
for i, line in enumerate(text.split('\n')): # 将整个文本按换行符 \n 分割成多个句子对
if num_examples and i > num_examples:
break
parts = line.split('\t') # 将每行句子对按制表符 \t 分成两个部分,即 parts[0] 为英语句子,parts[1] 为对应的法语句子
if len(parts) == 2:
source.append(parts[0].split(' '))
target.append(parts[1].split(' '))
return source, target
source, target = tokenize_nmt(text)
source[:6], target[:6]([['go', '.'],
['hi', '.'],
['run', '!'],
['run', '!'],
['who', '?'],
['wow', '!']],
[['va', '!'],
['salut', '!'],
['cours', '!'],
['courez', '!'],
['qui', '?'],
['ça', 'alors', '!']])
python
#@save
def show_list_len_pair_hist(legend, xlabel, ylabel, xlist, ylist):
"""绘制列表长度对的直方图"""
d2l.set_figsize()
_, _, patches = d2l.plt.hist(
[[len(l) for l in xlist], [len(l) for l in ylist]])
d2l.plt.xlabel(xlabel)
d2l.plt.ylabel(ylabel)
for patch in patches[1].patches:
patch.set_hatch('/')
d2l.plt.legend(legend)
show_list_len_pair_hist(['source', 'target'], '# tokens per sequence',
'count', source, target);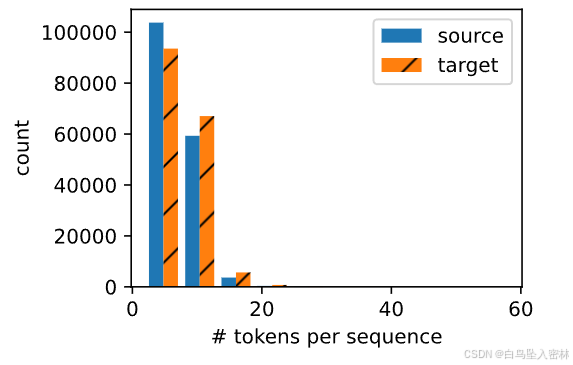
python
src_vocab = d2l.Vocab(source, min_freq=2,
reserved_tokens=['<pad>', '<bos>', '<eos>'])
len(src_vocab)10012
python
#@save
def truncate_pad(line, num_steps, padding_token):
"""截断或填充文本序列"""
if len(line) > num_steps:
return line[:num_steps] # 截断
return line + [padding_token] * (num_steps - len(line)) # 填充
truncate_pad(src_vocab[source[0]], 10, src_vocab['<pad>'])[3919, 80, 208, 208, 208, 208, 208, 208, 208, 208]
python
def build_array_nmt(lines, vocab, num_steps):
"""将机器翻译的文本序列转换成小批量"""
lines = [vocab[l] for l in lines]
lines = [l + [vocab['<eos>']] for l in lines]
array = torch.tensor([truncate_pad(
l, num_steps, vocab['<pad>']) for l in lines])
valid_len = (array != vocab['<pad>']).type(torch.int32).sum(1)
return array, valid_len
python
def load_data_nmt(batch_size, num_steps, num_examples=600):
"""返回翻译数据集的迭代器和词表"""
text = preprocess_nmt(read_data_nmt())
source, target = tokenize_nmt(text, num_examples)
src_vocab = d2l.Vocab(source, min_freq=2,
reserved_tokens=['<pad>', '<bos>', '<eos>'])
tgt_vocab = d2l.Vocab(target, min_freq=2,
reserved_tokens=['<pad>', '<bos>', '<eos>'])
src_array, src_valid_len = build_array_nmt(source, src_vocab, num_steps)
tgt_array, tgt_valid_len = build_array_nmt(target, tgt_vocab, num_steps)
data_arrays = (src_array, src_valid_len, tgt_array, tgt_valid_len)
data_iter = d2l.load_array(data_arrays, batch_size)
return data_iter, src_vocab, tgt_vocab
python
train_iter, src_vocab, tgt_vocab = load_data_nmt(batch_size=2, num_steps=8)
for X, X_valid_len, Y, Y_valid_len in train_iter:
print('X:', X.type(torch.int32))
print('X的有效长度:', X_valid_len)
print('Y:', Y.type(torch.int32))
print('Y的有效长度:', Y_valid_len)
breakX: tensor([[115, 164, 2, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5],
[ 83, 32, 2, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5]], dtype=torch.int32)
X的有效长度: tensor([4, 4])
Y: tensor([[ 6, 2, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5],
[100, 171, 6, 2, 4, 5, 5, 5]], dtype=torch.int32)
Y的有效长度: tensor([3, 5])编码器-解码器
python
from torch import nn
#@save
class Encoder(nn.Module):
"""编码器-解码器架构的基本编码器接口"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Encoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def forward(self, X, *args):
raise NotImplementedError
python
#@save
class Decoder(nn.Module):
"""编码器-解码器架构的基本解码器接口"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Decoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, *args):
raise NotImplementedError
def forward(self, X, state):
raise NotImplementedError
python
#@save
class EncoderDecoder(nn.Module):
"""编码器-解码器架构的基类"""
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, **kwargs):
super(EncoderDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, enc_X, dec_X, *args):
enc_outputs = self.encoder(enc_X, *args)
dec_state = self.decoder.init_state(enc_outputs, *args)
return self.decoder(dec_X, dec_state)序列到序列的学习
python
import collections
import math
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
python
#@save
class Seq2SeqEncoder(d2l.Encoder):
"""用于序列到序列学习的循环神经网络编码器"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqEncoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# 嵌入层
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.GRU(embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout=dropout)
def forward(self, X, *args):
# 输出'X'的形状:(batch_size,num_steps,embed_size)
X = self.embedding(X)
# 在循环神经网络模型中,第一个轴对应于时间步
X = X.permute(1, 0, 2)
# 如果未提及状态,则默认为0
output, state = self.rnn(X)
# output的形状:(num_steps,batch_size,num_hiddens)
# state的形状:(num_layers * num_directions,batch_size,num_hiddens)
return output, state
python
encoder = Seq2SeqEncoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8, num_hiddens=16,
num_layers=2)
encoder.eval()
X = torch.zeros((4, 7), dtype=torch.long)
output, state = encoder(X)
output.shapetorch.Size([7, 4, 16])
python
state.shapetorch.Size([2, 4, 16])
python
class Seq2SeqDecoder(d2l.Decoder):
"""用于序列到序列学习的循环神经网络解码器"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.GRU(embed_size + num_hiddens, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=dropout)
self.dense = nn.Linear(num_hiddens, vocab_size)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, *args):
return enc_outputs[1]
def forward(self, X, state):
# 输出'X'的形状:(batch_size,num_steps,embed_size)
X = self.embedding(X).permute(1, 0, 2)
# 广播context,使其具有与X相同的num_steps
context = state[-1].repeat(X.shape[0], 1, 1) # 使得其可以与 X 在时间步维度上拼接,使得每个时间步的输入都包含上下文信息
X_and_context = torch.cat((X, context), 2)
output, state = self.rnn(X_and_context, state)
output = self.dense(output).permute(1, 0, 2)
# output的形状:(batch_size,num_steps,vocab_size)
# state的形状:(num_layers * n_derection,batch_size,num_hiddens)
return output, state
python
decoder = Seq2SeqDecoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8, num_hiddens=16,
num_layers=2)
decoder.eval()
state = decoder.init_state(encoder(X))
output, state = decoder(X, state)
output.shape, state.shape(torch.Size([4, 7, 10]), torch.Size([2, 4, 16]))
python
#@save
def sequence_mask(X, valid_len, value=0):
"""在序列中屏蔽不相关的项"""
maxlen = X.size(1)
# print(torch.arange((maxlen), dtype=torch.float32, device=X.device)[None, :]< valid_len[:, None])
mask = torch.arange((maxlen), dtype=torch.float32,
device=X.device)[None, :] < valid_len[:, None]
X[~mask] = value
return X
X = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
sequence_mask(X, torch.tensor([1, 2]))tensor([[1, 0, 0],
[4, 5, 0]])
python
X = torch.ones(2, 3, 4)
sequence_mask(X, torch.tensor([1, 2]), value=-1)tensor([[[ 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[-1., -1., -1., -1.],
[-1., -1., -1., -1.]],
[[ 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[ 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[-1., -1., -1., -1.]]])
python
#@save
class MaskedSoftmaxCELoss(nn.CrossEntropyLoss):
"""带遮蔽的softmax交叉熵损失函数"""
# pred的形状:(batch_size,num_steps,vocab_size)
# label的形状:(batch_size,num_steps)
# valid_len的形状:(batch_size,)
def forward(self, pred, label, valid_len):
weights = torch.ones_like(label)
weights = sequence_mask(weights, valid_len)
self.reduction='none'
unweighted_loss = super(MaskedSoftmaxCELoss, self).forward(
pred.permute(0, 2, 1), label) # nn.CrossEntropyLoss 期望输入 pred 的形状为 (batch_size, vocab_size, num_steps),因此需要对 pred 进行转置操作 pred.permute(0, 2, 1) 以匹配这种形状。
weighted_loss = (unweighted_loss * weights).mean(dim=1)
return weighted_loss
python
loss = MaskedSoftmaxCELoss()
loss(torch.ones(3, 4, 10), torch.ones((3, 4), dtype=torch.long),
torch.tensor([4, 2, 0]))tensor([2.3026, 1.1513, 0.0000])
python
#@save
def train_seq2seq(net, data_iter, lr, num_epochs, tgt_vocab, device):
"""训练序列到序列模型"""
def xavier_init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
if type(m) == nn.GRU:
for param in m._flat_weights_names:
if "weight" in param:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m._parameters[param])
net.apply(xavier_init_weights)
net.to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = MaskedSoftmaxCELoss()
net.train()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss',
xlim=[10, num_epochs])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
timer = d2l.Timer()
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # 训练损失总和,词元数量
for batch in data_iter:
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, X_valid_len, Y, Y_valid_len = [x.to(device) for x in batch]
bos = torch.tensor([tgt_vocab['<bos>']] * Y.shape[0],
device=device).reshape(-1, 1)
dec_input = torch.cat([bos, Y[:, :-1]], 1) # 强制教学
Y_hat, _ = net(X, dec_input, X_valid_len)
l = loss(Y_hat, Y, Y_valid_len)
l.sum().backward() # 损失函数的标量进行"反向传播"
d2l.grad_clipping(net, 1)
num_tokens = Y_valid_len.sum()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
metric.add(l.sum(), num_tokens)
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (metric[0] / metric[1],))
print(f'loss {metric[0] / metric[1]:.3f}, {metric[1] / timer.stop():.1f} '
f'tokens/sec on {str(device)}')
python
embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout = 32, 32, 2, 0.1
batch_size, num_steps = 64, 10
lr, num_epochs, device = 0.005, 200, d2l.try_gpu()
train_iter, src_vocab, tgt_vocab = d2l.load_data_nmt(batch_size, num_steps)
encoder = Seq2SeqEncoder(len(src_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout)
decoder = Seq2SeqDecoder(len(tgt_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout)
net = EncoderDecoder(encoder, decoder) # 不要加d2l,否则报错
train_seq2seq(net, train_iter, lr, num_epochs, tgt_vocab, device)loss 0.020, 11904.7 tokens/sec on cuda:0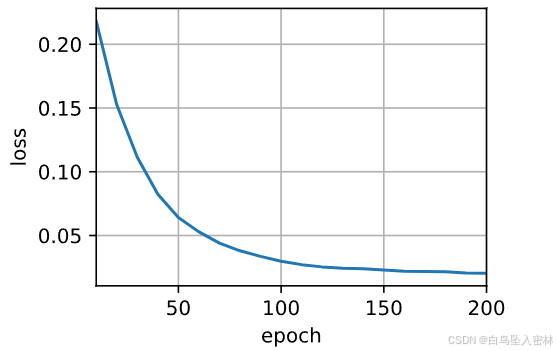
python
#@save
def predict_seq2seq(net, src_sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, num_steps,
device, save_attention_weights=False):
"""序列到序列模型的预测"""
# 在预测时将net设置为评估模式
net.eval()
src_tokens = src_vocab[src_sentence.lower().split(' ')] + [
src_vocab['<eos>']]
enc_valid_len = torch.tensor([len(src_tokens)], device=device)
src_tokens = d2l.truncate_pad(src_tokens, num_steps, src_vocab['<pad>'])
# 添加批量轴
enc_X = torch.unsqueeze(
torch.tensor(src_tokens, dtype=torch.long, device=device), dim=0)
enc_outputs = net.encoder(enc_X, enc_valid_len)
dec_state = net.decoder.init_state(enc_outputs, enc_valid_len)
# 添加批量轴
dec_X = torch.unsqueeze(torch.tensor(
[tgt_vocab['<bos>']], dtype=torch.long, device=device), dim=0)
output_seq, attention_weight_seq = [], []
for _ in range(num_steps):
Y, dec_state = net.decoder(dec_X, dec_state)
# 我们使用具有预测最高可能性的词元,作为解码器在下一时间步的输入
dec_X = Y.argmax(dim=2)
pred = dec_X.squeeze(dim=0).type(torch.int32).item()
# 保存注意力权重(稍后讨论)
if save_attention_weights:
attention_weight_seq.append(net.decoder.attention_weights)
# 一旦序列结束词元被预测,输出序列的生成就完成了
if pred == tgt_vocab['<eos>']:
break
output_seq.append(pred)
return ' '.join(tgt_vocab.to_tokens(output_seq)), attention_weight_seq
python
def bleu(pred_seq, label_seq, k): #@save
"""计算BLEU"""
pred_tokens, label_tokens = pred_seq.split(' '), label_seq.split(' ')
len_pred, len_label = len(pred_tokens), len(label_tokens)
score = math.exp(min(0, 1 - len_label / len_pred))
for n in range(1, k + 1):
num_matches, label_subs = 0, collections.defaultdict(int)
for i in range(len_label - n + 1):
label_subs[' '.join(label_tokens[i: i + n])] += 1
for i in range(len_pred - n + 1):
if label_subs[' '.join(pred_tokens[i: i + n])] > 0:
num_matches += 1
label_subs[' '.join(pred_tokens[i: i + n])] -= 1
score *= math.pow(num_matches / (len_pred - n + 1), math.pow(0.5, n))
return score
python
engs = ['go .', "i lost .", 'he\'s calm .', 'i\'m home .']
fras = ['va !', 'j\'ai perdu .', 'il est calme .', 'je suis chez moi .']
for eng, fra in zip(engs, fras):
translation, attention_weight_seq = predict_seq2seq(
net, eng, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, num_steps, device)
print(f'{eng} => {translation}, bleu {bleu(translation, fra, k=2):.3f}')go . => va !, bleu 1.000
i lost . => j'ai perdu ., bleu 1.000
he's calm . => il est mouillé paresseux ., bleu 0.548
i'm home . => je suis chez juste !, bleu 0.651代码来自:https://zh.d2l.ai/chapter_recurrent-neural-networks/sequence.html