案例
【前言:为了巩固之前的Python基础知识(一)到(五),并为后续使用Python作为数据处理的好帮手,我们一起来看几个例子】
使用工具:Echarts
-
Echarts 是一个由百度开源的数据可视化,而 Python 是一门富有表达力的语言,很适合用于数据处理。当数据分析遇上数据可视化时,pyecharts 诞生了。https://pyecharts.org
第三方包pyecharts就是echarts的python接口,方便python用户开发。 -
json :是一种轻量级的数据交互格式,本质上是一个带有特定格式的字符串,是在各种编程语言中流通的数据格式。
其格式可理解为:python数据类型的字典或元素为字典的列表。
pythonimport json # 将内容转换为json格式 data = [{"name":"米","age":12},{"name":"面","age":22},{"name":"粥","age":18}] # 其中ensure_ascii = False可以省略,其作用是不使用ASCII码将内容输出,而是直接将内容显示,可使中文正常显示 json_str = json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii = False) print(json_str) # 将json格式还原为列表或字典 py_type = json.loads(data) print(py_type)代码 作用 json.dumps() 将内容转换为json格式 json.loads() 将json格式转换为python数据类型 pyecharts中文使用手册:https://pyecharts.org/#/zh-cn/
pyecharts画廊:https://gallery.pyecharts.org/
常用工具网站:https://www.ab173.com/
配置类型
-
全局配置:使用set_global_opts方法,详细内容查看官方使用手册
-
局部配置:
一、折线图数据可视化
python
# 构建基础折线图
from pyecharts.charts import Line
from pyecharts.options import TitleOpts, LegendOpts, ToolboxOpts, VisualMapOpts, TooltipOpts, LabelOpts
# 得到折线图对象
line = Line()
# 添加x轴
line.add_xaxis(["中国", "美国", "德国"])
# 添加y轴,注意:此处数据均为测试而虚构
line.add_yaxis("GDP", [30, 20, 10], label_opts=LabelOpts(is_show=False))
# 全局配置
line.set_global_opts(
title_opts=TitleOpts(is_show=True, title="GDP显示", pos_left="center", pos_bottom="1%"),
legend_opts=LegendOpts(is_show=True),
toolbox_opts=ToolboxOpts(is_show=True),
visualmap_opts=VisualMapOpts(is_show=True),
tooltip_opts=TooltipOpts(is_show=True)
)
# 生成图表
line.render()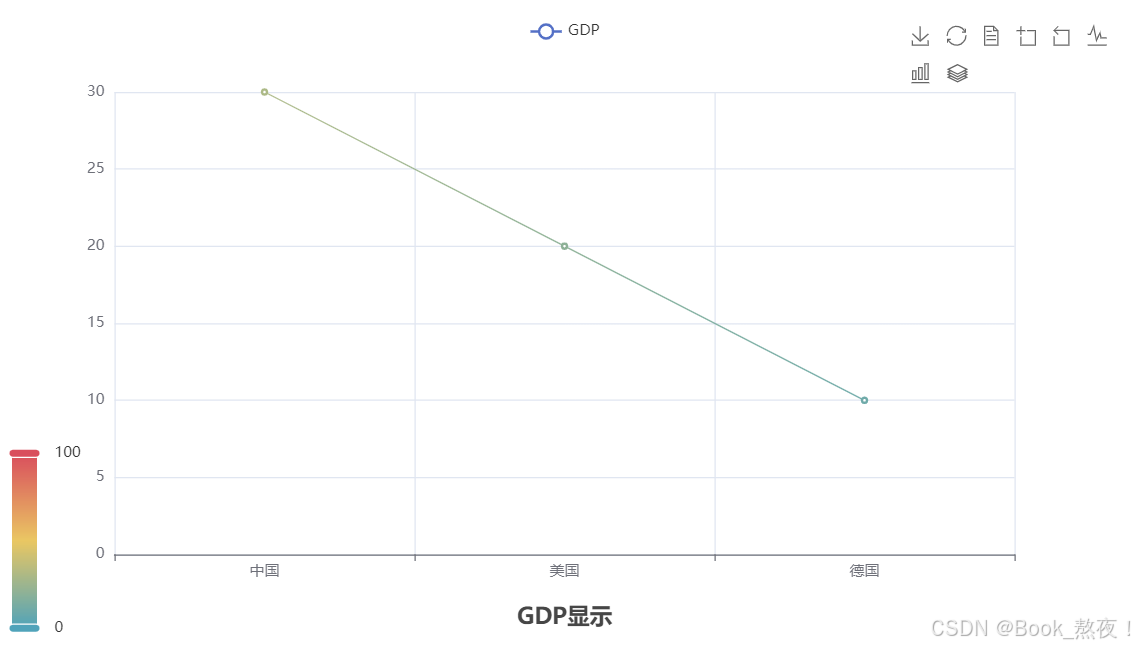
二、地图可视化
python
from pyecharts.charts import Map
from pyecharts.options import VisualMapOpts
map = Map()
data = [ # 注意数据需要以元组形式使用,注意:此处数据均为测试而虚构
("北京市", 100),
("上海市", 90),
("广东省", 80),
("台湾省", 70),
]
map.add("地图", data, "china")
map.set_global_opts(
visualmap_opts=VisualMapOpts(
is_show=True, # 是否显示
is_piecewise=True,# 是否分段
pieces=[
{"min":1, "max":49, "lable":"1-49", "color":"#CCFFFF"},
{"min":50, "max":79, "lable":"50-79", "color":"#FFFF99"},
{"min":80, "max":89, "lable":"80-89", "color":"#FF9966"},
{"min":90, "max":100, "lable":"90-100", "color":"#CC3333"},
]
)
)
map.render()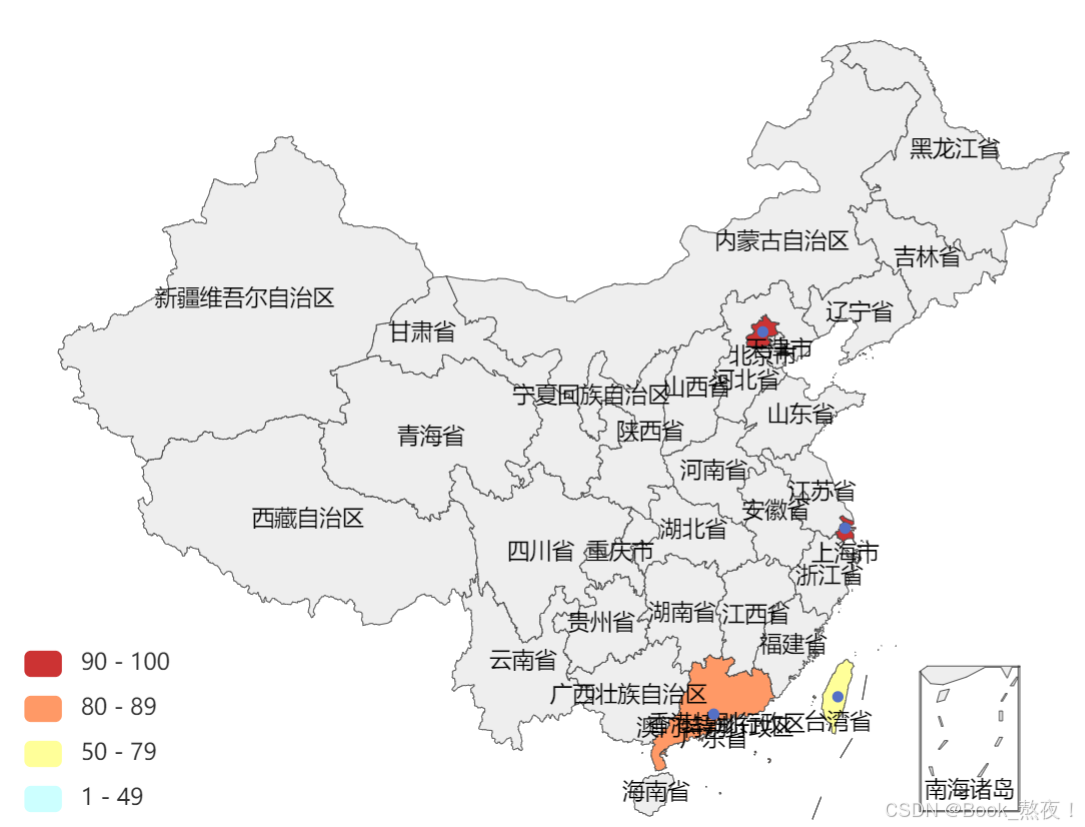
三、动态柱状图可视化
python
from pyecharts.options import *
from pyecharts.charts import Timeline, Bar
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
# 注意:此处数据均为测试而虚构
bar1 = Bar()
bar1.add_xaxis(["中国", "美国", "英国"])
bar1.add_yaxis("GDP", [35, 25, 10], label_opts=LabelOpts( # 将y轴上显示数值在图形右侧
position="right"
))
bar1.reversal_axis() # 反转xy轴
bar2 = Bar()
bar2.add_xaxis(["中国", "美国", "英国"])
bar2.add_yaxis("GDP", [45, 10, 25], label_opts=LabelOpts( # 将y轴上显示数值在图形右侧
position="right"
))
bar2.reversal_axis() # 反转xy轴
# 创建时间线
timeline = Timeline(
{"theme":ThemeType.LIGHT} # 设置全局主题颜色
)
timeline.add(bar1, "2022年GDP")
timeline.add(bar2, "2023年GDP")
# 设置自动播放
timeline.add_schema(
play_interval=1000, # 自动播放时间间隔,单位毫秒
is_timeline_show=True, # 自动播放时候是否显示时间线
is_auto_play=True, # 是否自动播放
is_loop_play=True # 是否循环播放
)
# 通过时间线绘制
timeline.render()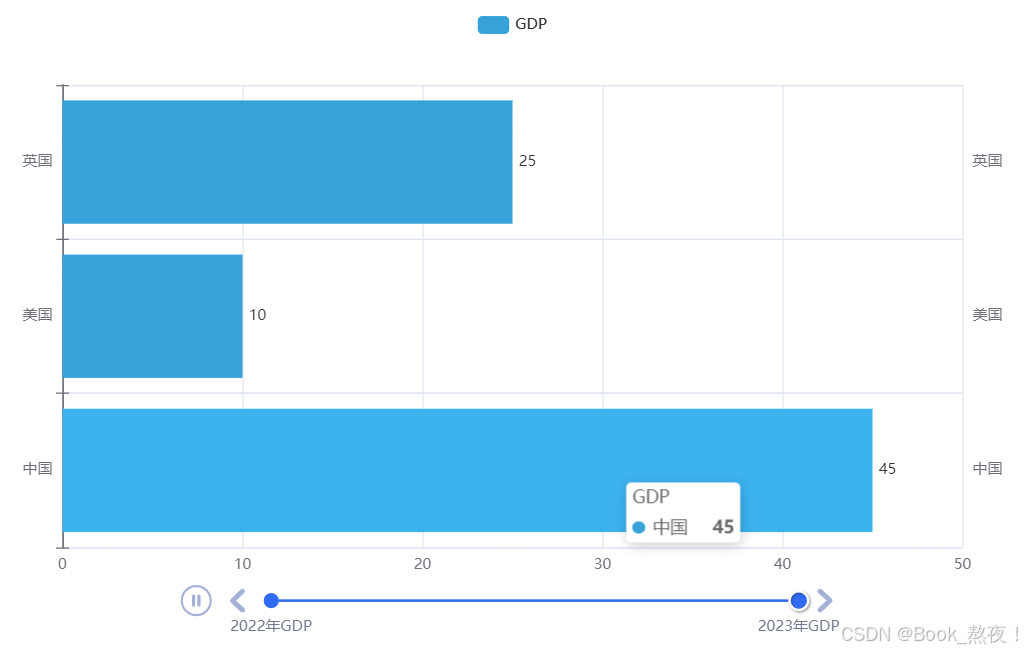
科学计数法表示的数据可以使用float()强制类型转换为数值
python
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.options import *
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
# 读取数据
f = open("D:/test.csv", 'r', encoding="UTF-8")
"""
原数据存储格式
年份,国家,gdp
年份,国家,gdp
年份,国家,gdp
年份,国家,gdp
............
"""
# 按行读取所有数据并存为列表
data_lines = f.readlines()
# 关闭文件
f.close()
# 删除第一条数据,本质上是清除多余数据
data_lines.pop(0)
# 定义一个空字典对象,为格式化存储数据做准备
data_dict = {}
"""
{年份1: [[国家,gdp], [国家,gdp],......],
年份2: [[国家,gdp], [国家,gdp],......],
年份3: [[国家,gdp], [国家,gdp],......],......}
"""
for line in data_lines: # 根据逗号分割数据,并分别存储
year = int(line.split(",")[0]) # 年份
country = line.split(",")[1] # 国家
gdp = line.split(",")[2] # gdp
# 判断字典中是否有指定的年份key,将同一年份下所有国家和gdp数据对应存储
try: # 有可能出现异常的语句
data_dict[year].append([country, gdp])
except KeyError as e: # 如果出现该异常,则证明该年份不存在
data_dict[year] = [] # 新建该年份key的value(数据类型为列表)
data_dict[year].append([country, gdp]) # 将[国家,gdp]列表作为一个元素追加到数据类型为列表的value中
# 创建时间线对象
timeline = Timeline(
{"theme": ThemeType.Light} # 设置主题颜色
)
# 由于字典的无序性,需要手动排序年份
sorted_year_list = sorted(data_dict.keys())
# 根据gdp从大到小排序
for year in sorted_year_list:
data_dict[year].sort(key=lambda element: element[1], reverse=True)
# 取出每年份gdp前8的国家与其gdp
year_data = data_dict[year][:8]
x_data = []
y_data = []
for country_gdp in year_data: # 将国家赋值给x轴,gdp赋值给y轴
x_data.append(country_gdp[0])
y_data.append(country_gdp[1])
# 构建柱状图
bar = Bar()
bar.add_xaxis("国家", x_data)
bar.add_yaxis("GDP(元)", y_data, label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))
# 反转xy轴
bar.reversal_axis()
bar.set_global_opts(
title_opts=TitleOpts(title=f"{year}年全球GDP前8数据")
)
timeline.add(bar, str(year))
# 设置时间线自动播放
timeline.add_schema(
play_interval=1000,
is_timeline_show=True,
is_loop_play=True,
is_auto_play=True
)
# 通过时间线绘制
timeline.render("全球GDP前8国家")【记录学习过程的笔记,欢迎大家一起讨论,会持续更新】