236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
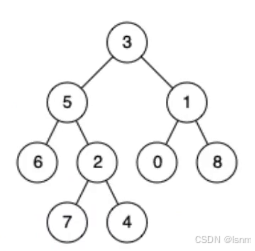
题目解释:
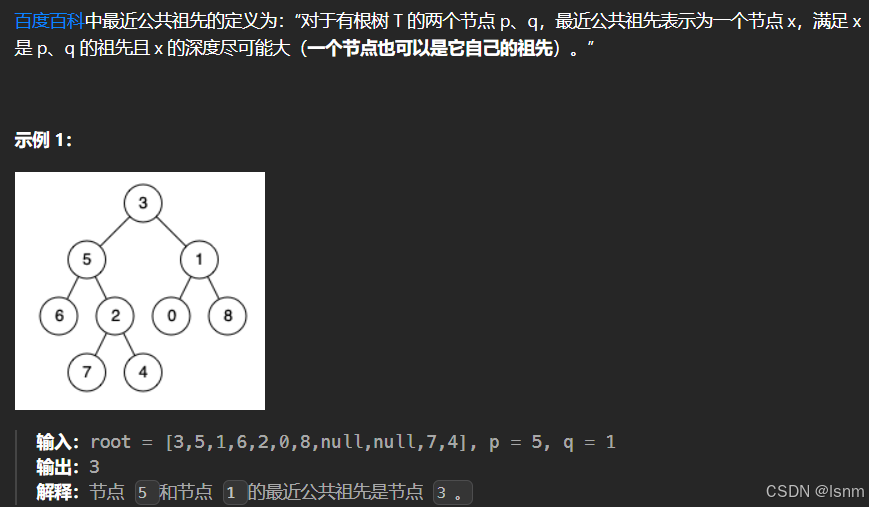
我们以这棵树为例,来观察找不同的最近公共祖先有何特点:
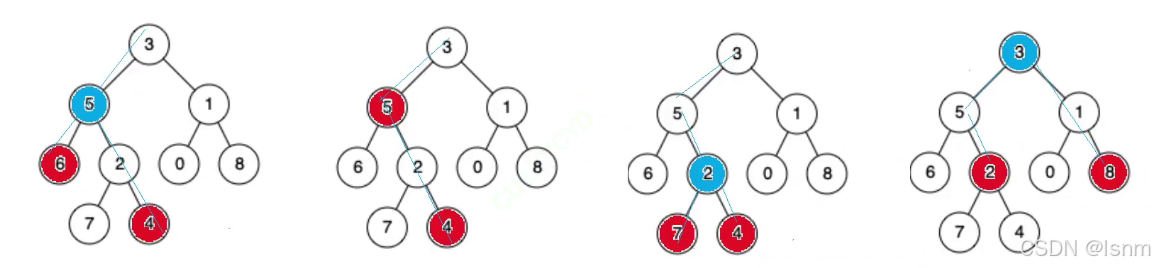
思路一:
除了第二种情况,最近公共祖先满足:一个节点在他的左边,一个节点在他的右边。
并且,其他公共祖先不满足这个条件,只有最近公共祖先满足这一点。
所以我们可以利用这个逻辑来破题:从根节点开始往下查找,找到的第一个满足"p和q分别在他的左右两侧的节点",就是要找的最近公共祖先。
先来特殊处理第二种情况:
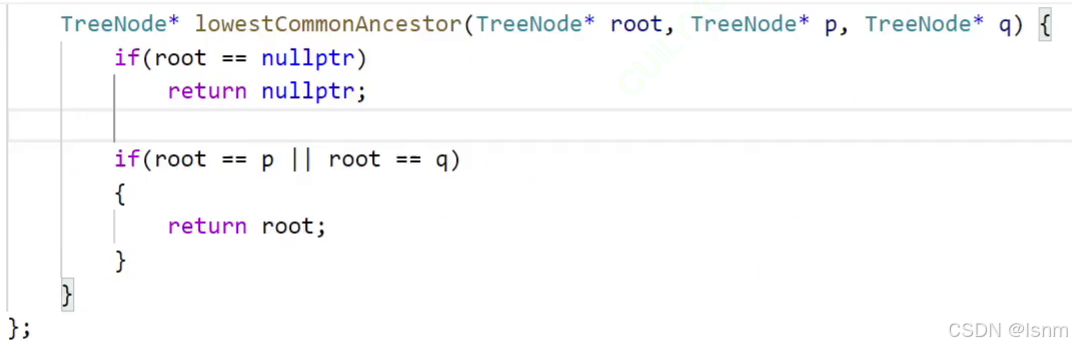
然后涉及到最关键的步骤:
分别用bool值封装q和p找位置的函数,便于依次罗列出q和p对于当前节点的位置(是否满足一左一右)
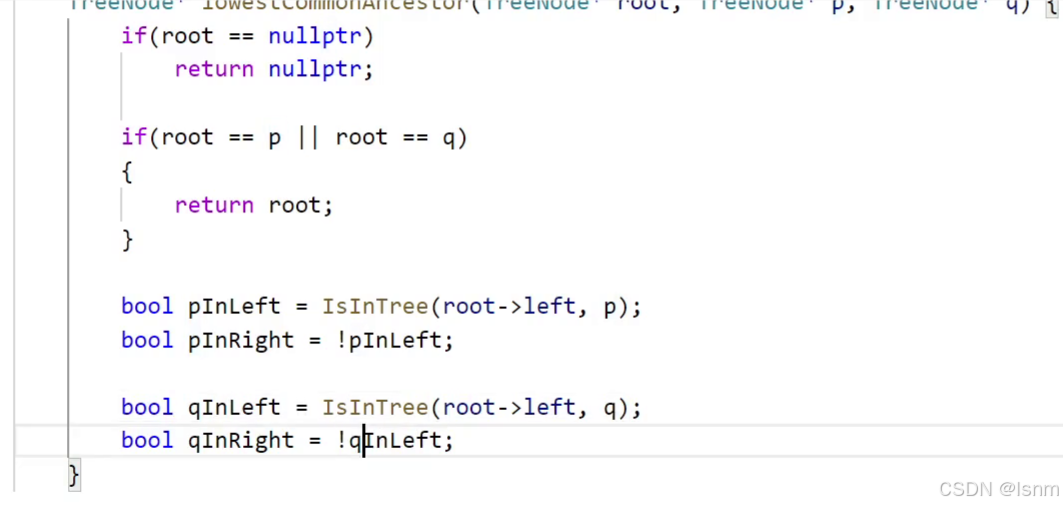
实现IsInTree:

完整代码:
cpp
bool IsInTree(TreeNode* tree,TreeNode* k){
if(tree==nullptr) return false;
return tree==k
|| IsInTree(tree->left,k)
|| IsInTree(tree->right,k);
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
//特殊处理本身存在爷孙或父子关系的情况
if(root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
//罗列出p和q是否存在的条件
bool PInLeft = IsInTree(root->left,p);
bool PInRight = !PInLeft;
bool QInLeft = IsInTree(root->left,q);
bool QInRight = !QInLeft;
//分类讨论
if((PInLeft && QInRight) || (QInLeft && PInRight)){
return root;
}else if(PInLeft && QInLeft){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
}else{
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
}
//return nullptr;
}
};但是实际运行速度并不理想: 运行速度几乎都要接近一秒了
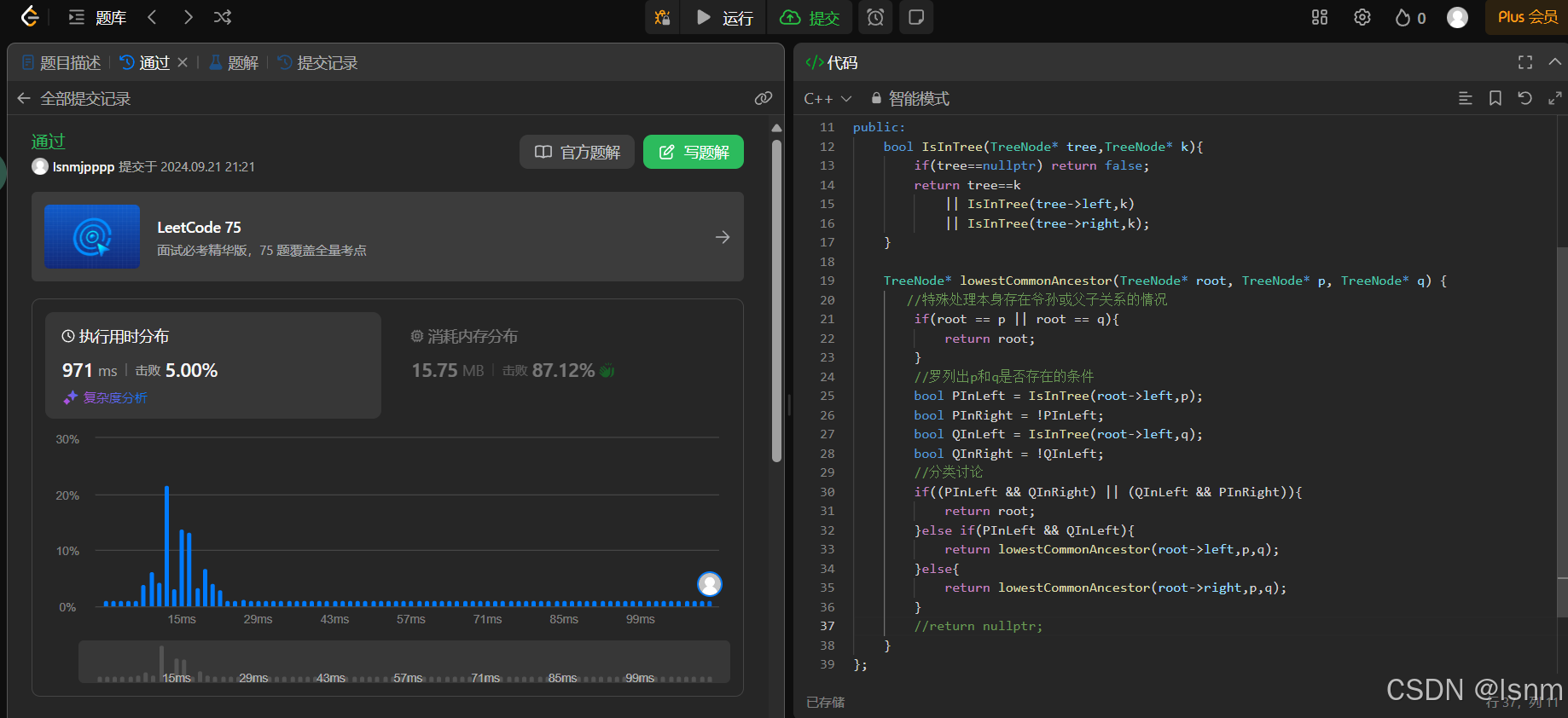
这样操作的时间复杂度是O(N^2):
因为我们的树是一个毫无数据存放逻辑的任意形状的二叉树。所以,每一次去判断IsInTree都是把当前root下面的数据都遍历一遍,因此其本质其实是:第一遍从3开始查左查右,第二次从5开始查左查右,再从6开始查左查右......
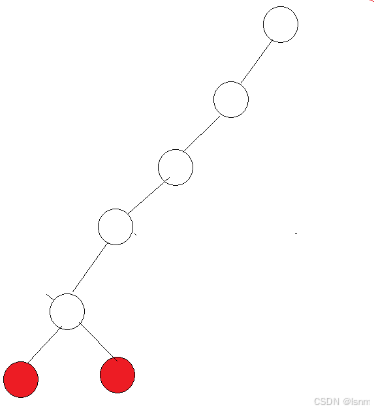
如果遇到最坏的如下图一样的环境:
其时间复杂度是O(N^2)
当然,如果越接近完全二叉树的情形,时间复杂度越低,最理想能达到O(n)
思路二:
如果我们能根据找祖先的两个节点往回走,一切都会很好解决。
这样就变成了两条相交链表找交点。
使用前序查找+栈来找记录路径,然后再进行一次"两条相交链表找交点"
比如这张图,要找7,那么我们的路径应该记录为:3-5-2-7
在遇到6这样的错误的分支方向时,我们先将其入栈,发现他不对就出栈。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool FindPath( stack<TreeNode*>& st , TreeNode* des , TreeNode* root){
if(root==nullptr) {
return false;
}
st.push(root);
if(root == des){
return true;
}else if((!FindPath(st,des,root->left))&&
(!FindPath(st,des,root->right))){
st.pop();
return false;
}
return true;
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
stack<TreeNode*> q_path;
stack<TreeNode*> p_path;
FindPath(q_path,q,root);
FindPath(p_path,p,root);
while(q_path.size()!=p_path.size()){
if(q_path.size()>p_path.size()) q_path.pop();
if(p_path.size()>q_path.size()) p_path.pop();
}
while(q_path.top()!=p_path.top()){
q_path.pop();
p_path.pop();
}
return q_path.top();
}
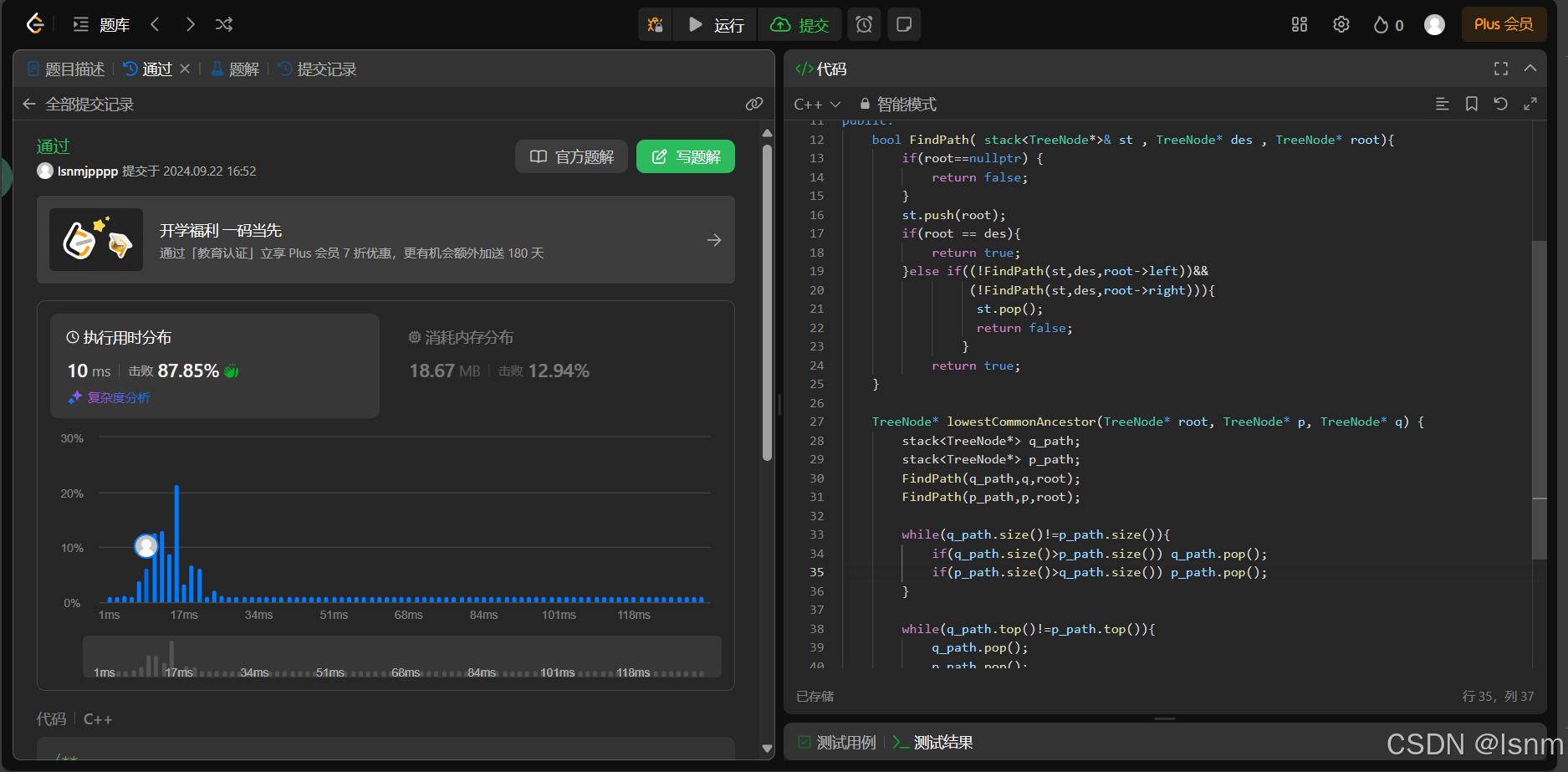
};可以发现现在这种方法提升了不少速度:
欢迎各位看官在评论区写出对这道题的其他解法。
