前言:
Java数据结构链表部分和顺序表有所相似:
首先都扩展了接口List,List里面的方法都会在LinkedList中重写。
其次都可以实现数据的增删查改等基础功能。
当然ArrayList相较于LinkedList有一定的缺陷,比如果在中间位置插入数据,在中间位置删除数据都比较麻烦,需要移动大量数据!LinkedList可以有效地解决移动数据的难题。
当然LinkedList也有自我的缺陷(在C语言阶段已经详细研究,大家可以翻看之前的博客),接下来就一起用Java的目光探究LinkedList。
自我实现MyLinkedList:
由于之前在C预研阶段已经实现过链表,可以翻看之前的内容仔细了解,接下来直接上代码:
无头单向不循环链表:
Ilist接口:
java
public interface IList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data);
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data);
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data);
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key);
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key);
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key);
//得到单链表的长度
public int size();
public void clear();
public void display();
}MyLinkedList类:
java
public void addIndex(int index, int data) throws IndexExpection{
if(index < 0||index>size()) {
throw new IndexExpection("非法访问");
}
ListNode cur = head;
if(head == null) {
head = new ListNode(data);
return ;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return ;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return ;
}
while(index-1 != 0) {
index--;
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
if(head == null) {
return ;
}
ListNode cur = head;
if(cur.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
while(cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
cur = cur.next.next;
return ;
}
}
if(cur.val == key) {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if(head == null) {
return ;
}
ListNode cur = head;
if(cur.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
while(cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
cur = cur.next.next;
}
}
if(cur.val == key) {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
int num = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
num++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return num;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
head = null;
}
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}但是这里与Java中给的LinkedList有所不同,不在什么地方?
Java中的LinkedList是一个无头双向不循环链表,所以此时我们还需要进行一个改进。
无头双向不循环链表:
直接上代码:
java
package LinkedDemo;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:无头双向不循环
* User: 29980
* Date: 2024-09-29
* Time: 12:21
*/
public class MyLinkedList implements IList{
static class ListNode {
private int val;
private ListNode prev;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode(int data){
this.val = data;
}
}
private ListNode head;
private ListNode last;
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null) {
head = last = node;
}else {
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null) {
last = head = node;
}
//ListNode cur = head;
// while(cur.next != null) {
// cur = cur.next;
// }
// cur.next = node;
// node.prev = cur;
node.prev = last.prev;
last = node;
}
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null) {
head = node;
return ;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return ;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return ;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while(index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next = cur;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
if(cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if(head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}else {
last = null;
}
}else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
if(cur.next != null) {
cur.prev = cur.next;
}else {
last = last.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
if(cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if(head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}else {
last = null;
}
}else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
if(cur.next != null) {
cur.prev = cur.next;
}else {
last = last.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int num = 0;
while(cur != null) {
num++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return num;
}
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
for(int i = 0;i<size();i++) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur.prev = null;
cur = tmp;
}
head = last = null;
}
}LinkedList的使用:
当然我们的核心还是在如何使用Java给定的LinkedList,首先我们再根据一下图片分析一次:
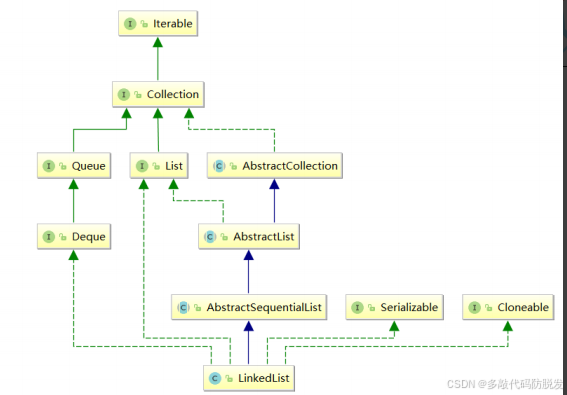
- LinkedList 实现了 List 接口
- LinkedList 的底层使用了双向链表
- LinkedList 没有实现 RandomAccess 接口,因此 LinkedList 不支持随机访问
- LinkedList 的任意位置插入和删除元素时效率比较高,时间复杂度为 O(1)
- LinkedList 比较适合任意位置插入的场景
LinkedList的构造方法:
LinkedList的构造方法有以下两种:
 一个是无参构造,另一个大家应该很少见是有参数,这个参数是Collection<?extends E> c ,是什么意思呢?
一个是无参构造,另一个大家应该很少见是有参数,这个参数是Collection<?extends E> c ,是什么意思呢?
第一:两个类必须都是实现了Collection接口的。
第二:两个类<>里面的参数必须满足继承关系。
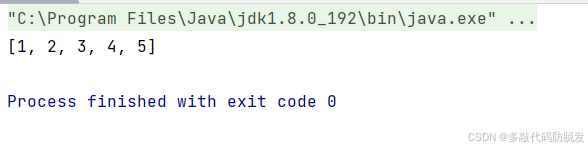
例如:
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
list1.add(3);
list1.add(4);
list1.add(5);
List<Object> list2 = new LinkedList<>(list1);
System.out.println(list2);
}
LinkedList遍历的方式:
遍历LinkedLisst的方式有三种:
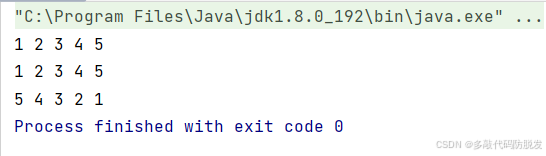
方式一:foreach打印
java
//第一种foreach遍历
for (int x:list) {
System.out.print(x+" ");
}
System.out.println();方式二:利用迭代器正向打印
java
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();方式三:利用反向迭代器打印:
java
ListIterator<Integer> it1 = list.listIterator(list.size());
while(it1.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.print(it1.previous()+" ");
} 打印结果如下: