目录
[2.1.1 法向量计算](#2.1.1 法向量计算)
[2.1.2 边界检测和移除](#2.1.2 边界检测和移除)
[2.1.3 边界检测和移除](#2.1.3 边界检测和移除)
PCL点云算法汇总及实战案例汇总的目录地址链接:
一、概述
在点云处理中,移除边缘不连续的点可以帮助提升数据的准确性,尤其是在3D物体的表面重建、特征提取等场景中。通过计算每个点的邻域信息,分析其与邻近点的距离或法向量变化,来识别并去除不连续的点。本文介绍了使用 PCL 中的BoundaryEstimation类来估计点云中的边界点,并移除那些边缘不连续的点。
1.1原理
边缘不连续点的检测通过计算点与其邻域点的法向量变化或距离差异来判断。具体原理如下:
- **法向量估计:**计算每个点的法向量及其邻域的法向量。
- **边界检测:**根据法向量的变化或邻域点的距离,判断点是否为边界点。
- **滤波移除:**通过设定边界点检测的阈值,移除那些不连续的边缘点。
1.2实现步骤
- 读取点云数据。
- 使用 NormalEstimation计算每个点的法向量。
- 使用 BoundaryEstimation 估计边界点,判断哪些点是不连续的边缘点。
- 移除不连续的边缘点。
- 可视化原始点云和移除不连续边缘点后的点云。
1.3应用场景
- **表面重建:**通过去除不连续的边缘点提升表面重建的精度。
- **特征提取:**去除不连续边缘点,提取更稳定的几何特征。
- **噪声去除:**移除位于边缘的离群点,增强数据的质量。
二、代码实现
2.1关键函数
2.1.1 法向量计算
首先通过 NormalEstimation 计算点云中每个点的法向量。
cpp
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
// 计算点云法向量
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr computeNormals(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud) // 输入点云
{
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
ne.setInputCloud(cloud);
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setKSearch(50); // 设置搜索邻域的点数量
ne.compute(*normals); // 计算法向量
return normals;
}2.1.2 边界检测和移除
使用 BoundaryEstimation 检测点云中的边缘点,并移除那些不连续的点。
cpp
#include <pcl/features/boundary.h>
// 检测点云中的边缘点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr detectBoundaries(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals) // 输入点云和法向量
{
pcl::BoundaryEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::Boundary> boundary_est;
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>);
boundary_est.setInputCloud(cloud);
boundary_est.setInputNormals(normals);
boundary_est.setSearchMethod(tree);
boundary_est.setKSearch(50); // 邻域点数
boundary_est.setAngleThreshold(M_PI / 2); // 设置角度阈值
boundary_est.compute(*boundaries); // 计算边缘点
return boundaries;
}
// 移除不连续的边缘点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr removeEdgePoints(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries) // 输入点云和边界点
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr filtered_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// 遍历每个点,如果该点不是边缘点(boundary_point == 0),则保留
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
{
if (boundaries->points[i].boundary_point == 0) // 边缘点的 boundary_point 属性为 1
{
filtered_cloud->points.push_back(cloud->points[i]);
}
}
return filtered_cloud;
}2.1.3 边界检测和移除
使用 BoundaryEstimation 检测点云中的边缘点,并移除那些不连续的点。
cpp
#include <pcl/features/boundary.h>
// 检测点云中的边缘点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr detectBoundaries(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals) // 输入点云和法向量
{
pcl::BoundaryEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::Boundary> boundary_est;
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>);
boundary_est.setInputCloud(cloud);
boundary_est.setInputNormals(normals);
boundary_est.setSearchMethod(tree);
boundary_est.setKSearch(50); // 邻域点数
boundary_est.setAngleThreshold(M_PI / 2); // 设置角度阈值
boundary_est.compute(*boundaries); // 计算边缘点
return boundaries;
}
// 移除不连续的边缘点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr removeEdgePoints(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries) // 输入点云和边界点
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr filtered_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// 遍历每个点,如果该点不是边缘点(boundary_point == 0),则保留
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
{
if (boundaries->points[i].boundary_point == 0) // 边缘点的 boundary_point 属性为 1
{
filtered_cloud->points.push_back(cloud->points[i]);
}
}
return filtered_cloud;
}2.2完整代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> // 用于加载和保存PCD文件
#include <pcl/point_types.h> // 定义点云数据类型
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h> // Kd树搜索方法
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> // 法向量计算
#include <pcl/features/boundary.h> // 边缘点检测
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> // 可视化库
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp> // 线程库
// 计算法向量
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr computeNormals(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud)
{
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
// 设置输入点云
ne.setInputCloud(cloud);
// 使用 Kd 树进行邻域搜索
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
// 设置邻域中的点数
ne.setKSearch(50);
// 计算法向量和曲率
ne.compute(*normals);
return normals;
}
// 检测边缘点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr detectBoundaries(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals)
{
pcl::BoundaryEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::Boundary> boundary_est;
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>);
// 设置输入点云和法向量
boundary_est.setInputCloud(cloud);
boundary_est.setInputNormals(normals);
// 设置 Kd 树搜索方法
boundary_est.setSearchMethod(tree);
// 设置邻域点数
boundary_est.setKSearch(50);
// 设置角度阈值,用于边界检测
boundary_est.setAngleThreshold(M_PI /8);
// 计算边缘点
boundary_est.compute(*boundaries);
return boundaries;
}
// 移除边缘不连续的点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr removeEdgePoints(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr filtered_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// 遍历每个点,如果该点不是边缘点(boundary_point == 0),则保留
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
{
if (boundaries->points[i].boundary_point == 0) // 边缘点的 boundary_point 属性为 1
{
filtered_cloud->points.push_back(cloud->points[i]);
}
}
return filtered_cloud;
}
// 可视化函数
void visualizePointClouds(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr filtered_cloud)
{
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("Edge Removal Viewer"));
// 创建视口1,显示原始点云
int vp_1;
viewer->createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_1); // 白色背景
viewer->addText("Original PointCloud", 10, 10, "vp1_text", vp_1);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_color(cloud, 255, 0, 0); // 原始点云红色
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud, cloud_color, "original_cloud", vp_1);
// 创建视口2,显示去除边缘点后的点云
int vp_2;
viewer->createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0.98, 0.98, 0.98, vp_2); // 浅灰色背景
viewer->addText("Filtered PointCloud", 10, 10, "vp2_text", vp_2);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> filtered_color(filtered_cloud, 0, 255, 0); // 绿色
viewer->addPointCloud(filtered_cloud, filtered_color, "filtered_cloud", vp_2);
// 设置点的大小
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "original_cloud", vp_1);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "filtered_cloud", vp_2);
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce(100);
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 读取点云数据
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("nosiy_bunny.pcd", *cloud) != 0)
{
return -1;
}
std::cout << "读取点的个数为: " << cloud->size() << " points" << std::endl;
// 计算法向量
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals = computeNormals(cloud);
// 检测边缘点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries = detectBoundaries(cloud, normals);
// 移除边缘不连续的点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr filtered_cloud = removeEdgePoints(cloud, boundaries);
// 可视化原始点云和移除边缘不连续点后的点云
visualizePointClouds(cloud, filtered_cloud);
return 0;
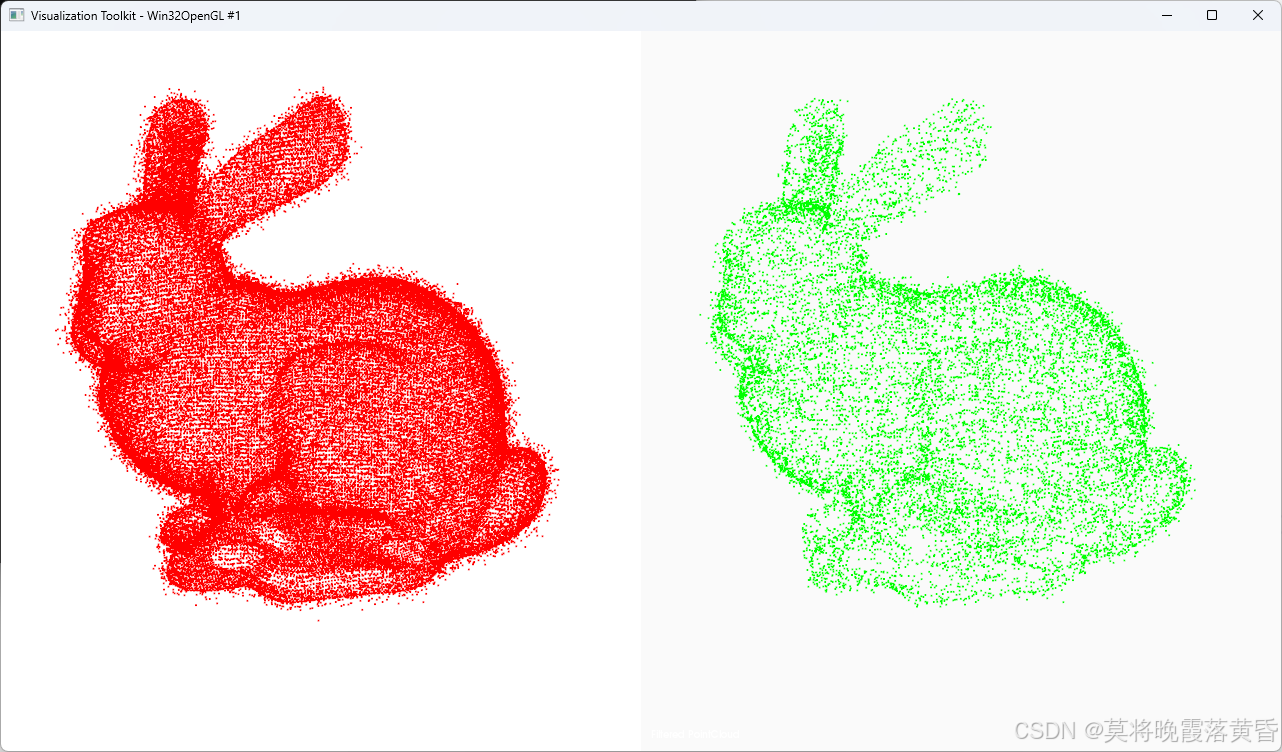
}三、实现效果