1 Spring Event框架
除了记录程序运行日志,在实际项目中一般还会记录操作日志,包括操作类型、操作时间、操作员、管理员IP、操作原因等等(一般叫审计)。
操作日志一般保存在数据库,方便管理员查询。通常的做法在每个请求方法中构建审计对象,并写入数据库,但这比较繁琐和冗余。更简便的做法是使用Spring Event框架进行统一处理。
Spring Event是Spring的事件通知机制,可以将相互耦合的代码解耦。Spring Event是监听者模式的一个具体实现。
监听者模式包含了监听者Listener、事件Event、事件发布者EventPublish,过程就是事件发布者EventPublish发布一个事件,被监听者Listener捕获到,然后执行事件Event相应的方法。
2 Spring Event案例
- 1)创建maven工程
spring-event-demo,并配置其pom.xml文件如下。由于Spring Event的相关API在spring-context包中,所以只需引入Spring相关依赖,而无需额外配置。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.hsgx</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-event-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>- 2)创建审计信息类
Audit、审计事件类AuditEvent、审计监听器类LogListener
java
package com.hsgx.event.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 审计信息
*/
@Data
public class Audit {
private String type; //操作类型
private LocalDateTime time; //操作时间
private String userName; //操作员
private String requestIp; //操作员IP
private String description; //操作原因
}
java
package com.hsgx.event.pojo;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
/**
* 定义审计事件
*/
public class AuditEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public AuditEvent(Audit audit) {
super(audit);
}
}
java
package com.hsgx.event.listener;
import com.hsgx.event.pojo.Audit;
import com.hsgx.event.pojo.AuditEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 审计监听器
*/
@Component
public class AuditListener {
// 异步监听AuditEvent事件
@Async
@EventListener(AuditEvent.class)
public void saveAudit(AuditEvent auditEvent) {
Audit audit = (Audit) auditEvent.getSource();
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
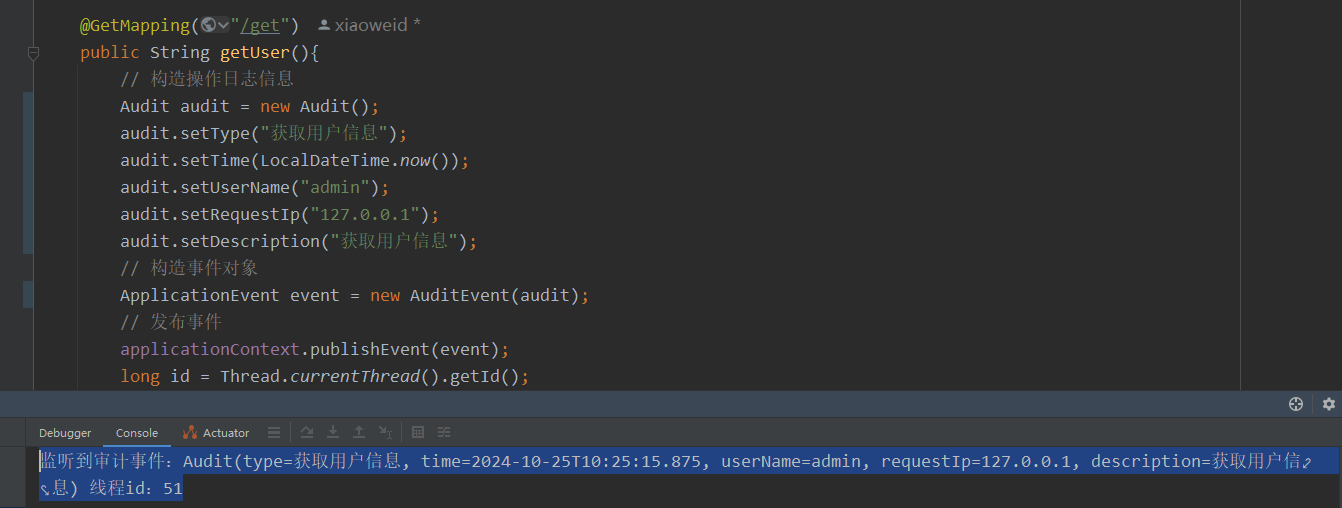
System.out.println("监听到审计事件:" + audit + " 线程id:" + id);
// 将日志信息保存到数据库...
}
}- 3)创建
UserController,用于发布事件
java
package com.hsgx.event.controller;
import com.hsgx.event.pojo.Audit;
import com.hsgx.event.pojo.AuditEvent;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 发布事件
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@GetMapping("/get")
public String getUser(){
// 构造操作日志信息
Audit audit = new Audit();
audit.setType("获取用户信息");
audit.setTime(LocalDateTime.now());
audit.setUserName("admin");
audit.setRequestIp("127.0.0.1");
audit.setDescription("获取用户信息");
// 构造事件对象
ApplicationEvent event = new AuditEvent(audit);
// 发布事件
applicationContext.publishEvent(event);
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
return "发布事件成功,线程id:" + id;
}
}- 5)创建启动类
SpringEventApp,使用@EnableAsync注解启用异步处理
java
package com.hsgx.event;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync //启用异步处理
public class SpringEventApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringEventApp.class,args);
}
}- 6)启动项目后访问
/user/get请求,触发发布事件,在监听器类AuditListener中监听到事件并进行相关操作
- 7)在
UserController中,需要注入ApplicationContext对象并调用publishEvent()方法手动发布事件 ,有点繁琐。我们可以通过创建一个审计注解@Audit,并通过切面拦截该注解的方式来完成。先引入AOP的依赖、hutool工具依赖:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0</version>
</dependency>- 8)创建审计注解
@Audit:
java
package com.hsgx.event.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Audit {
/**
* 描述
*/
String value();
/**
* 类型
*/
String type() default "";
}- 9)创建切面类
AuditAspect,做以下事情:
- 在切面类
AuditAspect中定义切点,拦截Controller中添加@Audit注解的方法- 在切面类
AuditAspect中定义前置通知,在前置通知方法doBefore()中收集操作相关信息封装为Audit对象并保存到ThreadLocal中- 在切面类
AuditAspect中定义成功返回通知,在成功返回通知方法doAfterReturning中通过ThreadLocal获取Audit对象并继续设置其他的成功操作信息,随后发布事件- 在切面类
AuditAspect中定义异常返回通知,在异常返回通知方法doAfterThrowable中通过ThreadLocal获取Audit对象并继续设置其他的异常操作信息,随后发布事件
java
package com.hsgx.event.aspect;
import cn.hutool.core.convert.Convert;
import cn.hutool.extra.servlet.ServletUtil;
import com.hsgx.event.pojo.Audit;
import com.hsgx.event.pojo.AuditEvent;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Objects;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
public class AuditAspect {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 用于保存线程中的审计对象
*/
private static final ThreadLocal<Audit> THREAD_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 定义Controller切入点拦截规则,拦截 @Audit 注解的方法
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.hsgx.event.annotation.Audit)")
public void auditAspect() {
}
/**
* 从ThreadLocal中获取审计对象,没有则创建一个
*/
private Audit getAudit() {
Audit audit = THREAD_LOCAL.get();
if (audit == null) {
return new Audit();
}
return audit;
}
/**
* 前置通知,收集操作相关信息封装为Audit对象并保存到ThreadLocal中
*/
@Before(value = "auditAspect()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) Objects.requireNonNull(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
Audit audit = getAudit();
audit.setTime(LocalDateTime.now());
audit.setRequestIp(ServletUtil.getClientIP(request));
// 操作员一般通过读取当前登录的管理员信息获取
audit.setUserName("zhangsan");
// 获取 @Audit 注解的信息
com.hsgx.event.annotation.Audit ann = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getAnnotation(com.hsgx.event.annotation.Audit.class);
if (ann != null) {
audit.setDescription(ann.value());
audit.setType(ann.type());
}
// 保存到线程容器
THREAD_LOCAL.set(audit);
}
/**
* 成功返回通知
*/
@AfterReturning(returning = "ret", pointcut = "auditAspect()")
public void doAfterReturning(Object ret) {
// 根据返回对象 ret 再做一些操作
Audit audit = getAudit();
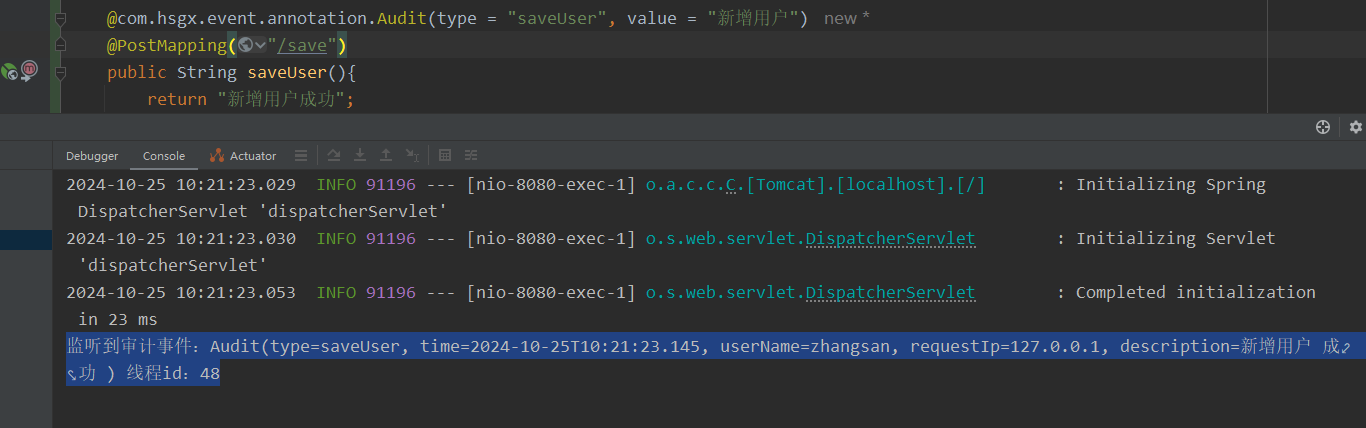
audit.setDescription(audit.getDescription() + " 成功 ");
// 发布事件
applicationContext.publishEvent(new AuditEvent(audit));
THREAD_LOCAL.remove();
}
/**
* 异常返回通知
*/
@AfterThrowing(throwing = "e", pointcut = "auditAspect()")
public void doAfterThrowable(Throwable e) {
// 根据异常返回对象 e 再做一些操作
Audit audit = getAudit();
audit.setDescription(audit.getDescription() + " 失败 " + e.getMessage());
// 发布事件
applicationContext.publishEvent(new AuditEvent(audit));
THREAD_LOCAL.remove();
}
}- 10)在
UserController中使用@Audit注解
java
// com.hsgx.event.controller.UserController
@com.hsgx.event.annotation.Audit(type = "saveUser", value = "新增用户")
@PostMapping("/save")
public String saveUser(){
return "新增用户成功";
}- 11)重启服务并调用
/user/save请求
...
本节完,更多内容查阅:后台管理系统的通用权限解决方案