论文概述
《基于现实迷宫地形的电脑鼠设计》是由吴润强、庹忠曜、刘文杰、项璟晨、孙科学等人于2023年发表的一篇优秀期刊论文。其针对现阶段电脑鼠计算量庞大且不适用于现实迷宫地形的问题,特基于超声波测距与传统迷宫算法原理,设计出一款可在现实迷宫地形下自动寻找出口的电脑鼠。该电脑鼠适用于岔路数量与道路宽度不定、多死路弯道并且相对较大的迷宫地形,具有适应性强、计算量小、兼容性和可塑性强等优点,对于现实迷宫地形下的自动应用具有一定研究价值。
关键词电脑鼠;超声波测距;迷宫算法;自动应用
该论文内容相对较多,特对其进行拆开分析,本文特围绕智能车驱动算法进行展开分析。
一、中线判断与中线对齐
中线判断即根据超声波探测所得到的L与R,判断出道路的中心直线,记此线为中线。基于之间超声波探头位于电脑鼠最中部并且可用于其近似代表电脑鼠位置的理论,当超声波探头沿着中线前进时,可认为电脑鼠沿着中线前进,此时电脑鼠距离左右的障碍物均足够远,可保证其在行驶过程中不会与障碍物相撞。
中线对齐即根据L、R与已知的两驱动轮间距D,计算出相关数据,判断出小车位于中线的左侧还是右侧。其中以小车位于中线右侧为例,先保持左驱动轮不动,右驱动轮向前行驶一定时间,致使车辆左进行偏转;再以相同的保持右驱动轮不动,驱动左驱动轮使车辆向右偏转相同角度,从而使得车辆中心恰好对齐中线位置,见图9。
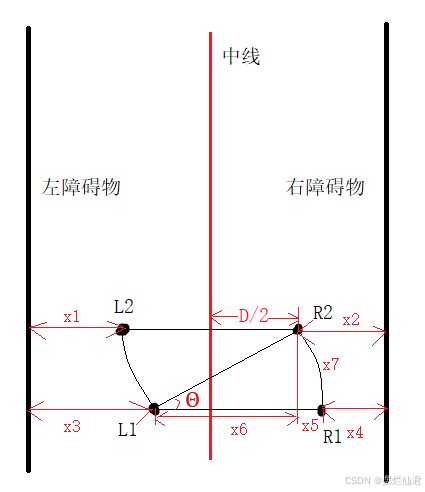
图9 中线对齐示意图
1.理论分析

2.实际应用

二、转弯判断与车辆转向
转弯判断与车辆转向均是基于超声波探测与迷宫算法下进行完成的,其具体流程图见图10。
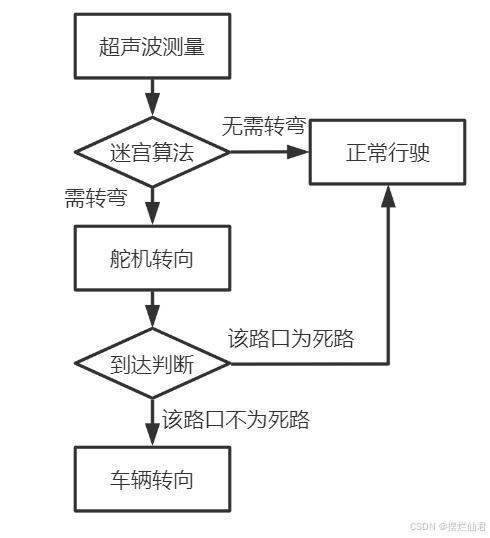
图10 转弯判断流程图
根据超声波测量的路口情况进行迷宫算法判断,若并不需要转弯则保持正常行驶,反之则将舵机转向需要转弯的方向,通过不断的超声波测距,根据是否有极大值的出现判断其是否到达路口。
以图9的情况为例,电脑鼠前往右侧的路口,则将转向舵机向右旋转九十度。同时车辆保持匀速前进,在前进的过程中不断进行超声波测距,而当车辆行驶图中路口时,其测量的数据便存在了极大值。此时小车停止运动,对路口再次进行超声波测量,根据路口判断原理分析该路口是否为死路。
为死路则将舵机转回前进方向,正常行驶;不为死路则停止右电机转动,单独工作左电机T时间,使小车向右旋转90度,进入新路口行驶。
根据此时情况将90度公式(19)计算可得:
对于大多数迷宫而言,车辆转向所需要的时间为一个定值。
三、车辆掉头
在智能的小车的避障研究中,若前方道路为死路则直接向后行驶或以一个轮胎为圆点旋转180度进行掉头。这不仅不适用我们的设计方案同时面对狭窄的现实道路时,也可能会出现车辆的掉头而使得车辆与障碍物相碰,见图11。
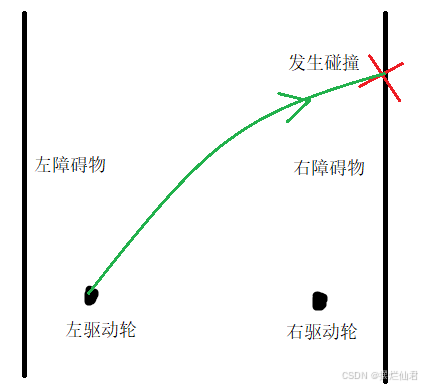
图11 掉头碰撞示意图
为使电脑鼠可以在道路宽度小于2D的狭窄情况进行掉头,特基于上述的中线对齐、车辆转向理论与公式(21)对掉头驱动进行改进,其运动情况见图12。
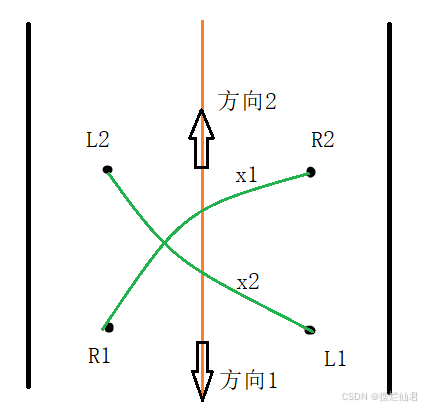
图12 车辆掉头示意图
当电脑鼠所前进的方向1为死路时,可先使其以L1为圆心,关闭左电机,单独工作右电机T时间,驱动右车轮从R1到达R2;同理以R2为圆心,关闭右电机,单独工作左电机T时间,驱动左车轮从L1到达L2。
此时的前进方向便从方向1改为了方向2,且电脑鼠在转向过程中不会与障碍物发生碰撞,完成转向后依然对齐中线行驶,在保证安全行驶的同时节省了二次中线对齐的时间损耗。
四、开源代码讲解
A*算法是一种启发式搜索算法,用于在图中找到从起点到终点的最短路径。我们将使用这个算法来规划智能车的路径。
python
import heapq
class Node:
def __init__(self, position, parent=None):
self.position = position
self.parent = parent
self.g = 0 # Cost from start to current node
self.h = 0 # Heuristic based estimated cost from current to end
self.f = 0 # Total cost
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.f < other.f
def heuristic(a, b):
return abs(a[0] - b[0]) + abs(a[1] - b[1]) # Manhattan distance
def a_star_search(start, end, grid):
start_node = Node(start, None)
end_node = Node(end, None)
open_list = []
closed_list = set()
heapq.heappush(open_list, start_node)
while open_list:
current_node = heapq.heappop(open_list)
closed_list.add(current_node.position)
if current_node.position == end_node.position:
path = []
while current_node is not None:
path.append(current_node.position)
current_node = current_node.parent
return path[::-1] # Return reversed path
(x, y) = current_node.position
neighbors = [(x-1, y), (x+1, y), (x, y-1), (x, y+1)]
for next in neighbors:
if next[0] < 0 or next[0] >= len(grid) or next[1] < 0 or next[1] >= len(grid[0]) or grid[next[0]][next[1]] == 1:
continue
if next in closed_list:
continue
neighbor_node = Node(next, current_node)
neighbor_node.g = current_node.g + 1
neighbor_node.h = heuristic(neighbor_node.position, end_node.position)
neighbor_node.f = neighbor_node.g + neighbor_node.h
if add_to_open(open_list, neighbor_node):
heapq.heappush(open_list, neighbor_node)
return None
def add_to_open(open_list, neighbor):
for node in open_list:
if neighbor == node and neighbor.g > node.g:
return False
return True
# Example usage
grid = [
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]
start = (0, 0)
end = (4, 4)
path = a_star_search(start, end, grid)
print("Path:", path)为了模拟智能车的换向掉头,我们可以创建一个简单的环境,其中包含障碍物和道路。智能车将使用A*算法来找到从起点到终点的路径,并执行掉头操作。
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_path(grid, path):
plt.imshow(grid, cmap='Greys', origin='lower')
for x, y in path:
plt.scatter(y, x, c='blue')
plt.scatter(path[0][1], path[0][0], c='green')
plt.scatter(path[-1][1], path[-1][0], c='red')
plt.show()
# Example usage
grid = [
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]
start = (0, 0)
end = (4, 4)
path = a_star_search(start, end, grid)
plot_path(grid, path)在实际应用中,智能车的控制系统将根据路径规划的结果来调整车辆的驱动和转向系统。这里我们使用一个简单的模拟来展示如何执行控制:
python
def execute_control(path):
print("Executing control...")
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
current_pos = path[i]
next_pos = path[i + 1]
print(f"Moving from {current_pos} to {next_pos}")
# Simulate movement
# In a real scenario, this would involve sending commands to the vehicle's actuators
# Example usage
execute_control(path)这个代码示例提供了一个基本的框架,展示了如何使用A*算法进行路径规划,并在模拟环境中执行控制。在实际应用中,可能需要根据具体的车辆硬件和环境条件进行调整和优化。