基本概念



-
满二叉树
-
完全二叉树
-

二叉树的性质





二叉树的存储结构
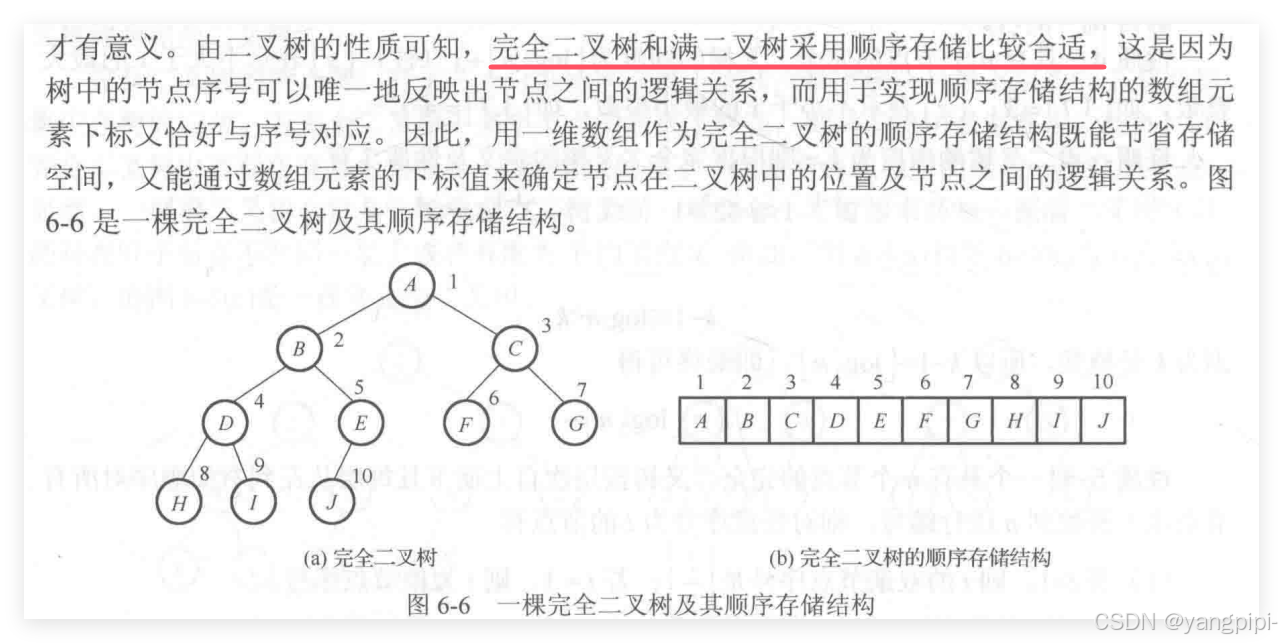
顺序存储结构
链式存储结构

二叉树的遍历(以二叉链表为例)
前序遍历
递归遍历
c
void Preorder(BSTree* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
printf("%c ",p->data);
Preorder(p->lchild);
Preorder(p->rchild);
}
}非递归遍历


cpp
void PreorderNoRecursive(BSTree* p)
{
/*
思路: 不断遍历左子树然后将其入栈,知道遇到NULL,弹栈,然后指向弹出元素的右子树
*/
std::stack<BSTree*> sta;
while (p!=NULL || !sta.empty())
{
if (p!=NULL)
{
printf("%c ", p->data);
sta.push(p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
p = sta.top();
sta.pop();
p = p->rchild;
}
}
}中序遍历
递归遍历
c
void Inorder(BSTree* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
Inorder(p->lchild);
printf("%c ", p->data);
Inorder(p->rchild);
}
}非递归遍历

c
void InorderNoRecursive(BSTree* p)
{
/*
思路: 不断将左子树入栈,直到遇到NULL,弹栈,访问,然后指向弹出元素的右子树
*/
std::stack<BSTree*> sta;
while (p != NULL || !sta.empty())
{
if (p != NULL)
{
sta.push(p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
p = sta.top();
sta.pop();
printf("%c ", p->data);
p = p->rchild;
}
}
}后序遍历
递归遍历
c
void Postorder(BSTree* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
Postorder(p->lchild);
Postorder(p->rchild);
printf("%c ", p->data);
}
}非递归遍历(困难)

设置访问标志b(一层)



cpp
void PostorderNoRecursive1(BSTree* p)
{
BSTree* sta[MAXSIZEBS];
int i = 0, b[MAXSIZEBS];
sta[0] = NULL;
do
{
if (p != NULL)
{
sta[++i] = p;
b[i] = 0; // 置*p的右子树未访问过的标志
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
p = sta[i--];
if (b[i + 1] == 0)
{
sta[++i] = p;
b[i] = 1; // 置*p的右子树已访问的标志
p = p->rchild;
}
else
{
printf("%c ",p->data);
p = NULL; // 指向*p的指针置空
}
}
} while (p != NULL || i > 0);
}二层循环


前序-> 后序

先依次将右子树依此压栈,直到右子树为NULL时,再压栈,访问此元素的左子树。最后将得到的元素反向输出即可。
c
void PostorderNoRecursive(BSTree* p)
{
std::stack<BSTree*> sta;
std::vector<char> vec;
while (p != NULL || !sta.empty())
{
if (p != NULL)
{
//printf("%c ", p->data);
vec.push_back(p->data);
sta.push(p);
p = p->rchild;
}
else
{
p = sta.top();
sta.pop();
p = p->lchild;
}
}
for (std::vector<char>::const_reverse_iterator it = vec.rbegin(); it != vec.rend(); it++)
{
printf("%c ",*it);
}
}层次遍历
c
void Transleve(BSTree* t)
{
/*
使用队列,依次访问每一个元素。
*/
// 层次遍历的方式一
//std::queue<BSTree*> de;
//BSTree* p;
//if (t != NULL)
//{
// printf("%c ", t->data);
// de.push(t);
//}
//else
// return;
//while (!de.empty())
//{
// p = de.front();
// de.pop();
// if (p->lchild != NULL)
// {
// printf("%c ", p->lchild->data);
// de.push(p->lchild);
// }
// if (p->rchild != NULL) //注意这里不是else if
// {
// printf("%c ", p->rchild->data);
// de.push(p->rchild);
// }
//}
// 层次遍历的方式2:
std::queue<BSTree*> de;
BSTree* p;
if (t != NULL)
de.push(t);
else
return;
while (!de.empty())
{
p = de.front();
printf("%c ", p->data);
de.pop();
if (p->lchild != NULL)
de.push(p->lchild);
if (p->rchild != NULL)
de.push(p->rchild);
}
}练习题
根据条件交换二叉树的左右子树

cpp
void Change(BSTree* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
if (p->lchild!=NULL&& p->rchild!=NULL&&p->lchild->data > p->rchild->data) // 如果左子树大于右子树的话,就交换左右子树
{
BSTree* tmp = p->lchild;
p->lchild = p->rchild;
p->rchild = tmp;
}
Change(p->lchild);
Change(p->rchild);
}
}查找元素
根据中序非递归查找
c
// 查找
// 搜素 根据中序非递归遍历查找元素
BSTree* Search_In_NoRecursive(BSTree* p, datatypeBS x)
{
std::stack<BSTree*> sta;
while (p != NULL || !sta.empty())
{
if (p != NULL)
{
sta.push(p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
p = sta.top();
sta.pop();
//printf("%c ", p->data);
if (p->data == x)
return p;
p = p->rchild;
}
}
return NULL;
}根据先序递归查找(易错)

c
BSTree* Search_Pre_Recursive(BSTree* bt, datatypeBS x)
{
BSTree* p = NULL;
if (bt != NULL)
{
/*printf("%c ", p->data);*/
if (bt->data == x)
return bt;
if (bt->lchild != NULL)
{
p = Search_Pre_Recursive(bt->lchild, x);
if (p != NULL)
return p;
}
if (bt->rchild != NULL)
{
p = Search_Pre_Recursive(bt->rchild, x);
if (p != NULL)
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
统计二叉树中叶子节点的个数
递归方法
c
// 统计叶子节点的个数
int Countleaf(BSTree* p)
{
if (p == NULL) // 空二叉树
return 0;
if (p->lchild == NULL && p->rchild == NULL) // 叶子节点
return 1;
return Countleaf(p->lchild) + Countleaf(p->rchild);
}非递归方法

c
int Countleaf_PreorderNoRecursive(BSTree* p)
{
/*
思路: 不断遍历左子树然后将其入栈,知道遇到NULL,弹栈,然后指向弹出元素的右子树
*/
int count = 0;
std::stack<BSTree*> sta;
while (p != NULL || !sta.empty())
{
if (p != NULL)
{
//printf("%c ", p->data);
if (p->lchild == NULL && p->rchild == NULL)
count++;
sta.push(p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
p = sta.top();
sta.pop();
p = p->rchild;
}
}
return count;
}求二叉树深度

c
// 求二叉树的深度
int Depth(BSTree* p)
{
int lchild = 0, rchild = 0;
if (p == NULL)
return 0;
else {
lchild = Depth(p->lchild)+1;
rchild = Depth(p->rchild)+1;
return lchild > rchild ? lchild : rchild;
}
}判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树

- 利用层序遍历,在将一个节点压入队列之前,如果其有右孩子而没有左孩子时则不是满二叉树。
c
// 判断一个二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int is_complete_binary_tree(BSTree* t)
{
std::queue<BSTree*> de;
BSTree* p;
if (t != NULL)
de.push(t);
else
return 1;
while (!de.empty())
{
p = de.front();
//printf("%c ", p->data);
de.pop();
if (p->lchild != NULL)
de.push(p->lchild);
else
{
if (p->rchild != NULL)
return 0; // 不是完全二叉树
}
if (p->rchild != NULL)
de.push(p->rchild);
}
return 1; // 是完全二叉树
}找出二叉树中最深的通道

c
// 求二叉树的最长深度并输出数值
int len = 0;
int longest_len = 0;
void longest_path(BSTree* T, char* path, char* longestpath)
{
int j, i;
if (T)//树不空
{
if (!T->lchild && !T->rchild)//当遇到叶子结点时,该条路径完毕
{
path[len] = T->data;//把结点数据放入数组
if (len > longest_len)//如果长于longest_len就替换
{
for (j = 0; j <= len; j++)//把路径复制到longestpath里面
longestpath[j] = path[j];
longest_len = len;//longest_len更新
}
}
else//当遇到的不是叶子结点时,该条路径继续
{
path[len++] = T->data;//结点放入数组,len++
longest_path(T->lchild, path, longestpath);
longest_path(T->rchild, path, longestpath);
len--;//每次退出递归len--
}
}
}注意,定义全局遍历的不要再头文件中定义。应该在一个.c文件中定义并且初始化。如果其他.c文件想使用的话,需要在头文件中使用·extern声明注意注意只是声明不要初始化。
在a.c中 int num = 1; 在a.h中 extern int num; 在b.c中只需要#include"a.h"即可在b.c中使用定义的全局变量num
二叉树的创建
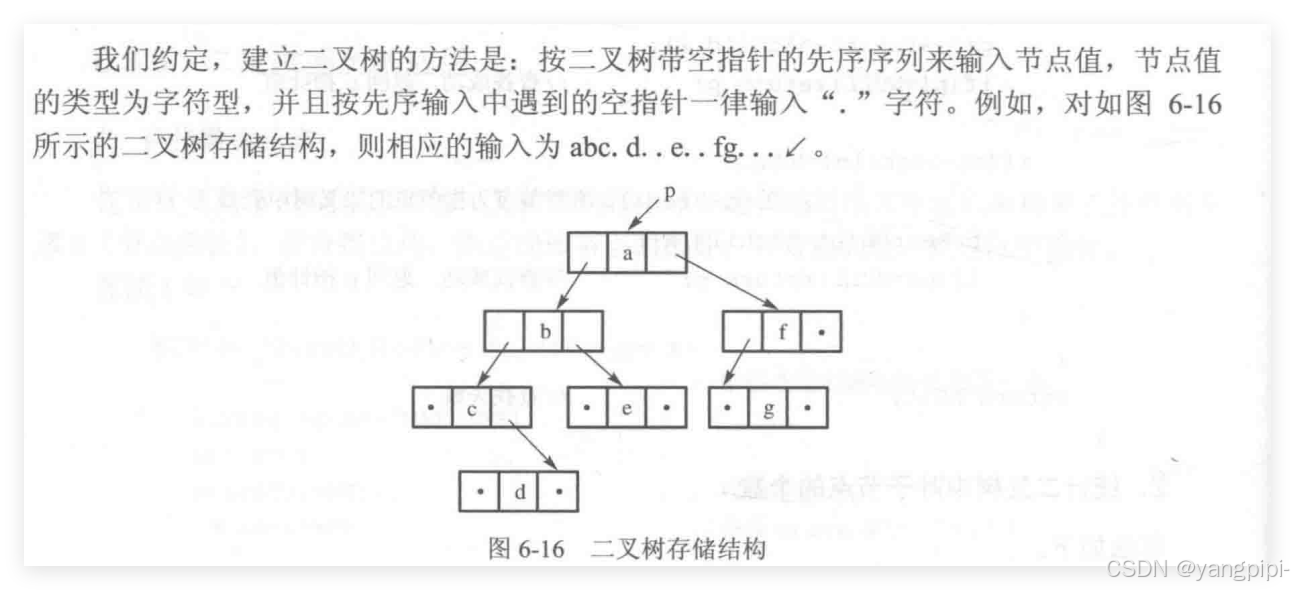
根据先序序列创建
cpp
void CreatebByPreorder(BSTree** p)
{
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
if (ch != '.')
{
*p = (BSTree*)malloc(sizeof(BSTree));
(*p)->data = ch;
CreatebByPreorder(&((*p)->lchild));
CreatebByPreorder(&((*p)->rchild));
}
else
*p = NULL;
}由遍历序列恢复二叉树
-
先序+中序 -》 可恢复
-

-
后序+中序-》可恢复
-

先序+中序 -》二叉树

在这里插入图片描述
c
// 根据 先序+中序-》 二叉树
void Pre_In_Oreder(char pred[], char ind[], int i, int j, int k, int h, BSTree** p)
{
*p = (BSTree*)malloc(sizeof(BSTree));
(*p)->data = pred[i]; // 首先构造头结点
// 从中序序列中找到头结点的位置
int m = k;
while (ind[m] != pred[i])
m++;
// 构造左子树
if (m == k) // 左子树为NULL
(*p)->lchild = NULL;
else
Pre_In_Oreder(pred,ind,i+1, i+m-k,k,m-1,&(*p)->lchild);
// 构造右子树
if (m == h) // 右子树为NULL
(*p)->rchild = NULL;
else
Pre_In_Oreder(pred, ind, i + m - k+1, j , m+1, h, &(*p)->rchild);
}- 主要是每次遍历先序序列的范围


c
int main()
{
BSTree* tree1;
char pred[] = "acbgdehfji";
char ind[] = "cgbahedjfi";
Pre_In_Oreder(pred, ind, 0, 9, 0, 9, &tree1); //void Pre_In_Oreder(char pred[], char ind[], int i, int j, int k, int h, BSTree** p)
printf("\nTransleve遍历结果:");
Transleve(tree1);
printf("\nPostorder遍历结果:");
Postorder(tree1);
return 0;
}后序+中序 -》二叉树

c
void Post_In_Oreder(char post[], char ind[], int i, int j, int k, int h, BSTree** p)
{
*p = (BSTree*)malloc(sizeof(BSTree));
(*p)->data = post[j]; // 首先构造头结点
// 从后序序列中找到头结点的位置
int m = k;
while (ind[m] != post[j])
m++;
// 构造左子树
if (m == k) // 左子树为NULL
(*p)->lchild = NULL;
else
Post_In_Oreder(post, ind, i, i + m - k-1, k, m - 1, &(*p)->lchild);
// 构造右子树
if (m == h) // 右子树为NULL
(*p)->rchild = NULL;
else
Post_In_Oreder(post, ind, i + m - k, j-1, m + 1, h, &(*p)->rchild);
}线索二叉树



线索化二叉树



c
// 线索二叉树------------------------------------------------
// 中序线索二叉树
void Thread(TBTree* p) // 对二叉树的进行线索化
{
if (p != NULL)
{
Thread(p->lchild);
if (p->lchild == NULL)
{
p->ltag = 1;
p->lchild = pre;
}
else {
p->ltag = 0;
}
if (pre->rchild == NULL)
{
pre->rtag = 1;
pre->rchild = p;
}
else {
pre->rtag = 0;
}
pre = p;
Thread(p->rchild);
}
}
TBTree* CreatThread(TBTree* b)// 建立中序线索二叉树
{
TBTree* root;
root = (TBTree*)malloc(sizeof(TBTree));
root->ltag = 0;
root->rtag = 1;
if (b == NULL)
root->lchild = root;
else {
root->lchild = b;
pre = root;
Thread(b);
pre->rchild = root;
pre->rtag = 1;
root->rchild = pre;
}
return root;
}访问线索二叉树
1. 在中序线索二叉树上查找任意节点的中序前驱节点

c
//在中序线索二叉树上查找任意节点p的中序前驱节点
TBTree* Inpre(TBTree* p)
{
TBTree* tmp;
if (p->ltag == 1)
return p->lchild;
else { // 有右孩子 :p的前驱节点就是以p为根节点的子树的最右节点
TBTree* tmp = p->lchild;
while (tmp->rtag == 0) //rtag为0表示有孩子
tmp = tmp->rchild;
}
}2. 在中序线索二叉树上查找任意节点的中序后继节点

c
//在中序线索二叉树上查找任意节点的中序后继节点
TBTree* InPoost(TBTree* p)
{
TBTree* tmp;
if (p->rtag == 1) // 没有左孩子
return p->rchild;
else { // 有右孩子:则p的后继节点就是以p的右孩子为子树的最左节点
tmp = p->rchild;
while (tmp->ltag == 0)
tmp = tmp->lchild;
}
}3. 中序遍历中序线索二叉树

c
void Inorder(TBTree* b)
{
TBTree* p = b->lchild;
while (p != b)
{
while (p->ltag == 0) // 找到第一个节点
p = p->lchild;
printf("%c ",p->data);
while (p->rtag == 1 && p != b) // 当后继线索存在且不是头结点时
{
printf("%c ",p->data);
p = p->rchild;
}
p = p->rchild;
}
}哈夫曼树(最优二叉树)


哈夫曼树构造




哈夫曼算法


树和森林
树的存储结构








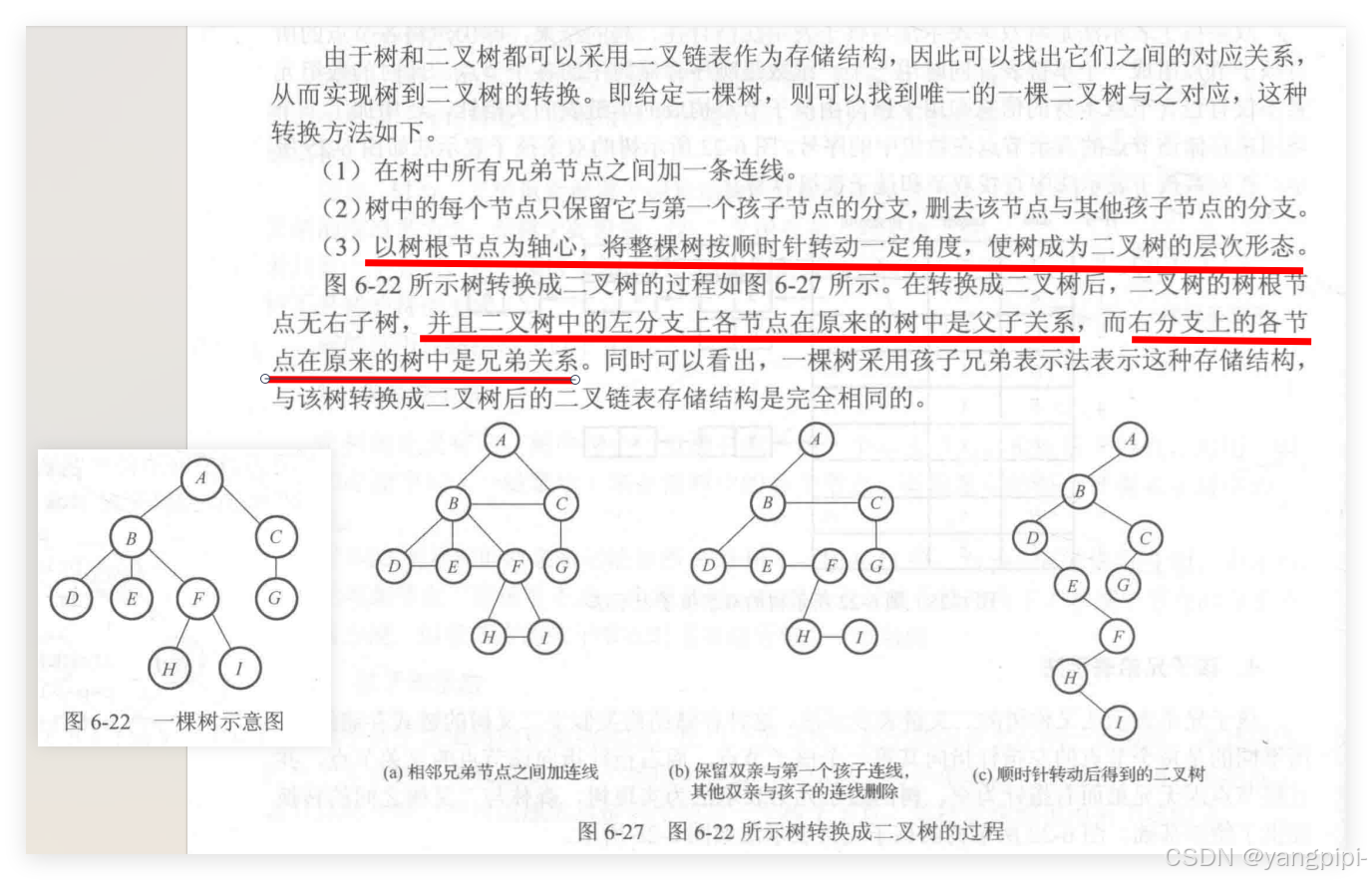
树->二叉树
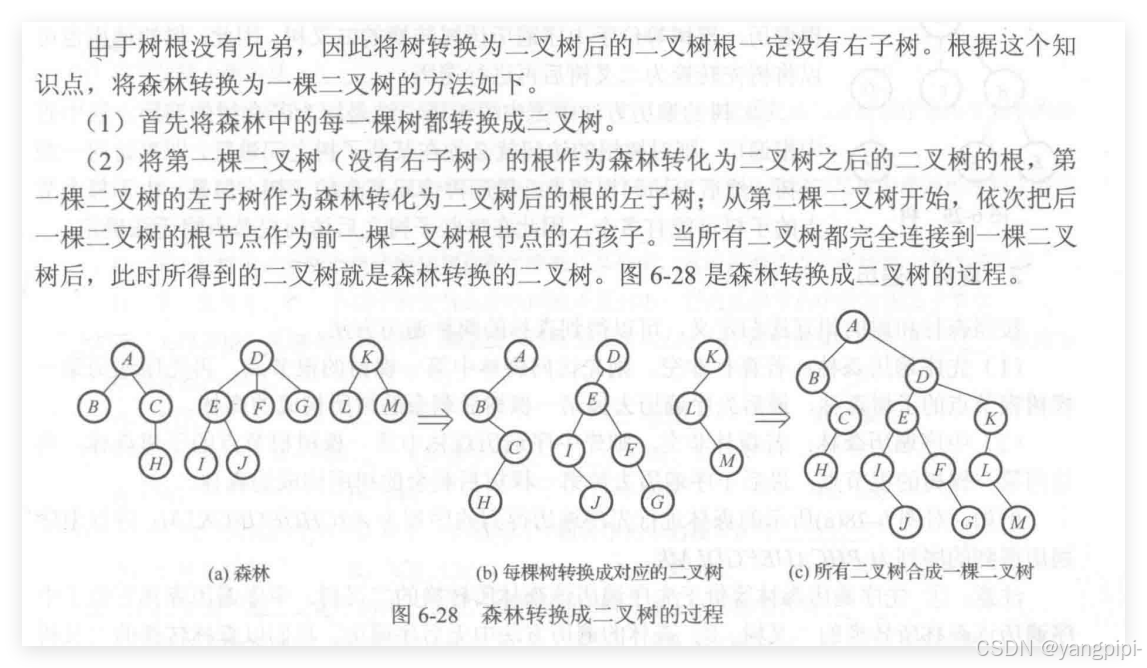
森林->二叉树
二叉树转换为树和森林

树的遍历



森林的遍历

