一、Hive的高级部分
1、序列化与反列化
在哪里听过这个词?--> 只要碰见将对象存入内存、硬盘、网络传输,对象必须序列化。对象可以想象为活物。
1、Java的序列化 (implements Serializable) 讲IO流以及Web开发的时候
2、MapReduce Hadoop抛弃了java的序列化方式,自己又创建了一套,implements Writable,原因是 Java的序列化 出来的数据太大了。
3、Hive 比如 select * from t_user; --> 查询就是硬盘的数据变为控制台输出的数据,这个过程是反序列化的。
假如 insert into t_user values(1,"张三") ; --> 将一个对象变为了一个hdfs上的数据 ,这个过程是序列化。
select过程
读取磁盘上的数据,创建row对象,这种从磁盘读取文件并转换为对象的过程称之为反序列化,底层用到了InputFormat。
insert过程
将内存中的row对象,存储为磁盘上的数据,这个过程是序列化的过程,底层用到了OutputFormat。
序列化与反序列化就需要用到分隔符
1|张三|20 解析 分隔符 | --> Row对象 --> Hive --> HDFS 对象的序列化
由上面可知,分隔符在序列化与反序列化的过程中非常的重要,所以要重点学习一下。
具体来讲,就是依据serde这个工具包:
SerDe是"Serializer and Deserializer"的简称。
Hive使用SerDe(和FileFormat)来读/写表的Row对象。
HDFS文件-> InputFileFormat -> <key,value> -> Deserializer -> Row对象
Row对象->Serializer -> <key,value> -> OutputFileFormat -> HDFS文件2、具体的Serde
l csv: 逗号分隔值
l tsv: tab分隔值
l json: json格式的数据 --在mr中,看见json数据,使用工具类解析 fastjson,jackson,gson等
l regexp: 数据需要复合正则表达式
以上这些分隔符都不是默认分隔符,默认分隔符是:^A 或者 \001
^A八进制编码体现为'\001'
它使用的类是serde这个工具包中的哪个类呢?--> LazySimpleSerDe
每一个分隔符,都对应一个具体的类。
1)使用默认分隔符进行演示
- 行分隔符:\n
- 列分隔符:^A创建数据:
1001^Azs^A23
1002^Alisi^A24
此处不要copy,copy也没有用,认真看注意事项中的文字
新建表:
create table if not exists csv1(
uid int,
uname string,
age int
);
-- 格式都没有指定,默认使用的就是LazySimpleSerde,记录分隔符是\n,列分隔符是^A
由于我们这个数据,它是用的默认分隔符,所以建表的时候不需要指定分隔符加载数据:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/csv1.txt' overwrite into table csv1;查询结果,发现数据正常导入。
2)使用逗号分隔符 csv
分隔符:列分隔符:逗号
常见数据: csv2.txt
1001,zs,23
1002,lisi,24新建表:
create table if not exists csv2(
uid int,
uname string,
age int
)row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';
hive (yhdb)> load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/csv2.txt' overwrite into table csv2;
Loading data to table yhdb.csv2
OK
Time taken: 0.552 seconds
hive (yhdb)> select * from csv2;
OK
csv2.uid csv2.uname csv2.age
1001 zs 23
1002 lisi 24
Time taken: 0.506 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
desc formatted csv2; 查看表结构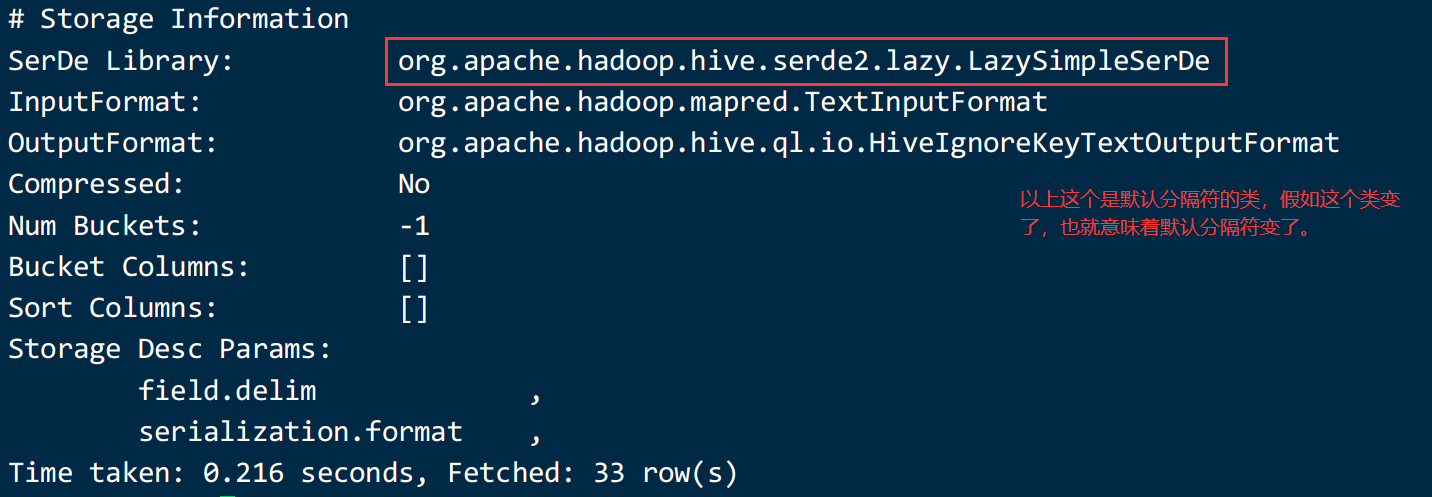
第二种建表语句:
drop table csv2;
create table if not exists csv2(
uid int,
uname string,
age int
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde';
# Storage Information
SerDe Library: org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde
InputFormat: org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat
OutputFormat: org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat
Compressed: No
Num Buckets: -1
Bucket Columns: []
Sort Columns: []
Storage Desc Params:
serialization.format 1
Time taken: 0.186 seconds, Fetched: 33 row(s)
数据导入并查看:
hive (yhdb)> load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/csv2.txt' overwrite into table csv2;
hive (yhdb)> select * from csv2;OpenCSVSerde还可以自定义分隔符
假如数据如下所示:使用数字7作为分隔符
10017zs723
10027lisi724新建表:
create table if not exists csv3(
uid int,
uname string,
age int
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde'
with serdeproperties(
"separatorChar"="7"
);
数据导入并查看:
hive (yhdb)> load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/csv3.txt' overwrite into table csv3;
hive (yhdb)> select * from csv3;3) json serde [最重要]
1、理论
json serde 可以是自己写的jar包也可以是第三方的jar包,要把这种jar包添加到hive的class path中
2、实践
将jar包放置在/opt/modules文件夹下,然后在hive中执行如下命令:
add jar /opt/modules/json-serde-1.3.8-jar-with-dependencies.jar;
先有json数据:
{"uid":"1","uname":"gaoyuanyuan","age":"18"}
{"uid":"2","uname":"gaolaozhuang","age":"42"}
create table if not exists json1(
uid int,
uname string,
age int
)
row format serde 'org.openx.data.jsonserde.JsonSerDe';
org.openx.data.jsonserde.JsonSerDe 这个类是第三方的类,所以要导入包加载数据并查询:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/json1.txt' into table json1;
hive (yhdb)> select * from json1;
OK
json1.uid json1.uname json1.age
1 gaoyuanyuan 18
2 gaolaozhuang 42第二个json解析的类,hive自带的:
'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe'
新建表:
create table if not exists json2(
uid int,
uname string,
age int
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe';
导入数据:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/json1.txt' into table json2;
导入之后:查询 select * from json2;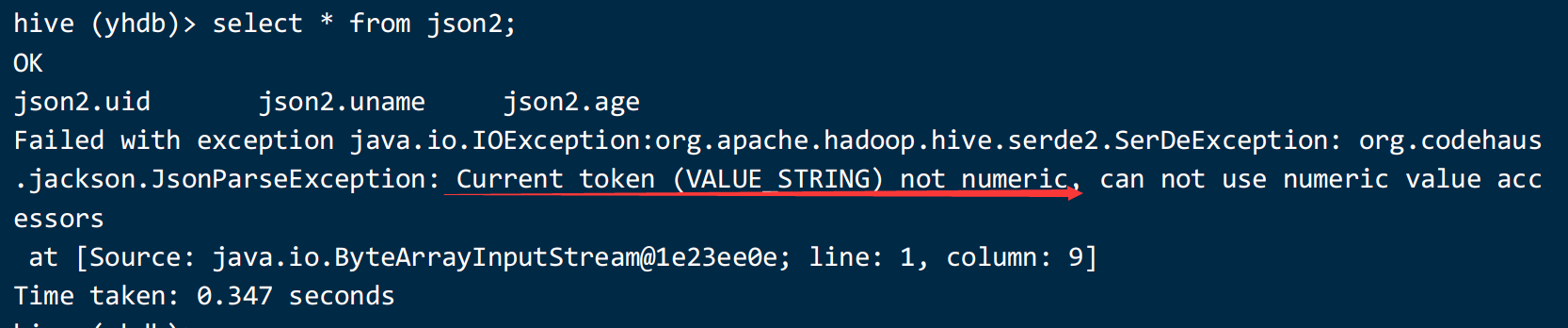
以上错误的意思是数据类型不匹配,表和数据的类型不匹配。
修改表的字段类型:
drop table json2;
create table if not exists json2(
uid string,
uname string,
age string
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe';假如以上使用时报类找不到异常,需要指定hive中lib的位置,一般是不报错的。
ClassNotFindExcption --> 一看到这个就是缺 jar 包
json格式数据表需要通过serde机制处理
在/opt/installs/hive/conf 下 找到 hive-site.xml 修改里面的值
在hive-site.xml中设置三方jar包
<property>
<name>hive.aux.jars.path</name>
<value>/opt/installs/hive/lib/</value>
</property>添加配置文件后还要重启metastore以及hive客户端。
4)复杂数据类型处理
数据如下所示:
json2.txt 中的数据如下:
zs math:100,98,76 chinese:98,96,100 english:100,99,90
ls math:60,80,70 chinese:90,66,91 english:50,51,70
思路是,将这个数据变为json(写java代码就可以) jackson、fastjson、gson等
{"uname":"zs","score":{"math":[100,98,76],"chinese":[98,96,100],"english":[100,99,90]}}
{"uname":"ls","score":{"math":[60,80,70],"chinese":[90,66,91],"english":[50,51,70]}}
建表:
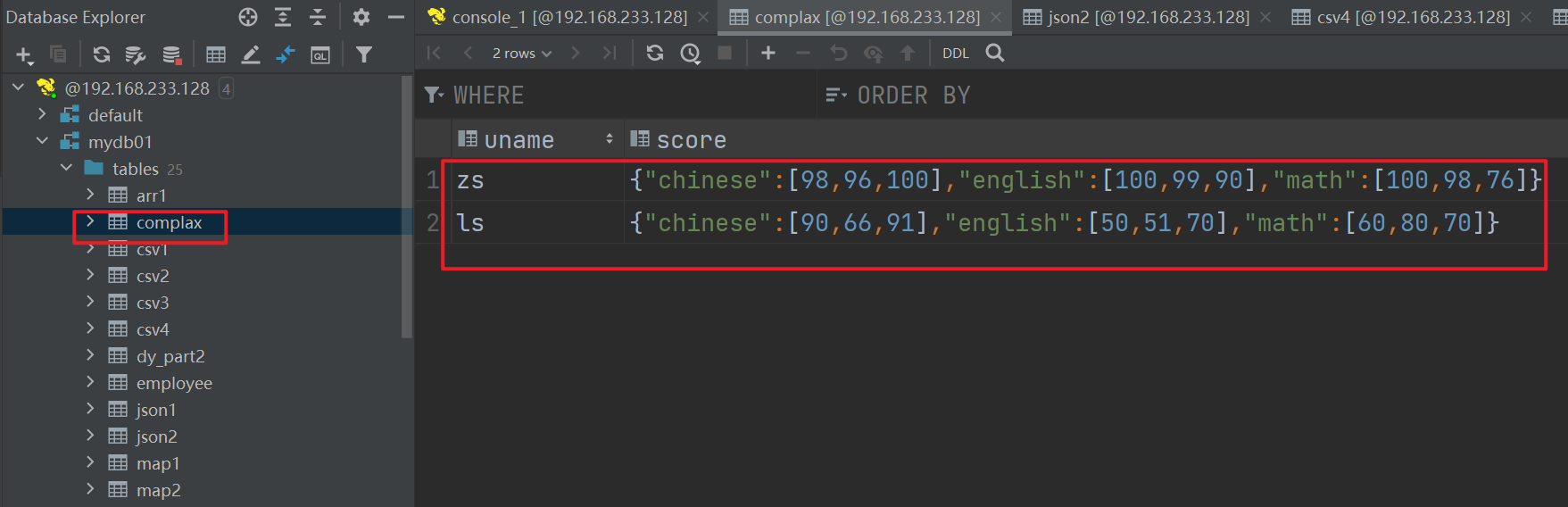
create table if not exists complex(
uname string,
score map<string,array<int>>
)
row format serde 'org.openx.data.jsonserde.JsonSerDe'
stored as textfile;
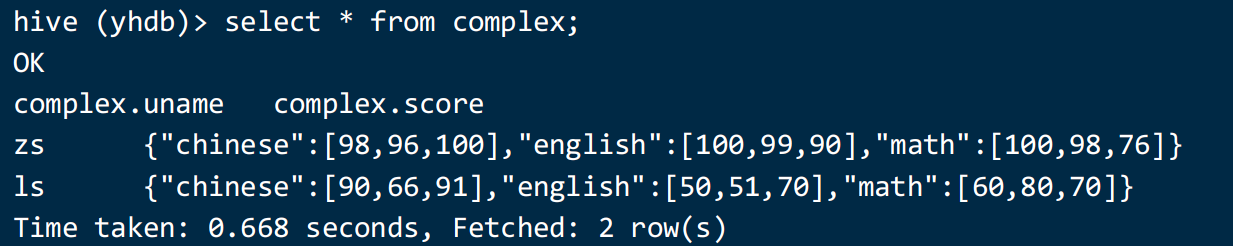
加载数据并查看是否正常解析:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/json2.txt' into table complex;
select * from complex;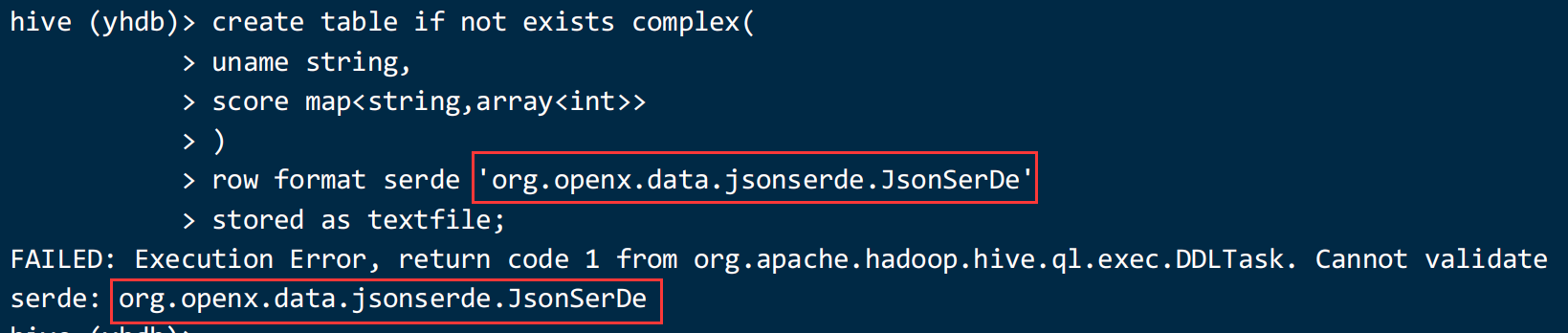
add jar /opt/modules/json-serde-1.3.8-jar-with-dependencies.jar;
一般将jar包上传至hdfs上,并且把这个语句添加到 .hiverc文件中
add jar hdfs://bigdata01:9820/lib/json-serde-1.3.8-jar-with-dependencies.jar;缺少jar包:为什么以前添加过了现在还要添加,原因是hive客户端关闭又开启,就需要重新添加
以上做法还可以这样做:
在 hive-site.xml 中指定 lib 的路径:
<property>
<name>hive.aux.jars.path</name>
<value>/opt/installs/hive/lib/</value>
</property>重启一下 metastore 和 hiveserver2 服务,此时一切正常。
5) Regex Serde
数据准备:
01||zhangsan||23
02||lisi||24创建一个表:
create table if not exists t_regex(
id string,
uname string,
age int
)row format delimited
fields terminated by '||';
加载数据:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/regex.txt' into table t_regex;
hive (yhdb)> select * from t_regex;
OK
t_regex.id t_regex.uname t_regex.age
01 NULL
02 NULL
Time taken: 0.425 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
发现解析是有问题的,只解析了一个 |
使用正则表达式解析:
drop table t_regex;
create table if not exists t_regex(
id string,
uname string,
age int
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe'
with serdeproperties(
'input.regex'='(.*)\\|\\|(.*)\\|\\|(.*)',
'output.format.string'='%1$s %2$s %3$s'
)
stored as textfile;
加载数据:
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/regex.txt' into table t_regex;
hive (yhdb)> select * from t_regex;
OK
t_regex.id t_regex.uname t_regex.age
01 zhangsan 23
02 lisi 24
Time taken: 0.351 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
结论是:不设置output.format.string 也是可以的。
RegexSerDe类是hive自带的,使用正则表达式来支持复杂的data导入。
在hive0.11中,自带了两个RegexSerDe类:
org.apache.Hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.RegexSerDe;
org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe;
这两个类的区别在:
org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe; 不支持output.format.string设定,设定了还会报警~~~~
org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.RegexSerDe;全部支持,功能比org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe更强大,推荐使用org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.RegexSerDe。
下面对RegexSerDe类的介绍都是指:org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.RegexSerDe
[08S01][1] Error while processing statement: FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. java.lang.RuntimeException: MetaException(message:org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.SerDeException org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.RegexSerDe only accepts string columns, but column[0] named uid has type int)总结:
Serde 其实就是序列化与反序列化,它的本质上讲的是如何解析文档数据,进入hive,如何从hive展示数据。
可以理解为分隔符,每一个分隔符都应的都有 某个具体的Serde 工具类。
创建表的时候,假如指定了某个Serde 就说明,默认解析格式被修改了,需要按照指定的格式进行解析。
第五题:
有如下数据,表示1、2、3三名学生选修了a、b、c、d、e、f中的若干课程
id course
1 a
1 b
1 c
1 e
2 a
2 c
2 d
2 f
3 a
3 b
3 c
3 e
根据如上数据,查询出如下结果,其中1表示选修,0表示未选修
id a b c d e f
1 1 1 1 0 1 0
2 1 0 1 1 0 1
3 1 1 1 0 1 0
SQL:
--第一种方法
select id,
sum(case when course='a' then 1 else 0 end ) a,
sum(case when course='b' then 1 else 0 end ) b,
sum(case when course='c' then 1 else 0 end ) c,
sum(case when course='d' then 1 else 0 end ) d,
sum(case when course='e' then 1 else 0 end ) e,
sum(case when course='f' then 1 else 0 end ) f
from zhoukao03 group by id;
--第二种方法
select id,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'a'),1,0) a,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'b'),1,0) b,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'c'),1,0) c,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'d'),1,0) d,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'e'),1,0) e,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'f'),1,0) f
from courses group by id;
假如查询出如下结果
id a b c d e f
1 选修 选修 选修 未选修 选修 未选修
2 选修 未选修 选修 选修 未选修 选修
3 选修 选修 选修 未选修 选修 未选修
create table courses (
id int,
course string
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by '\t';
load data local inpath '/home/hivedata/zuoye5.txt' into table courses;
select id,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'a'),'选修','未选修') a,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'b'),'选修','未选修') b,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'c'),'选修','未选修') c,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'d'),'选修','未选修') d,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'e'),'选修','未选修') e,
if(array_contains(collect_set(course),'f'),'选修','未选修') f
from courses group by id;