
文章目录
- 1、Half Wavelet Attention
- 2、代码实现
paper:HALFWAVELET ATTENTION ON M-NET+ FOR LOW-LIGHT IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
1、Half Wavelet Attention
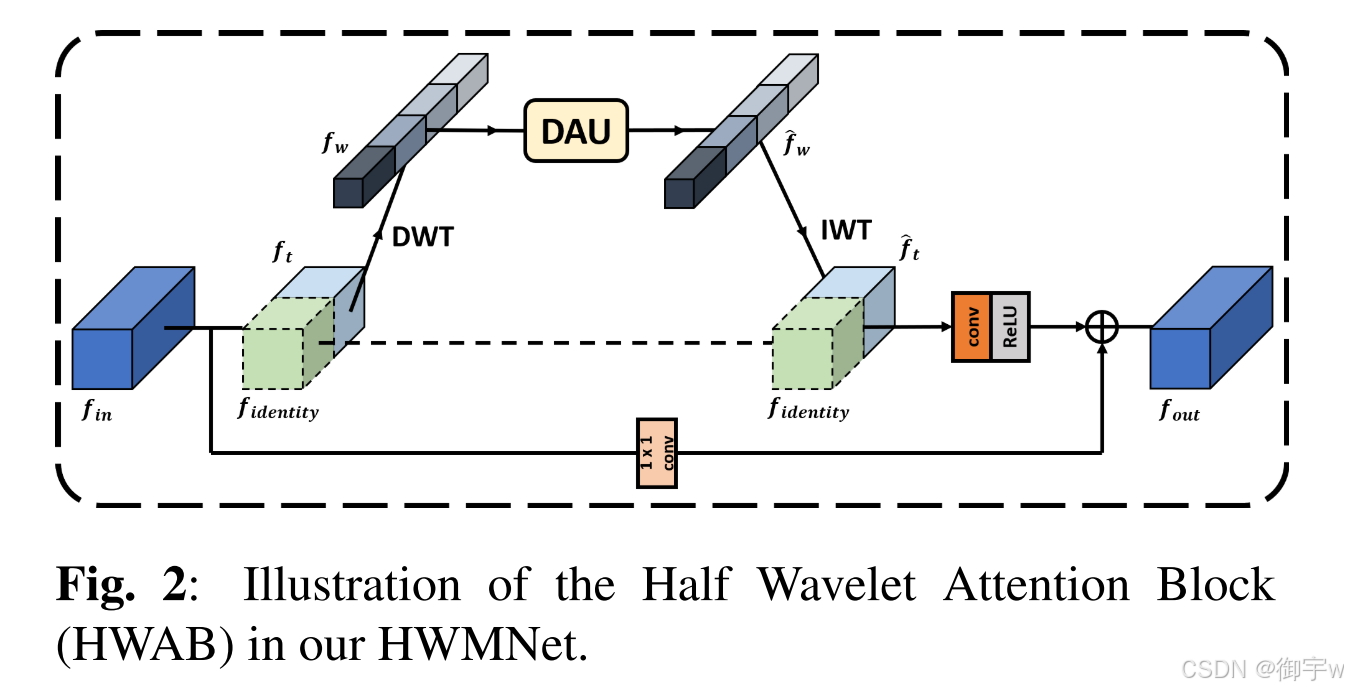
传统的图像增强方法主要关注图像在空间域的特征信息,而忽略了时频域上的特征信息。而小波变换能够将图像分解为不同频率的子带,从而在时频域上分析图像特征,捕获图像的细节信息。所以,这篇论文提出一种 半小波注意力(Half Wavelet Attention),旨在利用小波变换的优势,从另一个维度提取图像特征,丰富特征表达,从而提升低光图像增强的效果。
HWA 的核心思想是利用小波变换在时频域的特性,提取图像在另一维度上的特征信息,从而丰富图像的特征表达,提升低光图像增强的效果。HWA 模块通过将输入特征图分为两部分,一部分保持不变,另一部分进行离散小波变换,得到小波域特征图。
对于输入X,HWA 的实现过程:
- 特征分割: 将输入特征图沿通道维度分为两部分,一部分保持不变,另一部分进行离散小波变换。
- 注意力机制: 对小波域特征图进行通道注意力和空间注意力操作,提取加权特征图。
- 逆小波变换: 将加权小波域特征图进行逆小波变换,得到加权空间域特征图。
- 特征融合: 将加权空间域特征图与保持不变的特征图进行拼接,并进行残差连接和跳跃连接,得到最终的输出特征图。
HWA 的主要优势:
- 丰富特征表达: HWA 模块能够从另一个维度提取图像特征,丰富特征表达,从而提升低光图像增强的效果。
- 提升细节信息: 小波变换能够捕获图像的细节信息,HWA 模块能够有效提升图像的细节信息。
- 降低计算复杂度: HWA 模块中只有一半的特征图需要进行注意力机制操作,从而降低计算复杂度。
Half Wavelet Attention 结构图:
2、代码实现
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def dwt_init(x):
x01 = x[:, :, 0::2, :] / 2
x02 = x[:, :, 1::2, :] / 2
x1 = x01[:, :, :, 0::2]
x2 = x02[:, :, :, 0::2]
x3 = x01[:, :, :, 1::2]
x4 = x02[:, :, :, 1::2]
x_LL = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4
x_HL = -x1 - x2 + x3 + x4
x_LH = -x1 + x2 - x3 + x4
x_HH = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4
# print(x_HH[:, 0, :, :])
return torch.cat((x_LL, x_HL, x_LH, x_HH), 1)
def iwt_init(x):
r = 2
in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = x.size()
out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width = in_batch, int(in_channel / (r ** 2)), r * in_height, r * in_width
x1 = x[:, 0:out_channel, :, :] / 2
x2 = x[:, out_channel:out_channel * 2, :, :] / 2
x3 = x[:, out_channel * 2:out_channel * 3, :, :] / 2
x4 = x[:, out_channel * 3:out_channel * 4, :, :] / 2
h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width]).cuda() #
h[:, :, 0::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4
h[:, :, 1::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 + x3 - x4
h[:, :, 0::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 - x3 - x4
h[:, :, 1::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4
return h
class DWT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(DWT, self).__init__()
self.requires_grad = True
def forward(self, x):
return dwt_init(x)
class IWT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(IWT, self).__init__()
self.requires_grad = True
def forward(self, x):
return iwt_init(x)
def conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, bias=False, stride=1):
return nn.Conv2d(
in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size,
padding=(kernel_size // 2), bias=bias, stride=stride)
class SALayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=5, bias=False):
super(SALayer, self).__init__()
self.conv_du = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2, bias=bias),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
# torch.max will output 2 things, and we want the 1st one
max_pool, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
avg_pool = torch.mean(x, 1, keepdim=True)
channel_pool = torch.cat([max_pool, avg_pool], dim=1) # [N,2,H,W] could add 1x1 conv -> [N,3,H,W]
y = self.conv_du(channel_pool)
return x * y
class CALayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16, bias=False):
super(CALayer, self).__init__()
# global average pooling: feature --> point
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
# feature channel downscale and upscale --> channel weight
self.conv_du = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // reduction, 1, padding=0, bias=bias),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, channel, 1, padding=0, bias=bias),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.avg_pool(x)
y = self.conv_du(y)
return x * y
class HWB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feat, o_feat, kernel_size=3, reduction=16, bias=False, act=nn.ReLU()):
super(HWB, self).__init__()
self.dwt = DWT()
self.iwt = IWT()
modules_body = \
[
conv(n_feat*2, n_feat, kernel_size, bias=bias),
act,
conv(n_feat, n_feat*2, kernel_size, bias=bias)
]
self.body = nn.Sequential(*modules_body)
self.WSA = SALayer()
self.WCA = CALayer(n_feat*2, reduction, bias=bias)
self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(n_feat*4, n_feat*2, kernel_size=1, bias=bias)
self.conv3x3 = nn.Conv2d(n_feat, o_feat, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=bias)
self.activate = act
self.conv1x1_final = nn.Conv2d(n_feat, o_feat, kernel_size=1, bias=bias)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
# Split 2 part
wavelet_path_in, identity_path = torch.chunk(x, 2, dim=1)
# Wavelet domain (Dual attention)
x_dwt = self.dwt(wavelet_path_in)
res = self.body(x_dwt)
branch_sa = self.WSA(res)
branch_ca = self.WCA(res)
res = torch.cat([branch_sa, branch_ca], dim=1)
res = self.conv1x1(res) + x_dwt
wavelet_path = self.iwt(res)
out = torch.cat([wavelet_path, identity_path], dim=1)
out = self.activate(self.conv3x3(out))
out += self.conv1x1_final(residual)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.randn(1, 64, 128, 128).cuda()
model = HWB(64, 64).cuda()
output = model(x)
print(output.shape)