目录
[1.1 递归实现指数型枚举](#1.1 递归实现指数型枚举)
[1.2 递归实现排列型枚举](#1.2 递归实现排列型枚举)
[1.3 递归实现组合型枚举](#1.3 递归实现组合型枚举)
[1.4 带分数](#1.4 带分数)
[2.1 简单斐波那契](#2.1 简单斐波那契)
[2.2 费解的开关](#2.2 费解的开关)
[2.3 翻硬币](#2.3 翻硬币)
[2.4 飞行员兄弟](#2.4 飞行员兄弟)
1、递归
递归就是在函数内部自己调用自己
我们以递归的形式来实现斐波那契数列:0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
if(n == 1) return 0;
if(n == 2) return 1;
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}对于每一个递归,都可以画出一颗递归搜索树
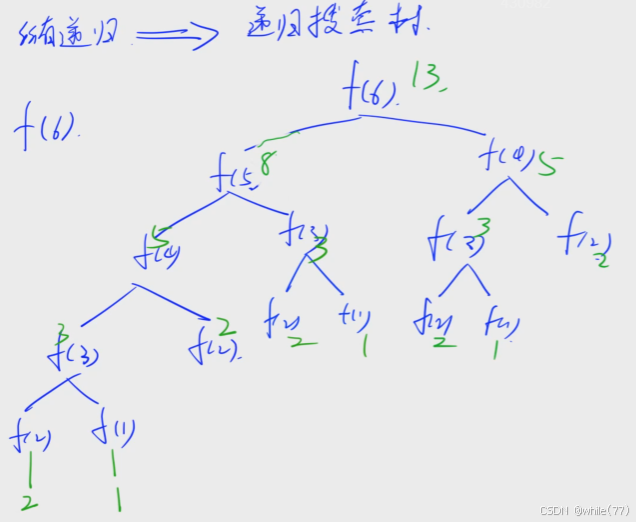
有n步,每一步都会分成两个分支,所以时间复杂度是O(2^n)
1.1 递归实现指数型枚举
这道题中,n是15,所以我们可以猜测时间复杂度是O(2^n)或O(n*2^n)
这道题我们可以采用DFS来做,对于DFS来说,搜索顺序非常重要。找到一个顺序,可以不重不漏地把每种方案找出。在这道题中,我们可以开一个数组,数组的1-n位,依次考虑每个数选或不选
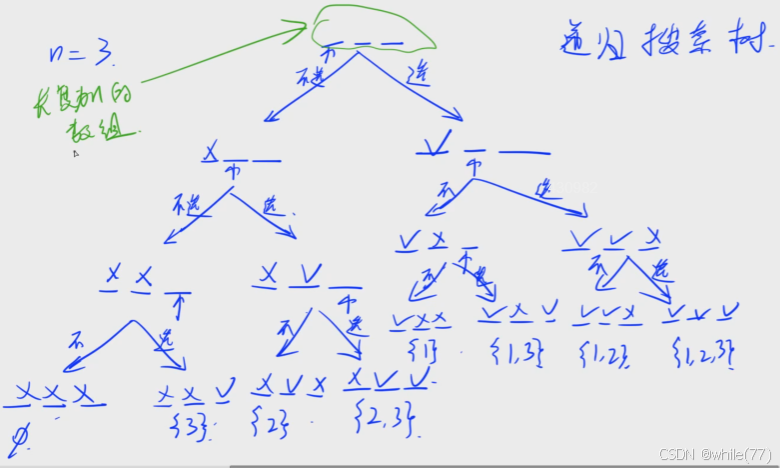
对于位置1, 2, 3, ..., n,都有选和不选两种情况,所以是2^n。并且还要将每种方案输出,所以,时间复杂度是O(n*2^n)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
int n, a[N];
void dfs(int u)
{
if(u > n)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
if(a[i] == 1)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
return ;
}
a[u] = 2;
dfs(u + 1);
a[u] = 1;
dfs(u + 1);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}1.2 递归实现排列型枚举
这道题也是采用DFS做。
顺序1:依次枚举每个数放到那个位置
顺序2:依次枚举每个位置放那个数
我们采用的是顺序2来做
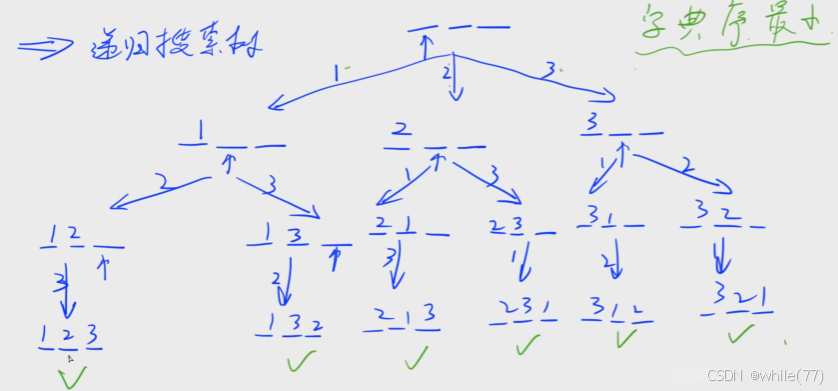
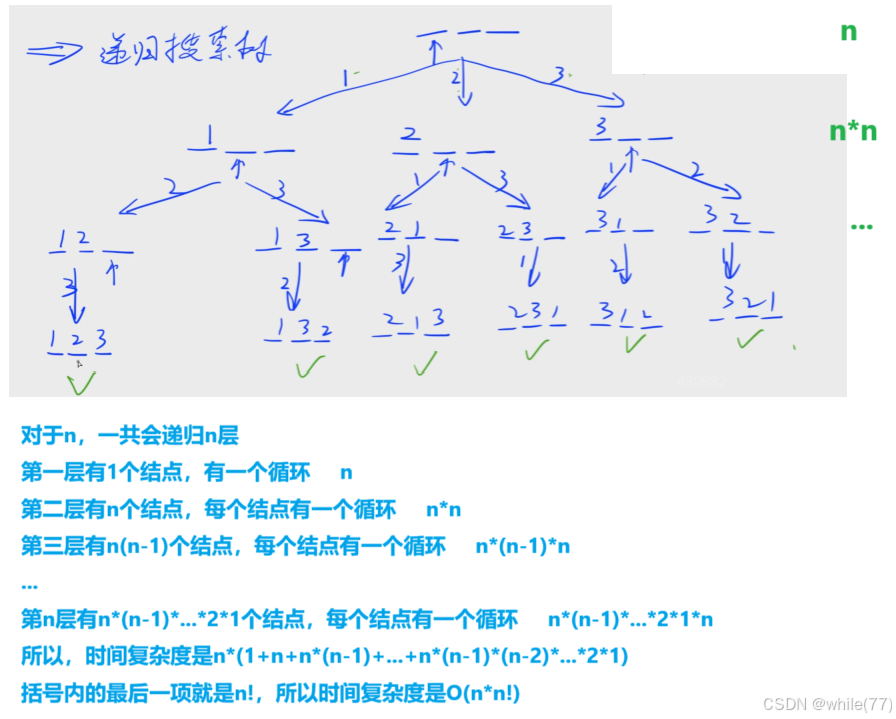
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int n, a[N];
bool st[N];
void dfs(int u)
{
if(u > n)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return ;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
if(!st[i])
{
st[i] = true;
a[u] = i;
dfs(u + 1);
st[i] = false;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}1.3 递归实现组合型枚举
排列是考虑顺序的,1 2 3和1 3 2是不一样的
组合是不考虑顺序的,1 2 3和1 3 2是一样的
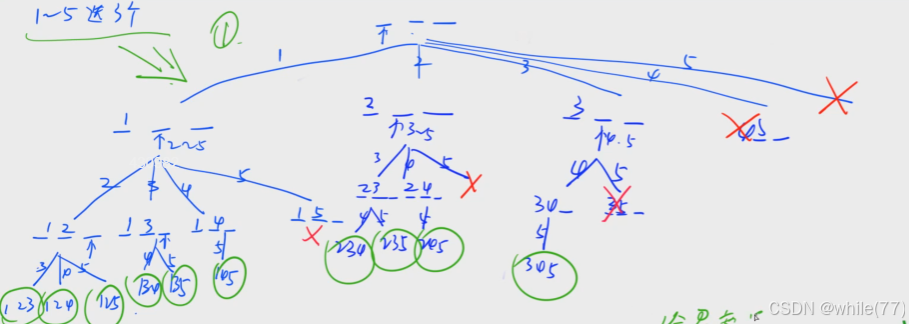
所以,在递归实现组合型枚举时,需要规定一个顺序,这样在枚举时就可以保证不重复了,这里以升序为例。也就是说,对于1 2 3,1 3 2,2 1 3,2 3 1,3 1 2,3 2 1我们只枚举1 2 3即可
顺序:从前往后,依次枚举每个位置是几
为了有序,我们只需要时刻保持相邻两个位置的数有序即可
排列类型枚举需要一个bool类型的判重数组,而组合类型枚举不需要,因为只需要保证顺序即可
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30;
int n, m;
int way[N];
void dfs(int u, int start) // u表示现在要填序列的第几位,start表示这一位可以从那个数开始填
{
if (u == m + 1)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) cout << way[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= n; i ++ )
{
way[u] = i;
dfs(u + 1, i + 1);
way[u] = 0; // 恢复现场
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
dfs(1, 1);
return 0;
}这样子仍然是不完美的,我们会发现,有些情况是需要剪枝的。若从start到n都选,仍然不够m个数,就没必要再向后进行了。即u-1+n-start+1<m
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30;
int n, m;
int way[N];
void dfs(int u, int start) // u表示现在要填序列的第几位,start表示这一位可以从那个数开始填
{
if (u + n - start < m) return; // 剪枝
if (u == m + 1)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) cout << way[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= n; i ++ )
{
way[u] = i;
dfs(u + 1, i + 1);
way[u] = 0; // 恢复现场
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
dfs(1, 1);
return 0;
}1.4 带分数
方法一
我们可以使用排列型枚举的方式,枚举出1-9的所有排列,再从中选出3个数,试试能不能完成
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int n, ans, a[N];
bool st[N];
int to_digit(int l, int r)
{
int res = 0;
for(int i = l;i <= r;i ++)
res = res * 10 + a[i];
return res;
}
void dfs(int u)
{
if(u == 10)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= 6;i ++)
{
int a = to_digit(1, i);
if(a >= n) return ;
for(int j = i + 1;j <= 8;j ++)
{
int b = to_digit(i + 1, j);
int c = to_digit(j + 1, 9);
if(b % c == 0) // 必须要整除
{
int m = a + b / c;
if(m == n) ans ++;
}
}
}
return ;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= 9;i ++)
if(!st[i])
{
st[i] = true;
a[u] = i;
dfs(u + 1);
st[i] = false;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
dfs(1);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
// 123|456|789
// [1, i], [i + 1, j], [j + 1, 9]方法二
在上面的方法中,我们是没用利用到n的
对于n = a + b / c,也就是c * n = c * a - b,我们可以只枚举出a和c,然后利用这个公式算出b。此时b是算出来的,而不是枚举出来的。在方法一中,如果a和c已经确定,b有3位数,需要枚举6次,而现在只需要1次
在代码实现中,我们是在a每一个叶子的地方去枚举c,在c每一个叶子的地方去计算b,然后判断是否成立。
判断b是否合法:
(1) 看b中是否有与a,c相同的数字,若某一位为0或已经出现过,返回false
(2) 看a,b,c的数字是否1-9都出现1次
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int n;
bool st[N], backup[N];
int ans;
bool check(int a, int c)
{
long long b = n * (long long)c - a * c;
if (!a || !b || !c) return false; // a,b,c都不能为0
memcpy(backup, st, sizeof st);
while (b)
{
int x = b % 10; // 取个位
b /= 10; // 个位删掉
if (!x || backup[x]) return false;
backup[x] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++ )
if (!backup[i])
return false;
return true;
}
void dfs_c(int a, int c)
{
if (check(a, c)) ans ++ ;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++ )
if (!st[i])
{
st[i] = true;
dfs_c(a, c * 10 + i);
st[i] = false;
}
}
void dfs_a(int a)
{
if (a >= n) return;
if (a) dfs_c(a, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++ ) // 枚举当前这一位可以用那些数字
if (!st[i])
{
st[i] = true;
dfs_a(a * 10 + i);
st[i] = false;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs_a(0);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}2、递推
递归是把一个问题分成同类子问题
递推是先计算出子问题,再推出原问题
我们使用递推的方式计算出斐波那契额数列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100;
int dp[N];
int fib(int n)
{
dp[1] = 0, dp[2] = 1;
for(int i = 3;i <= n;i ++) dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
return dp[i];
}当然,也可以使用滚动数组的方式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
if(n == 1) return 0;
if(n == 2) return 1;
int a = 0, b = 1;
for(int i = 3;i <= n;i ++)
{
int c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}2.1 简单斐波那契
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50;
int n, dp[N];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
dp[0] = 0, dp[1] = 1, dp[2] = 1;
for(int i = 3;i < n;i ++) dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++) cout << dp[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}2.2 费解的开关
在开关问题中,会有两条性质;
(1) 对于一种按的方式,顺序无所谓
(2) 求最优解时,每个位置最多按一次
在这道题中,我们会发现,当第一行的按法确定之后,后面4行的按法是确定的。因为这道题中按一个开关还会影响这个开关上下左右的一个开关,当第一行的按法确定之后,暗的位置只能通过第二行相应位置改变,后面的行也是以此类推。所以,我们只需要枚举第一行的所有情况,然后后面根据第一行的按法来按,然后看最后一行是否全亮即可,若全亮,证明这种按法是可行的
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n;
char g[5][5], backup[5][5];
int dx[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, 0}, dy[5] = {0, 0, 0, -1, 1};
void turn(int x, int y)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i ++ )
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= 5 || b < 0 || b >= 5) continue; // 在边界外,直接忽略即可
backup[a][b] ^= 1;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
while(n --)
{
int ans = 7;
for(int i = 0;i <5;i ++)
for(int j = 0;j < 5;j ++) cin >> g[i][j];
for(int op = 0;op < 32;op ++)
{
int step = 0;
memcpy(backup, g, sizeof g);
// op的二进制位是1就反转
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i ++)
if(op >> i & 1)
{
turn(0, i);
step ++;
}
// 第一行翻转完成,翻转剩下的4行
// 是否翻转根据前一行同一位置判断
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++)
for(int j = 0;j < 5;j ++)
if(backup[i][j] == '0')
{
turn(i + 1, j);
step ++;
}
// 判断一下最后一行,若最后一行全亮,则这个第一行的翻转方案可行
bool flag = false;
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i ++)
if(backup[4][i] == '0')
{
flag = true;
break;
}
if(!flag) ans = min(ans, step);
}
if(ans > 6) cout << -1 << '\n';
else cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}2.3 翻硬币
这道题属于一种提醒:给定一个初始状态和一个目标状态,再给一些操作,问从初始状态最少需要几步操作能到目标状态。常常采用bfs来做,但bfs的时间复杂度较高,在这道题中并不合适
因为这道题每次都需要按两个,所以我们可以抽象成一个开关控制两个的形式
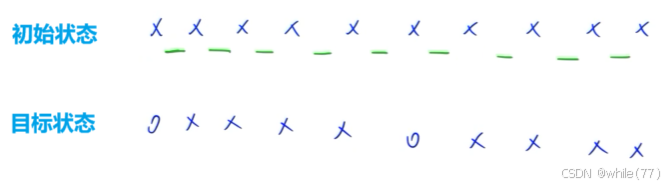
其中绿色的就代表开关。我们从第1个字符开始比较,一直到第n-1个字符,因为题目说了一定有解,所以最后一个不需要比较。当我们当前比较的字符不同时,就按一下能控制这个字符的开关(注意:这里每个开关也只能操作一次)
此时第一个字符不同,所以我们需要按一下第一个开关(这里只有第一个开关能操作第一个字符,所以我们只要从前向后枚举,不会出现我们当前正在比较的字符会被两个开关操作的情形)

重复这个步骤,直到第n - 1个

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string s1, s2;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> s1 >> s2;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < s1.size() - 1;i ++)
{
if(s1[i] != s2[i])
{
ans ++;
s1[i] = s2[i];
if(s1[i + 1] == '*') s1[i + 1] = 'o';
else s1[i + 1] = '*';
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}2.4 飞行员兄弟
这道题看起来是和费解的开关十分类似的,但是不能使用费解的开关中的方法,因为这道题操作一个把手后,不像费解的开关中一样只会影响上下左右相邻的4个开关,而是会影响同行同列的所有开关。同时我们发现,这道题的数据量较小,所以我们可以直接进行暴力枚举每一个位置变或不变。实现方法有两种
方法一
dfs
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 5;
int ans = 20, m;
vector<PII> v; // 存放答案操作了那些位置
void turn(int x, int y, vector<vector<char>>& g)
{
if (g[x][y] == '+') g[x][y] = '-';
else g[x][y] = '+';
// 改变第x行
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if (i == y) continue;
if (g[x][i] == '+') g[x][i] = '-';
else g[x][i] = '+';
}
// 改变第y行
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if (i == x) continue;
if (g[i][y] == '+') g[i][y] = '-';
else g[i][y] = '+';
}
}
void dfs(int x, int y, vector<PII>& res, int step, vector<vector<char>>& g)
{
if (step > ans) return;
if (y == 4)
{
x += 1;
if (x == 4)
{
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
if (g[i][j] == '+')
{
flag = true;
break;
}
if (!flag && step < ans)
{
ans = step;
v = res;
}
return;
}
else y = 0;
}
// 改变
res.push_back({ x, y });
turn(x, y, g);
dfs(x, y + 1, res, step + 1, g);
turn(x, y, g);
res.pop_back();
// 不改变
dfs(x, y + 1, res, step, g);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
vector<vector<char>> g(4, vector<char>(4)); // 记录起始状态
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) cin >> g[i][j];
vector<PII> res; // 记录从起始状态到当前状态操作了那些位置
dfs(0, 0, res, 0, g);
cout << ans << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i].first + 1 << " " << v[i].second + 1 << '\n';
}
return 0;
}方法二
也可以使用递推的做法
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 5;
char g[N][N], backup[N][N];
int get(int x, int y)
{
return x * 4 + y;
}
void turn_one(int x, int y)
{
if (g[x][y] == '+') g[x][y] = '-';
else g[x][y] = '+';
}
void turn_all(int x, int y)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
{
turn_one(x, i);
turn_one(i, y);
}
turn_one(x, y);
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) cin >> g[i];
vector<PII> res;
for (int op = 0; op < 1 << 16; op ++ )
{
vector<PII> temp;
memcpy(backup, g, sizeof g); // 备份
// 进行操作
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j ++ )
if (op >> get(i, j) & 1)
{
temp.push_back({i, j});
turn_all(i, j);
}
// 判断所有灯泡是否全亮
bool has_closed = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j ++ )
if (g[i][j] == '+')
has_closed = true;
if (has_closed == false)
{
if (res.empty() || res.size() > temp.size()) res = temp;
}
memcpy(g, backup, sizeof g); // 还原
}
cout << res.size() << endl;
for (auto op : res) cout << op.x + 1 << ' ' << op.y + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}