题目:79. 单词搜索
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中"相邻"单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
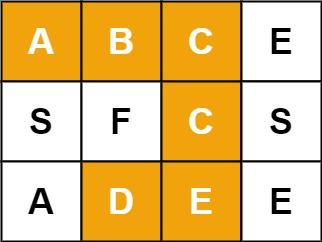
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
输出:true示例 2:
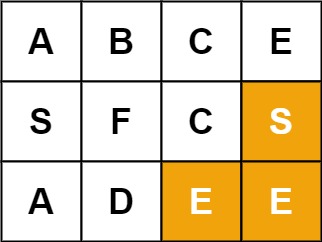
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
输出:true示例 3:
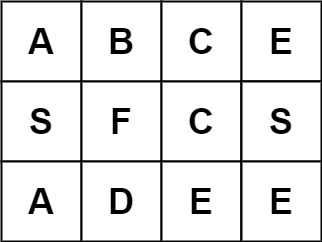
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
输出:false提示:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15board和word仅由大小写英文字母组成
一、模式识别
1.棋盘格:回溯法
棋盘格问题,回溯法典型应用,用回溯算法
层间:word内顺序访问
层内:board遍历或上一个字母上下左右
无需找到所有结果,找到第一个结果后返回
2.搜索方式
1.word首字母在board中二维遍历
2.word内(层间)顺序访问,剩余字母分别搜索上一个字母的上下左右
3.访问过的字母不可以重复访问
二.代码实现
1.基础实现
python
class Solution:
def get_candidate(self, board, visited, i, j):
candidate = []
if i - 1 >= 0 and not visited[i - 1][j]:
candidate.append((board[i - 1][j], i - 1, j))
if j - 1 >= 0 and not visited[i][j - 1]:
candidate.append((board[i][j - 1], i, j - 1))
if i + 1 < len(board) and not visited[i + 1][j]:
candidate.append((board[i + 1][j], i + 1, j))
if j + 1 < len(board[0]) and not visited[i][j + 1]:
candidate.append((board[i][j + 1], i, j + 1))
return candidate
def backtracking(self, board, word, visited, start_idx, i, j):
if start_idx == len(word):
return True
if start_idx == 0:
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[i])):
if board[i][j] == word[0]:
visited[i][j] = True
if self.backtracking(board, word, visited, 1, i, j):
return True
visited[i][j] = False
else:
for ch, a, b in self.get_candidate(board, visited, i, j):
if ch == word[start_idx]:
visited[a][b] = True
if self.backtracking(board, word, visited, start_idx + 1, a, b):
return True
visited[a][b] = False
return False
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
visited = [[False] * len(board[0]) for _ in range(len(board))]
return self.backtracking(board, word, visited, 0, -1, -1)start_idx记录访问顺序
visited用于标记访问过的字母
首字母二维遍历board
剩余字母层间顺序访问,层内访问上一个字母在board中的上下左右
耗时:2000ms-4000ms
2.启发式搜索
python
class Solution:
def get_candidate(self, board, i, j):
candidate = []
if i - 1 >= 0 and board[i - 1][j]:
candidate.append((board[i - 1][j], i - 1, j))
if j - 1 >= 0 and board[i][j - 1]:
candidate.append((board[i][j - 1], i, j - 1))
if i + 1 < len(board) and board[i + 1][j]:
candidate.append((board[i + 1][j], i + 1, j))
if j + 1 < len(board[0]) and board[i][j + 1]:
candidate.append((board[i][j + 1], i, j + 1))
return candidate
def backtracking(self, board, word, start_idx, i, j):
if start_idx == len(word):
return True
if start_idx == 0:
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[i])):
if board[i][j] == word[0]:
board[i][j] = False
if self.backtracking(board, word, 1, i, j):
return True
board[i][j] = word[0]
else:
for ch, a, b in self.get_candidate(board, i, j):
if ch == word[start_idx]:
board[a][b] = False
if self.backtracking(board, word, start_idx + 1, a, b):
return True
board[a][b] = word[start_idx]
return False
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
# visited = [[False] * len(board[0]) for _ in range(len(board))]
cnt=Counter(c for row in board for c in row)
if not cnt>=Counter(word):
return False
if cnt[word[-1]]<cnt[word[0]]:
word=word[::-1]
return self.backtracking(board, word, 0, -1, -1)在提交排行榜中看到的启发式搜索
思路:主要搜索开销都在第一步的board的遍历,于是从第一步开刀
实现逻辑:如果尾端字母在board出现频率低于首端则word反序
计算开销直接降到0ms-3ms