本系列为加州伯克利大学著名 Python 基础课程 CS61A 的课堂笔记整理,全英文内容,文末附词汇解释。
目录
[01 Natural Language Syntax](#01 Natural Language Syntax)
[02 Representing Syntax](#02 Representing Syntax)
[03 Reading Data](#03 Reading Data)
[04 Tree Representation](#04 Tree Representation)
[Ⅰ A tree Represented as a List of Tokens](#Ⅰ A tree Represented as a List of Tokens)
[Ⅱ Finding Branches](#Ⅱ Finding Branches)
[05 Manipulating Language](#05 Manipulating Language)
01 Natural Language Syntax
Programming languages and natural languages both have compositional syntax.
Utterances from the Suppes subject in the "Child Language Data Exchange System (CHILDES)" project.
02 Representing Syntax
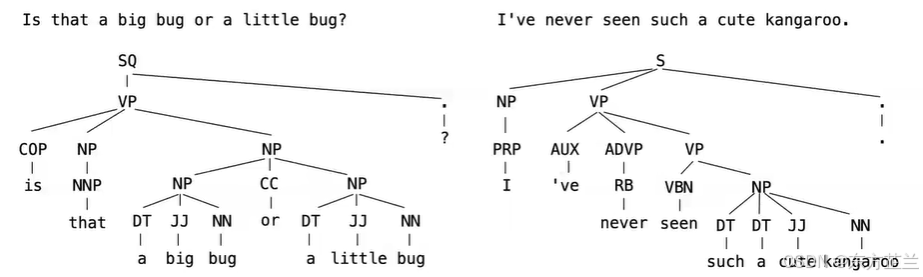
The tree data abstraction can represent the structure of a sentence.
python
# Tree data abstraction
def tree(label, branches = []):
for branch in branches:
assert is_tree(branch), 'branches must be trees'
return [label] + list(branches) # why list
def label(tree):
return tree[0]
def branches(tree):
return tree[1:]
def is_tree(tree):
if type(tree) != list or len(tree) < 1:
return False
for branch in branches(tree):
if not is_tree(branch):
return False
return True
def is_leaf(tree):
return not branches(tree)
def leaves(tree):
if is_leaf(tree):
return [label(tree)]
else:
return sum([leaves(b) for b in branches(tree)], [])
# Syntax
example = tree('ROOT',
[tree('FLAG',
[tree('NP',
[tree('DT', [tree('a')]),
tree('JJ', [tree('little')]),
tree('NN', [tree('bug')])]),
tree('.', [tree('.')])])])
from string import punctuation
contractions = ["n't", "'s", "'re", "'ve"]
def words(t):
"""Return the words of a tree as a string.
>>> words(example)
'a little bug'
"""
s = ''
for w in leaves(t):
no_space = (w in punctuation and w != '$') or w in contractions
if not s or no_space:
s = s + w
else:
s = s + ' ' + w
return s
def replace(t, s, w):
"""Return a tree like T with all nodes labeled S replaced by word W.
>>> words(replace(example, 'JJ', 'huge'))
'a huge bug.'
"""
if label(t) == s:
return tree(s, [tree(w)])
else:
return tree(label(t), [replace(b, s, w) for b in branches(t)])
python
>>> example
['ROOT', ['FLAG', ['NP', ['DT', ['a']], ['JJ', ['little']], ['NN', ['bug']]], ['.', ['.']]]]
>>> leaves(example)
['a', 'little', 'bug', '.']
>>> 'a little bug.'
'a little bug'
>>> words(example)
'a little bug'
>>> punctuation
'!"#$%&\'()*+,-/:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
>>> ['they', 'are', 'coming', 'over']
['they', 'are', 'coming', 'over']
>>> "they'are coming over"
"they'are coming over"
>>> replace(example, 'JJ', 'huge')
['ROOT', ['FLAG', ['NP', ['DT', ['a']], ['JJ', ['huge']], ['NN', ['bug']]], ['.', ['.']]]]
>>> words(replace(example, 'JJ', 'huge'))
'a huge bug.'03 Reading Data
Files, Strings, and Lists:
Some files are plain text and can be read into Python as either:
One string containing the whole contents of the file: open('/some/file.txt').read()
A list of strings, each containing one line: open('/some/file.txt').readlines()
Useful string methods for processing the contents of a file:
strip() returns a string without whitespace (spaces, tabs, etc.) on the ends
python
>>> ' hello '.strip()
'hello'split() returns a list of strings that were separated by whitespace
python
>>> 'hi there'.split()
['hi', 'there']replace(a, b) returns a string with all instances of string a replaced by string b
python
>>> '2+2'.replace('+', ' + ')
'2 + 2'
python
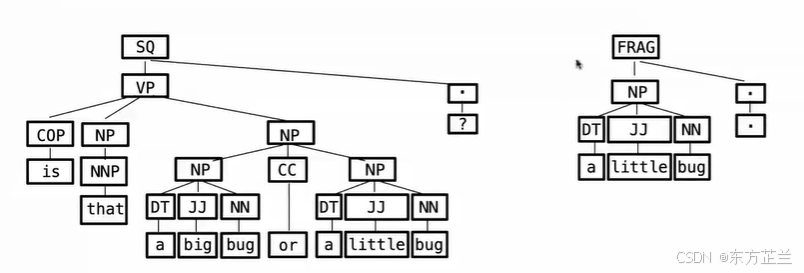
# Reading trees
examples = """
(ROOT (SQ (VP (COP is)
(NP (NN that))
(NP (NP (DT a) (JJ big) (NN bug))
(CC or)
(NP (NP (DT a) (JJ big) (NN bug))))
(. ?)))
(ROOT (FLAG (NP (DT a) (JJ little) (NN bug)) (. .)))
""".split('\n')
def read_trees(lines):
"""Return trees as lists of tokens from a list of lines.
>>> for s in read_trees(examples):
... print(' '.join(s[:20]), '...')
( ROOT ( SQ ( VP ( COP is ) ( NP ( NN that ) ) ( NP ( ...
( ROOT ( FLAG ( NP ( DT a ) ( JJ little ) ( NN bug ) ) ( ...
"""
trees = [] #其实是list嵌套list
tokens = []
for line in lines:
if line.strip():
tokens.expend(line.replace('(', ' ( ').replace(')', ' ) ').split())
if tokens.count(' ( ') == tokens.count(' ) '):
trees.append(tokens)
tokens = []
return trees
def all_trees(path = 'CHILDESTreebank-curr/suppes.parsed'):
return read_trees(open(path).readlines())
python
# 和上文中words()函数的功能一样,将list转化为string
>>> s = ['a', 'little', 'bug']
>>> ' '.join(s)
'a little bug'
>>> '+'.join(s)
'a+little+bug'
>>> len(examples)
11
>>> examples[1]
'(ROOT (SQ (VP (COP is)'
>>> s = examples[1].replace('(', ' ( ')
>>> s
' ( ROOT ( SQ ( VP ( COP is)'
>>> s.split()
['(', 'ROOT', '(', 'SQ', '(', 'VP', '(', 'COP', 'IS)']
>>> ts = read_trees(examples)
>>> len(ts)
2
python
>>> ts[0].count('(')
17
>>> ts[0].count(')')
17
>>> data = all_trees
>>> len(data)
35906

04 Tree Representation
Ⅰ A tree Represented as a List of Tokens
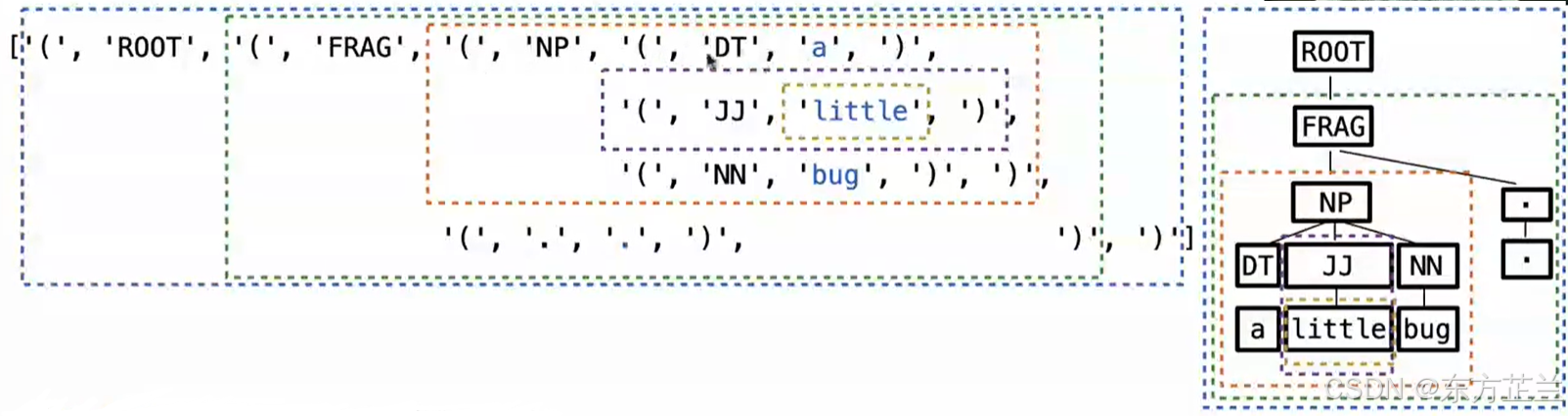
python
# Tree plus
def tree(label, branches = []):
if not branches:
return [label]
else:
#致力于把[]变成()并成为list的元素
return ['(', label] + sum(branches, []) + [')']
def label(tree):
if len(tree) == 1:
return tree[0]
else:
assert tree[0] == '(', tree
return tree[1]
#图示详见第Ⅱ部分
def branches(tree):
if len(tree) == 1:
return []
assert tree[0] == '(' #检查点1
opened = 1 #统计'('的个数
current_branch = []
all_branches = []
for token in t[2:]:
current_branch.append(token)
if token == '(':
opened += 1
elif token == ')':
opened -= 1
if opened == 1:
all_branches.append(current_branch)
current_branch = []
assert opened == 0 #检查点2
return all_branches
#调用了升级版tree函数,因此example为带'(', ')'的list
example = tree('FLAG',
[tree('NP',
[tree('DT', [tree('a')]),
tree('JJ', [tree('little')]),
tree('NN', [tree('bug')])]),
tree('.', [tree('.')])])Ⅱ Finding Branches
python
['(', 'NP', '(', 'DT', 'a', ')', '(', 'JJ', 'little', ')', '(', 'NN', 'bug', ')', ')']





python
~/lec $ python3 -i ex.py
python
>>> example
['(', 'FLAG', '(', 'NP', '(', 'DT', 'a', ')', '(', 'JJ', 'little', ')', '(', 'NN', 'bug', ')', ')', '(', '.', '.', ')', ')']
>>> leaves(example)
['a', 'little', 'bug', '.']
>>> words(example)
'a little bug.'
>>> replace(example, 'JJ', 'huge')
['(', 'FLAG', '(', 'NP', '(', 'DT', 'a', ')', '(', 'JJ', 'huge', ')', '(', 'NN', 'bug', ')', ')', '(', '.', '.', ')', ')']
>>> words(replace(example, 'JJ', 'huge'))
'a huge bug.'
python
>>> ts = all_trees()
>>> ts[123]
['(', 'ROOT', '(', 'FLAG', '(', 'NP', '(', 'DT', 'a', ')', '(', 'NN', 'rabbit', ')', '(', '.', '.', ')', ')', ')', ')']
>>> labels(ts[123])
'ROOT'
>>> words(ts[123])
'a rabbit.'05 Manipulating Language
python
def all_trees(path = 'CHILDESTreebank-curr/suppes.parsed'):
return read_trees(open(path).readlines())
def replace_all(s, w):
for t in all_trees():
r = replace(t, s, w)
if r != t: #我们确实改变了些什么
print(words(t))
print(words(r))
input() #直到用户输入返回键才停止执行该函数
python
>>> replace_all('NNS', 'bears')
python
>>> replace_all('NP', 'Oski')
附:词汇解释
utterance / ˈʌtərəns / 话语,表达、punctuation / ˌpʌŋktʃuˈeɪʃ(ə)n / 标点符号、contraction / kənˈtrækʃn / 缩写、plain / pleɪn / 纯粹的、whitespace 空格、strip / strɪp / 除去、split / splɪt / 分裂、tab 跳格、with instance of 以...为例、parse / pɑːrs /(计算机)句法分析、token (计算机)令牌,记号、manipulate / məˈnɪpjuleɪt / 操作