目录
[1. 创建链表](#1. 创建链表)
[2. 插入节点](#2. 插入节点)
[3. 删除节点](#3. 删除节点)
[4. 遍历链表](#4. 遍历链表)
[1. 反转链表(迭代法)](#1. 反转链表(迭代法))
[2. 检测环(快慢指针法)](#2. 检测环(快慢指针法))
一、为什么需要链表?
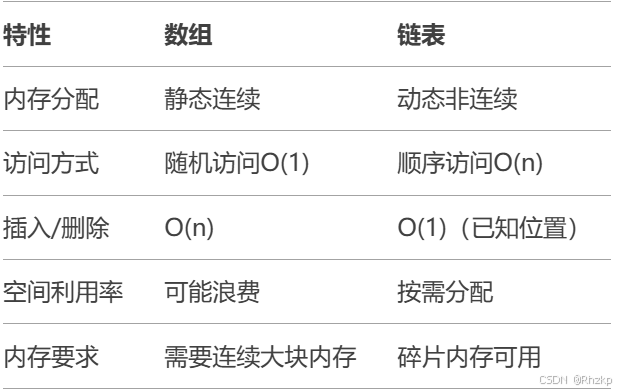
在C语言程序设计中,数组是最基础的数据结构,但它存在明显的局限性:
-
固定长度,无法动态扩展
-
插入/删除元素需要大量数据移动
-
内存空间要求连续
链表(Linked List)通过动态内存分配 和指针连接完美解决了这些问题。每个元素(节点)包含:
-
数据域 - 存储实际数据
-
指针域 - 存储下一个节点的地址
二、链表与数组的对比
三、链表节点定义
typedef struct Node {
int data; // 数据域
struct Node *next; // 指针域
} Node;四、链表基本操作
1. 创建链表
Node* createList(int data) {
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (head == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败!");
exit(1);
}
head->data = data;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}2. 插入节点
头插法(时间复杂度O(1))
void insertAtHead(Node** head, int data) {
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}尾插法(时间复杂度O(n))
void insertAtTail(Node* head, int data) {
Node* current = head;
while (current->next != NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
current->next = newNode;
}3. 删除节点
void deleteNode(Node** head, int key) {
Node *temp = *head, *prev;
// 删除头节点
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
*head = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
// 查找待删除节点
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp == NULL) return;
// 解除链接并释放内存
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}4. 遍历链表
void printList(Node* head) {
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}五、进阶操作
1. 反转链表(迭代法)
void reverseList(Node** head) {
Node *prev = NULL;
Node *current = *head;
Node *next = NULL;
while (current != NULL) {
next = current->next; // 保存下一个节点
current->next = prev; // 反转指针
prev = current; // 前移prev
current = next; // 前移current
}
*head = prev;
}2. 检测环(快慢指针法)
int hasCycle(Node *head) {
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
return 1; // 存在环
}
}
return 0; // 无环
}六、内存管理要点
必须检查malloc返回值
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (newNode == NULL) {
// 处理内存分配失败
}及时释放内存
void freeList(Node* head) {
Node* temp;
while (head != NULL) {
temp = head;
head = head->next;
free(temp);
}
}避免野指针
free(temp);
temp = NULL; // 释放后立即置空七、常见错误排查
-
段错误(Segmentation Fault)
-
访问已释放的内存
-
指针未初始化就使用
-
-
内存泄漏
-
使用valgrind工具检测
-
确保每个malloc都有对应的free
-
-
逻辑错误
-
忘记更新头指针
-
指针操作顺序错误
-
八、链表变体
双向链表
typedef struct DNode {
int data;
struct DNode *prev;
struct DNode *next;
} DNode;循环链表
// 尾节点指向头节点
head->next = head;带头节点的链表
-
统一操作逻辑
-
简化边界条件处理
九、应用场景
-
实现栈/队列
-
多项式运算
-
文件系统目录结构
-
图结构的邻接表
-
内存管理系统
十、完整示例代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
// [此处插入上述各个函数实现]
int main() {
Node* list = createList(5);
insertAtHead(&list, 2);
insertAtTail(list, 8);
printf("原始链表: ");
printList(list); // 输出: 2 -> 5 -> 8 -> NULL
reverseList(&list);
printf("反转后: ");
printList(list); // 输出: 8 -> 5 -> 2 -> NULL
deleteNode(&list, 5);
printf("删除后: ");
printList(list); // 输出: 8 -> 2 -> NULL
freeList(list);
return 0;
}总结
链表是C语言中最基础也最重要的数据结构之一,掌握链表需要理解:
-
指针的操作原理
-
动态内存管理机制
-
数据结构与算法的关系
建议通过以下方式巩固学习:
-
手写实现所有链表操作
-
使用调试工具观察内存变化
-
尝试实现双向链表等变体
-
解决LeetCode链表相关题目(如206反转链表、141环形链表)
掌握链表将为学习更复杂的数据结构(树、图等)打下坚实基础。