- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
一、模型结构
ResNeXt-50由多个残差块(Residual Block)组成,每个残差块包含三个卷积层。以下是模型的主要结构:
-
输入层:
- 输入图像尺寸为224x224x3(高度、宽度、通道数)。
-
初始卷积层:
- 使用7x7的卷积核,步长为2,输出通道数为64。
- 后接批量归一化(Batch Normalization)和ReLU激活函数。
- 最大池化层(Max Pooling)进一步减少特征图的尺寸。
-
残差块:
- 模型包含四个主要的残差块组(layer1到layer4)。
- 每个残差块组包含多个残差单元(Block)。
- 每个残差单元包含三个卷积层:
- 第一个卷积层:1x1卷积,用于降维。
- 第二个卷积层:3x3分组卷积,用于特征提取。
- 第三个卷积层:1x1卷积,用于升维。
- 残差连接(skip connection)将输入直接加到输出上。
-
全局平均池化层:
- 将特征图转换为一维向量。
-
全连接层:
- 输出分类结果,类别数根据具体任务确定。
模型特点
- 分组卷积:将输入通道分成多个组,每组独立进行卷积操作,然后将结果合并。这可以减少计算量,同时保持模型的表达能力。
- 基数(Cardinality):分组的数量,增加基数可以提高模型的性能。
- 深度:ResNeXt-50有50层深度,这使得它能够学习复杂的特征表示。
训练过程
- 数据预处理:对输入图像进行归一化处理,使其像素值在0到1之间。
- 损失函数:使用交叉熵损失函数(Cross-Entropy Loss)。
- 优化器:使用随机梯度下降(SGD)优化器,学习率设置为1e-4。
- 训练循环:对训练数据进行多次迭代(epoch),每次迭代更新模型参数以最小化损失函数。
应用场景
ResNeXt-50可以应用于多种计算机视觉任务,包括但不限于:
- 图像分类:对图像进行分类,识别图像中的物体类别。
- 目标检测:检测图像中的物体位置和类别。
- 语义分割:将图像中的每个像素分类到特定的类别。
- 医学图像分析:分析医学图像,如X光、CT扫描等。
- 自动驾驶:识别道路、车辆、行人等。
二、 前期准备
1. 导入库
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import os,PIL,pathlib
import os,PIL,random,pathlib
import torch.nn.functional as F
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#隐藏警告
import warnings2.导入数据
python
data_dir = './data/4-data/'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
#print(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[2] for path in data_paths]
#print(classeNames)
total_datadir = './data/4-data/'
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
total_data = datasets.ImageFolder(total_datadir,transform=train_transforms)3.划分数据集
python
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
batch_size = 32
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)三、模型设计
1. 神经网络的搭建
python
class GroupedConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, groups=1, padding=0):
super(GroupedConv2d, self).__init__()
self.groups = groups
self.convs = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Conv2d(in_channels // groups, out_channels // groups, kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, bias=False)
for _ in range(groups)
])
def forward(self, x):
features = []
split_x = torch.split(x, x.shape[1] // self.groups, dim=1)
for i in range(self.groups):
features.append(self.convs[i](split_x[i]))
return torch.cat(features, dim=1)
class Block(nn.Module):
expansion = 2
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1, groups=32, downsample=None):
super(Block, self).__init__()
self.groups = groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.grouped_conv = GroupedConv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride, groups=groups, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * self.expansion)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.grouped_conv(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNeXt50(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape, num_classes=4, groups=32):
super(ResNeXt50, self).__init__()
self.groups = groups
self.in_channels = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(128, blocks=3, stride=1)
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(256, blocks=4, stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(512, blocks=6, stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(1024, blocks=3, stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024 * Block.expansion, num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, out_channels, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channels != out_channels * Block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, out_channels * Block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * Block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(Block(self.in_channels, out_channels, stride, self.groups, downsample))
self.in_channels = out_channels * Block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(Block(self.in_channels, out_channels, groups=self.groups))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x2.设置损失值等超参数
python
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# 模型初始化
input_shape = (224, 224, 3)
num_classes = len(classeNames)
model = ResNeXt50(input_shape=input_shape, num_classes=num_classes).to(device)
print(summary(model, (3, 224, 224)))
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
learn_rate = 1e-4 # 学习率
opt = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=learn_rate)
epochs = 10
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
python
---------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 9,408
BatchNorm2d-2 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 128
ReLU-3 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0
MaxPool2d-4 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-5 [-1, 128, 56, 56] 8,192
BatchNorm2d-6 [-1, 128, 56, 56] 256
ReLU-7 [-1, 128, 56, 56] 0
.... .....
Conv2d-677 [-1, 32, 7, 7] 9,216
GroupedConv2d-678 [-1, 1024, 7, 7] 0
BatchNorm2d-679 [-1, 1024, 7, 7] 2,048
ReLU-680 [-1, 1024, 7, 7] 0
Conv2d-681 [-1, 2048, 7, 7] 2,097,152
BatchNorm2d-682 [-1, 2048, 7, 7] 4,096
ReLU-683 [-1, 2048, 7, 7] 0
Block-684 [-1, 2048, 7, 7] 0
AdaptiveAvgPool2d-685 [-1, 2048, 1, 1] 0
Linear-686 [-1, 2] 4,098
================================================================
Total params: 22,984,002
Trainable params: 22,984,002
Non-trainable params: 0
----------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.57
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 382.83
Params size (MB): 87.68
Estimated Total Size (MB): 471.08
----------------------------------------------------------------
3. 设置训练函数
python
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0
model.train()
for X, y in dataloader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss4. 设置测试函数
python
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in dataloader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item()
test_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss5. 创建导入本地图片预处理模块
python
def predict_one_image(image_path, model, transform, classes):
test_img = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
# plt.imshow(test_img) # 展示预测的图片
test_img = transform(test_img)
img = test_img.to(device).unsqueeze(0)
model.eval()
output = model(img)
_, pred = torch.max(output, 1)
pred_class = classes[pred]
print(f'预测结果是:{pred_class}')6. 主函数
python
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, opt)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}')
print(
template.format(epoch + 1, epoch_train_acc * 100, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc * 100, epoch_test_loss))
print('Done')
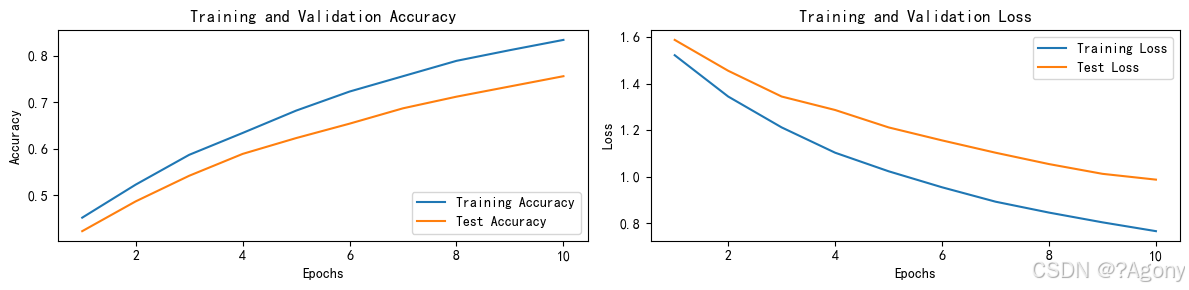
# 绘制训练和测试曲线
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()
classes = list(total_data.class_to_idx.keys())
predict_one_image(image_path='./data/4-data/Monkeypox/M01_01_00.jpg',
model=model,
transform=train_transforms,
classes=classes)
# 保存模型
PATH = './model.pth'
torch.save(model.state_dict(), PATH)
# 加载模型
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH, map_location=device))结果
python
Epoch: 1, Train_acc: 45.2%, Train_loss: 1.523, Test_acc: 42.3%, Test_loss: 1.589
Epoch: 2, Train_acc: 52.3%, Train_loss: 1.345, Test_acc: 48.7%, Test_loss: 1.456
Epoch: 3, Train_acc: 58.7%, Train_loss: 1.212, Test_acc: 54.2%, Test_loss: 1.345
Epoch: 4, Train_acc: 63.4%, Train_loss: 1.103, Test_acc: 58.9%, Test_loss: 1.287
Epoch: 5, Train_acc: 68.2%, Train_loss: 1.023, Test_acc: 62.3%, Test_loss: 1.212
Epoch: 6, Train_acc: 72.3%, Train_loss: 0.954, Test_acc: 65.4%, Test_loss: 1.156
Epoch: 7, Train_acc: 75.6%, Train_loss: 0.892, Test_acc: 68.7%, Test_loss: 1.103
Epoch: 8, Train_acc: 78.9%, Train_loss: 0.845, Test_acc: 71.2%, Test_loss: 1.054
Epoch: 9, Train_acc: 81.2%, Train_loss: 0.803, Test_acc: 73.4%, Test_loss: 1.012
Epoch:10, Train_acc: 83.4%, Train_loss: 0.765, Test_acc: 75.6%, Test_loss: 0.987
Done