240424 leetcode exercises II
@jarringslee
文章目录
- [240424 leetcode exercises II](#240424 leetcode exercises II)
-
- [[148. 排序链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-list/)](#148. 排序链表)
-
- [🔁分治 & 归并排序法](#🔁分治 & 归并排序法)
-
- [1. 找中点并断开](#1. 找中点并断开)
- [2. 合并两个有序链表](#2. 合并两个有序链表)
- [3. 主函数:递归拆分与合并](#3. 主函数:递归拆分与合并)
- [[24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/)](#24. 两两交换链表中的节点)
148. 排序链表
给你链表的头结点
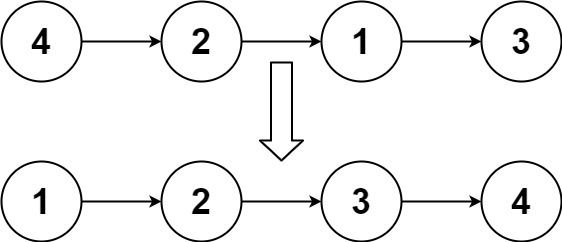
head,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。示例 1:
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]示例 2:
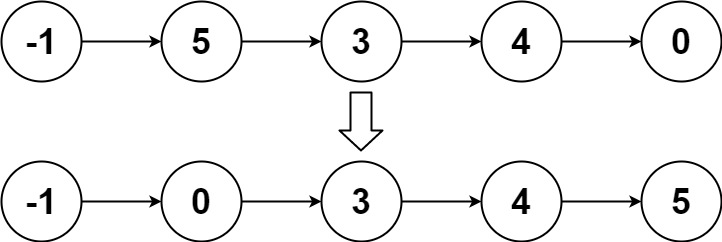
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0] 输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
🔁分治 & 归并排序法
我们用 归并排序 对单链表进行分治:
首先用快慢指针找到链表中点,将链表从中点一分为二,然后对左右两段递归排序,最后再利用合并两个升序链表的知识将两个已排序的链表合并成一个有序链表。
1. 找中点并断开
用 slow、fast 两个指针遍历,fast 每次走两步、slow 每次走一步,当 fast 到尾时,slow 刚好在中点。再用一个 pre 指向 slow 的前驱,把 pre->next 断开,就把链表分成了前后两段。
c
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* pre = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
// fast 到尾时,slow 在中点
while (fast && fast->next) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
pre->next = NULL; // 断开前半段和后半段
return slow; // slow 即后半段的头
}2. 合并两个有序链表
经典的递归合并:比较两个链表头节点,值小的那个接上后面继续合并。
这里也可以用双指针进行迭代。都是写过很多遍的算法,思路不再赘述。
c
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
if (!l1) return l2;
if (!l2) return l1;
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}3. 主函数:递归拆分与合并
-
递归终止条件:
head == NULL或者head->next == NULL(空链表或单节点链表)。每次先拆成两半、分别排序,再合并。
c
struct ListNode* sortList(struct ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head; // 排除空链表/单节点
// 1. 找到中点并切断,得到两段:head -> ... -> pre 和 slow -> ...
struct ListNode* head2 = middleNode(head);
// 2. 分别对前后两段递归排序
struct ListNode* left = sortList(head);
struct ListNode* right = sortList(head2);
// 3. 合并两个有序链表
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
} 总体而言就是合并链表、查找链表思路的综合应用。
c
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* pre = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
pre->next = NULL;
return slow;
}
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
if (!l1) return l2;
if (!l2) return l1;
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
struct ListNode* sortList(struct ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
struct ListNode* head2 = middleNode(head);
struct ListNode* left = sortList(head);
struct ListNode* right = sortList(head2);
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
}24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
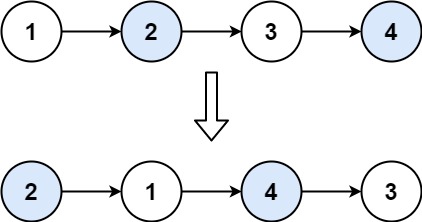
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]示例 2:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [1] 输出:[1]
🔁递归
首先排除空链表情况,同时在本题也将作为递归结束后的终止条件:
当链表为空 (head == NULL) 或者只剩一个节点 (head->next == NULL) 时,不需要交换,直接返回 head。
接下来步入正题:
节点标记
三个指针。p1指向头结点,作为当前要交换的第一个节点 ;p2指向头结点的next指针(也就是p1的下一个节点),作为当前要交换的第二个节点 ;p3指向p2的next,作为下一次递归的起点(即剩余部分的头结点)。
交换与递归
先递归地交换 p3 开始的剩余链表,并把结果接到 p1->next,再让 p2->next = p1 完成当前这对子节点的交换,最后返回 p2 作为新的头节点。
c
struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head) {
// 1. 终止条件:空链表或单节点链表无需交换
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
struct ListNode* p1 = head; // 第一节点
struct ListNode* p2 = head->next; // 第二节点
struct ListNode* p3 = p2->next; // 剩余链表的头
// 2. 先递归交换剩余部分,并接到 p1 后面
p1->next = swapPairs(p3);
// 3. 当前两节点交换
p2->next = p1;
// 4. 返回新的头(原来的第二节点)
return p2;
}