【数据结构】 LinkedList与链表
- [一、ArrayList 缺点](#一、ArrayList 缺点)
- 二、链表
-
- [2.1 链表的概念及结构](#2.1 链表的概念及结构)
- [2.2 链表的实现](#2.2 链表的实现)
-
- [2.2.1 create():手动创建链表(穷举法 )](#2.2.1 create():手动创建链表(穷举法 ))
- [2.2.2 display():打印链表](#2.2.2 display():打印链表)
- [2.2.3 size():求当前链表长度](#2.2.3 size():求当前链表长度)
- [2.2.4 contains(key):遍历链表,查看链表是否存在 key 这个值](#2.2.4 contains(key):遍历链表,查看链表是否存在 key 这个值)
- [2.2.5 addFirst():头插法](#2.2.5 addFirst():头插法)
- [2.2.6 addLast():尾插法](#2.2.6 addLast():尾插法)
- [2.2.7 addIndex():按位置插入](#2.2.7 addIndex():按位置插入)
- [2.2.8 remove():删除指定元素](#2.2.8 remove():删除指定元素)
- [2.2.9 removeAllKey():删除所有指定元素](#2.2.9 removeAllKey():删除所有指定元素)
- [2.2.10 clear():清空链表](#2.2.10 clear():清空链表)
- [三、链表 OJ 题](#三、链表 OJ 题)
-
- [3.1 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点](#3.1 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点)
- [3.2 反转⼀个单链表。](#3.2 反转⼀个单链表。)
- [3.3 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。](#3.3 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。)
- [3.4 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。](#3.4 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。)
- [3.5 将两个有序链表合并为⼀个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。](#3.5 将两个有序链表合并为⼀个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。)
- [3.6 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前。](#3.6 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前。)
- [3.7 链表的回文结构。](#3.7 链表的回文结构。)
- [3.8 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。](#3.8 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。)
- [3.9 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。](#3.9 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。)
- [3.10 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL。](#3.10 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL。)
- [四、LinkedList 的模拟实现(双向链表)](#四、LinkedList 的模拟实现(双向链表))
-
- [4.1 双链表的头插法](#4.1 双链表的头插法)
- [4.2 display()](#4.2 display())
- [4.3 contains()](#4.3 contains())
- [4.4 尾插法](#4.4 尾插法)
- [4.5 任意位置插入:addIndex()](#4.5 任意位置插入:addIndex())
- [4.6 删除一个节点:remove()](#4.6 删除一个节点:remove())
- [4.6 删除全部节点:removeAllKey()](#4.6 删除全部节点:removeAllKey())
- [4.7 clear():置空](#4.7 clear():置空)
- [五、LinkedList 的使用](#五、LinkedList 的使用)
-
- [5.1 LinkedList的构造](#5.1 LinkedList的构造)
- [5.2 LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍](#5.2 LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍)
- [5.3 LinkedList的遍历](#5.3 LinkedList的遍历)
- [六、ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别](#六、ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别)
一、ArrayList 缺点
- ArrayList 底层使⽤数组来存储元素。
- 由于其底层是⼀段连续空间,当在ArrayList任意位置插⼊或者删除元素时,就需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,时间复杂度为O(n) ,效率⽐较低,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。
- 因此:java集合中⼜引⼊了LinkedList,即链表结构。
二、链表
2.1 链表的概念及结构


2.2 链表的实现
2.2.1 create():手动创建链表(穷举法 )
(1)Java 代码实现
java
//手动创建一个链表:穷举法
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
this.head = node1;
}(2)创建链表的图解:

2.2.2 display():打印链表
(1)display() 打印链表 图解

(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head; // ✅ 用 cur 遍历,不改变 head
while (cur != null) {//如果head为空,则表示:遍历完了所有结点
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}2.2.3 size():求当前链表长度
java
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int usedSize = 0;
while(cur != null){
usedSize++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return usedSize;
}2.2.4 contains(key):遍历链表,查看链表是否存在 key 这个值
java
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//✅ 如果cur.next == null,表示 cur在最后一个节点处
//✅ 如果cur == null,表示 遍历完了整个链表
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}区分 "cur.next == null "与 "cur.next == null"
(a)如果cur.next == null,表示 cur在最后一个节点处

(b) 如果cur == null,表示 遍历完了整个链表

2.2.5 addFirst():头插法
(1)addFirst() 头插法 图解
a. 链表为空

b. 链表有很多结点

(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
listSize++;
/* if(head == null){
head = node;
}else{
//对于插入来说,一般建议 先绑定后边
node.next = head;
head = node;
}*/
}2.2.6 addLast():尾插法
(1)addLast() 尾插法 图解
a. 链表为空

b. 链表有很多结点


(2)Java 代码实现
java
//尾插法:(1)找到链表的尾巴 ------》 cur
//(2)cur.next = node;
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null){//表示链表为空
head = node;
listSize++;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;//找到链表的尾巴
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
listSize++;
}2.2.7 addIndex():按位置插入
(1)图解

(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void addIndex(int index, int data) throws ListIndexOutOfException{
checkIndexOfAdd(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
listSize++;
}
//findIndex:找到index -1 位置结点的地址
private ListNode findIndex(int index){
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while(count != index - 1){
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
private void checkIndexOfAdd(int index){
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
throw new ListIndexOutOfException("插入index位置不合法!,index="+ index);
}
}2.2.8 remove():删除指定元素
(1)图解

(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void remove(int key) {
if(head == null){
return;
}
if(head.val == key){
head = head.next;
listSize--;
return;
}
ListNode cur = findeNode(key);
if(cur == null){
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数据");
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
listSize--;
}
private ListNode findeNode(int key){
//找到第一个遇到的key 的前一个节点
//没有找到 返回null
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.next.val == key){
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}2.2.9 removeAllKey():删除所有指定元素
(1)图解
a. 一般情况

b. 第一个值(头结点)和后面的值为23:用 if 只能删掉头结点(放后面)

(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void removeALLKey(int key) {
if(head == null){
return;
}
/* while(head.val == key){
head =head.next;
}*/ //可能出现空指针异常
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode prev = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
prev.next = cur.next;
//cur= cur.next;
listSize--;
}else{
prev = cur;
//cur = cur.next;
}
cur= cur.next;
}
if(head.val == key){
head =head.next;
listSize--;
}
return head;
}2.2.10 clear():清空链表
(1)图解

(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void clear() {
head = null;
listSize = 0;
}【总代码】
- MySingleList
java
import java.util.List;
public class MySingleList implements IList{
static class ListNode{//静态内部类
private int val;
private ListNode next;//类型为ListNode,因为存的是 结点的地址
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;//head表示的当前列表的头结点,此时的头结点 只是存了第一个结点的引用
public int listSize;
//手动创建一个链表:穷举法
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
this.head = node1;
}
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
listSize++;
/* if(head == null){
head = node;
}else{
//对于插入来说,一般建议 先绑定后边
node.next = head;
head = node;
}*/
}
@Override
//尾插法:(1)找到链表的尾巴 ------》 cur
//(2)cur.next = node;
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null){//表示链表为空
head = node;
listSize++;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;//找到链表的尾巴
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
listSize++;
}
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) throws ListIndexOutOfException{
checkIndexOfAdd(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
listSize++;
}
//findIndex:找到index -1 位置结点的地址
private ListNode findIndex(int index){
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while(count != index - 1){
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
private void checkIndexOfAdd(int index){
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
throw new ListIndexOutOfException("插入index位置不合法!,index="+ index);
}
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//如果cur == null,表示 遍历完了整个链表
//如果cur.next == null,表示 cur在最后一个节点处
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
if(head == null){
return;
}
if(head.val == key){
head = head.next;
listSize--;
return;
}
ListNode cur = findeNode(key);
if(cur == null){
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数据");
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
listSize--;
}
private ListNode findeNode(int key){
//找到第一个遇到的key 的前一个节点
//没有找到 返回null
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.next.val == key){
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void removeALLKey(int key) {
if(head == null){
return;
}
/* while(head.val == key){
head =head.next;
}*/ //可能出现空指针异常
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode prev = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
prev.next = cur.next;
//cur= cur.next;
listSize--;
}else{
prev = cur;
//cur = cur.next;
}
cur= cur.next;
}
if(head.val == key){
head =head.next;
listSize--;
}
return head;
}
@Override
public int size() {/*
ListNode cur = head;
int usedSize = 0;
while(cur != null){
usedSize++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return usedSize;*/
return listSize++;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
head = null;
listSize = 0;
}
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head; // ✅ 用 cur 遍历,不改变 head
while (cur != null) {//如果head为空,则表示:遍历完了所有结点
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/*
public void display() {
while(head != null){//如果head为空,则表示:遍历完了所有结点
System.out.print(head.val+" ");
head = head.next;
//head走到下一个结点
}
System.out.println();
}
*/
}- IList
java
public interface IList {
//头插法
void addFirst(int data);
//尾插法
void addLast(int data);
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
void addIndex(int index,int data);
//查找关键字key是否包含在单链表当中
boolean contains(int key);
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的结点
void remove(int key);
//删除所有值为key的节点
void removeALLkey(int key);
//得到单链表的长度
int size();
//清空单链表
void clear();
//打印单链表
void display();
}- ListIndexOutOfException
java
public class ListIndexOutOfException extends RuntimeException{
public ListIndexOutOfException() {
}
public ListIndexOutOfException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}- Test
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySingleList mySingleList = new MySingleList();
mySingleList.addLast(23);
mySingleList.addLast(23);
mySingleList.addLast(23);
mySingleList.addLast(45);
mySingleList.display();
mySingleList.removeALLKey(23);
//mySingleList.display();
mySingleList.clear();
System.out.println(mySingleList.size());
}
public static void main2(String[] args) {
MySingleList mySingleList = new MySingleList();
mySingleList.addLast(12);
mySingleList.addLast(23);
mySingleList.addLast(34);
mySingleList.addLast(45);
mySingleList.addFirst(100);
/* mySingleList.display();
System.out.println(mySingleList.size());*/
try{
mySingleList.addIndex(3,99);
}catch(ListIndexOutOfException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
mySingleList.display();
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
/* ArrayList<Integer> arrayLusr = new ArrayList<>();
//第一次add的时候,会进行内存的分配 大小为10
//常用的链表类型:(1)单向 不带头 非循环 (2)双向 不带头 非循环 LinkedListt*/
MySingleList mySingleList = new MySingleList();
mySingleList.createList();
mySingleList.display();
mySingleList.contains(34);
boolean contains = mySingleList.contains(34);
System.out.println(contains);
}
}三、链表 OJ 题
3.1 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
(2)Java 代码实现
java
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode prev = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == val){
prev.next = cur.next;
}else{
prev = cur;
}
cur= cur.next;
}
if(head.val == val){
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}3.2 反转⼀个单链表。
(1)LC206. 反转链表

(2)图解



(3)Java 代码实现
java
public ListNode reverseList(){//反转链表
if(head == null){
return null;
}
//只有1个节点,反转和不反转 都是它本身
if(head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return head;
}
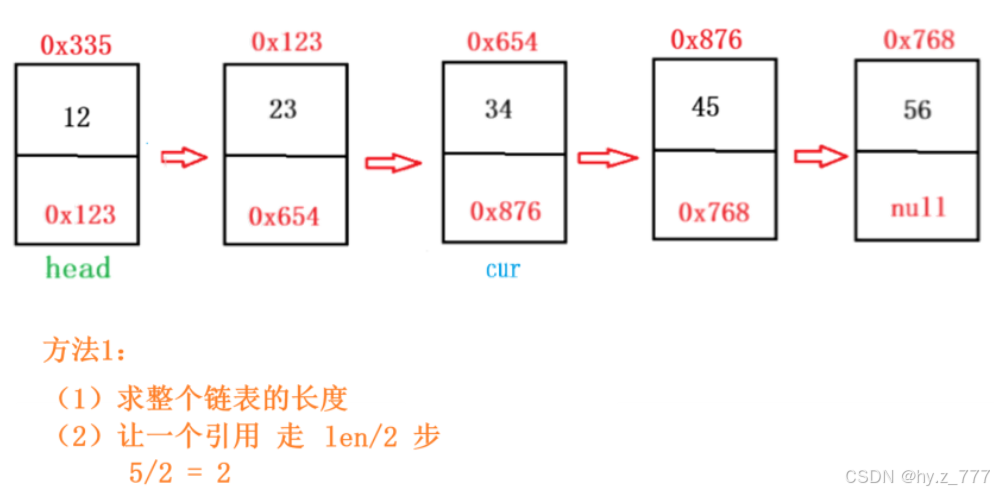
}3.3 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。

(2)图解
方法1:
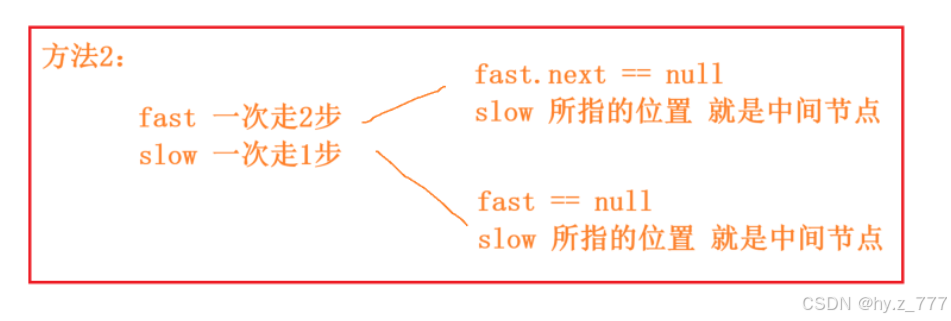
方法2:


(3)Java 代码实现
方法1:
java
//链表的中间节点
public ListNode middleNode(){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
int len = size();
int index = len / 2;
ListNode cur = head;
while(index != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}方法2:
java
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
//while(fast.next != null && fast != null) 空指针异常
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}3.4 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
(2)图解

(3)Java 代码实现
java
public int KthToLast(int k){
int len = size();
if(k <= 0 /*|| k > len*/){
return -1;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
//fast先走 k-1 步
int count = 0;
while(count != k-1){
fast = fast.next;
if(fast == null){
return -1;
}
count++;
}
//同时走
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow.val;
}3.5 将两个有序链表合并为⼀个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。


(2)图解


(3)Java 代码实现
java
public class Test {
public static MySingleList.ListNode mergeTwoLists(MySingleList.ListNode headA,MySingleList.ListNode headB){
//定义一个虚拟节点(表示头结点),此时设计到 获取静态内部类对象
MySingleList.ListNode newH = new MySingleList.ListNode(-1);
MySingleList.ListNode tmp = newH;
while(headA != null && headB != null){
if(headA.val < headB.val){
tmp.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
//tmp = tmp.next;
}else{
tmp.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
//tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
if(headA != null){
tmp.next = headA;
}
if(headB != null){
tmp.next = headB;
}
return newH.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySingleList mySingleList1 = new MySingleList();
mySingleList1.addLast(12);
mySingleList1.addLast(23);
mySingleList1.addLast(34);
mySingleList1.addLast(45);
mySingleList1.addLast(56);
mySingleList1.addLast(67);
mySingleList1.display();
System.out.println("===================");
MySingleList mySingleList2 = new MySingleList();
mySingleList2.addLast(12);
mySingleList2.addLast(23);
mySingleList2.addLast(34);
mySingleList2.addLast(45);
mySingleList2.addLast(56);
mySingleList2.addLast(67);
mySingleList2.display();
System.out.println("=================");
System.out.println("======= 合并 =====");
MySingleList.ListNode ret = mergeTwoLists(mySingleList1.head,mySingleList2.head);
mySingleList2.display(ret);
}3.6 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前。
(1)牛客:CM11 链表分割

(2)图解


考虑特殊情况,需手动置空:

(3)Java 代码实现
java
public ListNode partition(int x){
ListNode bs = null;
ListNode be = null;
ListNode as = null;
ListNode ae = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val < x){
//第一次插入
if(bs == null){
bs = be = cur;
}else{
be.next = cur;
be = cur;
}
//cur = cur.next;
}else{
//第一次插入
if(as == null){
as = ae = cur;
}else{
ae.next = cur;
ae = cur;
}
//cur = cur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(bs == null){
return as;
}
be.next = as;
if(as != null){
ae.next = null;
}
return bs;
}3.7 链表的回文结构。

(2)图解

解题思路:


考虑特殊情况:判断偶数个节点的回文

(3)Java 代码实现
java
public boolean chkPalindrome() {//链表的回文结构
if(head == null){
return false;
}
if(head.next == null){//只有一个节点
return true;
}
// 1.找中间节点的位置
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//2.开始翻转 后半部分
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while(cur != null){
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curN;
}
//3. 一个从头开始 一个从尾开始
while(head != slow){
if(head.val != slow.val){
return false;
}
//判断偶数情况
if(head.next == slow){
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}3.8 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
(1)LC106.相交链表





(2)图解


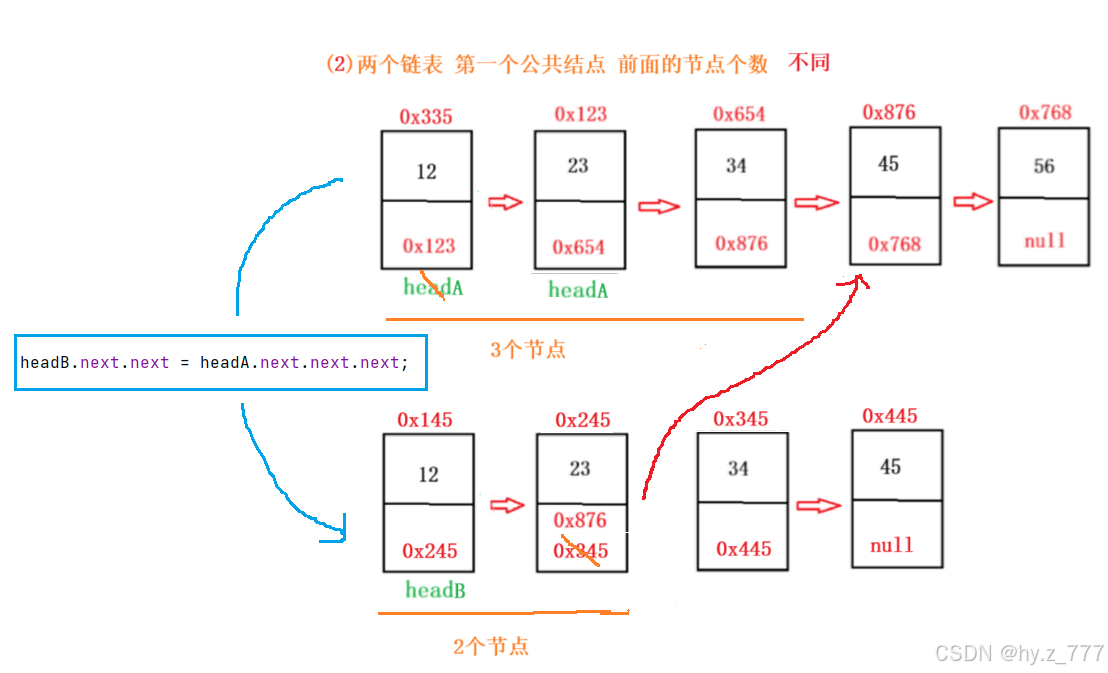

(3)Java 代码实现
java
//两个链表相交
public MySingleList.ListNode getIntersectionNode(MySingleList.ListNode headA,
MySingleList.ListNode headB){
//1.假定 A链表长 B链表短
MySingleList.ListNode pl = headA;
MySingleList.ListNode ps = headB;
//2.分别求2个链表的长度
int len1 = 0;
int len2 = 0;
while(pl != null){
len1++;
pl = pl.next;
}
while(ps != null){
len2++;
ps = ps.next;
}
pl = headA;
ps = headB;
//3.求长度的差值 len
int len = len1 - len2;
// len < 0 ==> pl = headB ps = headA len = len2 - len1
if(len < 0){
pl = headB;
ps = headA;
len = len2 - len1;
}
//4. 确定 pl指向的链表 一定是长链表; ps指向的节点 一定是短链表
//5.让 pl 走 len步
while(len != 0){
pl = pl.next;
len--;
}
//6.ps 和 pl 同时走 直到相遇
while(pl != ps){
pl = pl.next;
ps = ps.next;
}
if(pl == null){//2个链表 没相遇
return null;
}
return pl;
}测试
java
public static void createCut(MySingleList.ListNode headA,
MySingleList.ListNode headB) {
headB.next.next = headA.next.next.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySingleList mySingleList1 = new MySingleList();
mySingleList1.addLast(12);
mySingleList1.addLast(23);
mySingleList1.addLast(34);
mySingleList1.addLast(45);
mySingleList1.addLast(56);
mySingleList1.addLast(67);
mySingleList1.display();
System.out.println("===================");
MySingleList mySingleList2 = new MySingleList();
mySingleList2.addLast(13);
mySingleList2.addLast(25);
mySingleList2.addLast(35);
mySingleList2.addLast(146);
mySingleList2.addLast(156);
mySingleList2.display();
System.out.println("=================");
System.out.println("======= 测试 =====");
createCut(mySingleList1.head,mySingleList2.head);
MySingleList.ListNode ret = getIntersectionNode(mySingleList1.head,mySingleList2.head);
System.out.println(ret.val);
}输出结果:

3.9 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
(1)LC141.环形链表


(2)图解


(3)Java 代码实现
java
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head){//判断链表是否有环
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next!= null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}构造成环链表:
java
public void createLoop(){//构造 成环链表,在Test类中进行测试
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = head.next.next.next;
}Test 类 中进行测试:
java
public static void main(String[] args) {//测试 链表是否成环
MySingleList mySingleList1 = new MySingleList();
mySingleList1.addLast(12);
mySingleList1.addLast(23);
mySingleList1.addLast(34);
mySingleList1.addLast(45);
mySingleList1.addLast(56);
mySingleList1.addLast(67);
mySingleList1.display();
System.out.println("===================");
mySingleList1.createLoop();
//mySingleList1.display();死循环
boolean hasCycle = mySingleList1.hasCycle();
System.out.println(hasCycle);
}输出结果:

3.10 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL。
(1)LC142.环形链表Ⅱ


(2)图解



(3)Java 代码实现
java
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
return null;//没有环 就没有入口点
}
//推导出来的
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}四、LinkedList 的模拟实现(双向链表)

4.1 双链表的头插法
(1)图解


(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else{
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}测试:
java
package linkedlist;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addFirst(1);
myLinkedList.addFirst(2);
myLinkedList.addFirst(3);
myLinkedList.addFirst(4);
myLinkedList.display();
}
}输出结果:

4.2 display()
java
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.println(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}4.3 contains()
java
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}4.4 尾插法
(1)图解


(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else{
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = node;
}
}4.5 任意位置插入:addIndex()
(1)图解

(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void addIndex(int index, int data) throws ListIndexOutOfException{
int len = size();
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
throw new ListIndexOutOfException("双向链表index位置不合法:"+index);
}
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == len){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
node.next= cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
private ListNode findIndex(int index){
ListNode cur = head;
while(index != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}4.6 删除一个节点:remove()
(1)图解



(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
//判断是否为头节点
if(cur == head){
//删除头结点
head = head.next;
if(head == null){
//说明只有一个节点,且是头结点
last = null;
return;
}
head.prev = null;
}else{
//删除尾节点
if(cur == last){
last = last.prev;
last.next = null;
}else{
//删除中间节点
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
return;
}else{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}4.6 删除全部节点:removeAllKey()
java
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
//判断是否为头节点
if(cur == head){
//删除头结点
head = head.next;
if(head == null){
//说明只有一个节点,且是头结点
last = null;
return;
}
head.prev = null;
}else{
//删除尾节点
if(cur == last){
last = last.prev;
last.next = null;
}else{
//删除中间节点
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}4.7 clear():置空
(1)图解


(2)Java 代码实现
java
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode curN = cur.next;
//cur.val = null; 引用类型
cur.prev = null;
cur.next = null;
cur = curN;
}
head = null;
last = null;
}五、LinkedList 的使用
5.1 LinkedList的构造

java
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.addLast(1);
list.addLast(2);
list.addLast(3);
LinkedList<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList<>(list1);
list2.add(0,10);
list2.addAll(list);
}5.2 LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍

java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表⽰尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list);
// 在起始位置插⼊0
list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插⼊元素elem
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第⼀个元素,内部调⽤的是removeFirst()
list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第⼀个元素
list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
System.out.println(list);
// contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
if(!list.contains(1)){
list.add(0, 1);
}
list.add(1);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.indexOf(1));
// indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第⼀个elem的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1));
// lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第⼀个1的位置
int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
System.out.println(list);
// subList(from, to): ⽤list中[from, to)之间的元素构造⼀个新的LinkedList返回
List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(copy);
list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
5.3 LinkedList的遍历
java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {//遍历list的几种方法
//1.sout直接输出 遍历list
System.out.println("===== 1.sout直接输出 遍历list =====");
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.addLast(1);
list.addLast(2);
list.addLast(3);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println();
//2.for循环 遍历list
System.out.println("===== 2.for循环 ========");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//3.for(x : each) 遍历list
System.out.println("===== 3.for(x : each) 遍历list =====");
for(int x : list){
System.out.println(x +" ");
}
System.out.println();
//4. 使⽤iterator迭代器 正向遍历
System.out.println("====== 4. 使⽤iterator迭代器 正向遍历 ====");
Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator();//list、队列、集合 都能打印
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next()+" ");//打印it的下一个,同时it往后走
}
System.out.println();
//5. 使⽤listIterator迭代器 打印list
System.out.println("====== 5. 使⽤listIterator迭代器 打印list ====");
ListIterator<Integer> lit = list.listIterator();//通过迭代器 打印list
while(lit.hasNext()){
System.out.println(lit.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//6.listIterator 反向遍历
System.out.println("====== 6.listIterator 反向遍历 打印list ====");
ListIterator<Integer> lit2 = list.listIterator(list.size());
//ListIterator<Integer> lit2 = list.listIterator(2);
while(lit2.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(lit2.previous()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}输出结果:


六、ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别


