现象/问题:
existing symmetric teacher-student methods for semi-supervised 3D object detection have characterized simplicity, but impede the distillation performance between teacher and student because of the demand for an identical model structure and input data format.
现有的对称的用来进行半监督3D检测的教师-学生方法简单,但效果可能不好。因为它要求完全一致的模型架构和输入数据的格式。
the advantages of jointly updating the whole framework.
对称的可以online不固定教师,那么可以联合更新整个框架(教师和学生)。The offline asymmetric methods with a complex teacher model, constructed differently, can generate more precise pseudo labels, but is challenging to jointly optimize the teacher and student model.
离线的非对称方法有个较为复杂的教师模型,能产生更精确的伪标签,但是难以同时优化教师和学生模型。
the capacity of a strong teacher
离线的话,老师is frozen(不能同时更新教师和学生)但教师的能力比较强。

本文提出的方法:
-
优势:
can harness the capacity of a strong teacher while preserving the advantages of jointly updating the whole framework.兼具上述两个模型的优点。即可以联合更新教师和学生模型,又能保证模型的复杂性。
-
关键:
The essence is the proposed attention-based refinement model that can be seamlessly integrated into a vanilla teacher本文的关键在于这个
refinement model的设计。
teacher adopts an attention-based refinement model to summarize information from past and future timestamps (supporting frames) with the goal of improving the quality of the pseudo label on the current frame.老师模型能利用
refinement model总结过去和将来时间戳的信息从而改进在当前帧的伪标签的质量。(这个伪标签用来训练学生模型) -
这个
refinement model能解决的有挑战性的场景有:- objects detected in the current timestamp but with suboptimal box quality
- objects are missed in the current timestamp but are detected in supporting frames
- objects are neglected in all frames
分别通过
refinement model的PBA,DBA,STA来解决。
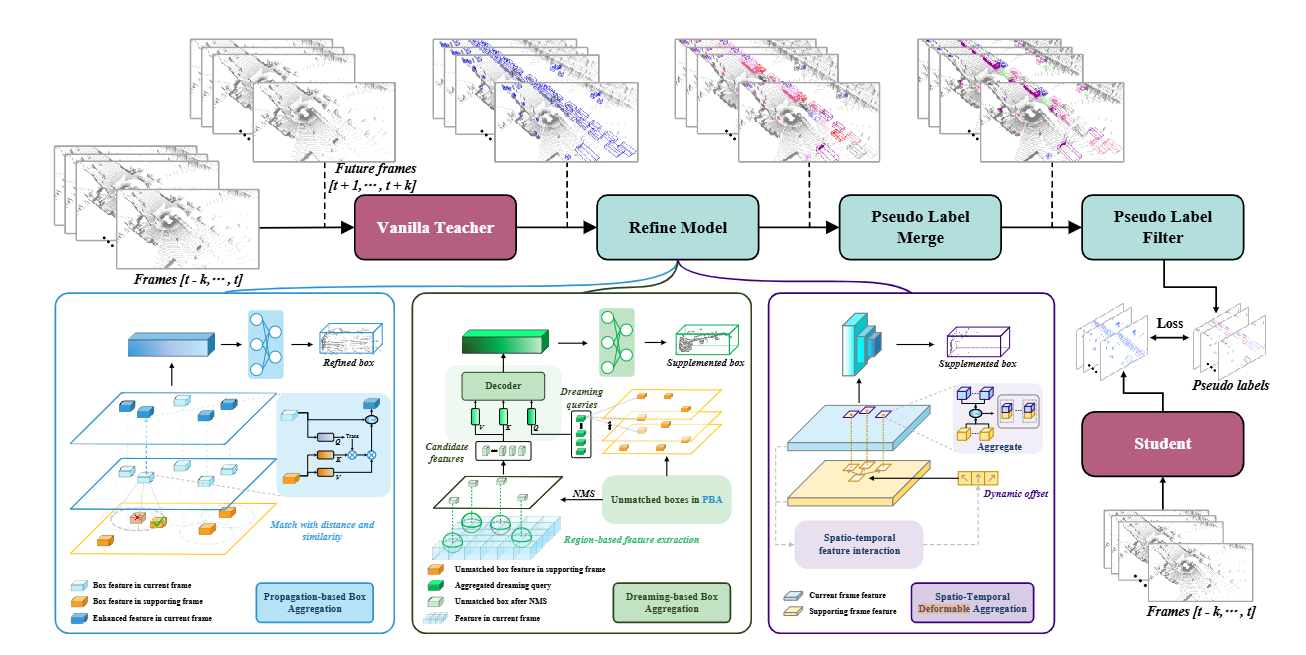
模型的介绍:
-
the vanilla teacher, which is a single-frame detector, predicts bounding boxes for all input frames ranging from t−k to t+k.
老师模型是一个单帧的检测器
-
the proposed attention-based refinement model, aggregates past and future information to refine the detection results from the vanilla single-frame detector.
refinement model聚合过去将来的信息来改善老师模型的检测效果(从而产生更好的伪标签来使得学生模型更好的更新参数)- PBA: Propagation-based Box Aggregation
focuses on improving the quality of the detected boxes in the current frame by propagating the boxes to supporting frames and then extracting target-related information - DBA: Dreaming-based Box Aggregation
address the false negatives in the current frame by aggregating detected boxes in supporting frames as dreaming queries and then verifying their presence in the current timestamp - STA: Spatio-Temporal feature Aggregation
alleviate the objects neglected in both the current frame and any supporting frames by fusing point cloud features from all frames using deformable attention
- PBA: Propagation-based Box Aggregation
-
a dual-threshold strategy is introduced to filter low-quality proposals and generate the pseudo labels for training the student model
-
update the teacher model
问题:为什么之前Teacher-Student Model中的offline asymmetric没人想到让Teacher模型保持和student模型一致的架构方便这俩同时更新参数呢?之前遇到的困难到底在哪里?本文解决了吗?本文的创新点相比于之前到底在哪里?
补充:
-
efficiencyVSeffectiveness:前者是效率,强调高效。后者是效力,强调有效。
-
offlineVSonline
based on whether the teacher model is frozen如果是的话就是
offline,否则是online

-
教师-学生模型(超简版):
- 教师模型的训练:
教师模型利用带有真实物体标签和完整空间信息的数据进行训练,如3D点云数据加上精确标注的物体类别和位置信息。
在这个上下文中,教师模型通过学习真实的物体关系和空间布局,能够准确地理解和表达自然语言指示下的3D场景。 - 学生模型的初始化与训练
学生模型具有与教师模型相同的架构,但其输入是未经完美标注的原始点云特征
训练过程中,教师模型将它学到的关于如何理解空间关系的知识以某种形式传递给学生模型,比如输出的概率分布、注意力权重或者经过压缩的中间层表示。 - 知识蒸馏
教师模型对同一输入数据生成预测结果,这些结果反映了高层次的关系推理和空间理解。学生模型则尝试模仿教师模型的行为,例如,在训练时,不仅最小化自身对于未标注数据的预测误差,还会根据教师模型提供的软目标(soft targets)调整自己的学习目标,即尽量让自己的输出靠近教师模型的输出。
参考文章:
A Simple Semi-Supervised Learning Framework for Object DetectionSelf-training with Noisy Student improves ImageNet classificationReMixMatch: Semi-Supervised Learning with Distribution Alignment and Augmentation AnchoringRethinking Pseudo Labels for Semi-supervised Object Detection
- 教师模型的训练:
-
EMA- 定义:
EMA指数移动平均,常用于教师模型的参数更新,以增强教师模型的稳定性并帮助学生模型更好地学习。 - 训练过程:将教师模型的参数初始化为学生模型的初始参数。教师模型的参数通过 EMA 方法更新,而不是直接通过梯度下降更新,学生模型正常训练,通过反向传播更新其参数。教师模型的输出作为指导,学生模型根据教师模型的预测进行知识学习。
- EMA更新公式: M = ( 1 − x ) M ′ + x M M=(1-x)M'+xM M=(1−x)M′+xM,
M指的是教师模型的参数,M'指的是学生模型的参数。(EMA本质上就是这个公式,它可以用在很多地方,在这里用在了模型的参数更新上。)
- 定义:
-
3D object detection with point clouds- 点云
Point Cloud是一种在三维空间中由大量离散点组成的数据集合,每个点包含自身的笛卡尔坐标(X、Y、Z),并可附带颜色、强度、时间戳等属性,用于描述物体的空间分布和表面特性。在同一空间参考系下,这些点共同勾勒出目标的外形轮廓。点云数据源主要包括激光雷达LiDAR、三维扫描仪以及基于摄影测量的点云重建技术,其中激光雷达以其高精度和远距离探测能力成为自动驾驶中最常见的点云获取手段。 - 3D点云检测步骤:
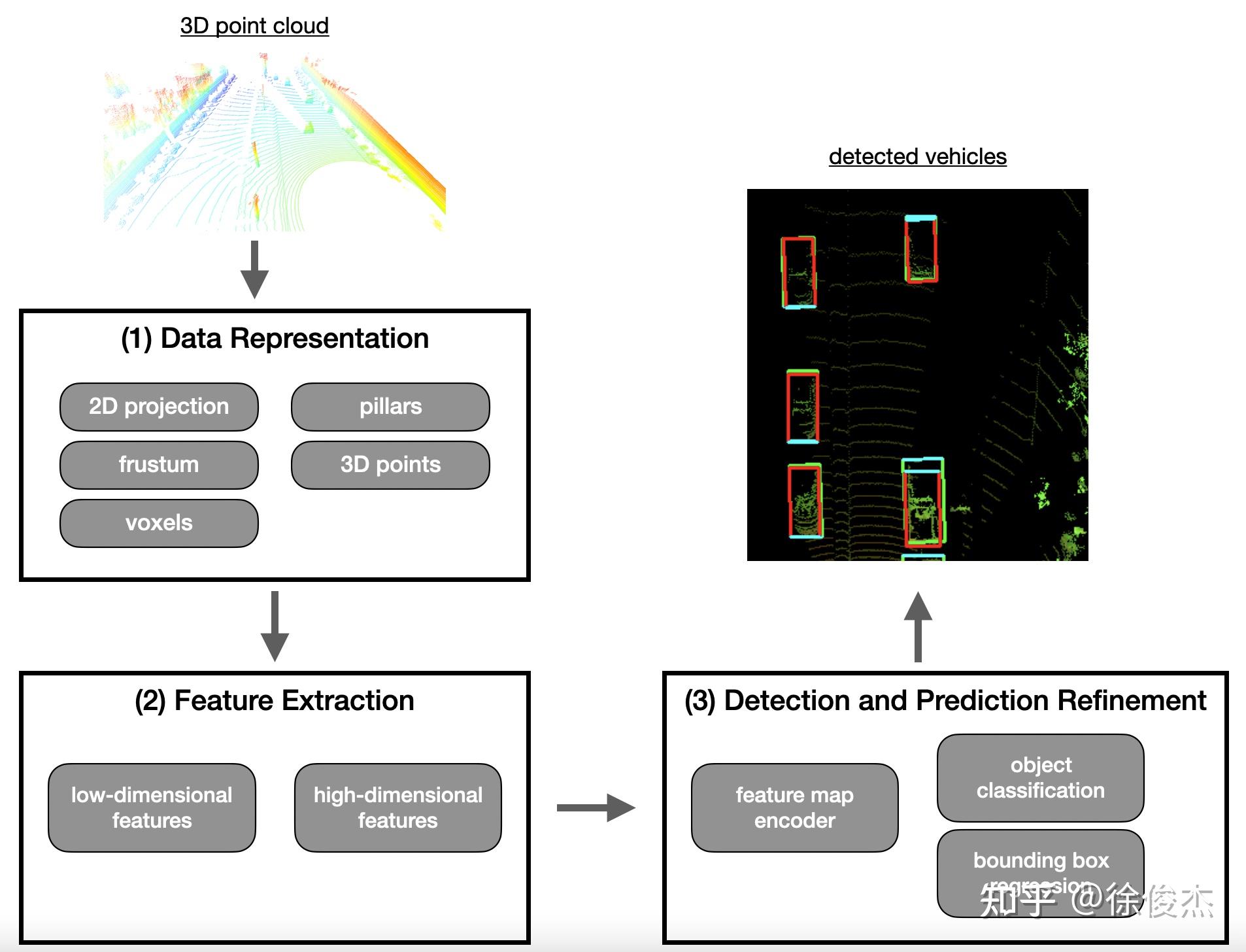
- 点云
-
LiDAR:Light Detection And Ranging激光雷达 -
3D数据的不同表示类型:
- 点云(Point clouds):三维空间(xyz坐标)点的集合。
- 体素网格(Voxel grids):体素是3D空间的像素。量化的,大小固定的点云。每个单元都是固定大小和离散坐标。
- 多边形网格(Polygon meshes):mesh是面片的集合
- 多视图表示(Multi-view representations):多视图表示是从不同模拟视点渲染的2D图像集合。

| 特性 | 点(Point) | 体素(Voxel) |
|---|---|---|
| 数据结构 | 非结构化,原始点云 | 规则化网格 |
| 信息保留 | 保留精确几何细节 | 可能因量化损失细节 |
| 计算效率 | 适合稀疏场景,无冗余计算 | 密集场景友好,但需处理空体素 |
| 典型方法 | PointNet++, PointPillars | VoxelNet, SECOND |