一、C语言的文件接口
1、打开文件
- 函数:

- 参数:
filename :打开在参数 filename 中指定其名称的文件,并将其与在将来的作中可以通过返回的FILE 指针标识的流相关联。
mode:以mode的权限打开,权限有一下几种
- 返回值
返回一个文件指针,该指针指向被执行的文件。
-
代码
cppFILE *fd=fopen("myfile","w") //以只写的方式打开文件
2、文件写入
-
函数:

-
参数:
prt:该指针指向需要写入文件的内容
size:每个元素的大小,以字节为单位
count:元素的个数
stream:需要写入到的文件
- 返回值:
写入成功将返回写入元素的个数
- 代码:
cpp
const char buffer[]={'a','b','c'};
FILE *fd=fopen("myfile","w");
fwrite(buffer,sizeof(char),sizeof(buffer),fd);
//向"myfile"文件中写入abc3、文件读取
函数:

参数:
ptr:一个指向大小至少为count的内存块的指针
size:要读取的每个元素的大小
count:要读取的元素个数
stream:指向要读取的文件的指针
返回值:
读取成功就返回读取元素的个数
代码:
cpp
char buffer[1024];
FILE *fd=fopen("myfile","r");
fread(buffer,sizeof(char),sizeof(buffer),fd);
//向"myfile"文件中读取4、关闭文件
函数:

参数:
stream:指向需要关闭的文件的文件指针
返回值:
关闭成功返回0,失败则返回-1
代码:
cpp
FILE *fd=fopen("myfile","r");
int n=fclose(fd);
//关闭文件"myfile"二、系统文件接口
1、打开文件
-
函数:
cpp#include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> int open(const char *pathname, int flags); int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode); -
作用:
打开一个文件
- 参数:
pathname:要打开的文件的名称
flags :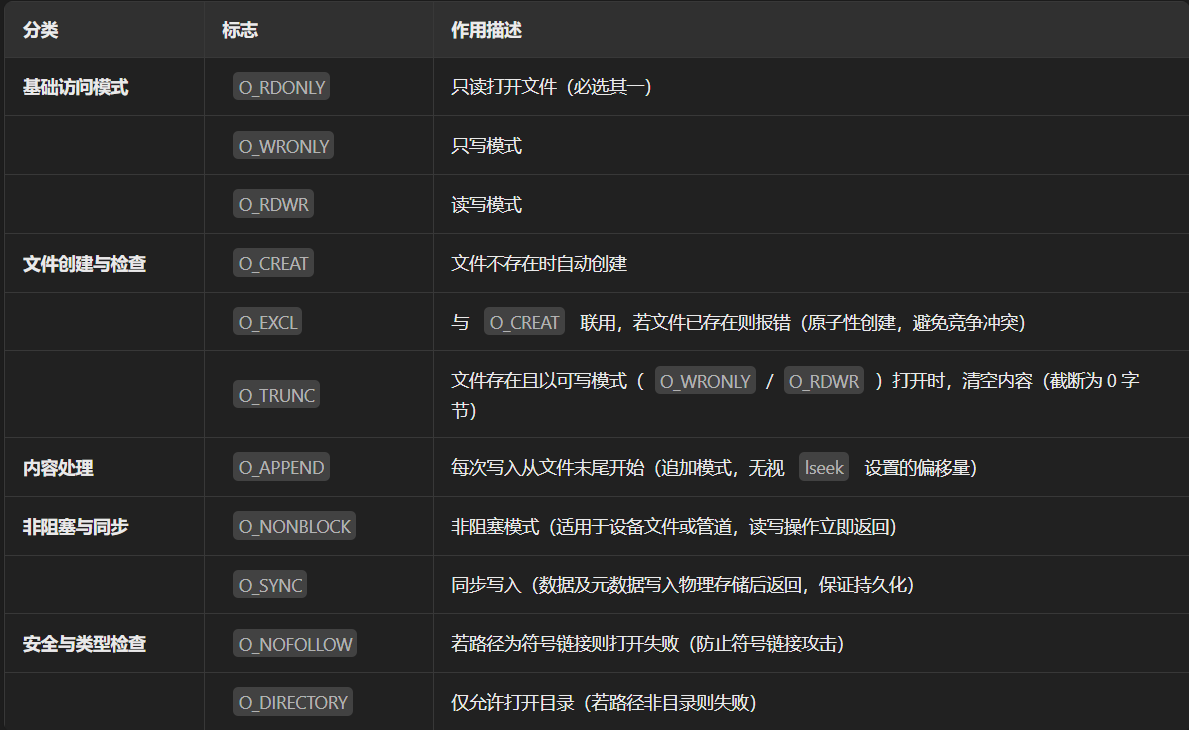
**mode:**如果flags中选择了O_CREAT时该文件的最终权限由mode和unmask共同决定
- 返回值:
打开成功就返回该文件的文件描述符,否则返回-1
- 代码:
cpp
// 只读打开现有文件
int fd = open("/etc/passwd", O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) { perror("open"); }
// 创建新文件并设置权限(若存在则报错)
fd = open("newfile.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, 0644);2、写文件
- 函数:
cpp
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);- 作用:
向文件中写入
- 参数:
fd:需要写入内容的文件描述符
buf:需要写入的内容
count:需要写入内容的大小以字节为单位
- 返回值:
成功时返回实际写入内容的大小,失败返回-1
- 代码:
cpp
ssize_t total = 0;
while (total < count) {
ssize_t n = write(fd, buf + total, count - total);
if (n == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR) continue; // 被中断则重试
break; // 其他错误处理
}
total += n;
}3、文件读取
- 函数:
cpp
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);- 作用:
向指定文件读取内容
- 参数:
fd:标识要读取的目标文件或设备(如普通文件、管道、套接字等)
buf:指向用户分配的内存区域,用于存储读取的数据
count:指定本次read请求读取的最大字节数
- 返回值:

- 代码:
cpp
ssize_t total = 0;
while (total < count) {
ssize_t n = read(fd, buf + total, count - total);
if (n == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR) continue;
break;
} else if (n == 0) {
break; // EOF
}
total += n;
}4、关闭文件
- 函数:
cpp
#include <unistd.h>
int close(int fd);- 作用:
关闭已经打开的文件
- 参数:
fd:需关闭的文件描述符,必须是有效的、已打开的描述符
返回值:
- 代码:
cpp
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int fd = open("example.txt", O_RDWR); // 打开文件
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open failed");
return 1;
}
// 文件操作(如 read/write)
char buf[1024];
ssize_t n = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
// 关闭文件并检查错误
if (close(fd) == -1) {
perror("close failed");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}