简单工厂模式(Simple Factory Pattern)
简单工厂模式(又称静态工厂模式 )是一种创建型设计模式 ,它通过一个工厂类 来封装对象的创建逻辑,客户端 无需直接实例化具体类,而是通过工厂类获取所需对象。
1.类图结构
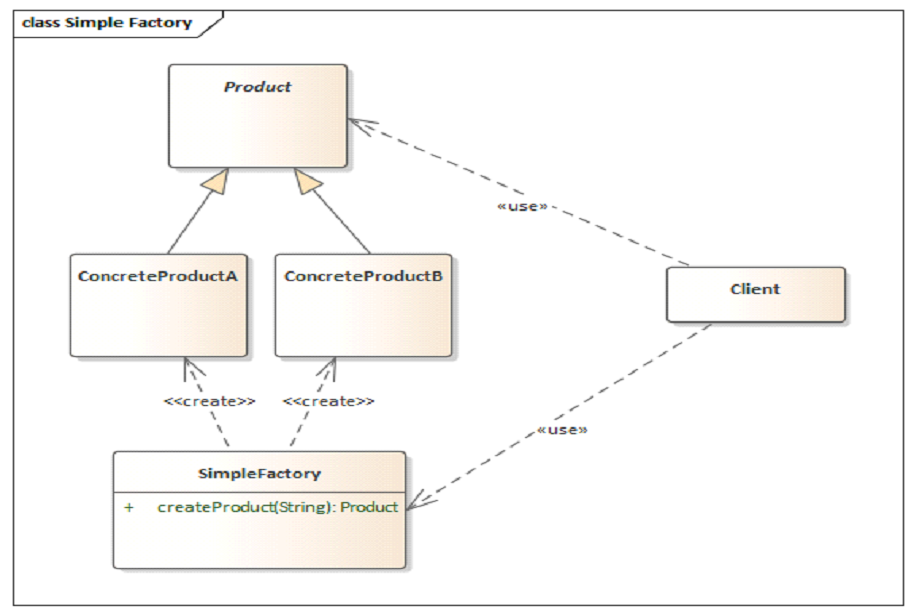
2.关键角色
| 角色 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Client | 客户端,一个或多个,调用SimpleFactory的createProduct()创建Product |
| SimpleFactory | 工厂类,根据Client的输入创建具体的 Product |
| Product | 抽象产品,定义产品行为,可以是抽象类或接口类,取决于实际场景 |
| ConcreteProductA ConcreteProductB | 具体产品,继承或实现 Product |
3. 代码示例
3.1 定义抽象产品
cpp
// 抽象形状类
class IShape
{
public:
virtual ~IShape() = default;
virtual double area() const = 0;
virtual void draw() const = 0;
};3.2 定义具体产品
cpp
// 具体形状类 - 圆形
constexpr double M_PI = 3.14;
class Circle : public IShape
{
public:
explicit Circle(std::initializer_list<double> args)
{
if (args.size() == 1) {
auto iter = args.begin();
radius = *iter;
}
if (radius <= 0) {
throw std::invalid_argument("Circle radius must be positive");
}
}
double area() const override
{
return M_PI * radius * radius;
}
void draw() const override
{
std::cout << "Drawing a circle with radius " << radius
<< " and area " << area() << std::endl;
}
private:
double radius;
};
// 具体形状类 - 矩形
class Rectangle : public IShape
{
public:
Rectangle(double w, double h) : width(w), height(h) {}
Rectangle(std::initializer_list<double> args)
{
if (args.size() == 2)
{
auto iter = args.begin();
width = *iter++;
height = *iter;
}
if (width <= 0 || height <= 0)
throw std::invalid_argument("Rectangle dimensions must be positive");
}
double area() const override {
return width * height;
}
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "Drawing a rectangle " << width << "x" << height
<< " with area " << area() << std::endl;
}
private:
double width, height;
};
// 具体形状类 - 三角形
class Triangle : public IShape
{
public:
Triangle(std::initializer_list<double> args)
{
if (args.size() == 3)
{
auto iter = args.begin();
a = *iter++;
b = *iter++;
c = *iter;
}
// 验证是否为有效三角形
if (a + b <= c || a + c <= b || b + c <= a) {
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid triangle sides");
}
}
double area() const override {
// 使用海伦公式计算面积
double s = (a + b + c) / 2;
return sqrt(s * (s - a) * (s - b) * (s - c));
}
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "Drawing a triangle with sides " << a << ", " << b << ", " << c
<< " and area " << area() << std::endl;
}
private:
double a, b, c;
};3.3 定义简单工厂
cpp
// 形状工厂类
class ShapeFactory
{
public:
static std::unique_ptr<IShape> createShape(const std::string& type, std::initializer_list<double> args)
{
if (type == "circle")
return std::make_unique<Circle>(args);
else if (type == "rectangle")
return std::make_unique<Rectangle>(args);
else if (type == "triangle")
return std::make_unique<Triangle>(args);
throw std::invalid_argument("Unknown shape type: " + type);
}
};3.4 客户端调用
cpp
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
int main()
{
try
{
// 创建圆形
auto circle = ShapeFactory::createShape("circle", {5.0});
circle->draw();
// 创建矩形
auto rectangle = ShapeFactory::createShape("rectangle", { 4.0, 6.0 });
rectangle->draw();
// 创建三角形
auto triangle = ShapeFactory::createShape("triangle", { 3.0, 4.0, 5.0 });
triangle->draw();
// 尝试创建无效形状会抛出异常
auto invalidCircle = ShapeFactory::createShape("circle", {-1.0});
auto invalidTriangle = ShapeFactory::createShape("triangle", {1.0, 2.0, 5.0});
}
catch (const std::exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "Error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return 1;
}4. 特点
✅ 优点
- 解耦 :客户端不直接依赖具体产品类,只依赖
Product接口和SimpleFactory。 - 职责分离:对象的创建逻辑集中在工厂类中,当有多个客户端时,仅需要修改工厂类代码。
- 简单易用:适用于产品种类较少、变化不频繁的场景。
❌ 缺点
- 违反开闭原则(OCP) :新增产品类型时,必须修改
SimpleFactory的逻辑(增加if-else分支)。 - 工厂类职责过重:如果产品种类很多,工厂方法会变得臃肿。
4. 对比其他工厂模式
| 模式 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 简单工厂 | 一个工厂类,通过 if-else 创建不同产品 |
产品种类少,变化少 |
| 工厂方法 | 每个产品对应一个工厂,符合开闭原则 | 产品种类多,可能扩展 |
| 抽象工厂 | 生产多个产品族(如不同风格的UI组件) | 需要创建一组相关对象 |
5. 适用场景
- 对象的创建逻辑较简单,且不会频繁变化。
- 客户端不需要关心具体实现类,只需获取产品实例。
- 适用于小型项目或工具类,如:
- 数据库驱动加载(
DriverManager.getConnection()) - 日志记录器(
LoggerFactory.getLogger())
- 数据库驱动加载(
6. 变体:静态工厂方法
如果工厂方法定义为 static,则称为静态工厂 (如 SimpleFactory::createProduct())。
优点 :无需实例化工厂类,直接调用。
缺点:无法通过继承改变创建方法的逻辑。
7. 总结
- 简单工厂 = 一个工厂类 + 条件判断创建对象
- 适合简单场景,但不适合复杂或可扩展的系统
- 如果需求可能变化,建议改用工厂方法或抽象工厂