个人能力:会限制大模型发挥?
一、简介
七月初全职独立开发,忙忙碌碌中已经过了四周,最近两个星期在做产品集成大模型的功能,所以在节奏上偏重开发这条线。
开发前感觉复杂,完成后感觉更复杂。
之前对于多款大模型的集成,更多是从技术角度调研文档,再加上重要的前端编程,自己也是半吊子水平,对时间把握上心里没底,所以准备用两周的时间,先把基础能力封装搭建好,方便后续的迭代扩展。
整体流程:【1】熟悉几款模型的接入文档,【2】集成文本模式的对话功能,【3】封装提示词动态管理。
为什么接入完成后感觉更复杂?
在接入并适配业务的过程中,不断的调整和优化提示词,见识到大模型各种场景下的文本能力,也让自己反思AI方向的能力不足,更是缺乏比较系统的知识和经验。
个人能力会限制大模型发挥,我成了AI的那什么猪队友。
为什么只接入文本能力?
在大模型的使用中,感觉最核心的是文本能力,即信息输入的理解和输出的效果,把有限的时间先放在这一块,争取在不断的提问和回复中,找到更加准确高效的对话方式。
遵循熟能生巧的思路,积累一定的文本能力之后,在此基础上挖掘应用场景。
虽然产品只集成了4款模型,但是开发却至少用了7款AI工具,涉及产品和前后端的全部环节,大模型在其他行业使用,效果如何不清楚。
在研发领域,绝对已成气候。
下面将从:集成原理、提示词、数据库、后端接口、前端对接,这5个维度总结整个开发流程。
二、集成原理
看了不少开源仓库的教程,以及各个模型的官方文档,这里更多是为了开阔思路,最终还是决定采用稳妥的方式,前端调用后端API,后端处理大模型对接和数据存储。
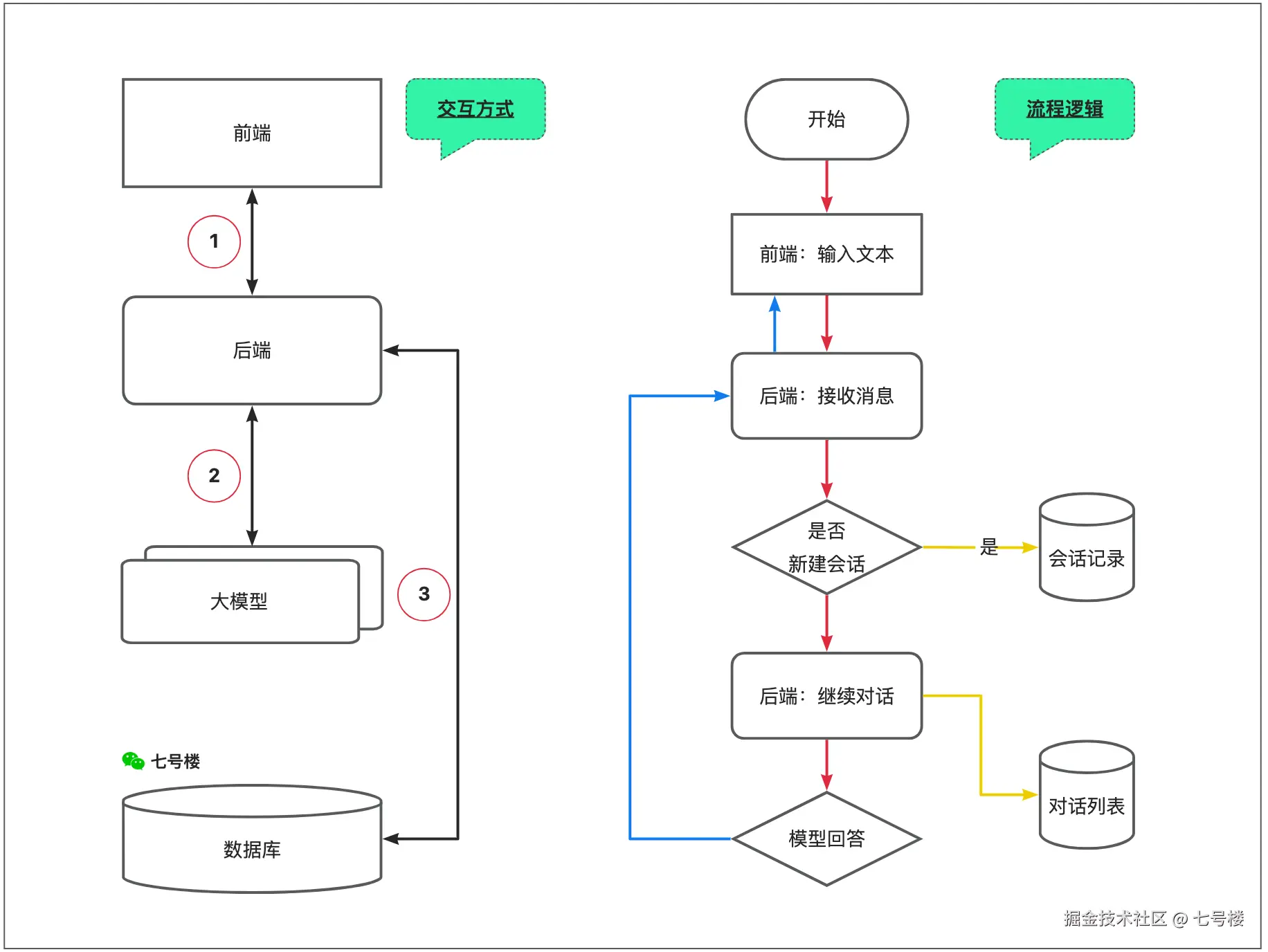
交互层面看,主要分为3段过程:【1】前后端,【2】后端和大模型,【3】后端和数据库。即产品本身的对话交互,对话调用第三方模型,对话消息的存储管理。
流程层面看,主要分为5段过程:【1】接收用户消息,【2】会话记录管理,【3】对话流程管理,【4】大模型调用,【5】前端输出回复。
三、提示词管理
在开始具体的代码编程之前,必须先了解提示词的基本用法,即不同身份角色所发出的消息类型。
java
public enum MessageType {
/**
* A {@link Message} of type {@literal user}, having the user role and originating
* from an end-user or developer.
* @see UserMessage
*/
USER("user"),
/**
* A {@link Message} of type {@literal assistant} passed in subsequent input
* {@link Message Messages} as the {@link Message} generated in response to the user.
* @see AssistantMessage
*/
ASSISTANT("assistant"),
/**
* A {@link Message} of type {@literal system} passed as input {@link Message
* Messages} containing high-level instructions for the conversation, such as behave
* like a certain character or provide answers in a specific format.
* @see SystemMessage
*/
SYSTEM("system"),
}- 用户类型的消息,具有用户角色,来自最终用户或开发人员,也就是产品中输入的文本。
- 系统类型的消息,是相对高级的指令,要求模型扮演的角色或身份以及约束行为,比在用户消息中设定的效果好。
- 助手类型的消息,模型响应用户生成的消息,也可以在对话的上下文中传递,可以聚焦会话的主题。
产品集成大模型的对话能力,最常用的就是三种消息类型,具体的场景可以具体的组合设计,AI的本质在追求智能,所以可以做一些跳脱的尝试挖掘模型能力。
四、数据库设计
目前开发的进度,数据库的设计只有4张关键的表,管理模型和提示词,以及对话数据的存储。
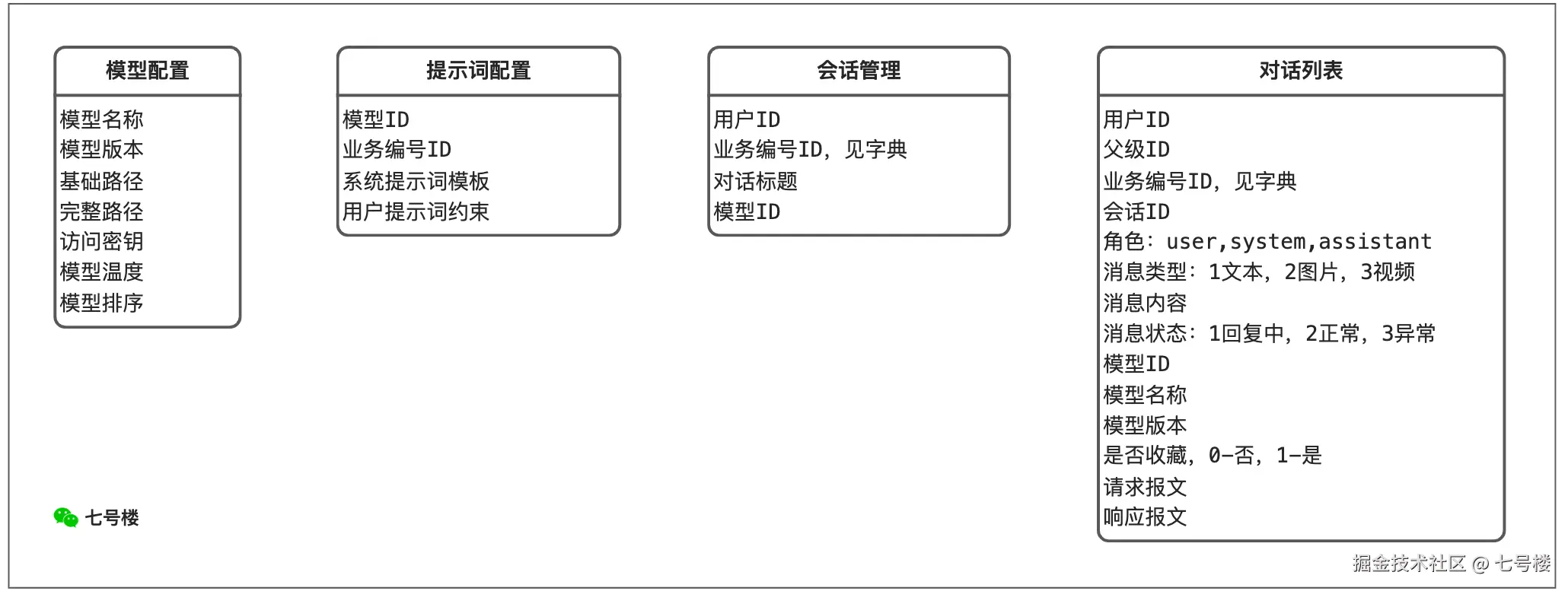
- 大模型配置表:统一封装API调用,可以动态添加和禁用集成的模型和版本,前面的内容已经写过。
- 提示词配置表:给大模型和使用场景,动态配置系统提示词,用户消息末尾加限制,参考的是LastSQL方式。
- 会话和消息表:这种就是常见设计,会话就是保存每轮对话用户的第一条消息,列表存放不同角色的输出。
对话模块表结构设计,问过几款主流的模型,给出的结构都很类似,只围绕产品需求做了小部分调整;模型和提示词表结构,是抽取模型组件的API参数。
五、接口设计
1、大模型API基础
使用的核心组件是spring-ai-openai的依赖包,主流的模型基本都适配了,该组件定义的模型API接口规范,这样有利于模型统一管理和切换。
xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${spring-ai-openai.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>- 消息(Message):用来封装一条具体的消息,结构涉及具体的角色和相应的内容。
- 提示词(Prompt):不同角色的文本指令或者问题,用来引导大模型的响应内容。
- 客户端(ChatClient):聊天客户端,与大模型交互的工具,封装了模型配置和调用的各种方法。
在具体的使用场景中,通常在提示词中设定系统和用户消息,用来引导模型的回复,通过客户端工具把指令发给具体的模型。
2、阻塞响应
在上篇内容SpringBoot3集成大模型中,使用的就是「阻塞」模式,请求发出后等大模型响应完成,再把结果回传给用户,这种在长文本中体验很差,比较适用内容简短的对话。
java
@GetMapping(value = "/client")
public String chatClient() {
String message = "讲个笑话,最好能把我听哭的那一种。";
return chatClient.prompt(new Prompt(message)).call().content();
}3、Flux流式响应
后端最初设计的是Flux接口,但是最终没有采用,用的是WebSocket会话方式,具体原因前端对接模块会细说。
大模型不会一次输出完整结果,而是逐步返回中间内容,需要完整的拼接起来才是全部内容,这样可以减少用户等待时间,也降低超时的风险。
java
@PostMapping(value = "/flux-chat",produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<ChatTextVO> fluxChat (@RequestBody UserTextDTO dto){
// 1、参数校验,模型ID和消息
if (ObjectUtil.hasNull(dto.getMsgText(),dto.getModelId())){
throw new BizExe(RepCode.PARAM_ERROR);
}
// 2、模型校验获取
ModelConfig model = modelConfigService.checkGetModel(dto.getModelId());
ChatClient myClient = ModelFactory.getModel(model.getModelVersion());
// 3、构建会话进程
chatService.buildUserChat(dto, model, MessageType.USER.getValue());
// 4、模型对话与本地业务
return myClient.prompt(new Prompt(dto.getMsgText())).stream().chatResponse()
.map(chunk -> {
// 消息响应片段
Generation generation = chunk.getResult();
AssistantMessage msg = generation.getOutput();
// 对话响应
ChatTextVO chatTextVO = new ChatTextVO();
chatTextVO.setBlockId(msg.getMetadata().get(ChatParamEnum.MSG_BLOCK_ID.getParam()).toString());
chatTextVO.setMessageType(msg.getMessageType().toString());
chatTextVO.setTextContent(msg.getContent());
return chatTextVO;
})
.doOnComplete(() -> {
log.info("流式响应结束,处理业务===>>>");
})
.doOnCancel(() -> {
log.info("流式响应取消,处理业务===>>>");
})
.doOnError(error -> {
log.info("请求失败: {}",error.getMessage());
});
}这里值得注意的问题,如果流式响应完整那最好,但用户可能主动结束等待,或者会发生错误,为了保证流程的完整,需要执行相应的中断方法完善业务逻辑。
4、WebSocket会话
此前写过SpringBoot3的系列教程,其中包括如何集成WebSocket组件,源码和案例都已归档在Git仓库,所以这一块就不展开详聊了,重点来看如何集成模型对话。
java
private static final ConcurrentHashMap<String,Disposable> chatFlow = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void socketChat(Session session, ChatTextDTO dto) throws Exception {
// 1、参数校验
if (ObjectUtil.hasNull(dto.getMsgText(),dto.getModelId())){
throw new BizExe(RepCode.PARAM_ERROR);
}
// 2、模型校验获取
ModelConfig model = modelConfigService.checkGetModel(dto.getModelId());
ChatClient myClient = ModelFactory.getModel(model.getModelVersion());
// 3、构建会话进程
this.buildUserChat(dto, model, MessageType.USER.getValue());
// 4、调用模型服务获取响应流
Disposable disposable = myClient.prompt(new Prompt(dto.getMsgText()))
.stream()
.chatResponse()
.doOnCancel(() -> {
log.info("会话结束,处理取消业务");
})
.subscribe(
chunk -> {
// 消息响应片段
Generation generation = chunk.getResult();
AssistantMessage msg = generation.getOutput();
// 响应消息主体
ChatTextVO chatTextVO = new ChatTextVO();
chatTextVO.setBlockId(msg.getMetadata().get(ChatParamEnum.MSG_BLOCK_ID.getParam()).toString());
chatTextVO.setMessageType(msg.getMessageType().toString());
chatTextVO.setTextContent(msg.getContent());
// 会话中响应数据
this.sendMessage(session, chatTextVO);
},
error -> {
log.error("流式处理出错", error);
},
() -> {
log.info("流式响应结束,开始处理业务===>>>");
}
);
// 方便Session中断时取消模型回复
chatFlow.put(session.getId(),disposable);
}
private void sendMessage(Session session, Object message) {
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(objMapper.writeValueAsString(message));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("发送WebSocket消息出错", e);
}
}基于WebSocket会话模式,其调用的依旧是流式接口,只不过增加了Session和ChatClient整体协调的复杂度,这种模式前端调用更加丝滑。
六、前端对接
1、接口对接思路
前端跟大模型对话的场景上,需要实现响应内容的分段输出。一是会提高接口的效率,二是减少用户不必要的等待时间,可以看到实时的内容。
前端是基于vue3和uni-app搭建的框架,所以用到了uni-app提供的request函数,调用这个流式接口。经过各种测试,该函数支持H5和小程序端,在app端不支持分段响应。永远都是把所有的响应一起返回。
于是找了其他办法,比如:1、封装XMLHttpRequest来实现SSE;2、使用分页和轮询模拟流;3、使用RenderJS,RenderJS是uni-app提供的一种运行在视图层的脚本技术,它可以直接操作视图层的DOM和BOM,特别适合处理高性能渲染需求。
第一种方式,在IOS运行没生效,第二种方式,觉得效率不高,第三种方式,小程序端不生效。
最后,左思右想,也参考了很多资料。还是采用websocket。
2、WebSocket对接和设计
WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议,它实现了浏览器与服务器之间的实时双向数据交换。
uni-app官方文档上就有专门支持WebSocket的函数,不管是H5端,小程序端,APP端都支持。所以果断采用了这个方案。
不过还是用后端的套路,避免过多的连接和断开连接,这样比较耗费资源,所以将用户的连接采用单例的方式进行管理。
展示一下完整的全局WebSocket管理器集成方案:
javascript
interface WebSocketConfig {
url: string
headers?: Record<string, string>
protocols?: string | string[]
}
interface WebSocketCallbacks {
onOpen?: (event: any) => void
onMessage?: (event: any) => void
onError?: (event: any) => void
onClose?: (event: any) => void
}
class WebSocketManager {
private static instance: WebSocketManager
private socketTask: any = null
private config: WebSocketConfig | null = null
private callbacks: WebSocketCallbacks = {}
private isConnecting = false
private reconnectTimer: any = null
private reconnectAttempts = 0
private maxReconnectAttempts = 5
private reconnectInterval = 3000
private constructor() {}
// 获取单例实例
static getInstance(): WebSocketManager {
if (!WebSocketManager.instance) {
WebSocketManager.instance = new WebSocketManager()
}
return WebSocketManager.instance
}
// 检查是否已连接
isConnected(): boolean {
return this.socketTask && this.socketTask.readyState === 1
}
// 连接WebSocket
async connect(config: WebSocketConfig, callbacks: WebSocketCallbacks = {}): Promise<boolean> {
// 如果已经连接且配置相同,直接返回
if (this.isConnected() && this.isSameConfig(config)) {
console.log('WebSocket已连接,复用现有连接')
this.updateCallbacks(callbacks)
return true
}
// 如果正在连接中,等待连接完成
if (this.isConnecting) {
console.log('WebSocket正在连接中,等待连接完成')
return this.waitForConnection()
}
// 关闭现有连接
if (this.socketTask) {
this.disconnect()
}
this.config = config
this.callbacks = callbacks
this.isConnecting = true
return new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('开始连接WebSocket:', config.url)
this.socketTask = uni.connectSocket({
url: config.url,
header: config.headers || {},
protocols: config.protocols,
success: () => {
console.log('WebSocket连接请求发送成功')
},
fail: (error) => {
console.error('WebSocket连接请求失败:', error)
this.isConnecting = false
this.callbacks.onError?.(error)
resolve(false)
}
})
// 连接打开
this.socketTask.onOpen((event: any) => {
console.log('WebSocket连接已打开')
this.isConnecting = false
this.reconnectAttempts = 0
this.clearReconnectTimer()
this.callbacks.onOpen?.(event)
resolve(true)
})
// 接收消息
this.socketTask.onMessage((event: any) => {
this.callbacks.onMessage?.(event)
})
// 连接错误
this.socketTask.onError((event: any) => {
console.error('WebSocket连接错误:', event)
this.isConnecting = false
this.callbacks.onError?.(event)
this.scheduleReconnect()
resolve(false)
})
// 连接关闭
this.socketTask.onClose((event: any) => {
console.log('WebSocket连接已关闭:', event)
this.isConnecting = false
this.callbacks.onClose?.(event)
// 如果不是主动关闭,尝试重连
if (event.code !== 1000) {
this.scheduleReconnect()
}
if (!this.isConnected()) {
resolve(false)
}
})
})
}
// 发送消息
send(data: string | ArrayBuffer): boolean {
if (!this.isConnected()) {
console.error('WebSocket未连接,无法发送消息')
return false
}
this.socketTask.send({
data: data,
success: () => {
console.log('WebSocket消息发送成功')
},
fail: (error: any) => {
console.error('WebSocket消息发送失败:', error)
}
})
return true
}
// 断开连接
disconnect(): void {
this.clearReconnectTimer()
if (this.socketTask) {
this.socketTask.close({
code: 1000,
reason: '主动断开连接'
})
this.socketTask = null
}
this.isConnecting = false
this.config = null
this.callbacks = {}
this.reconnectAttempts = 0
console.log('WebSocket连接已断开')
}
// 更新回调函数
updateCallbacks(callbacks: WebSocketCallbacks): void {
this.callbacks = { ...this.callbacks, ...callbacks }
}
// 获取连接状态
getStatus(): string {
if (this.isConnected()) return 'connected'
if (this.isConnecting) return 'connecting'
return 'disconnected'
}
}
// 导出单例实例
export const websocketManager = WebSocketManager.getInstance()
// 导出类型
export type { WebSocketConfig, WebSocketCallbacks }使用方式
简单使用
javascript
// 基本连接
const connected = await websocketManager.connect({
url: 'ws://example.com/socket',
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer token'
}
}, {
onMessage: (event) => {
console.log('收到消息:', event.data)
}
})检查连接状态
javascript
// 检查是否已连接
if (websocketManager.isConnected()) {
// 直接使用现有连接
websocketManager.send('hello')
} else {
// 需要先连接
await websocketManager.connect(config, callbacks)
}发送消息
javascript
// 发送消息
const success = websocketManager.send(JSON.stringify(data))
if (!success) {
console.error('发送失败,连接未建立')
}架构优势
性能优化
- 避免重复连接: 页面切换时复用连接
- 减少资源消耗: 单例模式减少内存占用
- 智能重连: 自动处理网络异常
代码简化
- 统一管理: 所有WebSocket逻辑集中管理
- 易于维护: 业务代码只需关注配置和回调
- 类型安全: 完整的TypeScript类型支持
扩展性强
- 多页面支持: 可在任意页面使用
- 配置灵活: 支持不同的URL和headers
- 回调自定义: 每个页面可定义自己的消息处理逻辑
3、websocket的设计优化
基于上面的封装,其实还有一点要考虑,WebSocket连接的断开时机,分了三个维度去考虑这个事情:
连接的断开时机
1. 应用进入后台时断开
- 时机: onHide 应用生命周期
- 原因: 节省资源,避免后台保持连接
- 优势: 系统资源优化,电池续航
2. 用户登出时断开
- 时机: 用户主动登出
- 原因: 安全考虑,避免无效连接
- 优势: 数据安全,连接清理
3. 长时间无活动时断开
- 时机: 设置定时器检测活动
- 原因: 避免僵尸连接
- 优势: 资源优化
所以对上面的WebSocketManager做了调整。
javascript
class WebSocketManager {
private static instance: WebSocketManager
private socketTask: any = null
private config: WebSocketConfig | null = null
private pageCallbacks: Map<string, WebSocketCallbacks> = new Map()
private currentPageId: string = ''
private connecting = false
private reconnectTimer: any = null
private reconnectAttempts = 0
private maxReconnectAttempts = 5
private reconnectInterval = 3000
// 连接管理相关
private lastActivityTime: number = Date.now()
private activityTimer: any = null
private inactivityTimeout = 30 * 60 * 1000 // 30分钟无活动自动断开
private isAppInBackground = false
// 发送消息
send(data: string | ArrayBuffer): boolean {
if (!this.isConnected()) {
console.error('WebSocket未连接,无法发送消息')
return false
}
// 记录用户活动
this.recordActivity()
this.socketTask.send({
data: data,
success: () => {
console.log('WebSocket消息发送成功')
},
fail: (error: any) => {
console.error('WebSocket消息发送失败:', error)
}
})
return true
}
// 记录用户活动
recordActivity(): void {
this.lastActivityTime = Date.now()
this.resetActivityTimer()
}
// 重置活动计时器
private resetActivityTimer(): void {
if (this.activityTimer) {
clearTimeout(this.activityTimer)
}
this.activityTimer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('WebSocket长时间无活动,自动断开连接')
this.disconnect()
}, this.inactivityTimeout)
}
// 应用进入后台
onAppHide(): void {
console.log('应用进入后台,断开WebSocket连接')
this.isAppInBackground = true
this.disconnect()
}
// 应用回到前台
onAppShow(): void {
console.log('应用回到前台')
this.isAppInBackground = false
}
// 用户登出时断开连接
onUserLogout(): void {
console.log('用户登出,断开WebSocket连接')
this.disconnect()
}
// 断开连接
disconnect(): void {
this.clearReconnectTimer()
this.clearActivityTimer()
if (this.socketTask) {
this.socketTask.close({
code: 1000,
reason: '主动断开连接'
})
this.socketTask = null
}
this.connecting = false
this.config = null
this.pageCallbacks.clear()
this.currentPageId = ''
this.reconnectAttempts = 0
console.log('WebSocket连接已断开')
}
// 清理活动计时器
private clearActivityTimer(): void {
if (this.activityTimer) {
clearTimeout(this.activityTimer)
this.activityTimer = null
}
}
}增加生命周期管理类
javascript
/**
* 应用生命周期管理
* 处理WebSocket连接的智能断开和重连
*/
import { websocketManager } from './websocket'
class AppLifecycleManager {
private static instance: AppLifecycleManager
private isInitialized = false
// 初始化应用生命周期监听
init(): void {
if (this.isInitialized) {
console.log('应用生命周期管理已初始化')
return
}
console.log('初始化应用生命周期管理')
// 监听应用隐藏(进入后台)
uni.onAppHide(() => {
console.log('应用进入后台')
websocketManager.onAppHide()
})
// 监听应用显示(回到前台)
uni.onAppShow(() => {
console.log('应用回到前台')
websocketManager.onAppShow()
})
// 监听网络状态变化
uni.onNetworkStatusChange((res) => {
console.log('网络状态变化:', res)
if (!res.isConnected) {
console.log('网络断开,断开WebSocket连接')
websocketManager.disconnect()
}
// 网络恢复时不自动重连,等待用户操作
})
this.isInitialized = true
}
// 用户登出时调用
onUserLogout(): void {
console.log('用户登出,清理WebSocket连接')
websocketManager.onUserLogout()
}
}
// 导出单例实例
export const appLifecycleManager = AppLifecycleManager.getInstance()最后,是断开连接的用法。
javascript
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
import { appLifecycleManager } from '@/utils/app-lifecycle';
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
actions: {
// 退出登录
logout() {
this.userInfo = null;
this.token = '';
this.isLoggedIn = false;
// 清除本地存储
uni.removeStorageSync('token');
uni.removeStorageSync('userInfo');
// 断开WebSocket连接
appLifecycleManager.onUserLogout();
}
}
});上面贴了部分核心代码,不过都是以自己后端的角度去考虑的。
最后,呼应上面,再列举不断开连接的情况。
不断开的情况
1. 页面切换时
- 保持连接: 在home和square页面间切换
- 原因: 提供流畅的用户体验
- 优势: 快速响应,无需重新连接
2. 应用回到前台时
- 不自动重连: 等待用户主动操作
- 原因: 按需连接,节省资源
- 优势: 用户控制连接时机
3. 网络恢复时
- 不自动重连: 等待用户发送消息时重连
- 原因: 避免不必要的连接
- 优势: 按需连接
4、WebSocket最后总结
这套封装,使WebSocket连接完全抽离为全局管理,首次进入页面会检查连接状态,有连接就复用,没有就初始化,外部只需要定义URL和请求头即可。
并且,连接也具有完整的智能管理策略,能够在合适的时机自动断开连接,既保证了用户体验,又优化了资源使用。
七、写在最后
对于大模型的集成,本质就是第三方API的调用,刚开始做的时候也有点犯难,不过花时间和心思研究文档之后,其实原理并不算复杂。
所谓套壳大模型的产品,体验上的差距更多在于:开发者对模型能力的理解和运用。有句话现在越来越认可,人工智能时代:模型本身即产品。
plain
文档仓库:
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-java-note
源码仓库:
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-mound