PyTorch 是一个开源深度学习框架
PyTorch 是动态图框架,TensorFlow 1.x 是静态图框架
静态图和动态图的区别
简介
静态图(Static Graph)是在运行前就把整个模型结构"画死"的图;动态图(Dynamic Graph)是在运行时一边运行一边"画图"的模型结构。
区别展示
你可以把模型比作"做饭的菜谱",来看这两种图的区别:
| 类别 | 类比 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 静态图 | 提前写好菜谱 | 执行前构建好计算图,运行时按图执行,优化快但不灵活 |
| 动态图 | 边做边调整 | 每一步运行时动态创建计算图,调试更方便,更灵活 |
📦 举例对比
静态图 严格按菜谱执行的新手厨师
python
# TensorFlow 1.x 静态图版:做面包 + 炖汤加盐(先写流程图)
import tensorflow as tf
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution() # 兼容 TF 1.x 风格
# Step 1: 构建菜谱图(只写,不执行)
flour = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32, name="flour")
salt = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32, name="salt")
bread = flour * 2 # 面包 = 面粉 * 2
soup = salt + 2 # 汤 = 盐 + 2
final_score = bread + soup # 总分 = 面包 + 汤
# Step 2: 开始下厨(运行图)
with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
result = sess.run(final_score, feed_dict={
flour: 300.0,
salt: 5.0
})
print("总分值:", result) # 输出 600 + 7 = 607动态图 边做边走的灵活厨子
python
# PyTorch 动态图版:做面包 + 炖汤加盐,边做边写步骤
import torch
# Step 1: 准备材料(定义变量)
flour = torch.tensor(300.0, requires_grad=True) # 面粉,单位克
salt = torch.tensor(5.0, requires_grad=True) # 盐,单位克
# Step 2: 动态进行计算(做菜)
# 做面包:面粉翻倍
bread = flour * 2
# 炖汤:加一点盐
soup = salt + 2
# 总菜品分值 = 面包量 + 汤咸度(举例)
final_score = bread + soup
# Step 3: 模拟反向传播(计算各食材对最终分值的影响)
final_score.backward()
# Step 4: 打印结果
print("总分值:", final_score.item()) # 输出面包 + 汤的"总分"
print("面粉的贡献(梯度):", flour.grad) # 面粉对总分的影响:2
print("盐的贡献(梯度):", salt.grad) # 盐对总分的影响:1PyTorch的基本概念
Tensor = 张量
Tensor 是 PyTorch 中存储数据的基本单位,类似于"高级的多维数组"。
常见Tensor
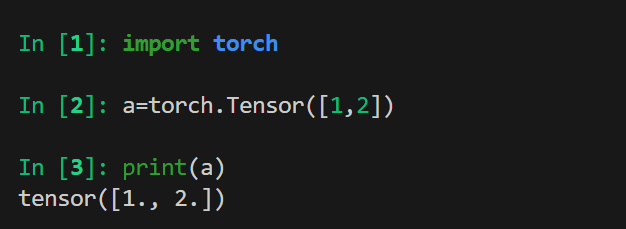
python
import torch
a=torch.Tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
print(a)
print(a.type())
''' 几种特殊的tensor'''
a = torch.ones(2,2)
print(a)
print(a.type())
a = torch.eye(2,2)
print(a)
print(a.type())
a = torch.zeros(2,2)
print(a)
print(a.type())
print(''' 随机 ''')
a = torch.rand(2,2)
print(a)
print(a.type())
''' 正态分布
mean : 均值
std : 标准差
'''
print(''' 正态分布 ''')
a = torch.normal(mean=torch.rand(5),std=torch.rand(5))
print(a)
print(a.type())
print(''' 均匀 ''')
a = torch.Tensor(2,2).uniform_(-1,1)
print(a)
print(a.type())
print(''' 序列 ''')
a = torch.arange(0,10,1)
print(a)
print(a.type())
print(''' 序列: 等间隔的 n 个数字 ''')
a =torch.linspace(2,10,3)
print(a)
print(a.type())Tensor的属性
类型(
dtype)、所存储设备名称(device)、内存布局的对象(layout)
稀疏的张量
当前非 0 元素 个数 越少越稀疏
python
import torch
dev = torch.device("cpu")
dev = torch.device("cuda:0")
a = torch.tensor([2,2],device=dev,dtype=torch.float32)
print(a)
###############################
#坐标
i = torch.tensor([[0,1,2],[0,1,2]])
#坐标值
v = torch.tensor([1,2,3])
x = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i,v,(4,4))
print(x)
x = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i,v,(4,4)).to_dense()
print(x)
x = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i,v,(4,4),
device=dev,
dtype=torch.float32).to_dense()
print(x)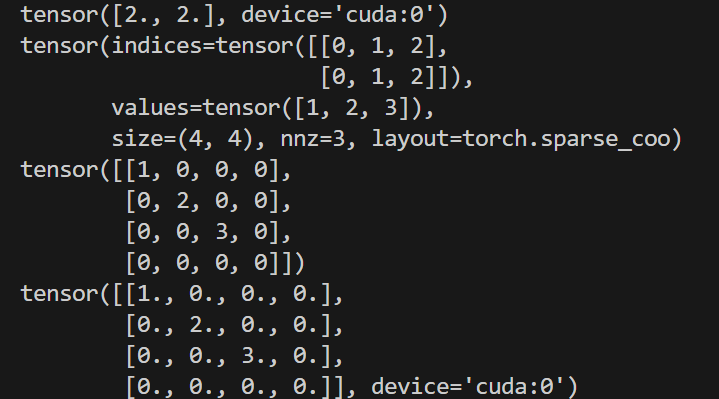
算数运算
python
import torch
a = torch.rand(2,3)
b = torch.rand(2,3)
b = 3.0
''' 加法 add '''
print(f"a + b = {a+b}")
print(f"torch.add(a,b) = {torch.add(a,b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
print(f"a.add_(b)={a.add_(b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
''' 减法 sub '''
print("=== sub ====")
print(f"a - b = {a-b}")
print(f"torch.sub(a,b) = {torch.sub(a,b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
print(f"a.sub_(b)={a.sub_(b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
''' 乘法 mul '''
print("=== 乘法 mul ===")
print(f"a * b = {a*b}")
print(f"torch.mul(a,b) = {torch.mul(a,b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
print(f"a.mul_(b)={a.mul_(b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
''' 除法 div'''
print("=== 除法 div ===")
print(f"a / b = {a/b}")
print(f"torch.div(a,b) = {torch.div(a,b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
print(f"a.div_(b)={a.div_(b)}")
print(f"a = {a}")
''' 取整/取余运算 '''
print("=== 取整/取余运算 ===")
a = torch.tensor([1.2,2.5,3.7])
print(f"向下取整 {a.floor()}")
print(f"向上取整 {a.ceil()}")
print(f"四舍五入 {a.round()}")
print(f"取余 {a%2}")
print(f"裁剪到[0,3] {a.clamp(0,3)}")
print(f"只取小数部分 {a.frac()}")
''' 矩阵乘法 matmul '''
print("=== 矩阵乘法 matmul ===")
a = torch.ones(2,1)
b = torch.ones(1,2)
print(f"a @ b = {a @ b}")
print(f"torch.matmul(a,b) = {torch.matmul(a,b)}")
print(f"torch.mm(a,b) = {torch.mm(a,b)}")
print(f"a.mm={a.mm(b)}")
''' 高维tensor '''
print("=== 高维tensor ===")
a = torch.ones(1,2,3,4)
b = torch.ones(1,2,4,3)
print(f"a.matmul(b) = {a.matmul(b)}")
print(f"{a.matmul(b).shape}")
''' pow '''
print("=== pow ===")
a = torch.tensor([1,2])
print(f"a.pow(2) = {a.pow(3)}")
print(f"a**3 = {a**3}")
print(f"a.pow_(2) = {a.pow_(3)}")
print(f"a.pow = {a.pow}")
''' 指数运算 exp '''
print("=== 指数运算 exp ===")
a = torch.tensor([1,2],dtype=torch.float32)
print(f"a.exp() = {a.exp()}")
print(f"a = {a}")
print(f"a.exp_() = {a.exp_()}")
print(f"a = {a}")
''' 对数运算 log '''
print("=== 对数运算 log ===")
a = torch.tensor([1,2],dtype=torch.float32)
print(f"torch.log(a) = {torch.log(a)}")
print(f"a.log() = {a.log()}")
print(f"a = {a}")
print(f"a.log_() = {a.log_()}")
print(f"a = {a}")
''' sqrt 开根号 :如果值为负数,则运算结果nan'''
print("=== sqrt ===")
a = torch.tensor([1,2],dtype=torch.float32)
print(f"torch.sqrt(a) = {torch.sqrt(a)}")
print(f"a.sqrt() = {a.sqrt()}")
print(f"a = {a}")
print(f"a.sqrt_() = {a.sqrt_()}")
print(f"a = {a}")in-place
就地操作,直接修改原来变量,不使用临时变量。如:
add_、sun_、mul_等
广播机制
当两个张量的形状不一样 时,PyTorch 会"自动扩展它们",让它们能正常进行运算。
满足条件:其中有一个值为1,或者值相等
例子
python
import torch
x = torch.tensor([10, 20, 30]) # shape = [3]
y = torch.tensor(2) # shape = []
z = x + y
print(z) # 输出:[12, 22, 32]比较运算
python
'''比较运算'''
a = torch.rand([2,3])
b = torch.rand([2,3])
print(a)
print(b)
# 比较两个张量中元素是否相等,返回布尔值张量
print(torch.eq(a,b))
# 比较两个张量中所有元素是否不相等,返回布尔值张量
print(torch.equal(a,b))
# 比较两个张量中元素是否不等于,返回布尔值张量
print(torch.ne(a,b))
# 比较两个张量中元素是否大等于,返回布尔值张量
print(torch.ge(a,b))
# 比较两个张量中元素是否小于等于,返回布尔值张量
print(torch.gt(a,b))
# 比较两个张量中元素是否小于,返回布尔值张量
print(torch.le(a,b))
# 比较两个张量中元素是否大于,返回布尔值张量
print(torch.lt(a,b))排序
dim: 指定排序的维度 ,默认为0
descending: 是否降序排序 ,默认为False
k: 指定返回前k个元素 ,默认为None
python
'''排序
dim: 指定排序的维度,默认为0
descending: 是否降序排序,默认为False
'''
print("=== 排序 ===")
a = torch.tensor([1, 4, 2, 4,8, 5])
print(a.shape)
print(a.sort())
print(torch.sort(a,dim=0,descending=True))
a= torch.tensor([[1, 4, 2, 4,8, 5],[1, 4, 2, 4,8, 5]])
print(a)
print(a.sort(dim=1,descending=False))前 k 个最大(或最小)和 第 k 个
python
'''前 k 个最大(或最小)的元素和索引'''
print("=== 前k个最大(或最小)的元素和索引 ===")
a = torch.tensor([3, 1, 4, 2, 5])
# 取前 3 个最大的元素(默认行为)
values, indices = torch.topk(a, k=3)
print(values) # tensor([5, 4, 3])
print(indices) # tensor([4, 2, 0])
# 取前 2 个最小的元素
values, indices = torch.topk(a, k=2, largest=False)
print(values) # tensor([1, 2])
print(indices) # tensor([1, 3])
'''张量中第 k 小的元素和索引'''
print("=== 张量中第 k 小的元素和索引 ===")
a = torch.tensor([3, 1, 4, 2, 5])
# 取第 3 小的元素(默认行为)
values, indices = torch.kthvalue(a, k=3)
print(values) # tensor(3)
print(indices) # tensor(0)
# 取第 2 小的元素
values, indices = torch.kthvalue(a, k=2)
print(values) # tensor(2)
print(indices) # tensor(3)数据合法性校验
isfinite: 判断是否是正常的有限 数值
isinf: 专门判断是否是无穷大
isnan: 专门判断是否是 NaN
python
'''
isfinite 判断是否是正常的有限数值
isinf 专门判断是否是无穷大
isnan 专门判断是否是 NaN
'''
print("=== 判断是否是正常的有限数值 ===")
import torch
x = torch.tensor([1.0, float('inf'), float('-inf'), float('nan'), 0.0])
print(x)
print(torch.isfinite(x)) # tensor([ True, False, False, False, True])
print(torch.isinf(x)) # tensor([False, True, True, False, False])
print(torch.isnan(x)) # tensor([False, False, False, True, False])三角函数
python
import torch
# 1. 基础三角函数(输入为弧度)
x = torch.tensor([0.0, torch.pi/2, torch.pi, 3*torch.pi/2])
print("sin:", torch.sin(x)) # tensor([ 0.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 8.7423e-08, -1.0000e+00])
print("cos:", torch.cos(x)) # tensor([ 1.0000e+00, 6.1232e-17, -1.0000e+00, -1.8369e-16])
print("tan:", torch.tan(x)) # tensor([ 0.0000e+00, 1.6331e+16, -8.7423e-08, 5.4437e+15])
# 2. 反三角函数(返回值为弧度)
y = torch.tensor([-1.0, 0.0, 1.0])
print("asin:", torch.asin(y)) # tensor([-1.5708, 0.0000, 1.5708]) # arcsin结果
print("acos:", torch.acos(y)) # tensor([ 3.1416, 1.5708, 0.0000]) # arccos结果
print("atan:", torch.atan(y)) # tensor([-0.7854, 0.0000, 0.7854]) # arctan结果
# atan2(处理象限问题)
a = torch.tensor([1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0])
b = torch.tensor([1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0])
print("atan2:", torch.atan2(a, b)) # tensor([ 0.7854, 2.3562, -2.3562, -0.7854])
# 3. 双曲函数
z = torch.tensor([0.0, 1.0, -1.0])
print("sinh:", torch.sinh(z)) # tensor([ 0.0000, 1.1752, -1.1752]) # 双曲正弦
print("cosh:", torch.cosh(z)) # tensor([1.0000, 1.5431, 1.5431]) # 双曲余弦
print("tanh:", torch.tanh(z)) # tensor([ 0.0000, 0.7616, -0.7616]) # 双曲正切
# 4. 角度转换
degrees = torch.tensor([0.0, 90.0, 180.0])
radians = torch.deg2rad(degrees)
print("角度转弧度:", radians) # tensor([0.0000, 1.5708, 3.1416])
radians = torch.tensor([0.0, torch.pi/2, torch.pi])
degrees = torch.rad2deg(radians)
print("弧度转角度:", degrees) # tensor([ 0., 90., 180.])其他数学函数
torch.abs()
计算输入张量每个元素的绝对值
python
x = torch.tensor([-1, 2, -3.5])
print(torch.abs(x)) # tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.5])torch.sign()
返回输入张量每个元素的符号(正为 1,负为 - 1,零为 0)
python
x = torch.tensor([-1, 2, 0, -3.5])
print(torch.sign(x)) # tensor([-1., 1., 0., -1.])torch.sigmoid()
计算输入张量每个元素的 Sigmoid 值,将值映射到
(0,1)区间
python
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 1.0, -1.0])
print(torch.sigmoid(x)) # tensor([0.5000, 0.7311, 0.2689])torch.erf()
计算输入张量每个元素的高斯误差函数
python
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 1.0, -1.0])
print(torch.erf(x)) # tensor([ 0.0000, 0.8427, -0.8427])torch.lerp()
在两个张量之间进行线性插值,lerp(start, end, weight) 计算 start + weight*(end-start)
python
a = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
b = torch.tensor([4.0, 5.0, 6.0])
print(torch.lerp(a, b, 0.5)) # tensor([2.5, 3.5, 4.5])torch.erfinv()
计算输入张量每个元素的误差函数的逆
python
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.8427])
print(torch.erfinv(x)) # tensor([0.0000, 1.0000])torch.addcdiv()
计算
input + value * (tensor1 / tensor2),用于避免中间张量创建
python
input = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0])
t1 = torch.tensor([4.0, 6.0])
t2 = torch.tensor([2.0, 3.0])
print(torch.addcdiv(input, 0.5, t1, t2)) # tensor([2.0, 3.0])torch.addcmul()
计算
input + value * (tensor1 * tensor2),用于避免中间张量创建
python
input = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0])
t1 = torch.tensor([2.0, 3.0])
t2 = torch.tensor([3.0, 4.0])
print(torch.addcmul(input, 0.5, t1, t2)) # tensor([4.0, 8.0])torch.neg()
计算输入张量每个元素的负值(乘以 - 1)
python
x = torch.tensor([1, -2, 3.5])
print(torch.neg(x)) # tensor([-1.0, 2.0, -3.5])torch.cumprod()
沿着指定维度计算张量元素的累积乘积
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(torch.cumprod(x, dim=0)) # tensor([1, 2, 6, 24])torch.reciprocal()
计算输入张量每个元素的倒数(1/x)
python
x = torch.tensor([2.0, 4.0, 0.5])
print(torch.reciprocal(x)) # tensor([0.5000, 0.2500, 2.0000])torch.cumsum()
沿着指定维度计算张量元素的累积和
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(torch.cumsum(x, dim=0)) # tensor([ 1, 3, 6, 10])torch.rsqrt()
计算输入张量每个元素的平方根的倒数
(1/√x)
python
x = torch.tensor([4.0, 9.0, 1.0])
print(torch.rsqrt(x)) # tensor([0.5000, 0.3333, 1.0000])统计学相关函数
torch.mean()
计算张量所有元素的平均值
python
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
print(torch.mean(x)) # tensor(2.)torch.sum()
计算张量所有元素的总和
python
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
print(torch.sum(x)) # tensor(6.)torch.prod()
计算张量所有元素的乘积
python
x = torch.tensor([2.0, 3.0, 4.0])
print(torch.prod(x)) # tensor(24.)torch.max()
返回张量中的最大元素
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 5, 3])
print(torch.max(x)) # tensor(5)torch.min()
返回张量中的最小元素
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 5, 3])
print(torch.min(x)) # tensor(1)torch.argmax()
返回最大值的索引位置
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 5, 3])
print(torch.argmax(x)) # tensor(1)torch.argmin()
返回最小值的索引位置
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 5, 3])
print(torch.argmin(x)) # tensor(0)torch.std()
返回张量元素的标准差
python
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
print(torch.std(x)) # tensor(1.)torch.var()
返回张量元素的方差
python
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
print(torch.var(x)) # tensor(1.)torch.median()
返回中间值(排序后居中那个)
python
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 5.0, 3.0])
print(torch.median(x)) # tensor(3.)torch.mode()
返回张量中最常出现的元素及其索引
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2])
mode, index = torch.mode(x)
print(mode, index) # tensor(3), tensor(1)torch.histc()
将输入张量的值分桶,统计频率(仅适用于浮点张量)
python
x = torch.tensor([1., 2., 1., 2., 5.])
print(torch.histc(x, bins=5, min=1, max=5))
# tensor([2., 0., 2., 0., 1.])torch.bincount()
统计每个非负整数出现的次数
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 4])
print(torch.bincount(x))
# tensor([0, 3, 2, 1, 1])分布函数
torch.distributions
torch.distributions.Normal()
用于创建一个正态分布对象,包含均值和标准差
python
from torch.distributions import Normal
dist = Normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0)
sample = dist.sample() # 从正态分布中采样
log_prob = dist.log_prob(torch.tensor(0.0)) # 计算对数概率
print(sample, log_prob)torch.distributions.Bernoulli()
适用于只有两个可能结果的情况(0 或 1)
python
from torch.distributions import Bernoulli
dist = Bernoulli(probs=0.7)
sample = dist.sample()
log_prob = dist.log_prob(sample)
print(sample, log_prob)torch.distributions.Binomial()
适用于重复试验中成功次数的建模
python
from torch.distributions import Binomial
dist = Binomial(total_count=10, probs=0.5)
sample = dist.sample()
print(sample)torch.distributions.Categorical()
用于单次从多个类别中采样
python
from torch.distributions import Categorical
dist = Categorical(probs=torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.7]))
sample = dist.sample()
print(sample)torch.distributions.Uniform()
在指定区间内均匀采样
python
from torch.distributions import Uniform
dist = Uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0)
sample = dist.sample()
print(sample)torch.distributions.Exponential()
建模等待时间等事件
python
from torch.distributions import Exponential
dist = Exponential(rate=1.0)
sample = dist.sample()
print(sample)torch.distributions.MultivariateNormal()
用于多维正态分布建模
python
from torch.distributions import MultivariateNormal
mean = torch.zeros(2)
cov = torch.eye(2)
dist = MultivariateNormal(mean, covariance_matrix=cov)
sample = dist.sample()
print(sample)torch.distributions.Gumbel()
常用于极值建模、用于 Gumbel-Softmax 技巧
python
from torch.distributions import Gumbel
dist = Gumbel(loc=0.0, scale=1.0)
sample = dist.sample()
print(sample)随机抽样
torch.rand()
生成 [0, 1) 区间的均匀分布随机数
python
x = torch.rand(2, 3)
print(x)torch.randn()
生成均值为0、标准差为1的正态分布随机数
python
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(x)torch.randint()
生成给定范围内的随机整数
python
x = torch.randint(low=0, high=10, size=(2, 3))
print(x)torch.randperm()
返回 0 到 n-1 的随机排列(打乱顺序)
python
x = torch.randperm(5)
print(x) # 如 tensor([2, 0, 3, 1, 4])torch.manual_seed()
确保随机结果可复现(固定随机数序列)
python
torch.manual_seed(42)
print(torch.rand(2)) # 每次运行结果一致torch.multinomial()
根据给定概率分布,从元素中有放回/无放回地抽样
python
weights = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.6])
sample = torch.multinomial(weights, num_samples=5, replacement=True)
print(sample)torch.bernoulli()
根据给定概率,采样 0 或 1(类似投硬币)
python
probs = torch.tensor([0.2, 0.8, 0.5])
sample = torch.bernoulli(probs)
print(sample)范数运算
torch.norm()
计算张量的范数(如 L1、L2 范数等)
python
x = torch.tensor([3.0, 4.0])
print(torch.norm(x)) # 默认是 L2 范数,结果为 5.0
print(torch.norm(x, p=1)) # L1 范数,结果为 7.0torch.linalg.norm()
计算矩阵或向量的各种矩阵范数(推荐使用)
python
x = torch.tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]])
print(torch.linalg.norm(x)) # Frobenius 范数
print(torch.linalg.norm(x, ord='nuc')) # 核范数(奇异值之和)torch.nn.functional.normalize()
范数 = 一个数,用来表示一组数"有多大"
对张量按指定范数进行归一化
python
import torch.nn.functional as F
x = torch.tensor([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]])
out = F.normalize(x, p=2, dim=1)
print(out)矩阵分解
torch.linalg.svd()
奇异值分解(Singular Value Decomposition)
把一个矩阵拆成三个矩阵 U、S、V,使得 A = U @ diag(S) @ Vᴴ
python
A = torch.tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]])
U, S, Vh = torch.linalg.svd(A)
print(U, S, Vh)torch.linalg.eig()
计算方阵的特征值和特征向量
可用于对称矩阵或一般方阵的特征分解
python
A = torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., 1.]])
eigvals, eigvecs = torch.linalg.eig(A)
print(eigvals, eigvecs)torch.linalg.eigh()
专门用于对称矩阵的特征值分解(更稳定)
返回实数特征值和特征向量
python
A = torch.tensor([[2., -1.], [-1., 2.]])
eigvals, eigvecs = torch.linalg.eigh(A)
print(eigvals, eigvecs)torch.linalg.qr()
QR分解:将矩阵分解为正交矩阵Q和上三角矩阵R
python
A = torch.tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]])
Q, R = torch.linalg.qr(A)
print(Q, R)torch.linalg.cholesky()
Cholesky分解:用于对称正定矩阵,返回下三角矩阵L使 A = L @ L.T
python
A = torch.tensor([[4., 2.], [2., 3.]])
L = torch.linalg.cholesky(A)
print(L)