目录
[优雅实现 Spring RabbitMQ 多交换机多队列绑定](#优雅实现 Spring RabbitMQ 多交换机多队列绑定)
[1. 配置定义(枚举方式)](#1. 配置定义(枚举方式))
[2. 声明式配置工厂](#2. 声明式配置工厂)
[3. 生产者服务(通用发送方法)](#3. 生产者服务(通用发送方法))
[4. 消费者抽象基类](#4. 消费者抽象基类)
[5. 具体消费者实现](#5. 具体消费者实现)
[6. 配置中心扩展(YAML 配置)](#6. 配置中心扩展(YAML 配置))
[1. 架构优势](#1. 架构优势)
[2. 扩展点设计](#2. 扩展点设计)
优雅实现 Spring RabbitMQ 多交换机多队列绑定
在需要创建多个交换机、每个交换机绑定多个队列的场景中,通过合理设计可以显著提高代码的复用性和扩展性。以下是针对 3 个交换机各绑定 3 个队列的优雅实现方案:
一、核心设计思路
-
配置驱动:使用枚举或配置类定义交换机、队列和路由键
-
工厂模式:创建交换机、队列和绑定的工厂方法
-
自动绑定:通过反射或配置自动创建绑定关系
-
模板方法:复用消费者处理逻辑
二、完整实现代码
1. 配置定义(枚举方式)
public enum RabbitConfigEnum {
// 订单业务
ORDER_EXCHANGE(
"order.direct.exchange",
ExchangeTypes.DIRECT,
Arrays.asList(
new QueueConfig("order.create.queue", "order.create"),
new QueueConfig("order.pay.queue", "order.pay"),
new QueueConfig("order.cancel.queue", "order.cancel")
)
),
// 库存业务
INVENTORY_EXCHANGE(
"inventory.topic.exchange",
ExchangeTypes.TOPIC,
Arrays.asList(
new QueueConfig("inventory.deduct.queue", "inventory.deduct"),
new QueueConfig("inventory.restore.queue", "inventory.restore.*"),
new QueueConfig("inventory.alert.queue", "inventory.alert.#")
)
),
// 通知业务
NOTIFICATION_EXCHANGE(
"notification.fanout.exchange",
ExchangeTypes.FANOUT,
Arrays.asList(
new QueueConfig("email.notification.queue", ""), // Fanout 不需要路由键
new QueueConfig("sms.notification.queue", ""),
new QueueConfig("push.notification.queue", "")
)
);
private final String exchangeName;
private final ExchangeType exchangeType;
private final List<QueueConfig> queueConfigs;
RabbitConfigEnum(String exchangeName, ExchangeType exchangeType, List<QueueConfig> queueConfigs) {
this.exchangeName = exchangeName;
this.exchangeType = exchangeType;
this.queueConfigs = queueConfigs;
}
// 队列配置内部类
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public static class QueueConfig {
private final String queueName;
private final String routingKey;
}
// 交换机类型枚举
public enum ExchangeType {
DIRECT, TOPIC, FANOUT
}
// 获取所有配置
public static List<RabbitConfigEnum> getAllConfigs() {
return Arrays.asList(values());
}
}2. 声明式配置工厂
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfigFactory {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMQConfigFactory.class);
@Bean
public Declarables createRabbitElements() {
List<Declarable> declarables = new ArrayList<>();
for (RabbitConfigEnum config : RabbitConfigEnum.getAllConfigs()) {
// 创建交换机
AbstractExchange exchange = createExchange(
config.getExchangeName(),
config.getExchangeType()
);
declarables.add(exchange);
logger.info("Created exchange: {}", config.getExchangeName());
// 为交换机创建队列和绑定
for (RabbitConfigEnum.QueueConfig queueConfig : config.getQueueConfigs()) {
Queue queue = new Queue(queueConfig.getQueueName(), true);
declarables.add(queue);
Binding binding = createBinding(
exchange,
queue,
queueConfig.getRoutingKey(),
config.getExchangeType()
);
declarables.add(binding);
logger.info("Created queue '{}' bound to '{}' with routing key '{}'",
queueConfig.getQueueName(),
config.getExchangeName(),
queueConfig.getRoutingKey());
}
}
return new Declarables(declarables);
}
private AbstractExchange createExchange(String name, RabbitConfigEnum.ExchangeType type) {
return switch (type) {
case DIRECT -> new DirectExchange(name, true, false);
case TOPIC -> new TopicExchange(name, true, false);
case FANOUT -> new FanoutExchange(name, true, false);
};
}
private Binding createBinding(AbstractExchange exchange, Queue queue,
String routingKey, RabbitConfigEnum.ExchangeType type) {
return switch (type) {
case DIRECT, TOPIC -> BindingBuilder.bind(queue)
.to(exchange)
.with(routingKey);
case FANOUT -> BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to((FanoutExchange) exchange);
};
}
// 统一消息转换器
@Bean
public MessageConverter jsonMessageConverter() {
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}3. 生产者服务(通用发送方法)
@Service
public class RabbitMQProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 通用消息发送方法
*
* @param exchange 交换机名称
* @param routingKey 路由键
* @param message 消息内容
*/
public void sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, message, m -> {
MessageProperties props = m.getMessageProperties();
props.setContentType(MessageProperties.CONTENT_TYPE_JSON);
props.setTimestamp(new Date());
return m;
});
logger.debug("Sent message to {}[{}]: {}", exchange, routingKey, message);
}
/**
* 按业务发送消息(推荐)
*
* @param config 业务配置
* @param routingKey 路由键
* @param message 消息内容
*/
public void sendByConfig(RabbitConfigEnum config, String routingKey, Object message) {
sendMessage(config.getExchangeName(), routingKey, message);
}
}4. 消费者抽象基类
public abstract class AbstractRabbitConsumer<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractRabbitConsumer.class);
/**
* 通用消息处理模板
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @param channel RabbitMQ通道
* @param tag 消息标签
*/
@RabbitHandler
public void handleMessage(T message, Channel channel,
@Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) {
try {
// 1. 业务处理
processMessage(message);
// 2. 手动ACK确认
channel.basicAck(tag, false);
logger.debug("Message processed: {}", message);
} catch (BusinessException e) {
// 业务异常处理
handleBusinessException(e, message, channel, tag);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 系统异常处理
handleSystemException(e, message, channel, tag);
}
}
/**
* 业务处理抽象方法(子类实现)
*/
protected abstract void processMessage(T message) throws BusinessException;
/**
* 业务异常处理(可重写)
*/
protected void handleBusinessException(BusinessException e, T message,
Channel channel, long tag) throws IOException {
logger.error("Business error processing message: {}", message, e);
// 拒绝消息但不重试
channel.basicReject(tag, false);
}
/**
* 系统异常处理(可重写)
*/
protected void handleSystemException(Exception e, T message,
Channel channel, long tag) throws IOException {
logger.error("System error processing message: {}", message, e);
// 拒绝消息并重新入队
channel.basicReject(tag, true);
}
}5. 具体消费者实现
// 订单创建消费者
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "order.create.queue")
public class OrderCreateConsumer extends AbstractRabbitConsumer<Order> {
@Autowired
private InventoryService inventoryService;
@Override
protected void processMessage(Order order) throws BusinessException {
// 减库存
inventoryService.deductStock(order.getProductId(), order.getQuantity());
// 记录订单
orderService.saveOrder(order);
// 发送创建事件
eventPublisher.publishOrderCreated(order);
}
// 重写异常处理
@Override
protected void handleBusinessException(BusinessException e, Order order,
Channel channel, long tag) throws IOException {
if (e instanceof InventoryShortageException) {
// 库存不足特殊处理
orderService.markAsPending(order);
channel.basicAck(tag, false);
} else {
super.handleBusinessException(e, order, channel, tag);
}
}
}
// 库存告警消费者
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "inventory.alert.queue")
public class InventoryAlertConsumer extends AbstractRabbitConsumer<InventoryAlert> {
@Override
protected void processMessage(InventoryAlert alert) {
// 发送告警通知
notificationService.sendAlert(
alert.getProductId(),
alert.getCurrentLevel()
);
// 记录告警日志
alertService.logAlert(alert);
}
}6. 配置中心扩展(YAML 配置)
# application.yml
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: rabbitmq-prod.example.com
port: 5672
username: ${RABBIT_USER}
password: ${RABBIT_PASS}
virtual-host: /prod
listener:
simple:
acknowledge-mode: manual
concurrency: 3
max-concurrency: 10
prefetch: 20
# 自定义交换机配置(可选扩展)
rabbit:
exchanges:
- name: order.direct.exchange
type: DIRECT
queues:
- name: order.create.queue
routing-key: order.create
- name: order.pay.queue
routing-key: order.pay
- name: order.cancel.queue
routing-key: order.cancel
- name: inventory.topic.exchange
type: TOPIC
queues:
- name: inventory.deduct.queue
routing-key: inventory.deduct
- name: inventory.restore.queue
routing-key: inventory.restore.*
- name: inventory.alert.queue
routing-key: inventory.alert.#三、设计优势与扩展点
1. 架构优势
| 设计特点 | 优势 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 配置枚举化 | 集中管理所有配置,避免硬编码 | 多环境部署 |
| 工厂模式 | 统一创建逻辑,减少重复代码 | 新增交换机/队列 |
| 抽象消费者 | 统一异常处理和ACK机制 | 所有消费者 |
| 通用生产者 | 简化消息发送接口 | 所有业务场景 |
2. 扩展点设计
扩展点 1:动态添加新交换机
// 添加新业务配置
RabbitConfigEnum.NEW_EXCHANGE = new RabbitConfigEnum(
"new.exchange",
ExchangeTypes.DIRECT,
Arrays.asList(
new QueueConfig("new.queue1", "key1"),
new QueueConfig("new.queue2", "key2")
)
);扩展点 2:自定义绑定逻辑
// 重写绑定工厂方法
private Binding createCustomBinding(AbstractExchange exchange, Queue queue,
String routingKey, ExchangeType type) {
if ("special.binding".equals(routingKey)) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue)
.to(exchange)
.with(routingKey)
.and(createCustomArguments()); // 自定义参数
}
return createBinding(exchange, queue, routingKey, type);
}扩展点 3:基于配置文件的动态配置
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "rabbit")
public class DynamicRabbitConfig {
private List<ExchangeConfig> exchanges;
@Bean
public Declarables dynamicDeclarables() {
// 类似工厂方法实现,从配置文件读取
}
@Getter @Setter
public static class ExchangeConfig {
private String name;
private String type;
private List<QueueBinding> queues;
}
@Getter @Setter
public static class QueueBinding {
private String name;
private String routingKey;
}
}四、最佳实践建议
1.命名规范
// 业务.类型.功能
String exchangeName = "order.direct.exchange";
String queueName = "inventory.topic.alert.queue";
String routingKey = "order.payment.completed";2.监控增强
// 在生产者中添加监控埋点
public void sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(metricsRegistry);
// ...发送逻辑
sample.stop(metricsRegistry.timer("rabbit.produce.time",
"exchange", exchange,
"routingKey", routingKey));
}3.单元测试方案
@SpringBootTest
public class RabbitConfigTest {
@Autowired
private RabbitAdmin rabbitAdmin;
@Test
public void testExchangeAndQueueCreation() {
// 验证所有交换机已创建
for (RabbitConfigEnum config : RabbitConfigEnum.values()) {
Exchange exchange = new DirectExchange(config.getExchangeName());
assertTrue(rabbitAdmin.getExchangeInfo(exchange.getName()) != null);
// 验证队列绑定
for (QueueConfig qc : config.getQueueConfigs()) {
Queue queue = new Queue(qc.getQueueName());
assertTrue(rabbitAdmin.getQueueInfo(queue.getName()) != null);
}
}
}
}4.消费者弹性配置
# 针对不同队列配置不同消费者参数
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
order:
concurrency: 5
max-concurrency: 20
notification:
concurrency: 2
max-concurrency: 5五、架构演进方向
1.配置中心集成
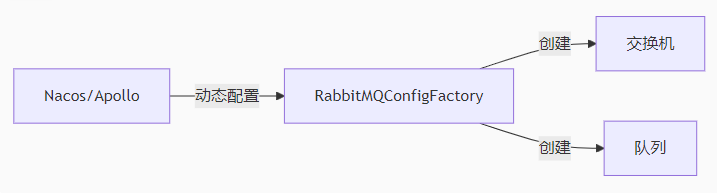
2.消息路由服务
@Service
public class MessageRouter {
private Map<MessageType, RabbitConfigEnum> routingMap;
public void routeMessage(MessageType type, Object message) {
RabbitConfigEnum config = routingMap.get(type);
producer.sendByConfig(config, config.getDefaultKey(), message);
}
}3.流量控制中间件
@Around("@annotation(rabbitListener)")
public Object rateLimit(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
if (!rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
// 返回特殊响应,触发消费者暂停
return new RateLimitExceededResponse();
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}这种设计通过配置驱动、工厂模式和模板方法,实现了高可复用的 RabbitMQ 集成方案,能够轻松应对业务扩展需求,同时保持代码的简洁性和可维护性。