(1)程序阅读
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main(){
int i,j,n;
cin >> n;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(j = 1; j <= n - i;j++)
cout << " ";
for(j = 1; j < i; j++)
cout << "*";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main(){
int i,j,n;
cin >> n;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++){
j = i - 1;
while(j > 1 && i % j != 0)
j--;
cout << i << "(" << j << ")\n";
}
return 0;
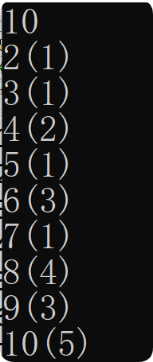
}
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main() {
int i, m, n = 0;
for(i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
m = i % 2;
while(m-- > 0) n++;
}
cout << m << "," << n;
return 0;
}
-1,3
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << n << "=";
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for(; n % i == 0;) {
n = n / i;
cout << i;
if(n != 1) cout << "*";
}
}
return 0;
}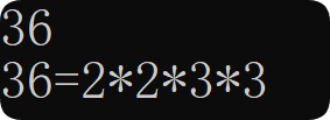


cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
assert(1 <= n && n <= 20);
for (int row = 1; row <= n; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col <= n + row - 1; col++) {
if (col <= n - row) {
cout << " ";
} else {
cout << "*";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
assert(1 <= n && n <= 10);
for(int row = 1; row <= n; row++) {
int i = 1;
for(int col = 1; col <= n + row - 1; col++) {
if(col < n - row + 1) {
cout << " ";
} else {
cout << i++;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
for(int row = n - 1; row >= 1; row--) {
int i = 1;
for(int col = 1; col <= n + row - 1; col++) {
if(col < n - row + 1) {
cout << " ";
} else {
cout << i++;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}

cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
assert(1 <= n && n <= 9);
for(int row = 1; row <= n; row++) {
for(int col = 1; col <= row; col++) {
cout << col << "*" << row << "=" << col*row << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
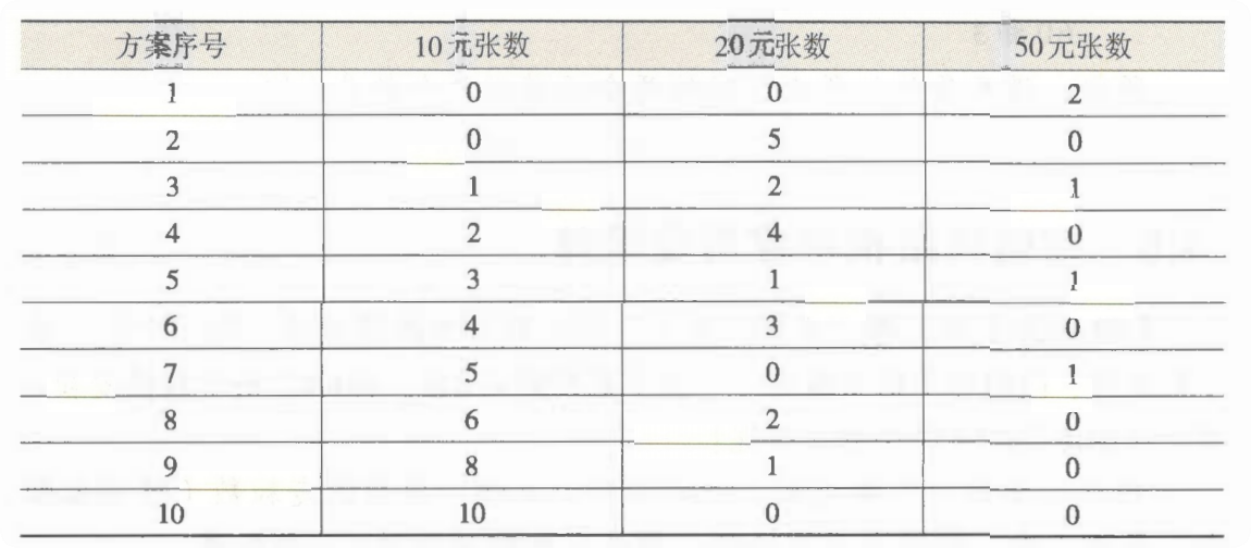
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
assert(100 <= n);
int ways = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= n / 50; i++) {
ways += (n - i * 50) / 20 + 1;
}
cout << ways << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//汤永红
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
assert(n >= 1);
int sumOfDigits = 0;
while(1) {
while(n > 0) {
sumOfDigits += n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
if (sumOfDigits < 10) {
break;
} else {
n = sumOfDigits;
sumOfDigits = 0;
}
}
cout << sumOfDigits << endl;
return 0;
}
典型的数论题目,考查的是最大公约数(gcd)与最小公倍数(lcm)的定义和性质。
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x0, y0;
cin >> x0 >> y0;
if (y0 % x0 != 0) {
cout << 0 << endl; // 如果不能整除,直接输出0
return 0;
}
int k = y0 / x0;
int count = 0;
for (int a = 1; a * a <= k; ++a) {
if (k % a == 0) {
int b = k / a;
// 计算 a 和 b 的最大公约数(不用函数)
int m = a, n = b;
while (n != 0) {
int r = m % n;
m = n;
n = r;
}
int d = m; // 此时 d = gcd(a, b)
if (d == 1) {
if (a == b)
count += 1; // (a, a) 只算一种
else
count += 2; // (a, b) 和 (b, a) 算两种
}
}
}
cout << count << endl;
return 0;
}