前言
RAG通常的流程是先从向量数据库里根据用户输入检索相关文档,然后用语言模型生成回答。
Self-RAG,就是在RAG的基础上加了"反思"步骤。这种方法能让LLM自己控制什么时候检索、怎么评估相关性、怎么批评自己的回答,以及怎么调整行为,从而提高回答的准确性和真实性。
Self-RAG的动机
传统的RAG流程不管相关性如何,也不管是否真的需要检索,都会检索固定数量的文档。Self-RAG通过让模型自己决定是否需要检索、哪些段落要包括进来,以及什么时候要批评或者调整回答,来增强这个流程。这种"反思"的方法能让LangGraph的流程变得更加动态和灵活。
Self-RAG用到的"反思"标记
Self-RAG用了一些特殊的标记(叫"反思标记")来标记检索和生成过程中的各种决策:
- 检索标记(Retrieve Token):决定是否要进行检索。
- 相关性标记(ISREL Token):判断检索到的文档是否和问题相关。
- 支持性标记(ISSUP Token):确保生成的回答是基于检索到的文档的。
- 有用性标记(ISUSE Token):衡量生成的回答是否真的有用。
这些标记能让模型变得更加灵活,还能让它在生成回答的过程中实时调整自己的行为,从而最大化回答的相关性、真实性和上下文准确性。
示例代码
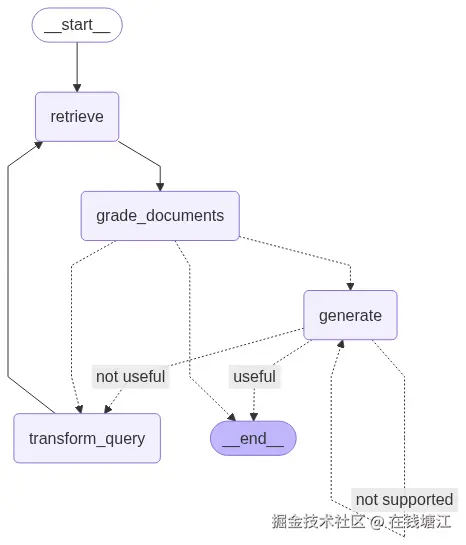
构建一个示例,下面是流程图
python
from typing import List, TypedDict
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_community.embeddings import DashScopeEmbeddings
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain.schema import Document # Import the Document class
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_text_splitters import CharacterTextSplitter
# pip install pypdf
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
# pip install beautifulsoup4
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
load_dotenv()
embeddings = DashScopeEmbeddings(
dashscope_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
model="text-embedding-v4",
)
model = ChatOpenAI(model="qwen-plus",
base_url=os.getenv("BASE_URL"),
api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
temperature=0,
streaming=True)
def load_from_url(url: str) -> List[Document]:
return WebBaseLoader(url).load()
def split_docs(docs: List[Document]) -> List[Document]:
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=250, chunk_overlap=0)
return text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
def create_db(docs: List[Document]):
if len(docs) <= 10:
res = Chroma.from_documents(documents=docs, embedding=embeddings)
else:
first_docs = docs[:10]
res = Chroma.from_documents(documents=first_docs, embedding=embeddings)
left = 10
while left < len(docs):
right = min(left + 10, len(docs))
seg_docs = docs[left:right]
res.add_documents(seg_docs)
left += 10
return res
docs = load_from_url("https://faiss.ai/")
db = create_db(split_docs(docs))
retriever = db.as_retriever()
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""
使用以下上下文简洁地回答问题:
Question: {question}
Context: {context}
Answer:
""")
rag_chain = (prompt | model | StrOutputParser())
class GraphState(TypedDict):
question: str
generation: str
documents: List[str]
# Retrieval Grader setup
class GradeDocuments(BaseModel):
binary_score: str = Field(description="Documents are relevant to the question, 'yes' or 'no'")
# 获取文档评分
retrieval_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""
您是一名评分员,负责评估文档是否与用户的问题相关。
Document: {document}
Question: {question}
Is the document relevant? Answer 'yes' or 'no'.
You must respond using JSON format with the following structure:
{{"binary_score": "yes or no"}}
""")
retrieval_grader = retrieval_prompt | model.with_structured_output(GradeDocuments)
class GradeHallucinations(BaseModel):
binary_score: str = Field(description="Answer is grounded in the documents, 'yes' or 'no'")
# 答案是否基于文档
hallucination_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""
你是一名评分员,评估答案是否基于检索到的文档。
Documents: {documents}
Answer: {generation}
Is the answer grounded in the documents? Answer 'yes' or 'no'.
You must respond using JSON format with the following structure:
{{"binary_score": "yes or no"}}
""")
hallucination_grader = hallucination_prompt | model.with_structured_output(GradeHallucinations)
class GradeAnswer(BaseModel):
binary_score: str = Field(description="Answer addresses the question, 'yes' or 'no'")
# 答案解决问题程度评分
answer_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""
你是一名评分员,评估答案是否解决了用户的问题。
Question: {question}
Answer: {generation}
Does the answer address the question? Answer 'yes' or 'no'.
You must respond using JSON format with the following structure:
{{"binary_score": "yes or no"}}
""")
answer_grader = answer_prompt | model.with_structured_output(GradeAnswer)
def retrieve(state):
print("-- 获取文档 --")
question = state["question"]
documents = retriever.invoke(question)
print("documents=", len(documents))
return {"documents": documents, "question": question}
def generate(state):
print("-- 生成答案 --")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
generation = rag_chain.invoke({"context": documents, "question": question})
return {"documents": documents, "question": question, "generation": generation}
# 文档相关性处理
def grade_documents(state):
print("-- 文档相关性处理 --")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
relevant_docs = []
for doc in documents:
response = retrieval_grader.invoke({"question": question, "document": doc.page_content})
if response.binary_score == "yes":
relevant_docs.append(doc)
print("relevant_docs=", len(relevant_docs))
return {"documents": relevant_docs, "question": question}
# 决定是继续生成还是转换查询。
def decide_to_generate(state):
print("-- 决定是继续生成还是转换查询 --")
if not state["documents"]:
print("转换查询")
return "transform_query" # No relevant docs found; rephrase query
print("生成")
return "generate" # Relevant docs found; proceed to generate
# 检查生成是否基于检索到的文档,并回答问题。
def grade_generation_v_documents_and_question(state):
print("-- 检查生成是否基于检索到的文档 --")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
generation = state["generation"]
# Step 1: Check if the generation is grounded in documents
hallucination_check = hallucination_grader.invoke({"documents": documents, "generation": generation})
print("hallucination_check=", hallucination_check)
if hallucination_check.binary_score == "no":
return "not supported" # Regenerate if generation isn't grounded in documents
# Step 2: Check if generation addresses the question
answer_check = answer_grader.invoke({"question": question, "generation": generation})
print("answer_check=", answer_check)
return "useful" if answer_check.binary_score == "yes" else "not useful"
# 如果初始尝试没有产生相关文档,则重新表述查询以改进检索。
def transform_query(state):
print("-- 问题描述重写 --")
# 问题描述重写
transform_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""
您是一个问题重写器,可以将输入问题转换为更好的版本,以优化检索相关文档。
Original question: {question}
请提供一个重新表述的问题.
""")
question_rewriter = transform_prompt | model | StrOutputParser()
question = state["question"]
# Rephrase the question using LLM
transformed_question = question_rewriter.invoke({"question": question})
return {"question": transformed_question, "documents": state["documents"]}
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
workflow.add_node("retrieve", retrieve)
workflow.add_node("generate", generate)
workflow.add_node("grade_documents", grade_documents)
workflow.add_node("transform_query", transform_query)
workflow.add_edge(START, "retrieve")
workflow.add_edge("retrieve", "grade_documents")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"grade_documents",
decide_to_generate,
{
"transform_query": "transform_query",
"generate": "generate"
})
workflow.add_edge("transform_query", "retrieve")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"generate",
grade_generation_v_documents_and_question,
{
"not supported": "generate",
"useful": END,
"not useful": "transform_query"
})
app = workflow.compile(checkpointer=MemorySaver())
# Example input
config = {
"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"},
"recursion_limit": 50
}
inputs = {"question": "解释下faiss如何工作的,内部的基本原理和性能参数"}
# inputs = {"question": "解释下faiss如何工作的"}
# inputs = {"question": "解释下地球如何自转的"}
for output in app.stream(inputs, config=config,
stream_mode="values", debug=False):
current_state = app.get_state(config)
v = current_state.values
print("*" * 50)
# print("output", output)
print("question", v["question"])
print("generation", v["generation"] if "generation" in v else "")
print("documents", len(v["documents"]) if "documents" in v else 0)
print()问一个可以查到资料的问题
markdown
**************************************************
question 解释下faiss如何工作的,内部的基本原理和性能参数
generation
documents 0
-- 获取文档 --
documents= 4
**************************************************
question 解释下faiss如何工作的,内部的基本原理和性能参数
generation
documents 0
-- 文档相关性处理 --
relevant_docs= 3
-- 决定是继续生成还是转换查询 --
生成
**************************************************
question 解释下faiss如何工作的,内部的基本原理和性能参数
generation
documents 3
-- 生成答案 --
-- 检查生成是否基于检索到的文档 --
hallucination_check= binary_score='yes'
answer_check= binary_score='yes'
**************************************************
question 解释下faiss如何工作的,内部的基本原理和性能参数
generation Faiss 是一个用于高效**相似性搜索**和**向量聚类**的库,适用于大规模密集向量集合。其基本原理是:
- 给定一组 $d$ 维向量 $x_i$,Faiss 在内存中构建一个数据结构;
- 当给定一个新的查询向量 $x$ 时,它可以高效地找出与 $x$ 最相似(如余弦相似度或欧氏距离最近)的若干个向量。
**内部机制**包括使用近似最近邻(ANN)算法,如倒排索引(IVF)、乘积量化(PQ)等,以在精度与速度之间取得平衡。
**性能参数**包括:
- 向量维度 $d$;
- 数据集大小(可支持超出内存的规模);
- 搜索精度(可通过调整索引类型和参数调节);
- 查询延迟(Faiss 优化了查询速度,尤其在 GPU 上)。
Faiss 支持 C++ 和 Python,部分算法可在 GPU 上运行。
documents 3问一个查不到资料的问题 下面可以看到一直在转换问题表述,但是一直查不到资料,不能得出最总的结论
markdown
**************************************************
question 解释下地球如何自转的
generation
documents 0
-- 获取文档 --
documents= 4
**************************************************
question 解释下地球如何自转的
generation
documents 0
-- 文档相关性处理 --
relevant_docs= 0
-- 决定是继续生成还是转换查询 --
转换查询
**************************************************
question 解释下地球如何自转的
generation
documents 0
-- 问题描述重写 --
**************************************************
question 解释下地球如何自转的
generation
documents 0
-- 获取文档 --
documents= 4
**************************************************
question 重新表述的问题:
**地球是如何进行自转的?请解释其自转的原理和周期。**
这个版本更明确地指出了需要解释的内容,包括自转的机制和周期,有助于检索更相关、更详细的科学资料。
generation
documents 4
-- 文档相关性处理 --
relevant_docs= 0
-- 决定是继续生成还是转换查询 --
转换查询
**************************************************
question 重新表述的问题:
**地球是如何进行自转的?请解释其自转的原理和周期。**
这个版本更明确地指出了需要解释的内容,包括自转的机制和周期,有助于检索更相关、更详细的科学资料。
generation
documents 4
-- 问题描述重写 --
**************************************************
question 重新表述的问题:
**地球自转的原理是什么?它的自转周期是如何定义的?**
这个版本将问题拆分为两个具体方面------"原理"和"周期",有助于更精准地检索关于地球自转机制及其时间特性的相关资料。
generation
documents 0
-- 获取文档 --
documents= 4
**************************************************
question 重新表述的问题:
**地球自转的原理是什么?它的自转周期是如何定义的?**
这个版本将问题拆分为两个具体方面------"原理"和"周期",有助于更精准地检索关于地球自转机制及其时间特性的相关资料。
generation
documents 0
-- 文档相关性处理 --
relevant_docs= 0
-- 决定是继续生成还是转换查询 --
转换查询
**************************************************
question 重新表述的问题:
**地球自转的原理是什么?它的自转周期是如何定义的?**
这个版本将问题拆分为两个具体方面------"原理"和"周期",有助于更精准地检索关于地球自转机制及其时间特性的相关资料。
generation
documents 0
-- 问题描述重写 --
**************************************************
question 重新表述的问题:
**地球自转的原理是什么?它的自转周期是如何定义的?**
这个版本将问题拆分为两个具体方面------"原理"和"周期",有助于更精准地检索关于地球自转机制及其时间特性的相关资料。
generation
documents 0
-- 获取文档 --
documents= 4
**************************************************
question 重新表述的问题:
**地球是如何实现自转的?其自转周期又是如何测定和定义的?**
这个版本更清晰地引导对地球自转机制及其周期性测量方法的探究,有助于检索更具体、相关的科学资料。
generation
documents 4
-- 文档相关性处理 --
...结束不了总结
自我反思节点的作用
这些自我反思节点让Self-RAG能够持续评估和改进检索和生成过程。如果检索结果不相关或者不够用,它就会重新查询。这种机制特别适合处理那些模棱两可或者特别复杂的问题。
局限性
虽然Self-RAG让RAG的工作流程变得更灵活了,但它也带来了一些复杂性:
- 延迟:因为要多走几轮反思循环,处理时间会变长。
- 资源占用:需要更多的计算资源来支持这种反复的反思。
- 实现难度:设计带有反馈循环的自适应工作流程,需要很小心地调整和优化。