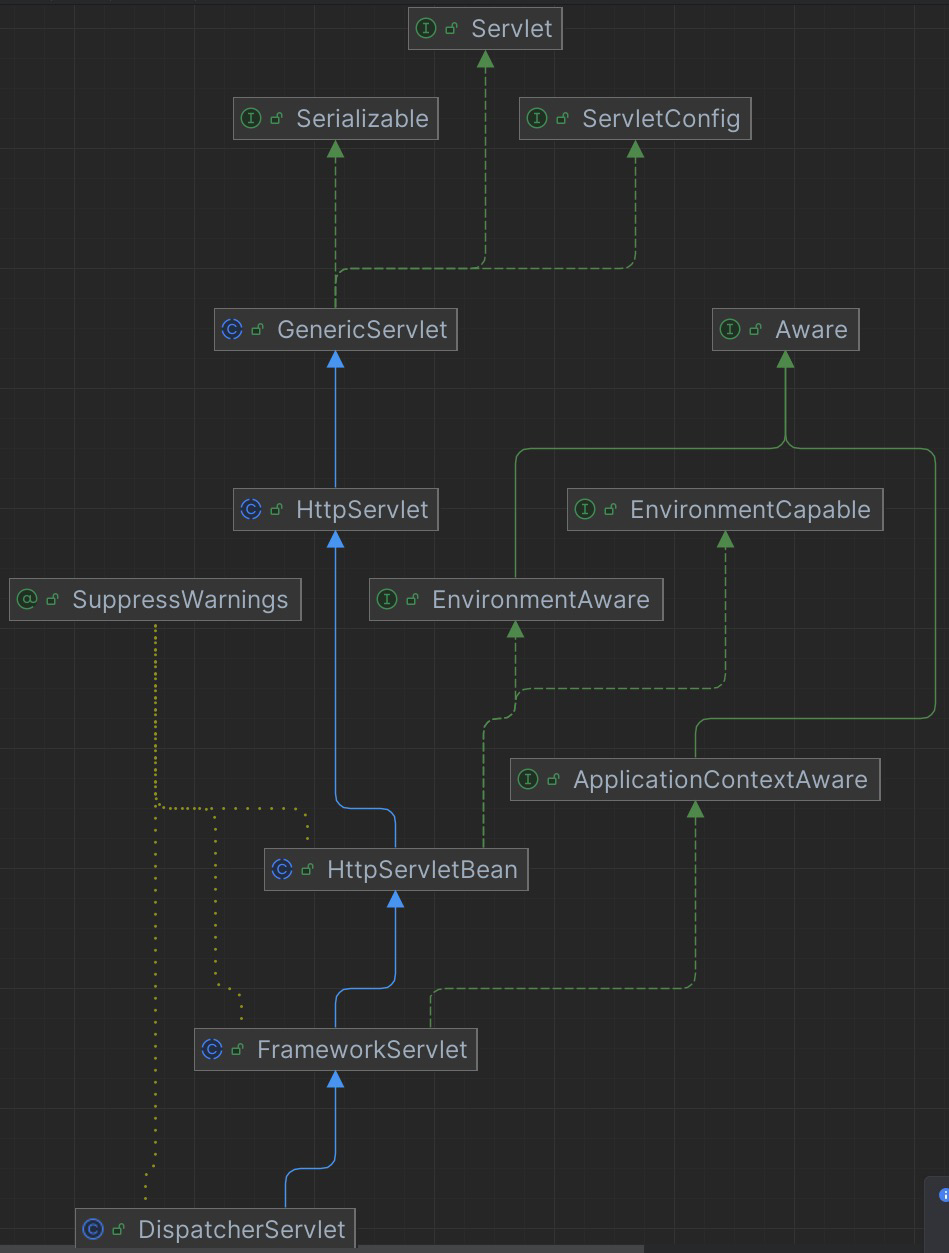
一 Servlet 接口
java
public interface Servlet {
void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException;
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
String getServletInfo();
void destroy();
}javax 的 Servlet 接口为网络服务的顶层接口,代表的是服务器中请求处理的容器。其拥有生命周期管理的三个方法,分别为 init 初始化方法、用于处理网络请求的 service 方法以及容器销毁时调用的 destroy 方法。除了上述三个生命周期管理方法外还拥有两个用于获取当前 Servlet 容器信息的方法:分别为获取容器配置的 getServletConfig 及容器基础信息的 getServletInfo 方法。
二 ServletConfig 接口
java
public interface ServletConfig {
String getServletName();
ServletContext getServletContext();
String getInitParameter(String var1);
Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames();
}ServletConfig 接口用于获取当前 Servlet 容器相关信息。其总共有 4 个方法,分别为获取容器名的 getServletName 方法,获取容器上下文 ServletContext 对象的 getServletContext 方法,获取指定初始化属性值的 getInitParameter 方法以及获取容器所有初始化属性名的 getInitParameterNames 方法。
三 GenericServlet 抽象类
GenericServlet 抽象类为 Servlet 接口的协议无关实现类,其实现了 Servlet、ServletConfig 及 Serializable 三个借口,提供了 Servlet 接口的一些基础实现。
1 属性
java
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {
private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.LocalStrings";
private static ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.LocalStrings");
private transient ServletConfig config;
}GenericServlet 抽象类中只有一个存储当前容器 ServletConfig 配置的 config 类属性。
2 Servlet 接口实现
java
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
public String getServletInfo() {
return "";
}
public abstract void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return this.config;
}
public void destroy() {
}
}GenericServlet 抽象类实现了 Servlet 接口中除 service 方法的其余 4 个方法。其中 init 方法只是直接将传入的配置保存到 config 属性之中,而 destroy 方法则是空实现;getServletInfo 方法则直接返回空字符串同时 getServletConfig 直接获取当前容器中的 config 属性值。
3 ServletConfig 接口实现
java
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {
public String getServletName() {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getServletName();
}
}
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getServletContext();
}
}
public String getInitParameter(String name) {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getInitParameter(name);
}
}
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
} else {
return sc.getInitParameterNames();
}
}
}GenericServlet 抽象类对 ServletConfig 接口的所有方法实现全是直接调用 getServletConfig 方法的结果对应方法,值得注意的是在 getServletConfig 方法未获取到容器配置时直接抛出本地适配化的 err.servlet_config_not_initialized 异常;
4 其余方法
java
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {
public void log(String msg) {
this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + msg);
}
public void log(String message, Throwable t) {
this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t);
}
}GenericServlet 抽象类除了上述方法外,还拥有两个用于日志打印的 log 方法;
四 HttpServlet 抽象类
HttpServlet 抽象类为 http 协议基类,其主要工作对不同 http 方法进行了分发。
1 属性
java
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
private static final String METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE";
private static final String METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD";
private static final String METHOD_GET = "GET";
private static final String METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS";
private static final String METHOD_POST = "POST";
private static final String METHOD_PUT = "PUT";
private static final String METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE";
private static final String HEADER_IFMODSINCE = "If-Modified-Since";
private static final String HEADER_LASTMOD = "Last-Modified";
private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings";
private static ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings");
}HttpServlet 抽象类没有任何类属性,只有标识 http 请求方法名与 Modified 缓存请求头常量。
2 方法
2.1 service 方法
java
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
if (req instanceof HttpServletRequest && res instanceof HttpServletResponse) {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
this.service(request, response);
} else {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
long lastModified;
if (method.equals("GET")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1L) {
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(304);
}
}
} else if (method.equals("HEAD")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) {
this.doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("TRACE")) {
this.doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method};
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg);
}
}
}HttpServlet 抽象类只实现了 Servlet 接口的 service 方法,在 service 方法中通过过滤 http 类型的 resp 与 res 参数来基本实现 http 协议;同时增加了一个 HttpServletRequest 与 HttpServletResponse 参数类型的 service 方法的重载,该重载方法主要是对不同类型的请求进行分发调用对应的 do 方法进行实际处理;
2.2 do 方法
2.2.1 doOptions 方法
java
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
protected void doOptions(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Method[] methods = this.getAllDeclaredMethods(this.getClass());
boolean ALLOW_GET = false;
boolean ALLOW_HEAD = false;
boolean ALLOW_POST = false;
boolean ALLOW_PUT = false;
boolean ALLOW_DELETE = false;
boolean ALLOW_TRACE = true;
boolean ALLOW_OPTIONS = true;
for(int i = 0; i < methods.length; ++i) {
String methodName = methods[i].getName();
if (methodName.equals("doGet")) {
ALLOW_GET = true;
ALLOW_HEAD = true;
} else if (methodName.equals("doPost")) {
ALLOW_POST = true;
} else if (methodName.equals("doPut")) {
ALLOW_PUT = true;
} else if (methodName.equals("doDelete")) {
ALLOW_DELETE = true;
}
}
StringBuilder allow = new StringBuilder();
if (ALLOW_GET) {
allow.append("GET");
}
if (ALLOW_HEAD) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("HEAD");
}
if (ALLOW_POST) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("POST");
}
if (ALLOW_PUT) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("PUT");
}
if (ALLOW_DELETE) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("DELETE");
}
if (ALLOW_TRACE) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("TRACE");
}
if (ALLOW_OPTIONS) {
if (allow.length() > 0) {
allow.append(", ");
}
allow.append("OPTIONS");
}
resp.setHeader("Allow", allow.toString());
}
private Method[] getAllDeclaredMethods(Class<? extends HttpServlet> c) {
Class<?> clazz = c;
Method[] allMethods;
for(allMethods = null; !clazz.equals(HttpServlet.class); clazz = clazz.getSuperclass()) {
Method[] thisMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
if (allMethods != null && allMethods.length > 0) {
Method[] subClassMethods = allMethods;
allMethods = new Method[thisMethods.length + subClassMethods.length];
System.arraycopy(thisMethods, 0, allMethods, 0, thisMethods.length);
System.arraycopy(subClassMethods, 0, allMethods, thisMethods.length, subClassMethods.length);
} else {
allMethods = thisMethods;
}
}
return allMethods != null ? allMethods : new Method[0];
}
}doOptions 方法直接通过 getAllDeclaredMethods 方法获取从当前类到 HttpServlet 所有类中的所有方法,随后允许根据不同实现了不同的 do 方法来允许对应请求方法:实现了 doGet 方法支持 get 与 head 请求、实现了 doPost 方法支持 POST 请求、实现 doPut 方法支持 PUT 请求及通过实现 doDelete 方法来支持 DELETE 请求;除了上述请求外 TRACE 与 OPTIONS 请求时默认支持的。
2.2.2 doTrace 方法
java
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
protected void doTrace(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String CRLF = "\r\n";
StringBuilder buffer = (new StringBuilder("TRACE ")).append(req.getRequestURI()).append(" ").append(req.getProtocol());
Enumeration<String> reqHeaderEnum = req.getHeaderNames();
while(reqHeaderEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = (String)reqHeaderEnum.nextElement();
buffer.append(CRLF).append(headerName).append(": ").append(req.getHeader(headerName));
}
buffer.append(CRLF);
int responseLength = buffer.length();
resp.setContentType("message/http");
resp.setContentLength(responseLength);
ServletOutputStream out = resp.getOutputStream();
out.print(buffer.toString());
}
}doTrace 方法直接使用手动拼接 TRACE 响应,并将请求头写入响应并返回。
2.2.3 其余 do 方法
java
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected void doHead(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
NoBodyResponse response = new NoBodyResponse(resp);
this.doGet(req, response);
response.setContentLength();
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_put_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected void doDelete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_delete_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
}其余 do 方法都是直接返回不支持该请求的消息。
四 HttpServletBean 抽象类
HttpServletBean 为 spring httpServlet 的抽象基类,其处理继承了 HttpServlet 以外还实现了 EnvironmentCapable 与 EnvironmentAware 接口,提供了获取 spring 环境变量的功能。
1 属性
java
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
@Nullable
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
private final Set<String> requiredProperties = new HashSet<>(4);
}HttpServletBean 抽象类拥有两个属性,其中 environment 属性保存的是当前 spring 的环境变量,通过实现 EnvironmentAware 接口的 setEnvironment 方法通过 spring 自动注入,同时可以通过 getEnvironment 方法获取,注意若未注入则会在获取时将其初始化为空 StandardServletEnvironment 对象;
java
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment, "ConfigurableEnvironment required");
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
}
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
}requiredProperties 属性则保存的是子类必须的属性名,子类可以在构造函数之中通过 addRequiredProperty 方法添加元素;
java
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
protected final void addRequiredProperty(String property) {
this.requiredProperties.add(property);
}
}2 方法
2.1 init
java
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
}init 方法首先通过当前 servletConfig 配置与 requiredProperties 属性创建 ServletConfigPropertyValues 对象提取当前配置属性值;随后在获取到的属性不为空时,通过 initBeanWrapper 方法与 BeannWrapper 对象封装类对当前 servlet 对象进行初始化并为属性赋值;最后调用 initServletBean 方法初始化 servletBean 对象。initBeanWrapper 与 initServletBean 方法都是空实现,具体实现由其子类提供。
java
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
protected void initBeanWrapper(BeanWrapper bw) throws BeansException {
}
protected void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
}
}2.2 getServletName
java
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
@Override
@Nullable
public String getServletName() {
return (getServletConfig() != null ? getServletConfig().getServletName() : null);
}
}getServletName 方法直接调用当前配置的 getServletName 方法。
3 ServletConfigPropertyValues 内部类
java
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues {
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
Set<String> missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ?
new HashSet<>(requiredProperties) : null);
Enumeration<String> paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = paramNames.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}
}ServletConfigPropertyValues 类继承自 MutablePropertyValues 类,其构造函数在将 config 中的参数提取出来的同时,扩展了必要参数验证;
四 FrameworkServlet 抽象类
FrameworkServlet 抽象类为 spring 框架的基础 Servlet 对象,其提供了框架 Servlet 的基础配置及 webApplicationContext 上下文的初始化。
1 属性
1.1 常量
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
public static final String DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_SUFFIX = "-servlet";
public static final Class<?> DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = XmlWebApplicationContext.class;
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX = FrameworkServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT.";
private static final String INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS = ",; \t\n";
}FrameworkServlet 抽象类拥有 4 个常量,分别是默认命名空间后缀、默认 web 应用上下文配置类、servlet 上下文前缀及初始化配置分隔符;
1.2 类变量
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Nullable
private String contextAttribute;
private Class<?> contextClass = DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS;
@Nullable
private String contextId;
@Nullable
private String namespace;
@Nullable
private String contextConfigLocation;
private final List<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>> contextInitializers =
new ArrayList<>();
@Nullable
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
@Nullable
private String contextInitializerClasses;
private boolean publishContext = true;
private boolean publishEvents = true;
private boolean threadContextInheritable = false;
private boolean dispatchOptionsRequest = false;
private boolean dispatchTraceRequest = false;
private boolean enableLoggingRequestDetails = false;
private boolean webApplicationContextInjected = false;
private volatile boolean refreshEventReceived;
private final Object onRefreshMonitor = new Object();
}FrameworkServlet 抽象类虽然拥有很多个类变量,但根据功能大致可以分为两类。一类保存的是程序上下文,另一类则是 Servlet 开关。上下文相关属性有用于查询 WebApplicationContext 配置的 contextAttribute 属性,用于表征 WebApplicationContext 上下文实现类的 contextClass 属性,用于保存上下文 id 的 contextId 属性,用于保存 servlet 命名空间的 namespace,表征上下文配置位置的 contextConfigLocation,保存上下文初始化器列表的 contextInitializers 属性,保存上下文初始化器类名的 contextInitializerClasses 及当前实际使用的 WebApplicationContext 上下文配置;开关控制器则有控制是否将上下文发布为全局的 publishContext,控制是否在请求结束时发布 servlet 请求处理事件的 publishEvents 属性,控制是否暴露当前上下文与属性给子线程的 threadContextInheritable 属性,控制是否分发 OPTIONS 、TRACE请求的 dispatchOptionsRequest 与 dispatchTraceRequest 属性,控制是否记录请求详情日志(debug、trace)的 enableLoggingRequestDetails 属性, 是否已经通过 setApplicationContext 设置程序上下文的 webApplicationContextInjected 属性;除了上述属性外,还提供 onRefresh 方法调用的监控,分别为是否调用的标识 refreshEventReceived 及保存 onRefresh 方法执行监视器锁的 onRefreshMonitor 属性。
2 基础方法
2.1 构造方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
public FrameworkServlet() {
}
public FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
this.webApplicationContext = webApplicationContext;
}
}该类拥有两个构造方法,一个是无参构造方法,另一个构造方法则拥有一个 webApplicationContext 参数,其直接为 webApplicationContext 属性赋值;
2.1 set 与 get 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
public void setContextClass(Class<?> contextClass) {
this.contextClass = contextClass;
}
public Class<?> getContextClass() {
return this.contextClass;
}
public void setContextId(@Nullable String contextId) {
this.contextId = contextId;
}
@Nullable
public String getContextId() {
return this.contextId;
}
public void setNamespace(String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace;
}
public String getNamespace() {
return (this.namespace != null ? this.namespace : getServletName() + DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_SUFFIX);
}
public void setContextConfigLocation(@Nullable String contextConfigLocation) {
this.contextConfigLocation = contextConfigLocation;
}
@Nullable
public String getContextConfigLocation() {
return this.contextConfigLocation;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void setContextInitializers(@Nullable ApplicationContextInitializer<?>... initializers) {
if (initializers != null) {
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : initializers) {
this.contextInitializers.add((ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>) initializer);
}
}
}
public void setContextInitializerClasses(String contextInitializerClasses) {
this.contextInitializerClasses = contextInitializerClasses;
}
public void setPublishContext(boolean publishContext) {
this.publishContext = publishContext;
}
public void setPublishEvents(boolean publishEvents) {
this.publishEvents = publishEvents;
}
public void setThreadContextInheritable(boolean threadContextInheritable) {
this.threadContextInheritable = threadContextInheritable;
}
public void setDispatchOptionsRequest(boolean dispatchOptionsRequest) {
this.dispatchOptionsRequest = dispatchOptionsRequest;
}
public void setDispatchTraceRequest(boolean dispatchTraceRequest) {
this.dispatchTraceRequest = dispatchTraceRequest;
}
public void setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(boolean enable) {
this.enableLoggingRequestDetails = enable;
}
public boolean isEnableLoggingRequestDetails() {
return this.enableLoggingRequestDetails;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
if (this.webApplicationContext == null && applicationContext instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
this.webApplicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) applicationContext;
this.webApplicationContextInjected = true;
}
}
}该类中的 set 与 get 方法中只有 getNamespace 与 setApplicationContext 方法存在特殊处理:getNamespace 方法在 namespace 属性为空时直接返回当前 Servlet 名称拼接上 DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_SUFFIX 常量值,而 setApplicationContext 方法则只有在 webApplicationContext 属性为空且 applicationContext 为 WebApplicationContext 对象时才会为 webApplicationContext 属性赋值同时将 webApplicationContextInjected 属性置为 true;
3 方法
3.1 initServletBean 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
}FrameworkServlet 抽象类实际功能就是对 Servlet 进行初始化,核心就是通过 initServletBean 方法实现的。initServletBean 方法主要就是在调用了 initWebApplicationContext 方法为 webApplicationContext 属性进行赋值了之后,调用 initFrameworkServlet 方法进一步初始化及一些日志打印。
3.2 initWebApplicationContext 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
}initWebApplicationContext 方法首先调用 WebApplicationContextUtils 类的 getWebApplicationContext 方法获取当前 Servlet 配置中保存的 WebApplicationContext 根上下文。在 webApplicationContext 已完成注入时直接将其保存到 wac 变量中,在其为 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 对象其不是活动的时,没有父上下文将其父上下文设置为获取到的根上下文,同时调用 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 配置与刷新 wac 变量。在 webApplicationContext 属性为空时,尝试使用 findWebApplicationContext 查找上下文,若还没找到则调用 createWebApplicationContext 方法创建上下文;最后根据 refreshEventReceived 与 publishContext 属性调用 onRefresh 方法与以 contextAttribute 属性名发布上下文;
3.2.1 findWebApplicationContext 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Nullable
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
WebApplicationContext wac =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?");
}
return wac;
}
}findWebApplicationContext 方法在 contextAttribute 属性不为空时从当前 Servlet 配置中获取对应上下文,若不存在对应上下文时直接抛出异常。
3.2.2 createWebApplicationContext 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable WebApplicationContext parent) {
return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent);
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
}createWebApplicationContext 方法首先调用 BeanUtils 工具类的 instantiateClass 方法创建 contextClass 属性对应对象,随后为其设置环境变量值、父上下文及本地配置并调用 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 方法对其配置并刷新。
3.2.3 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
protected void postProcessWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
}
}configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 方法在其 wac 参数的 id 还是默认值时为其设置 id,在 contextId 不为空时设置为该值,否则通过 APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX 常量、上下文路径及 servlet 名字生成 id。之后为其设置 Servlet 上下文、Servlet 配置及命名空间,并增加 SourceFilteringListener 监听器。之后调用 postProcessWebApplicationContext 与 applyInitializers 方法分别进行后处理及初始化。
3.2.4 applyInitializers 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext wac) {
String globalClassNames = getServletContext().getInitParameter(ContextLoader.GLOBAL_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM);
if (globalClassNames != null) {
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(globalClassNames, INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
this.contextInitializers.add(loadInitializer(className, wac));
}
}
if (this.contextInitializerClasses != null) {
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.contextInitializerClasses, INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
this.contextInitializers.add(loadInitializer(className, wac));
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.contextInitializers);
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> initializer : this.contextInitializers) {
initializer.initialize(wac);
}
}
}applyInitializers 方法使用上下文中定义的初始化器按顺序对 wac 属性进行初始化。其首先调用 loadInitializer 方法将上下文的 GLOBAL_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM 属性中定义的全局初始化器与 contextInitializerClasses 属性中定义的初始化器加载并保存到 contextInitializers 属性之中并对其进行排序,最后逐一调用初始化器的 initialize 方法对 wac 参数对象进行初始化。
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> loadInitializer(
String className, ConfigurableApplicationContext wac) {
try {
Class<?> initializerClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, wac.getClassLoader());
Class<?> initializerContextClass =
GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializerClass, ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
if (initializerContextClass != null && !initializerContextClass.isInstance(wac)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format(
"Could not apply context initializer [%s] since its generic parameter [%s] " +
"is not assignable from the type of application context used by this " +
"framework servlet: [%s]", initializerClass.getName(), initializerContextClass.getName(),
wac.getClass().getName()));
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(initializerClass, ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format("Could not load class [%s] specified " +
"via 'contextInitializerClasses' init-param", className), ex);
}
}
}loadInitializer 方法使用 wac 参数对应类加载器加载并创建 className 对应的对象。
3.3 service 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
}service 方法做的第一件事就是扩展了 PATCH 请求方法的处理,其主要是通过调用 processRequest 方法实现的,其余请求还是调用父对象的 service 方法处理。
3.3.1 do 请求的实现
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
protected final void doPut(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
protected final void doDelete(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doOptions(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
if (this.dispatchOptionsRequest || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
processRequest(request, response);
if (response.containsHeader("Allow")) {
// Proper OPTIONS response coming from a handler - we're done.
return;
}
}
// Use response wrapper in order to always add PATCH to the allowed methods
super.doOptions(request, new HttpServletResponseWrapper(response) {
@Override
public void setHeader(String name, String value) {
if ("Allow".equals(name)) {
value = (StringUtils.hasLength(value) ? value + ", " : "") + HttpMethod.PATCH.name();
}
super.setHeader(name, value);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void doTrace(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
if (this.dispatchTraceRequest) {
processRequest(request, response);
if ("message/http".equals(response.getContentType())) {
// Proper TRACE response coming from a handler - we're done.
return;
}
}
super.doTrace(request, response);
}
}get、post、put 及 delete 请求对应的 do 方法也是直接通过调用 processRequest 方法实现的;而 doTrace 与 doOptions 方法则需要判断 dispatchTraceRequest 与 dispatchOptionsRequest 开关是否打开了,只有打开了才会使用 processRequest 方法处理对应请求,否则则是直接调用父类的对应方法进行处理,在 processRequest 处理后判断是否拥有对应请求头,没有也是会调用父类的对应请求;其中 doOptions 还判断了当前请求是否为前置获取许可的请求,是的话也是调用 processRequest 方法进行处理,同时在调完了父方法处理之后,需在 Allow 响应值中添加 PATCH 方法;
3.3.2 processRequest 方法
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
@Nullable
protected LocaleContext buildLocaleContext(HttpServletRequest request) {
return new SimpleLocaleContext(request.getLocale());
}
@Nullable
protected ServletRequestAttributes buildRequestAttributes(HttpServletRequest request,
@Nullable HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable RequestAttributes previousAttributes) {
if (previousAttributes == null || previousAttributes instanceof ServletRequestAttributes) {
return new ServletRequestAttributes(request, response);
}
else {
return null; // preserve the pre-bound RequestAttributes instance
}
}
private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request,
@Nullable LocaleContext localeContext, @Nullable RequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
if (localeContext != null) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(localeContext, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
if (requestAttributes != null) {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
}
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception;
}processRequest 方法可以分为三步,第一步是设置请求地区信息上下文与属性的同时封存之前地区信息上下文与属性,第二步调用 doservice 方法实际处理请求,最后则是在请求处理完成后进行重置上下文、记录日志及发布请求等其他后处理。当前地区信息上下文时利用 request 请求对象执行 buildLocaleContext 方法创建的,在当前类中直接利用 request 请求的区域信息创建 SimpleLocaleContext 对象作为当前请求地区信息上下文;而绑定的 RequestAttributes 只有在之前属性不为空或为 ServletRequestAttributes 时才会进行替换;
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
private void resetContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request,
@Nullable LocaleContext prevLocaleContext, @Nullable RequestAttributes previousAttributes) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(prevLocaleContext, this.threadContextInheritable);
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(previousAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
}resetContextHolders 方法直接将当前线程中保存的请求地区信息与属性还原到之前的封存的;
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
private void logResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable Throwable failureCause, WebAsyncManager asyncManager) {
if (!logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
return;
}
DispatcherType dispatchType = request.getDispatcherType();
boolean initialDispatch = (dispatchType == DispatcherType.REQUEST);
if (failureCause != null) {
if (!initialDispatch) {
// FORWARD/ERROR/ASYNC: minimal message (there should be enough context already)
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unresolved failure from \"" + dispatchType + "\" dispatch: " + failureCause);
}
}
else if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
logger.debug("Failed to complete request: " + failureCause);
}
return;
}
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Exiting but response remains open for further handling");
return;
}
int status = response.getStatus();
String headers = ""; // nothing below trace
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
Collection<String> names = response.getHeaderNames();
if (this.enableLoggingRequestDetails) {
headers = names.stream().map(name -> name + ":" + response.getHeaders(name))
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
}
else {
headers = names.isEmpty() ? "" : "masked";
}
headers = ", headers={" + headers + "}";
}
if (!initialDispatch) {
logger.debug("Exiting from \"" + dispatchType + "\" dispatch, status " + status + headers);
}
else {
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.resolve(status);
logger.debug("Completed " + (httpStatus != null ? httpStatus : status) + headers);
}
}
}logResult 方法只有在当前日志级别为 debug 时才会执行,其在执行出现异常时直接会打印对应的错误;异步请求在异步任务开始执行后打印对应日志;其他请求则会按需打印响应头与响应状态;
java
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
private void publishRequestHandledEvent(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
long startTime, @Nullable Throwable failureCause) {
if (this.publishEvents && this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// Whether or not we succeeded, publish an event.
long processingTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.webApplicationContext.publishEvent(
new ServletRequestHandledEvent(this,
request.getRequestURI(), request.getRemoteAddr(),
request.getMethod(), getServletConfig().getServletName(),
WebUtils.getSessionId(request), getUsernameForRequest(request),
processingTime, failureCause, response.getStatus()));
}
}
@Nullable
protected String getUsernameForRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
Principal userPrincipal = request.getUserPrincipal();
return (userPrincipal != null ? userPrincipal.getName() : null);
}
}publishRequestHandledEvent 方法在需要发布事件时直接向 webApplicationContext 中发布 ServletRequestHandledEvent 事件;
五 DispatcherServlet 类
DispatcherServlet 类为 spring mvc 的核心 Servlet 对象,其提供了 spring mvc 框架请求调度功能。
1 属性
1.1 常量
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
public static final String MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "multipartResolver";
public static final String LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "localeResolver";
public static final String THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "themeResolver";
public static final String HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME = "handlerMapping";
public static final String HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME = "handlerAdapter";
public static final String HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "handlerExceptionResolver";
public static final String REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME = "viewNameTranslator";
public static final String VIEW_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "viewResolver";
public static final String FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME = "flashMapManager";
public static final String WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT";
public static final String LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".LOCALE_RESOLVER";
public static final String THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".THEME_RESOLVER";
public static final String THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".THEME_SOURCE";
public static final String INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".INPUT_FLASH_MAP";
public static final String OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP";
public static final String FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".FLASH_MAP_MANAGER";
public static final String EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".EXCEPTION";
public static final String PAGE_NOT_FOUND_LOG_CATEGORY = "org.springframework.web.servlet.PageNotFound";
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "DispatcherServlet.properties";
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX = "org.springframework.web.servlet";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}FrameworkServlet 抽象类拥有非常多的常量,但大概分为三类:以 BEAN_NAME 结尾的是对象名、以 ATTRIBUTE 结尾的是使用到的属性名以及其他属性(PAGE_NOT_FOUND_LOG_CATEGORY 保存的是未匹配到任意 handler 时日志打印消息,分别保存默配置文件位置的 DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH 及默认配置中的属性前缀 DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX);
java
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager默认配置在静态代码块中根据 DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH 常量(上面展示的 DispatcherServlet.properties 默认配置文件)加载到 defaultStrategies 属性之中。
1.2 类变量
DispatcherServlet 类的属性大面上可以分为三类,分别为通用属性,handler 处理器相关和 view 视图处理相关。
1.2.1 通用属性
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private boolean cleanupAfterInclude = true;
@Nullable
private MultipartResolver multipartResolver;
@Nullable
private LocaleResolver localeResolver;
/** ThemeResolver used by this servlet. */
@Nullable
private ThemeResolver themeResolver;
/** FlashMapManager used by this servlet. */
@Nullable
private FlashMapManager flashMapManager;
}通用属性有 cleanupAfterInclude、MultipartResolver 、localeResolver 及 themeResolver 四个;其中 cleanupAfterInclude 用于开启 include 请求之后清理请求属性,multipartResolver、localeResolver 与 themeResolver 属性则是当前使用的对应解析器,flashMapManager 属性用于重定向请求数据的临时存储;
1.2.2 handler 处理器
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
/** Detect all HandlerMappings or just expect "handlerMapping" bean?. */
private boolean detectAllHandlerMappings = true;
/** Detect all HandlerAdapters or just expect "handlerAdapter" bean?. */
private boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters = true;
/** Detect all HandlerExceptionResolvers or just expect "handlerExceptionResolver" bean?. */
private boolean detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers = true;
/** Throw a NoHandlerFoundException if no Handler was found to process this request? *.*/
private boolean throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound = false;
/** List of HandlerMappings used by this servlet. */
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
/** List of HandlerAdapters used by this servlet. */
@Nullable
private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters;
/** List of HandlerExceptionResolvers used by this servlet. */
@Nullable
private List<HandlerExceptionResolver> handlerExceptionResolvers;
}属性中与 handler 处理器有关的属性有 7 个:其中四个是开关,分别是用于是否从上下文加载所有 HandlerMapping 对象的 detectAllHandlerMappings 开关,是否从上下文加载所有 HandlerAdapter 对象的 detectAllHandlerAdapters 开关,是否从上下文加载所有 HandlerExceptionResolver 对象的 detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers 开关及控制是否在未查询到指定处理器报错的开关 throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound,前三个开关默认值为 true,置为 false 时只会加载上述常量中定义对应对象名的对象;其余还有保存处理器映射对象 HandlerMapping 的 handlerMappings 属性、保存处理器适配器 HandlerAdapter 的 handlerAdapters 属性及保存处理器异常解析器 HandlerExceptionResolver 的 handlerExceptionResolvers 属性;
1.2.3 view 视图
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
/** Detect all ViewResolvers or just expect "viewResolver" bean?. */
private boolean detectAllViewResolvers = true;
/** RequestToViewNameTranslator used by this servlet. */
@Nullable
private RequestToViewNameTranslator viewNameTranslator;
/** List of ViewResolvers used by this servlet. */
@Nullable
private List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
}属性中与 view 视图有关的属性有 4 个:分别是用于是否从上下文加载所有 ViewResolver 对象的 detectAllViewResolvers 开关,保存 resquest 请求到视图名转换器 RequestToViewNameTranslator 的 viewNameTranslator 属性、保存处理器适配器 HandlerAdapter 的 handlerAdapters 属性及保存视图解析器 ViewResolver 的 viewResolvers 属性;
2 方法
2.1 构造方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
public DispatcherServlet() {
super();
setDispatchOptionsRequest(true);
}
public DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
super(webApplicationContext);
setDispatchOptionsRequest(true);
}
}DispatcherServlet 类拥有两个构造方法,他们唯一区别为是否是否从外部传入了上下文;同时他们都会将 dispatchOptionsRequest 属性置为 true,表明 DispatcherServlet 类默认支持处理 Options 请求。
2.2 onRefresh 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
}onRefresh 方法直接调用 initStrategies 方法对属性进行初始化,在 initStrategies 方法则是逐一调用所有初始化方法对除开关以外的所有属性进行初始化。
2.2.1 initMultipartResolver 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initMultipartResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.multipartResolver = context.getBean(MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, MultipartResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.multipartResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.multipartResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Default is no multipart resolver.
this.multipartResolver = null;
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No MultipartResolver '" + MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "' declared");
}
}
}
}initMultipartResolver 方法直接尝试从 context 上下文中获取 MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME 常量名对应的 MultipartResolver 对象然后赋值给 multipartResolver 属性,若上下文未定义则是直接将该属性置为 null。
2.2.2 initLocaleResolver 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initLocaleResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.localeResolver = context.getBean(LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, LocaleResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.localeResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// We need to use the default.
this.localeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, LocaleResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No LocaleResolver '" + LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
}initLocaleResolver 方法与 initMultipartResolver 方法一样首先会尝试从 context 上下文中获取 LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME 常量名对应的 LocaleResolver 对象然后赋值给 localeResolver 属性,未定义时也是置为 null。
2.2.3 initThemeResolver 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initThemeResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.themeResolver = context.getBean(THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ThemeResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.themeResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.themeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// We need to use the default.
this.themeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, ThemeResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No ThemeResolver '" + THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.themeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
}initThemeResolver 方法与 initMultipartResolver 方法一样。
2.2.4 initHandlerMappings 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
}initHandlerMappings 方法首先会将 handlerMappings 属性置为 null,随后根据 detectAllHandlerMappings 开关值为该属性赋值;若该开关打开了就会将上下文中所有的 HandlerMapping 对象全部保存到 handlerMappings 属性之中,否则只会将名为 HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME 的 HandlerMapping 对象保存到 handlerMappings 属性中,若上述为获取到任何 HandlerMapping 对象则会通过 getDefaultStrategies 方法将默认 HandlerMapping 对象加载到 handlerMappings 属性之中。
2.2.5 initHandlerAdapters 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
}initHandlerAdapters 与 initHandlerMappings 方法一样根据 detectAllHandlerAdapters 开关值为 handlerAdapters 属性赋值。
2.2.6 initHandlerExceptionResolvers 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initHandlerExceptionResolvers(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers) {
// Find all HandlerExceptionResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerExceptionResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils
.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerExceptionResolvers in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerExceptionResolvers);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerExceptionResolver her =
context.getBean(HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerExceptionResolver.class);
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = Collections.singletonList(her);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, no HandlerExceptionResolver is fine too.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least some HandlerExceptionResolvers, by registering
// default HandlerExceptionResolvers if no other resolvers are found.
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers == null) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerExceptionResolvers declared in servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
}initHandlerExceptionResolvers 与 initHandlerMappings 方法一样根据 detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers 开关值为 handlerExceptionResolvers 属性赋值。
2.2.7 initRequestToViewNameTranslator 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initRequestToViewNameTranslator(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.viewNameTranslator =
context.getBean(REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.viewNameTranslator.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.viewNameTranslator);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// We need to use the default.
this.viewNameTranslator = getDefaultStrategy(context, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RequestToViewNameTranslator '" + REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.viewNameTranslator.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
}initRequestToViewNameTranslator 方法通过与 initMultipartResolver 方法一样的逻辑为 viewNameTranslator 属性赋值,其中有个区别,在未从上下文获取到时获取赋默认值。
2.2.8 initViewResolvers 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initViewResolvers(ApplicationContext context) {
this.viewResolvers = null;
if (this.detectAllViewResolvers) {
// Find all ViewResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, ViewResolver> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, ViewResolver.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep ViewResolvers in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.viewResolvers);
}
}
else {
try {
ViewResolver vr = context.getBean(VIEW_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ViewResolver.class);
this.viewResolvers = Collections.singletonList(vr);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default ViewResolver later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one ViewResolver, by registering
// a default ViewResolver if no other resolvers are found.
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, ViewResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No ViewResolvers declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
}initViewResolvers 与 initHandlerMappings 方法一样根据 detectAllViewResolvers 开关值为 viewResolvers 属性赋值。
2.2.9 initFlashMapManager 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initFlashMapManager(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.flashMapManager = context.getBean(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME, FlashMapManager.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.flashMapManager.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.flashMapManager);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// We need to use the default.
this.flashMapManager = getDefaultStrategy(context, FlashMapManager.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No FlashMapManager '" + FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.flashMapManager.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
}initFlashMapManager 方法通过与 initRequestToViewNameTranslator 方法一样的逻辑为 initFlashMapManager 属性赋值。
2.2.10 getDefaultStrategy 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected <T> T getDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
List<T> strategies = getDefaultStrategies(context, strategyInterface);
if (strategies.size() != 1) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"DispatcherServlet needs exactly 1 strategy for interface [" + strategyInterface.getName() + "]");
}
return strategies.get(0);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Unresolvable class definition for DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" +
className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", err);
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<>();
}
}
protected Object createDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<?> clazz) {
return context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().createBean(clazz);
}
}getDefaultStrategies 方法获取 strategyInterface 类名对应默认值,并按照,对值进行分割,并调用 createDefaultStrategy 方法创建对象保存到 List 列表之中并返回。
2.3 doService 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
@Nullable
public final ThemeSource getThemeSource() {
return (getWebApplicationContext() instanceof ThemeSource ? (ThemeSource) getWebApplicationContext() : null);
}
}doService 方法主要是对打印了请求信息,将必要参数保存到请求之中后调用 doDispatch 方法实际对请求进行调度,并在调度完成之后再必要的情况下,恢复 include 请求的属性快照;在请求调度之前首先将 include 请求中绑定的属性保存到属性快照之中,随后依次将程序上下文、localeResolver 属性、themeResolver 属性及 ThemeSource 模版元数据绑定到请求上,同时若设置了 flashMapManager 属性设置则会尝试从其中恢复重定向的前保存的数据并绑定到请求之上,并在 flashMapManager 属性也绑定到请求之上。
2.3.1 logRequest 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void logRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String params;
if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(request.getContentType(), "multipart/")) {
params = "multipart";
}
else if (isEnableLoggingRequestDetails()) {
params = request.getParameterMap().entrySet().stream()
.map(entry -> entry.getKey() + ":" + Arrays.toString(entry.getValue()))
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
}
else {
params = (request.getParameterMap().isEmpty() ? "" : "masked");
}
String queryString = request.getQueryString();
String queryClause = (StringUtils.hasLength(queryString) ? "?" + queryString : "");
String dispatchType = (!request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.REQUEST) ?
"\"" + request.getDispatcherType().name() + "\" dispatch for " : "");
String message = (dispatchType + request.getMethod() + " \"" + getRequestUri(request) +
queryClause + "\", parameters={" + params + "}");
if (traceOn) {
List<String> values = Collections.list(request.getHeaderNames());
String headers = values.size() > 0 ? "masked" : "";
if (isEnableLoggingRequestDetails()) {
headers = values.stream().map(name -> name + ":" + Collections.list(request.getHeaders(name)))
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
}
return message + ", headers={" + headers + "} in DispatcherServlet '" + getServletName() + "'";
}
else {
return message;
}
});
}
private static String getRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) {
String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uri == null) {
uri = request.getRequestURI();
}
return uri;
}
}logRequest 方法会打印请求的 uri、请求参数、请求体参数请求头等。
2.3.2 restoreAttributesAfterInclude 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void restoreAttributesAfterInclude(HttpServletRequest request, Map<?, ?> attributesSnapshot) {
// Need to copy into separate Collection here, to avoid side effects
// on the Enumeration when removing attributes.
Set<String> attrsToCheck = new HashSet<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attrsToCheck.add(attrName);
}
}
// Add attributes that may have been removed
attrsToCheck.addAll((Set<String>) attributesSnapshot.keySet());
// Iterate over the attributes to check, restoring the original value
// or removing the attribute, respectively, if appropriate.
for (String attrName : attrsToCheck) {
Object attrValue = attributesSnapshot.get(attrName);
if (attrValue == null) {
request.removeAttribute(attrName);
}
else if (attrValue != request.getAttribute(attrName)) {
request.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue);
}
}
}
}restoreAttributesAfterInclude 方法首先移除请求属性快照中不存在的属性,同时将同名请求属性还原为请求快照中的值。
2.4 doDispatch 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
}doDispatch 方法第一时间使用 WebAsyncUtils 类的 getAsyncManager 方法获取或新建请求对应的 WebAsyncManager 异步控制器并以 WEB_ASYNC_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE 名字绑定到请求上;随后通过 checkMultipart 方法验证并将 multipart 请求转换为 MultipartHttpServletRequest 对象,之后尝试通过 getHandler 方法获取对应 HandlerExecutionChain 处理器链对象,未获取到时调用 noHandlerFound 方法处理并返回,随后使用 getHandlerAdapter 方法获取对应适配器,随后使用适配器验证 get 与 header 请求的 lastModified 值,未更改直接返回;之后再依次调用处理器的 applyPreHandle 方法、handle 方法及 applyPostHandle 方法对请求依次进行拦截器预处理、实际业务处理及拦截器后处理;值得注意的是如果任务是异步处理的话不会进行后处理直接返回,否则在请求后处理之前还会调用 applyDefaultViewName 方法设置默认视图名。若该过程中出现任意异常全部直接保存或转换为 NestedServletException 保存到 dispatchException 变量之中,同时调用 processDispatchResult 对调度结果进行发布结果等处理,最后还会处理一下异步请求及 Multipart 请求资源清理;
2.4.1 checkMultipart 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) {
if (request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.REQUEST)) {
logger.trace("Request already resolved to MultipartHttpServletRequest, e.g. by MultipartFilter");
}
}
else if (hasMultipartException(request)) {
logger.debug("Multipart resolution previously failed for current request - " +
"skipping re-resolution for undisturbed error rendering");
}
else {
try {
return this.multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request);
}
catch (MultipartException ex) {
if (request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for error dispatch", ex);
// Keep processing error dispatch with regular request handle below
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
// If not returned before: return original request.
return request;
}
private boolean hasMultipartException(HttpServletRequest request) {
Throwable error = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE);
while (error != null) {
if (error instanceof MultipartException) {
return true;
}
error = error.getCause();
}
return false;
}
}checkMultipart 方法用于验证并将普通请求解析为 MultipartHttpServletRequest 请求对象;其首先通过 multipartResolver 解析器属性判断请求是否为 mutipart 请求(content-type 是否为 multipart 相关值),不是 mutipart 请求直接返回原始请求对象,否则将会判断是否已经被解析了或出现了异常,从而避免重复解析或重复出现异常;上述验证完成后才会通过 multipartResolver 对请求进行解析并返回;
2.4.2 noHandlerFound 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void noHandlerFound(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (pageNotFoundLogger.isWarnEnabled()) {
pageNotFoundLogger.warn("No mapping for " + request.getMethod() + " " + getRequestUri(request));
}
if (this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound) {
throw new NoHandlerFoundException(request.getMethod(), getRequestUri(request),
new ServletServerHttpRequest(request).getHeaders());
}
else {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}noHandlerFound 方法根据 throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound 属性来采取不同方式处理未查询到处理器异常,开关打开时直接抛出 NoHandlerFoundException 异常否则将直接使用 response 对象发送 404 状态响应;
2.4.3 processDispatchResult 方法
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
}processDispatchResult 方法在 exception 为 ModelAndViewDefiningException 类型异常时直接从该异常中获取 ModelAndView 模型对象并保存到 mv 变量之中,不是但异常不为空则会调用 processHandlerException 方法生成异常 ModelAndView 对象并更新到 mv 变量中并将 errorView 值更新为是否处理获取异常视图;随后若 mv 不为空且未被清理(拥有任意视图或模型),会调用 render 方法提交视图或模型到响应之中,同时在 mv 是通过 processHandlerException 方法生成的则会调用 WebUtils 的 clearErrorRequestAttributes 方法在视图发布完成后清理异常属性;之后若为异步请求则直接返回,最后在 mappedHandler 参数不为空时,调用他的 triggerAfterCompletion 方法执行拦截器的完成后处理;
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// Success and error responses may use different content types
request.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
// Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers...
ModelAndView exMv = null;
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {
for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
}
if (exMv != null) {
if (exMv.isEmpty()) {
request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
return null;
}
// We might still need view name translation for a plain error model...
if (!exMv.hasView()) {
String defaultViewName = getDefaultViewName(request);
if (defaultViewName != null) {
exMv.setViewName(defaultViewName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using resolved error view: " + exMv, ex);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using resolved error view: " + exMv);
}
WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName());
return exMv;
}
throw ex;
}
}2.4.4 render 方法
processHandlerException 方法首先第一步就是移除请求关联可用的 ContentType 值,若 handlerExceptionResolvers 属性为空或未通过其中的元素解析出任意视图时直接抛出 ex 属性值,若解析出的视图没有任何内容直接将 ex 绑定到请求 EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE 属性上并返回 null,解析结果不包含视图则会尝试为其设置默认视图名,最后调用 WebUtils 的 exposeErrorRequestAttributes 方法将异常及一些默认参数绑定到请求之中并返回该视图与模型对象。
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] ");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
}render 方法首先利用 localeResolver 属性为 response 响应设置地区,随后通过 resolveViewName 方法或 mv 直接获取的两种方式获取对应视图,未获取到直接抛出 ServletException 异常;之后将 respose 响应状态更新为 mv 的状态值,最后通过获取的视图发布 mv 内部模型;
java
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
@Nullable
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, Object> model,
Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}resolveViewName 方法使用视图名与地区参数调用 viewResolvers 属性中元素的 resolveViewName 方法获取 view 视图对象。