I.矩阵
数学 #贪心 #构造
题目

思路
首先考虑有数最受条件的约束,因此尝试令数\(x\)沿着某方向前进\(x\)后回到原地:
\[\begin{align} (x+x+1)\%n-1&=x\\ \\ (2x+1)\%n&=x+1\\ \\ 2x+1&\equiv x+1\mod n\\ \\ x&\equiv 0\mod n \end{align} \]
则有\(x\)为\(n\)的因数
因此,当\(x\)为\(n\)的因数时,\(x\)无法在\(n\)方向上进行移动,\(m\)方向同理
因此,\(x=lcm(n,m)\)时,\(x\)一定无法移动
因此\(lcm(n,m)\)必须为最后一个填入的数字,可以利用这一点进行\(YES/NO\)的判断
接下来通过观察贪心地进行填空:
- 尝试将一列填满后再填下一列
- 尝试每填完一个数就变换一次移动方向,比如这次在列方向上向下移动,下一次列方向上的移动就向上,这样可以保证移动后不会踩到已经被填过的格子
代码实现
代码由\(phaethon 90\)书写
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define endl '\n'
ll gcd(ll a,ll b)
{
if(b==0) return a;
else return gcd(b,a%b);
}
void eachT()
{
ll n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
if(n/gcd(n,m)*m<n*m)
{
cout<<"NO\n";
return;
}
vector<vector<int>>mp(n+1,vector<int>(m+1,0));
int i=0,j=0,cnt=0;
int dirn=1,dirm=1;
mp[0][0] = ++cnt;
while(cnt<n*m)
{
if(cnt%n==0)
{
j = (j+cnt%m*dirm+m*m)%m;
mp[i][j] = ++cnt;
dirm *= -1;
}
else
{
i = (i+cnt%n*dirn+n*n)%n;
mp[i][j] = ++cnt;
dirn *= -1;
}
}
cout<<"YES\n";
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
cout<<mp[i][j]<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t=1;
// cin>>t;
while(t--) eachT();
return 0;
}E.老师与好感度
dp #线性dp
题目

思路
由于\(0\leq a_{i}\leq 100\),很容易想到要枚举最后出现的\(m\)个数,考虑\(m=2\)的情况,即枚举两个目标\(tar_{1},tar_{2}\)(\(target\))
状态表示:
\(dp[i][j]\)表示从\(1\)遍历到\(i\),第\(i\)个学生的好感度变为\(tar_{j}\)(\(1\leq j\leq 2\))的最小总天数
状态转移:
\[\begin{align} &dp[i][j]=\min_{0\leq k\leq[m=2]}\{dp[i][j]\ , \ dp[i-1][k]+ \max\{ tar_{j}-a_{i}-(tar_{k}-a_{i-1})\ ,\ 0 \} \},0\leq j\leq[m=2]\\ \\ &if(tar_{j}-a_{i}<0)dp[i][j]=inf \end{align} \]
当\(m=2\)的时候,\(dp[i][j]\)将由\(i-1\)时的两个状态转移过来,分别是选\(tar_{1},tar_{2}\)的状态
要与\(0\)取\(max\)是因为\(a_{i}\)与\(tar\)的差距可能比较小,仅用之前的天数就可以达到目标
枚举\(tar_{1},tar_{2}\),每次都取全局最小值即可
注意,\(tar_{1}\)的上下界分别为\(a_{i}\)的最大值与最小值,\(tar_{2}\)的上下界分别为\(200\)与\(tar_{1}\)
\(tar_{2}\)的上界不是\(a_{i}\)的最大值,因为可能会有区间覆盖在\(a_{i}\)最大值上使得它变大
最坏情况下,\(a_{i}\)的最大值被覆盖的次数量级为\(o(n)\),因此上界设为\(100+100\)即可
代码实现
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); i --)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
constexpr int inf = 1e9 + 5;
// #define int ll
const int up=155;
void chmin(int&x,int y){
x=min(x,y);
}
void chmax(int&x,int y){
x=max(x,y);
}
const int N=405;
int a[N],dp[N][2],t[2];
void eachT() {
int n,m;cin>>n>>m;
int ma=0,mi=inf;
rep(i,1,n){
cin>>a[i];
chmax(ma,a[i]);
chmin(mi,a[i]);
dp[i][0]=dp[i][1]=inf;
}
int ans=inf;
rep(tar1,mi,ma){
rep(tar2,tar1,up){
t[0]=tar1,t[1]=tar2;
dp[1][0]=t[0]-a[1];
dp[1][1]=(m==2)?t[1]-a[1]:inf;
if(dp[1][0]<0)dp[1][0]=inf;
if(dp[1][1]<0)dp[1][1]=inf;
rep(i,2,n){
rep(j,0,(m==2)){
rep(k,0,(m==2)){
chmin(dp[i][j],max(t[j]-a[i]-(t[k]-a[i-1]),0)+dp[i-1][k]);
if(t[j]-a[i]<0)dp[i][j]=inf;
}
}
}
chmin(ans,min(dp[n][0],dp[n][1]));
rep(i,2,n)dp[i][0]=dp[i][1]=inf;
}
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
ll t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
eachT();
}
}F. 老师和 Yuuka 逛商场
线段树 #线段树二分
题目

思路
由于要确定两个隔板,非常容易想到的一个思路便是\(o(n)\)遍历左隔板,\(o(\log n)\)查找最优右隔板,总复杂度\(o(n\log n)\)
设集合\(S_{l}\)表示区间\([1,l]\)内的元素(去重),那么\([l+1,n]\)内能对答案有贡献的数字必然要属于\(S_{l}\),因此我们可以将\([l+1,n]\)这一段序列视作只剩下了属于\(S_{l}\)的元素
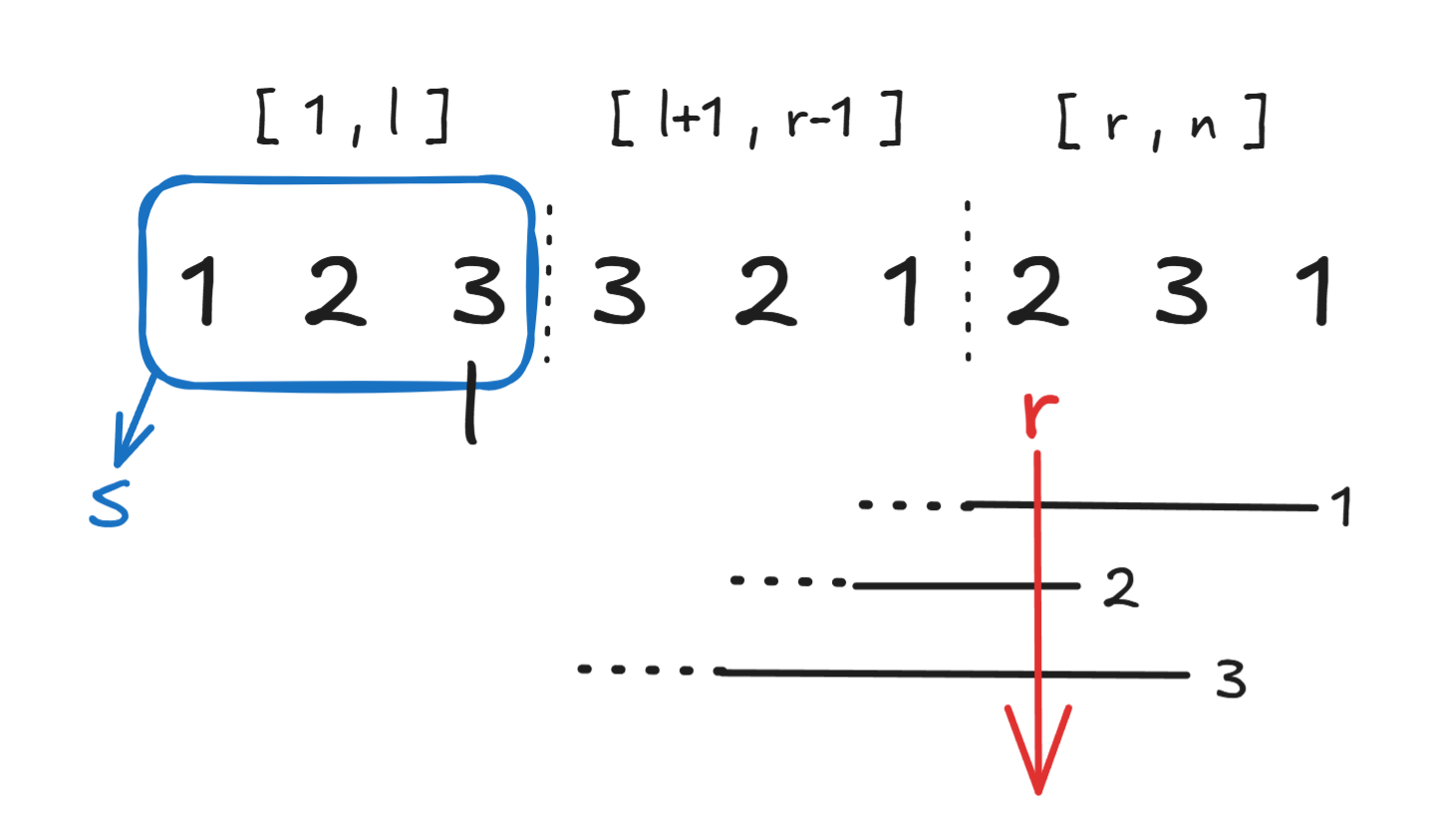
我们将序列分为三段:\([1,l],[l+1,r-1],[r,n]\)
目标即使得\([l+1,r-1],[r,n]\)中共同元素的数量尽可能大
因此我们对每个元素在区间\([l+1,n]\)中最早出现和最晚出现的位置\(lpos,rpos\)进行维护,当指针落于元素\(x\)的\([lpos,rpos]\)中时便说明该指针的左边与右边必定都有元素\(x\)出现
每次移动\(l\)指针的时候,都使用队列\(deque\)更新元素\(a[l]\)的\(lpos,rpos\)
接着,使用线段树对区间\([lpos+1,rpos]\)进行区间\(+1\),同时维护区间的最大值
为什么左端点是\(lpos+1\)呢?
这是为了保证指针\(r\)坐落于区间中的时候,\([r,n]\)上必定有元素\(x\),\([l+1,r-1]\)上也必定有元素\(x\)
考虑边缘情况,若\(r=lpos+1\),那么\(r-1=lpos\),刚好将最左边的元素\(x\)包含进了区间中
令\(r\)指针落在区间\([l+1,n]\)的\(max\)值的点上,此时左右区间必定有\(max\)值个相同元素,此处便是最优分割处
如何在线段树上找到这个\(max\)值的位置呢?
我们可以在线段树上二分,通过\(pair\)来储存\(max\)的值与位置:
-
\(pair\!<\!int,int\!>\)类型的\(find(p,l,r)\)函数
- 传回的\(pair\)中,\(first\)为\(max\)的值,\(second\)为\(max\)值的位置
- 功能:查询区间\([l,r]\)内的单点最大值及其位置
- 对比左右子树的\(max\)值,选择\(max\)值较大的子树分裂查询
-
\(pair\!<\!int,int\!>\)类型的\(query(p,l,r,ql,qr)\)函数
- 传回的\(pair\)中,\(first\)为\(max\)的值,\(second\)为\(max\)值的位置
- 功能:查询区间\([ql,qr]\)内的单点最大值及其位置
- 若\([l,r]\)被\([ql,qr]\)完全覆盖,那么可以直接调用\(find(p,l,r)\)
- 否则需要分裂查询左子树与右子树,返回左右子树中的较大者
为什么要设计两个函数来二分查找?
因为给定的\(ql,qr\)不一定是某个已知线段树节点所维护的区间\(l,r\),可能需要分裂成多个区间进行比较
通过\(query\)函数将\([ql,qr]\)分裂成一个个已知区间\([l,r]\),再通过\(find\)函数在线段树上查找
每次更新\(l\)指针时,先删去\(a[l]\)的\([lpos+1,rpos]\),\(a[l]\)的\(deque\)进行\(pop\_front\)之后再加回\([lpos'+1,rpos]\)
调用\(query(1,1,n,l+2,n)\)查询区间\([l+2,n]\)中的最大值与位置以确定最优的\(r\)指针
之所以是\(l+2\)的原因是,当\(r\)取\(l+2\)的时候,\(r-1\)为\(l+1\),与之前讨论的边界情况相符
注意\(l,r\)分别初始化为\(2,3\),以防\(n=3\)的情况
一直取全局最大值即可
代码实现
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); i --)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
constexpr int inf = 1e9;
#define int ll
// #define double long double
const int N = 1e5 + 5e4 + 5;
int n, a[N];
unordered_map<int, deque<int>>mp;
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
int add[N << 2], ma[N << 2];
void pushup(int p) {
ma[p] = max(ma[ls], ma[rs]);
}
void pushdown(int p, int l, int r) {
if (add[p]) {
ma[ls] += add[p];
ma[rs] += add[p];
add[ls] += add[p];
add[rs] += add[p];
add[p] = 0;
}
}
void modify(int p, int l, int r, int x, int y, int val) {
if (x <= l && r <= y) { ma[p] += val; add[p] += val; return; }
pushdown(p, l, r);
if (x <= mid)modify(ls, l, mid, x, y, val);
if (y > mid)modify(rs, mid + 1, r, x, y, val);
pushup(p);
}
pair<int, int> find(int p, int l, int r) {
if (l == r)return { ma[p],l };
pushdown(p, l, r);
if (ma[ls] >= ma[rs])return find(ls, l, mid);
else return find(rs, mid + 1, r);
}
pair<int, int> query(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if (ql > r || qr < l) return { -1,-1 };
if (ql <= l && r <= qr) return find(p, l, r);
pushdown(p, l, r);
auto left = query(ls, l, mid, ql, qr);
auto right = query(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr);
return left.first >= right.first ? left : right;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
ma[p] = add[p] = 0;
if (l == r)return;
build(ls, l, mid); build(rs, mid + 1, r);
}
void eachT() {
cin >> n;
mp.clear();
build(1, 1, n);
unordered_multiset<int>sl;
rep(i, 1, n) {
cin >> a[i];
mp[a[i]].push_back(i);
}
int ans = 0, ansl = 2, ansr = 3;
rep(l, 1, n) {
if (!sl.count(a[l])) {
mp[a[l]].pop_front();
int posl = mp[a[l]].front(), posr = mp[a[l]].back();
if (posl + 1 <= posr)modify(1, 1, n, posl + 1, posr, 1);
} else {
int posl = mp[a[l]].front(), posr = mp[a[l]].back();
if (posl + 1 <= posr)modify(1, 1, n, posl + 1, posr, -1);
mp[a[l]].pop_front();
if (mp[a[l]].size() >= 2) {
int posl = mp[a[l]].front(), posr = mp[a[l]].back();
if (posl + 1 <= posr)modify(1, 1, n, posl + 1, posr, 1);
}
}
sl.insert(a[l]);
pair<int, int> now = query(1, 1, n, l + 2, n);
if (ans < now.first) {
ans = now.first;
ansl = l + 1, ansr = now.second;
}
}
cout << ans << '\n' << ansl << " " << ansr << '\n';
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
ll t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
eachT();
}
}K. 神奇集合
强联通分量 #树上背包 #dp
题目

思路
注意到题目中添加的新边为返祖边 ,一旦选择了该连通块中的任意一个点,那么这整个连通块都必须要选择,因此考虑对图进行\(tarjan\)缩点
缩点过程中,将新点的权值、入度进行记录
由于原图是树,则添加返祖边缩点后仍然是一棵树
建好新图后遍历所有新节点,找出入度为0的点记为根节点
从根节点进入,\(dfs\)过程中进行树上背包dp:
状态表示:
\(dp[u][j]=1 /0\)代表以\(u\)为根的子树中,是否存在总权值为\(j\)的神奇集合
状态转移:
\[\begin{align} &sum_{u}\geq i\geq 0,sum_{son}\geq j\geq 0:dp[u][i+j]\ |=dp[u][i]\&dp[son][j]\\ \\ &dp[u][sum_{u}]=1 \end{align} \]
从\(u\)节点已经遍历的所有可能权值中取出权值为\(i\)的情况,从\(son\)节点的所有可能权值中取出权值为\(j\)的情况,二者可以转移到\(dp[u][i+j]\)的状态中
最后考虑整个子树都选上的情况\(dp[u][sum_{u}]\)
答案即为\(\sum_{i=0}^{N} dp[root][i]\)
代码实现
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
#include<stack>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
#define int ll
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++)
#define per(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); i --)
#define see(stl) for(auto&ele:stl)cout<<ele<<" "; cout<<'\n';
constexpr int inf = 1e9 + 5;
// #include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
// using namespace __gnu_pbds;
const int N=1e4+5;
int w[N];
struct node{
set<int>e;
int dfn,low,in,scc;
}a[N];
struct node1{
set<int>e;
int siz,deg,w,sum;
}na[N];
int tot,cnt;
stack<int>st;
void tarjan(int u){
a[u].dfn=a[u].low=++tot;
st.push(u),a[u].in=1;
for(auto&son:a[u].e){
if(!a[son].dfn){
tarjan(son);
a[u].low=min(a[u].low,a[son].low);
}else if(a[son].in){
a[u].low=min(a[u].low,a[son].low);
}
}
if(a[u].dfn==a[u].low){
int v;++cnt;
do{
v=st.top(),st.pop(),a[v].in=0;
a[v].scc=cnt,++na[cnt].siz;
na[cnt].w+=w[v];
}while(u!=v);
}
}
int n;
void build(){
rep(i,1,n){
for(auto&son:a[i].e){
if(a[i].scc!=a[son].scc){
na[a[i].scc].e.insert(a[son].scc);
na[a[son].scc].deg++;
}
}
}
}
bool dp[N][N];
int dfs(int u,int fa){
int sum=0;
dp[u][0]=1;
for(auto&son:na[u].e){
if(son==fa)continue;
sum+=dfs(son,u);
per(i,na[u].sum,0){
per(j,na[son].sum,0){
dp[u][i+j]|=dp[u][i]&dp[son][j];
}
}
na[u].sum=sum;
}
sum+=na[u].w;
na[u].sum=sum;
dp[u][sum]=1;
return sum;
}
void eachT() {
cin>>n;
rep(i,1,n)cin>>w[i];
rep(i,1,n-1){
int u,v;cin>>u>>v;
a[u].e.insert(v);
}
int m;cin>>m;
rep(i,1,m){
int u,v;cin>>u>>v;
if(u!=v)a[u].e.insert(v);
}
rep(i,1,n){
if(!a[i].scc)tarjan(i);
}
build();
int rt;
rep(i,1,cnt){
if(na[i].deg==0)rt=i;
}
dfs(rt,0);
int cnt=0;
rep(i,0,N-1)if(dp[rt][i])cnt++;
cout<<cnt<<'\n';
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
ll t = 1;
// cin >> t;
while (t--) {
eachT();
}
}