关注我的公众号:【编程朝花夕拾】,可获取首发内容。

01 引言
批量插入数据是我们业务中经常遇到的,我们习惯了手搓sql如:
sql
insert into user_info (`name`, `age`, `created_time`) values
<foreach item ="item" collection="list" separator=",">
(#{item.name}, #{item.age}, #{item.createdTime})
</foreach>这样的脚本,适用于数据量不大的情况,基本满足业务需求,但是却存在安全隐患。当传输的数据量过大时,可能会引起异常。
本节,我们将对比不同的写法以及响应的时间的消耗。
02 日常批量插入
insert into tb (col1, col2) values (val1, val2),......
上面的这种写法确实比一条条的数据入库的速度快太多,我们这里只横向对比不同的批量插入。我们先看看Mysql官方给的Insert执行的流程。
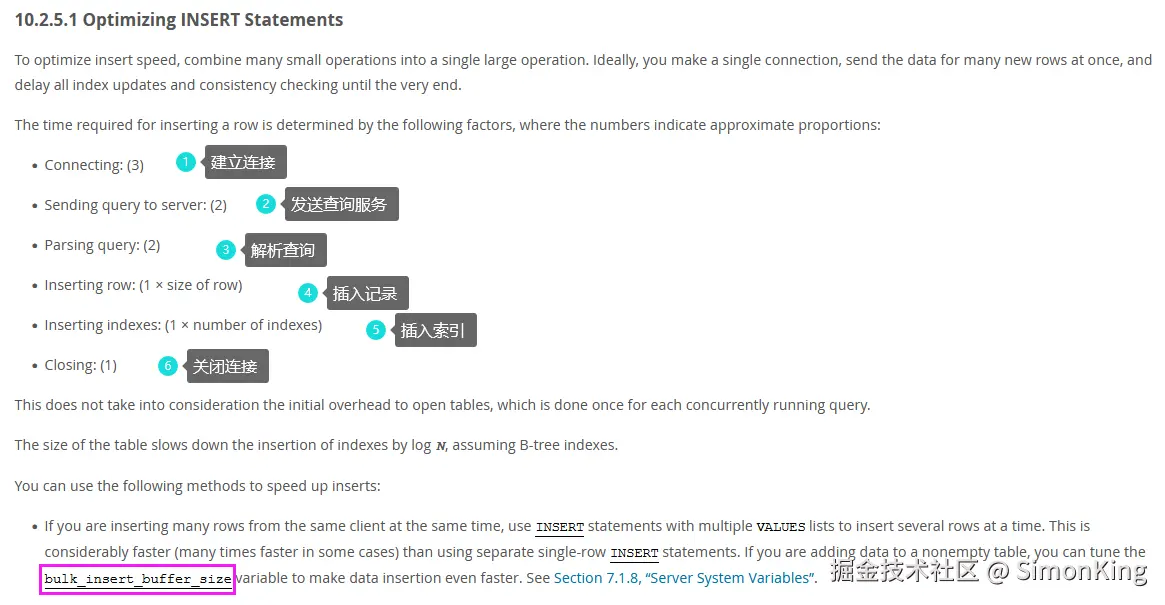
官网地址:dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/...
2.1 安全隐患
所谓的安全隐患,其实就是Mysql的一些配置。而这些配置直接影响sql是否会执行以及执行的效率。
bulk_insert_buffer_size:max_allowed_packet
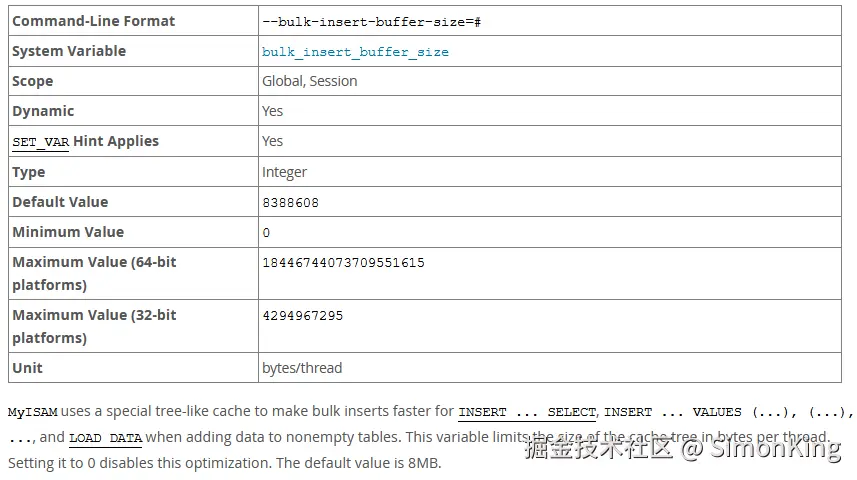
bulk_insert_buffer_size
Myisam引擎参数,在使用myisam引擎执行INSERT ... SELECT,INSERT ... VALUES (...), (...), ...,LOAD DATA INFILE批量插入时,会采用一种缓存树的内存结构来优化插入速度。默认8M。
max_allowed_packet
控制了 MySQL 服务器接收和发送的最大数据包的大小,默认64M。
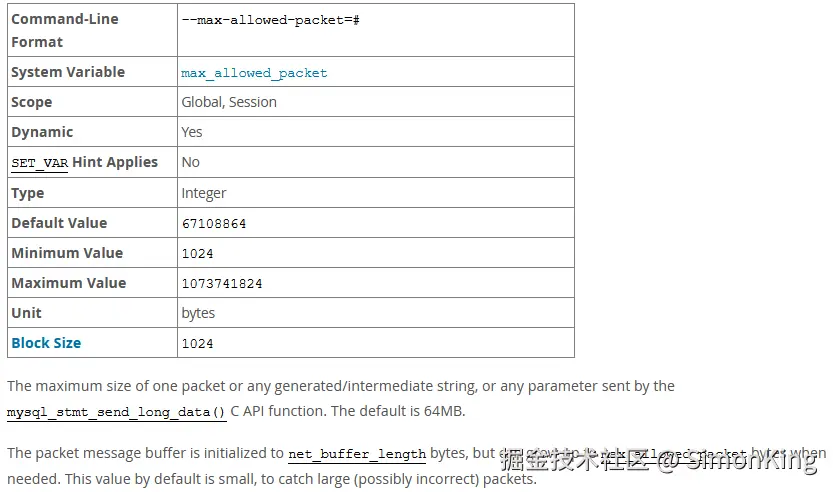
因为小编测试的Mysql引擎使用的是innodb,所以暂时不考虑第一个参数。小编准备了10条数据一次全部插入到数据库,就报错了:
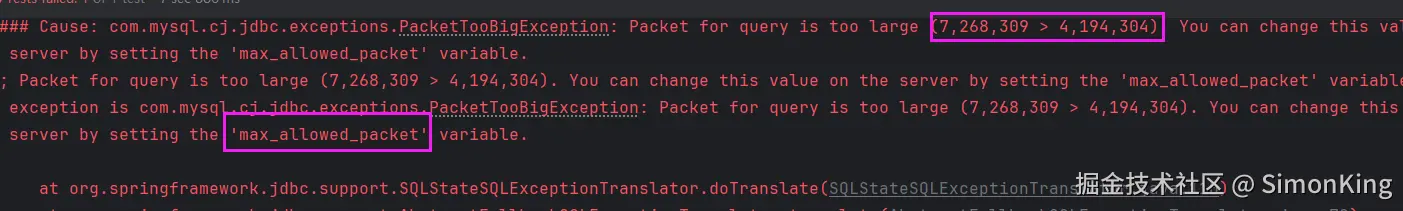
所以呢,当一次插入的数据达到一定的数据就会出现异常。
2.2 分批插入
我们通过1W条数据测试一下,不同数据插入的结果:
java
@Test
public void test01() {
List<UserInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("test" + i);
userInfo.setAge(new Random().nextInt(1,90));
userInfo.setCreatedTime(LocalDateTime.now());
list.add(userInfo);
}
List<List<UserInfo>> partition = Lists.partition(list, 5000);
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
for (List<UserInfo> userInfos : partition) {
userInfoMapper.insertBatch(userInfos);
}
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("1W 条数据每隔1000插入,耗时:"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()+"ms");
// 1W 条数据字节直接插入,耗时:1342ms
// 1W 条数据每隔500插入,耗时:1270ms
// 1W 条数据每隔1000插入,耗时,耗时:1257ms
// 1W 条数据每隔2000插入,耗时,耗时:1142ms
// 1W 条数据每隔5000插入,耗时,耗时:1153ms
}脚本
java
@Insert("""
<script>
insert into user_info (`name`, `age`, `created_time`) values
<foreach item ="item" collection="list" separator=",">
(#{item.name}, #{item.age}, #{item.createdTime})
</foreach>
</script>
""")
void insertBatch(@Param("list") List<UserInfo> list);从直接的结果来看,我们发现:
每次插入2000条左右时,耗时相对比较少。也就是说2000左右时我们每次插入数据的最佳数据量。当然这个和数据库引擎,字段量等有一定关系。
批量插入并不是数据越多越快。
我们可以从stackoverflow上找到类似的答案:
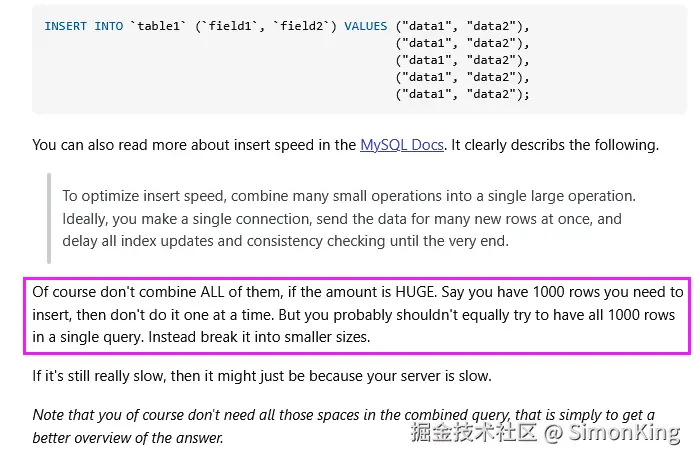
地址:stackoverflow.com/questions/1...
Redgate上也有人专门做了不同数据量对于批量插入的测试:
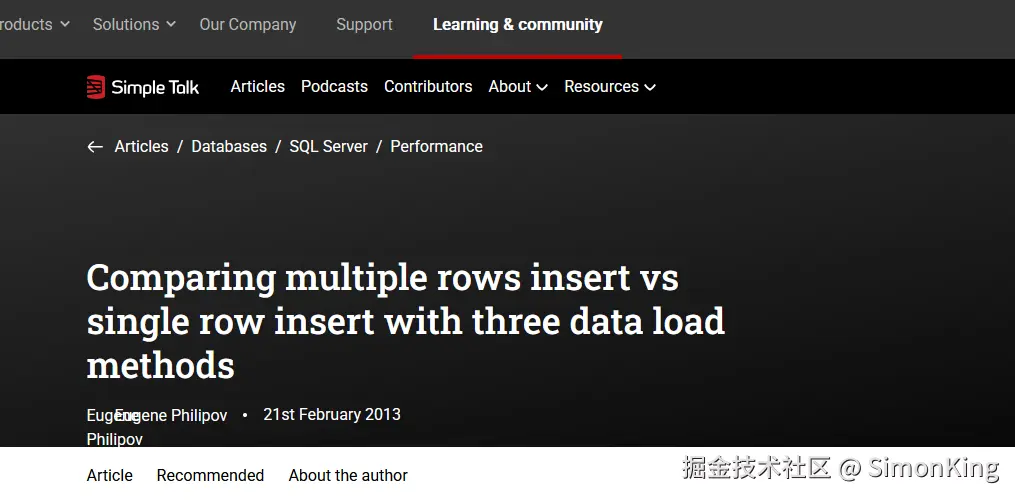
www.red-gate.com/simple-talk...
03 Mybaits-Plus批量插入
Mybaits-Plus简称MP。它本身提供了三种批量插入的方法:
insert(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize)MybatisBatch.Method<?>InsertBatchSomeColumn
3.1 insert
java
@Test
public void test03() {
List<UserInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("test" + i);
userInfo.setAge(new Random().nextInt(1,90));
userInfo.setCreatedTime(LocalDateTime.now());
list.add(userInfo);
}
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
userInfoMapper.insert(list, 2000);
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("1W 条数据每隔500插入,耗时:"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()+"ms");
// 1W 条数据批量提交插入,耗时:11918ms
// 1W 条数据每隔500插入,耗时:12856ms
// 1W 条数据每隔1000插入,耗时:11700ms
// 1W 条数据每隔2000插入,耗时:12031ms
// 1W 条数据每隔5000插入,耗时:11745ms
}我们可以看到对于1W条数据的处理,MP的这种方式是很耗时的。平均在10s以上,但是同样可以得到结论每一批1000条左右时,效果最好。这也是框架默认的分割参数。
慢的原因
关键的代码如下:
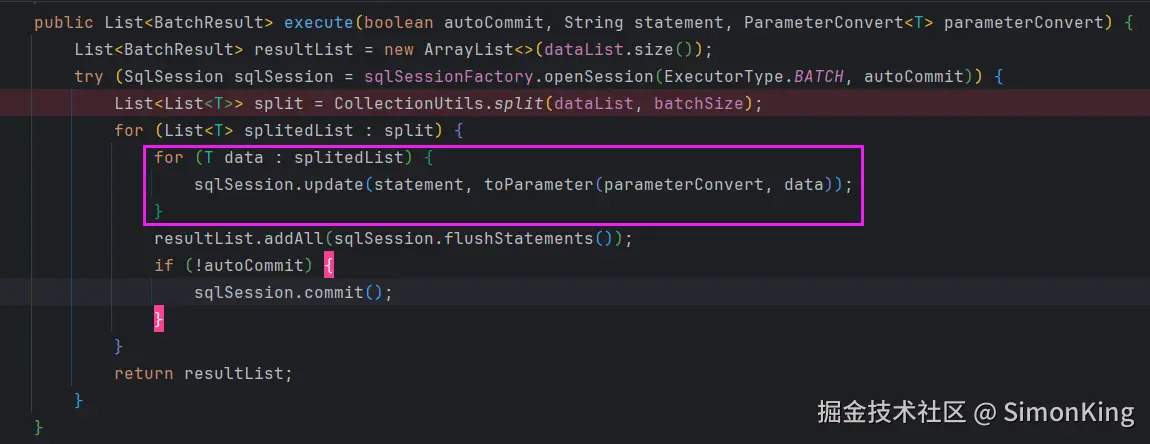
源码用了双层for循环,每一条数据都拼接成几个完整的SQL执行,最后提交事务。类似下面的脚本:
sql
START TRANSACTION;
-- 执行一系列SQL语句
insert into tb (col1, col2) values (val1, val2);
insert into tb (col1, col2) values (val1, val2);
-- ......
-- 提交事务
COMMIT;3.2 MybatisBatch.Method<?>
java
@Test
public void test05() {
List<UserInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("test" + i);
userInfo.setAge(new Random().nextInt(1,90));
userInfo.setCreatedTime(LocalDateTime.now());
list.add(userInfo);
}
List<List<UserInfo>> partition = Lists.partition(list, 5000);
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
for (List<UserInfo> userInfos : partition) {
MybatisBatch<UserInfo> mybatisBatch = new MybatisBatch<>(sqlSessionTemplate.getSqlSessionFactory(), userInfos);
MybatisBatch.Method<UserInfo> method = new MybatisBatch.Method<>(UserInfoMapper.class);
mybatisBatch.execute(method.insert());
}
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("1W 条数据批量提交插入,耗时:"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()+"ms");
// 1W 条数据批量提交插入,耗时:12866ms
// 1W 条数据每500条批量提交插入,耗时:12624ms
// 1W 条数据每1000条批量提交插入,耗时:12953ms
// 1W 条数据每2000条批量提交插入,耗时:12501ms
// 1W 条数据每5000条批量提交插入,耗时:11670ms
}3.3 InsertBatchSomeColumn
java
@Test
public void test06() {
List<UserInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("test" + i);
userInfo.setAge(new Random().nextInt(1,90));
userInfo.setCreatedTime(LocalDateTime.now());
list.add(userInfo);
}
List<List<UserInfo>> partition = Lists.partition(list, 5000);
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
for (List<UserInfo> userInfos : partition) {
userInfoMapper.insertBatchSomeColumn(userInfos);
}
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("1W 条数据批量提交插入,耗时:"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()+"ms");
// 1W 条数据批量提交插入,耗时:1425ms
// 1W 条数据每500条批量提交插入,耗时:1483ms
// 1W 条数据每1000条批量提交插入,耗时:1413ms
// 1W 条数据每2000条批量提交插入,耗时:1492ms
// 1W 条数据每5000条批量提交插入,耗时:1549ms
}从运行的结果来看,这种方式才是类似我们手搓的的脚本,效率杠杠的。
04 启用Mybaits的Batch
脚本同2.2中的脚本,仅仅开启Batch属性。
java
@Test
public void test07() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionTemplate.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
UserInfoMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserInfoMapper.class);
List<UserInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("test" + i);
userInfo.setAge(new Random().nextInt(1,90));
userInfo.setCreatedTime(LocalDateTime.now());
list.add(userInfo);
}
List<List<UserInfo>> partition = Lists.partition(list, 5000);
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
for (List<UserInfo> userInfos : partition) {
mapper.insertBatch(userInfos);
}
sqlSession.commit();
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("1W 条数据批量提交插入,耗时:"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()+"ms");
// 1W 条数据批量提交插入,耗时:1181ms
// 1W 条数据每500条批量提交插入,耗时:1201ms
// 1W 条数据每1000条批量提交插入,耗时:1174ms
// 1W 条数据每2000条批量提交插入,耗时:1139ms
// 1W 条数据每5000条批量提交插入,耗时:1184ms
}开启ExecutorType.BATCH确实比ExecutorType.SIMPLE快了一丢丢。
05 小结
批量插入面对小数据量的时,几乎没有任何区别,可以随意使用。一旦数据量比较大时,我们就需要斟酌,选择合适的插入方法,可以帮我们节省很多资源和时间。