在处理海量的非结构化文本时,如何高效且准确地提取结构化信息(如实体、关系、属性)一直是一个棘手的问题。传统方案如正则表达式或基于规则的解析器虽然简单,但往往缺乏灵活性、难以适应复杂语境,且维护成本居高不下。随着大型语言模型的兴起,利用其自然语言理解能力进行信息抽取,正在成为主流的新范式。 LangExtract正是基于这一背景诞生的一个Python框架。它并非仅仅是对 API 的简单封装,而是围绕 "Schema 驱动抽取"思想构建的,具备高度可扩展性和生产级能力的解决方案。
一、核心特性
LangExtract的设计理念,使它在众多抽取工具中脱颖而出,主要优势包括:
1. Schema 驱动抽取 只需定义一个 Pydantic 模型,LangExtract会自动生成提示词,引导 LLM 返回符合 Schema 的 JSON 数据,并转化为 Python 对象。
2. 可插拔的Provider架构 内置支持 Google Gemini、OpenAI 以及本地的 Ollama 模型。可以轻松切换后端,甚至接入自研或开源 API,极大提升了灵活性。
3. 智能分块与并行处理 针对长文档,LangExtract会自动进行智能切分,并支持并行化处理,再统一聚合结果。这既解决了 LLM 的上下文限制问题,又提升了整体效率。
4. 高度可扩展性 几乎每个环节都可定制:提示词模板、分块策略、Provider 实现等,都能通过注册表和插件系统扩展,方便与实际业务场景结合。
5. 结果可视化 内置高亮与 HTML 可视化工具,特别适合命名实体识别等任务。结果可交互查看,也能方便地共享和质检。
二、代码结构解析
LangExtract的代码主要位于langextract/目录下,各模块职责明确:
javascript
langextract/
├── schema.py # 定义核心数据结构,如 ExtractionInput, ExtractionResult
├── extraction.py # 提取流程的控制器和编排逻辑
├── factory.py # 提供顶层 API 入口
├── prompting.py # 根据 Schema + 文本生成提示词
├── chunking.py # 文本分块逻辑
├── inference.py # 负责调用底层 LLM
├── providers/ # 各类 Provider 的实现(openai.py, gemini.py, ollama.py)
├── plugins.py # 插件系统,用于加载扩展
└── registry.py # 注册表,管理可扩展组件数据流大致分为以下步骤:
-
用户入口(factory.py)
- 用户调用 langextract.extract() 发起任务。
-
提取编排(extraction.py)
- 将长文本切块(chunking.py)
- 生成提示词(prompting.py)
- 调用 Provider 获取结果(inference.py)
-
Provider 执行(providers/)
- 如 openai.py,与对应 LLM API 通信,返回结果。
-
结果解析与验证
- 使用 Pydantic Schema 校验并转为 Python 对象。
-
结果聚合
- 如果有多块输入,系统会自动合并为完整结果。
三、快速上手
以《罗密欧与朱丽叶》为例,我们希望从文本中提取人物的名字和描述。
- 定义提示词和提取规则
python
import langextract as lx
import textwrap
# 1. Define the prompt and extraction rules
prompt = textwrap.dedent("""\
Extract characters, emotions, and relationships in order of appearance.
Use exact text for extractions. Do not paraphrase or overlap entities.
Provide meaningful attributes for each entity to add context.""")- 提供一个高质量的示例来指导模型
python
# Provide a high-quality example to guide the model
examples = [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text="ROMEO. But soft! What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun.",
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="character",
extraction_text="ROMEO",
attributes={"emotional_state": "wonder"}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="emotion",
extraction_text="But soft!",
attributes={"feeling": "gentle awe"}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="relationship",
extraction_text="Juliet is the sun",
attributes={"type": "metaphor"}
),
]
)
]- 准备文本并执行抽取
python
# The input text to be processed
input_text = "Lady Juliet gazed longingly at the stars, her heart aching for Romeo"
# Run the extraction
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=input_text,
prompt_description=prompt,
examples=examples,
model_id="gemini-2.5-flash",
)
print(f"result:{result}")
# Save the results to a JSONL file
lx.io.save_annotated_documents([result], output_name="extraction_results.jsonl", output_dir=".")
# Generate the visualization from the file
html_content = lx.visualize("extraction_results.jsonl")
with open("visualization.html", "w") as f:
if hasattr(html_content, 'data'):
f.write(html_content.data) # For Jupyter/Colab
else:
f.write(html_content)预期输出:
提供可视化结果,可以看到提取的实体: 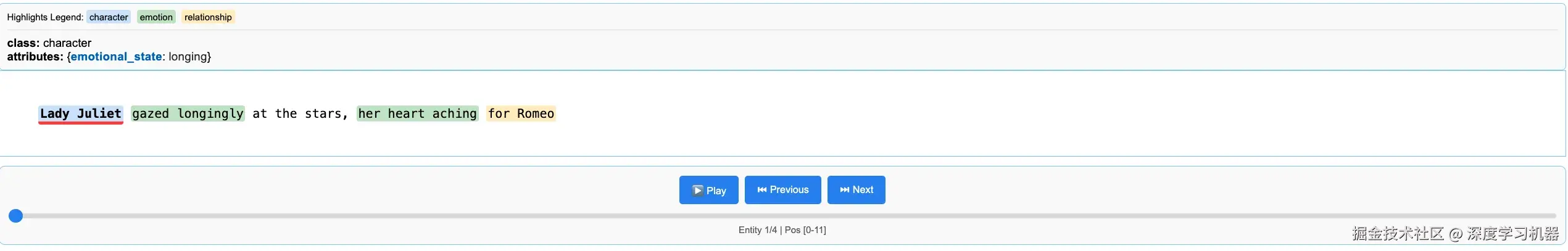
还可以看到提取到的不同tokens之间的相对位置关系,这对于溯源比较有帮助:
javascript
{"extractions": [{"extraction_class": "character", "extraction_text": "Lady Juliet", "char_interval": {"start_pos": 0, "end_pos": 11}, "alignment_status": "match_exact", "extraction_index": 1, "group_index": 0, "description": null, "attributes": {"emotional_state": "longing"}}, {"extraction_class": "emotion", "extraction_text": "gazed longingly", "char_interval": {"start_pos": 12, "end_pos": 27}, "alignment_status": "match_exact", "extraction_index": 2, "group_index": 1, "description": null, "attributes": {"feeling": "longing"}}, {"extraction_class": "emotion", "extraction_text": "her heart aching", "char_interval": {"start_pos": 42, "end_pos": 58}, "alignment_status": "match_exact", "extraction_index": 3, "group_index": 2, "description": null, "attributes": {"feeling": "sorrowful longing"}}, {"extraction_class": "relationship", "extraction_text": "for Romeo", "char_interval": {"start_pos": 59, "end_pos": 68}, "alignment_status": "match_exact", "extraction_index": 4, "group_index": 3, "description": null, "attributes": {"type": "romantic"}}], "text": "Lady Juliet gazed longingly at the stars, her heart aching for Romeo", "document_id": "doc_b68c0b33"}四、LangExtract实战:使用语义检索+实体图谱的Hybrid RAG
RAG在工业界的应用已经比较成熟了,除了最基本的语义检索外,还有使用Rerank进行重排序、语义和关键字结合的混合检索,以及Graph RAG等基于知识图谱的方案。使用LangExtract可以在一定程度下替代Graph RAG这种token杀手,相当于一种Hybrid RAG的方案,并且成本相对可控。以下是一个简单的demo:
- 基本设置 导入所有需要的包,这里使用
langchain内置的FAISS作为向量数据库:
python
import langextract as lx
import textwrap
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from openai import OpenAI- 文档向量化 使用最基本的
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter进行切分:
python
# ========== 演示文本 ==========
corpus_text = """
Romeo and Juliet is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare.
Romeo is a young man from the Montague family.
Juliet is a young woman from the Capulet family.
They fall in love at first sight.
Tybalt, Juliet's cousin, hates Romeo deeply.
Friar Laurence secretly helps the lovers marry, hoping to end the family feud.
Mercutio, Romeo's close friend, is witty and bold.
Their love faces many obstacles, leading to a tragic ending.
"""
# ========== 切分文本 ==========
splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=150, chunk_overlap=20)
docs = splitter.create_documents([corpus_text])
for doc in docs:
print("doc:", doc)
print('\n\n')
# ========== 向量化 & 存入向量数据库 ==========
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(
model='xxx',
api_key="sk-xxx",
base_url='xxx'
)
vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(docs, embeddings)简单的分块效果:
javascript
doc: page_content='Romeo and Juliet is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare.
Romeo is a young man from the Montague family.'
doc: page_content='Juliet is a young woman from the Capulet family.
They fall in love at first sight.
Tybalt, Juliet's cousin, hates Romeo deeply.'
doc: page_content='Friar Laurence secretly helps the lovers marry, hoping to end the family feud.
Mercutio, Romeo's close friend, is witty and bold.'
doc: page_content='Their love faces many obstacles, leading to a tragic ending.'- 语义检索
python
query "Tell me about Juliet's family and her relationships."
retrieved_docs = vectorstore.similarity_search(query, k=2)
for d in retrieved_docs:
print("d:", d.page_content)
print('\n\n')检索出两个相似的chunks:
javascript
d: Their love faces many obstacles, leading to a tragic ending.
d: Juliet is a young woman from the Capulet family.
They fall in love at first sight.
Tybalt, Juliet's cousin, hates Romeo deeply.- 定义LangExtract提取规则,并进行实体提取
python
# 定义规则
prompt = textwrap.dedent("""\
Extract characters, emotions, and relationships in order of appearance.
Use exact text for extractions. Do not paraphrase or overlap entities.
Provide meaningful attributes for each entity to add context.""")
examples = [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text="ROMEO. But soft! What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun.",
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="character",
extraction_text="ROMEO",
attributes={"emotional_state": "wonder"}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="emotion",
extraction_text="But soft!",
attributes={"feeling": "gentle awe"}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="relationship",
extraction_text="Juliet is the sun",
attributes={"type": "metaphor"}
),
]
)
]
# 开始提取
graph_entities = []
for d in retrieved_docs:
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=d.page_content,
prompt_description=prompt,
examples=examples,
model_id="gemini-2.5-flash",
)
graph_entities.append(result)
for r in graph_entities:
print("r:", r)
print('\n\n')提取出的实体关系:
javascript
r: AnnotatedDocument(extractions=[Extraction(extraction_class='relationship', extraction_text='Their love', char_interval=CharInterval(start_pos=0, end_pos=10), alignment_status=<AlignmentStatus.MATCH_EXACT: 'match_exact'>, extraction_index=1, group_index=0, description=None, attributes={'type': 'romantic'}), Extraction(extraction_class='emotion', extraction_text='tragic ending', char_interval=CharInterval(start_pos=46, end_pos=59), alignment_status=<AlignmentStatus.MATCH_EXACT: 'match_exact'>, extraction_index=2, group_index=1, description=None, attributes={'feeling': 'unfortunate'})], text='Their love faces many obstacles, leading to a tragic ending.')
r: AnnotatedDocument(extractions=[Extraction(extraction_class='character', extraction_text='Juliet', char_interval=CharInterval(start_pos=0, end_pos=6), alignment_status=<AlignmentStatus.MATCH_EXACT: 'match_exact'>, extraction_index=1, group_index=0, description=None, attributes=None), Extraction(extraction_class='relationship', extraction_text='They fall in love at first sight.', char_interval=CharInterval(start_pos=49, end_pos=82), alignment_status=<AlignmentStatus.MATCH_EXACT: 'match_exact'>, extraction_index=2, group_index=1, description=None, attributes={'type': 'romantic'}), Extraction(extraction_class='character', extraction_text='Tybalt', char_interval=CharInterval(start_pos=83, end_pos=89), alignment_status=<AlignmentStatus.MATCH_EXACT: 'match_exact'>, extraction_index=3, group_index=2, description=None, attributes=None), Extraction(extraction_class='relationship', extraction_text="Juliet's cousin", char_interval=CharInterval(start_pos=91, end_pos=106), alignment_status=<AlignmentStatus.MATCH_EXACT: 'match_exact'>, extraction_index=4, group_index=3, description=None, attributes={'type': 'familial'}), Extraction(extraction_class='emotion', extraction_text='hates Romeo deeply', char_interval=CharInterval(start_pos=108, end_pos=126), alignment_status=<AlignmentStatus.MATCH_EXACT: 'match_exact'>, extraction_index=5, group_index=4, description=None, attributes={'feeling': 'hatred'})], text="Juliet is a young woman from the Capulet family.\nThey fall in love at first sight.\nTybalt, Juliet's cousin, hates Romeo deeply.")- Hybrid RAG
python
rag_context = "\n".join([d.page_content for d in retrieved_docs])
graph_context = "\n".join([str(r) for r in graph_entities])
final_context = f"""
Semantic Context:
{rag_context}
Graph Entities:
{graph_context}
"""
client = OpenAI(
api_key="sk-xxx",
base_url="xxx"
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[{
'role': 'user',
'content': f"Based on the following context, answer the query:\n{query}\n\n{final_context}"
}],
model='xxx'
)
print("\n=== Final Answer===")
print(response.choices[0].message.content)将语义检索与实体图谱结合后的回答效果,除了相关的段落外,还包含了提取出的关系,进一步丰富回答的效果:
javascript
=== Final Answer===
Juliet is a young woman from the **Capulet family**, a prominent house in Verona. Her familial relationships include:
- **Tybalt**: He is Juliet's cousin and holds a deep hatred for **Romeo**, the son of the rival Montague family. This antagonism adds tension to Juliet's secret romance with Romeo.
- **Romeo Montague**: Though not part of her family, Juliet develops a passionate romantic relationship with Romeo. They fall in love at first sight, but their love is fraught with obstacles due to the feud between their families, ultimately leading to a tragic ending.
Juliet's ties to her family---particularly the Capulet loyalty expected of her---clash with her love for Romeo, driving the central conflict of their story.五 总结
在LLM能力越来越强的今天,大部分传统的NLP任务已经没有必要专门训练一个模型去解决了,很多都可以使用LLM来处理,甚至不需要进行微调,如使用开源的VLM做版本分析和文档提取已经超过很多传统的Pipeline方法了。LangExtract也是利用LLM进行NER和KIE,只不过定义好了基本的框架,允许用户根据实际情况调整需要的Prompt和Example。