目录
8.从源代码说明6个exec内部都使用了execve系统调用
1.知识回顾
参见OS24.【Linux】进程等待 (下) 和 进程程序替换(上)文章
2.让exec系列函数执行自己的可执行文件
mycommand.c编译为mycommand可执行文件
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Mycommand is running ......\n");
return 0;
}main.c编译为main可执行文件
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
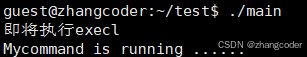
printf("即将执行execl\n");
execl("mycommand","mycommand",NULL);//mycommand可以不用加具体的路径,因为mycommand和main在同一个目录下
printf("execl已经执行完了\n");
return 0;
}编写makefile,让其生成多个可执行文件
cpp
.PHONY:all
all:mycommand main
mycommand:mycommand.c
gcc -o $@ $^ -std=c99
main:main.c
gcc -o $@ $^ -std=c99
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f mycommand main注意: .PHONY:all和all:mycommand main是必须要加的,否则make会gcc只生成一个写在前的可执行文件(即只生成mycommand,而不生成main)

运行结果:
3.让exec系列函数利用bash执行shell脚本文件
让exec系列函数利用bash执行shell脚本文件来演示C语言调用脚本语言
写一个简单的shell脚本
新建一个shell.sh,sh是shell脚本的后缀名
脚本语言由解释器解释,因此必须在shell.sh中注明用哪个解释器解释

下面填上路径即可:
cpp
#! /usr/bin/bash通过#!来设置运行shell创建一个什么样的进程来执行此脚本,而且#!可以调用任何一个解释器,例如python
然后添加要执行的命令:
cpp
#! /usr/bin/bash
echo "Hello World!"检查是否能正常运行可以手动使用bash命令:

使用exec系列函数调用shell脚本
test.c写入:
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
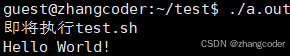
printf("即将执行test.sh\n");
sleep(1);
execl("/usr/bin/bash","bash","test.sh",NULL);//注意第一个/要加!
return 0;
}运行结果:
当然也可以写python脚本(前提要安装python),test.sh改成:

cpp
#! /usr/bin/python3
print("Hello Python!")main.c改成:
bash
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("即将执行test.sh\n");
sleep(1);
execl("/usr/bin/python3","python3","test.sh",NULL);//注意第一个/要加!
return 0;
}运行结果:
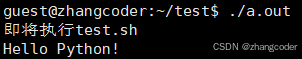
结论:不同语言之间可以相互调用,因为无论是哪个语言编写的程序,其运行起来本质都是进程
4.验证exec系列函数传入了参数
编译main.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
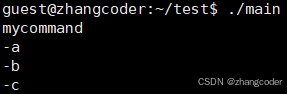
char *const argv[]={"mycommand","-a","-b","-c",NULL};
execv("./mycommand",argv);
return 0;
}编译mycommand.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
for (int i=0;argv[i];i++)
printf("%s\n",argv[i]);
return 0;
}将mycommand和main放在同一目录下,运行结果:
5.验证exec系列函数传入了环境变量
将main可执行文件中自制的环境变量传到mycommand,然后mycommand调用env命令打印
编译main.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[],char* envp[])
{
execle("./mycommand","mycommand",NULL,envp);
return 0;
}编译mycommand.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[],char* envp[])
{
execle("/usr/bin/env","env",NULL,envp);
return 0;
}将mycommand和main放在同一目录下,运行结果:
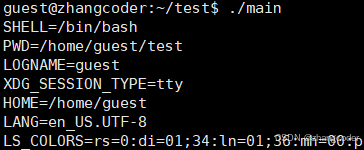
之前在OS22.【Linux】初识进程地址空间文章提到过:进程地址空间是含有存放命令行参数和环境变量的区域的
环境变量也是数据,创建子进程的时候,环境变量就已经被子进程(上方的main进程)继承下去了
结论:程序替换执行时,环境变量不会被替换
6.给子进程传递环境变量的方法
由于环境变量信息不随程序替换而替换,而是会一路让所有子进程继承.那么给子进程传递环境变量的方法:
新增环境变量
彻底替换
putenv函数
putenv将环境变量添加到调用进程的上下文
编译main.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
pid_t id = fork();
putenv("TEST=100");
if(id < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
else if(id == 0)//子进程
{
printf("子进程的pid:%d, ppid:%d\n", getpid(), getppid());
execlp("./mycommand","mycommand",NULL);
}
else//父进程得到子进程的PID
{
sleep(2);
printf("父进程准备回收子进程\n");
sleep(2);
pid_t ret = wait(NULL);
if(ret < 0)//返回-1等待失败
{
perror("wait failed");
}
if (ret == id)
{
printf("父进程回收子进程成功,子进程的pid:%d\n", ret);
}
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}编译mycommand.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
execlp("env","env",NULL);//ls没有带路径
return 0;
}将mycommand和main放在同一目录下,运行结果:
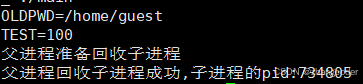
但bash查不到:
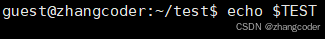
TEST是在./main进程下产生的,具有临时性,./main结束后,TEST也就销毁了
结论: 新增环境变量可以使用putenv,将环境变量添加到调用进程的上下文,这样就能被子进程继承
自定义环境变量,彻底替换原有的环境变量
编译main.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
else if(id == 0)//子进程
{
printf("子进程的pid:%d, ppid:%d\n", getpid(), getppid());
char *const envp[]={"TEST=100",NULL};
//彻底替换从./main那里继承而来的环境变量
//./main的环境变量又是从bash那里继承而来的
//bash的环境变量又是从操作系统那里继承而来的
execle("./mycommand","./mycommand",NULL,envp);
}
else//父进程得到子进程的PID
{
sleep(2);
printf("父进程准备回收子进程\n");
sleep(2);
pid_t ret = wait(NULL);
if(ret < 0)//返回-1等待失败
{
perror("wait failed");
}
if (ret == id)
{
printf("父进程回收子进程成功,子进程的pid:%d\n", ret);
}
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}编译mycommand.c
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[],char* envp[])
{
execlp("env","env",NULL);//ls没有带路径
return 0;
}将mycommand和main放在同一目录下,运行结果:老的环境变量被覆盖了,即彻底替换
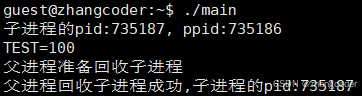
结论:像这样execle("./mycommand","./mycommand",NULL,++envp++)的是环境变量的覆盖,不是追加,老的环境变量不在了
7.execve系统调用
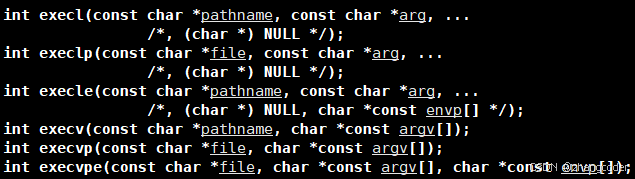
上面6个函数的底层最终都调用了execve
注意到:上面6个函数位于3号手册,是库函数
而execve处于2号手册,是系统调用
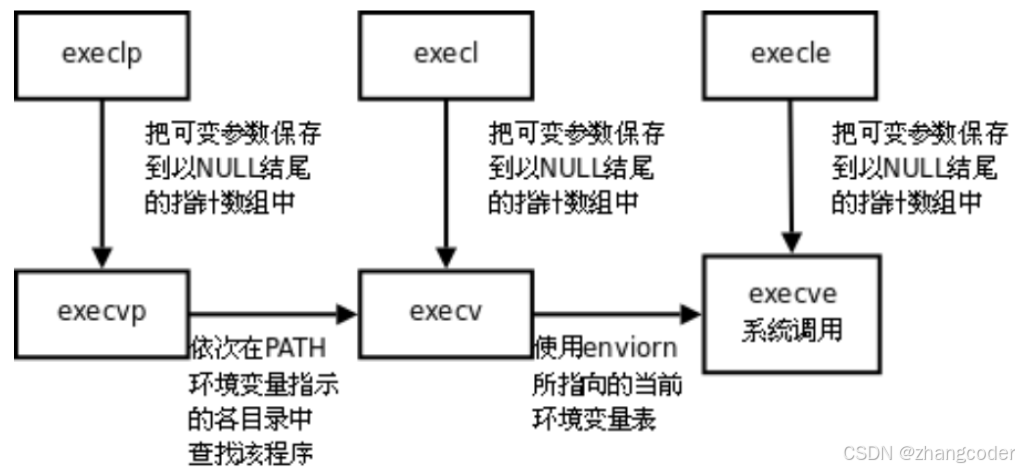
8.从源代码说明6个exec内部都使用了execve系统调用
在glibc-2.42(2025-07-28发布,可以从https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/libc/?C=M;O=A下载)源代码的posix的文件夹中,有exec系列函数和execve系统调用的源代码:
execv函数:
cpp
/* Execute PATH with arguments ARGV and environment from `environ'. */
int
execv (const char *path, char *const argv[])
{
return __execve (path, argv, __environ);
}execl函数:
节选了关键代码
cpp
int execl (const char *path, const char *arg, ...)
{
//......
int ret = __execve (path, (char *const *) argv, __environ);
//......
return ret;
}
libc_hidden_def (execl)execle函数:
节选了关键代码
cpp
/* Execute PATH with all arguments after PATH until a NULL pointer,
and the argument after that for environment. */
int execle (const char *path, const char *arg, ...)
{
//......
int ret = __execve (path, (char *const *) argv, (char *const *) envp);
//......
return ret;
}
libc_hidden_def (execle)execvp函数:
节选了关键代码
cpp
/* Execute FILE, searching in the `PATH' environment variable if it contains
no slashes, with arguments ARGV and environment from `environ'. */
int execvp(file, argv)
const char* file;
char* const argv[];
{
if (strchr(file, '/') != NULL)
{
/* Don't search when it contains a slash. */
__execve(file, argv, __environ);
if (errno == ENOEXEC)
{
//......
if (script_argv != NULL)
{
scripts_argv(file, argv, argc, script_argv);
__execve(script_argv[0], script_argv, __environ);
free(ptr);
}
}
}
else
{
//......
do
{
//......
__execve(startp, argv, __environ);
if (errno == ENOEXEC)
{
//......
__execve(script_argv[0], script_argv, __environ);
}
//......
} while (*p++ != '\0');
//......
}
/* Return the error from the last attempt (probably ENOENT). */
return -1;
}
libc_hidden_def(execvp)execlp函数:
节选了关键代码,内部调用了execvp函数
cpp
/* Execute FILE, searching in the `PATH' environment variable if
it contains no slashes, with all arguments after FILE until a
NULL pointer and environment from `environ'. */
int
execlp(const char* file, const char* arg, ...)
{
//......
int ret = execvp(file, (char* const*)argv);
//......
return ret;
}
libc_hidden_def(execlp)execvpe函数:
节选了关键代码,其中weak_alias (__execvpe, execvpe)说明execvpe是__execvpe函数的别名, __execvpe调用了__execvpe_common函数,后者又调用了__execve
cpp
/* Execute FILE, searching in the `PATH' environment variable if it contains
no slashes, with arguments ARGV and environment from ENVP. */
int
__execvpe (const char *file, char *const argv[], char *const envp[])
{
return __execvpe_common (file, argv, envp, true);
}
weak_alias (__execvpe, execvpe)
static int __execvpe_common(const char* file, char* const argv[], char* const envp[],
bool exec_script)
{
//......
/* Don't search when it contains a slash. */
if (strchr(file, '/') != NULL)
{
__execve(file, argv, envp);
if (errno == ENOEXEC && exec_script)
maybe_script_execute(file, argv, envp);
return -1;
}
//......
for (const char* p = path; ; p = subp)
{
//......
__execve(buffer, argv, envp);
//......
}
//......
return -1;
}结论:6个exec内部都使用了execve系统调用(__execve)