最近腾讯也开源了一个端到端视觉语言模型POINTS-Reader,在OCR任务上表现不错;至此,国内已经有不少专门针对OCR任务进行训练的开源VLM了。成绩打榜是一方面,实际用起来效果如何、好不好用可能又是另一方面。因此,本文将对比几款最近比较流行的VLM模型,通过不同的Prompt测试模型在PDF上的文本识别效果。
对比模型
| 名称 | 类型 | 架构 | 大小 | 多语言 | 输出格式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2.5VL-3B | General VLM | Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration | 3B | 是 | - |
| MinerU2.0-2505-0.9B | Expert VLM | Mineru2QwenForCausalLM | 0.9B | 是 | - |
| MonkeyOCR-3B | Expert VLM | Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration | 3B | 是 | - |
| OCRflux-3B | Expert VLM | Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration | 3B | 是 | 固定 |
| POINTS-Reader | Expert VLM | POINTSV15ChatModel | 3B | 中英 | - |
Expert VLM 指以OCR这类任务为主要目标进行训练的VLM
效果测试
测试图片
选择一张典型的PDF论文的截图,包含表格、图片、段落等信息。 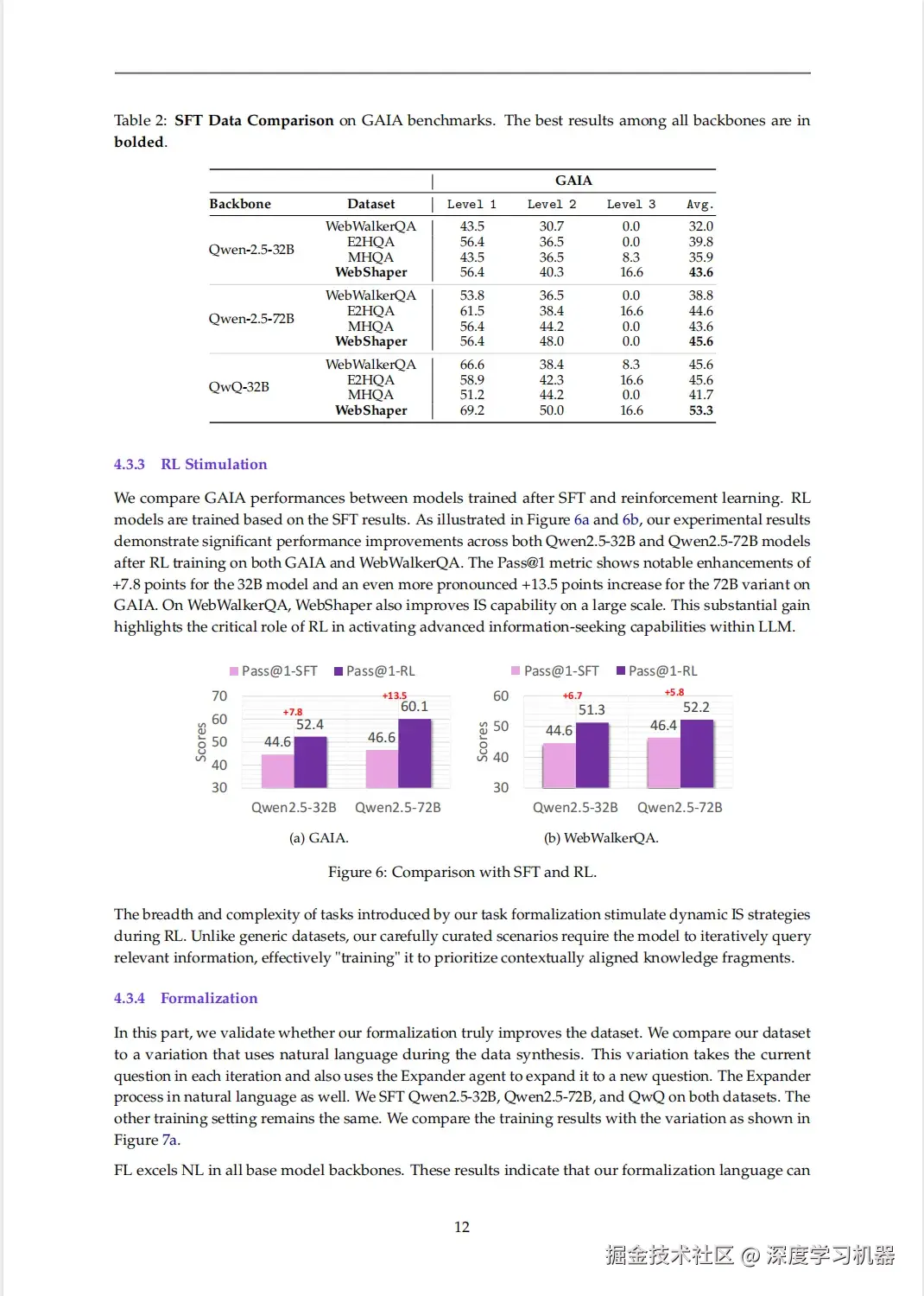
测试Prompt
为了验证不同模型对Prompt的灵敏度和效果,测试了如下几个典型的Prompt,涵盖从简单的文字提取到复杂的版面结构提取。
1. 简单提取所有的文字
python
prompt_1 = """extract all the text from the image"""2. 提取文字和表格
python
prompt_2 = """
Please extract all the text from the image with the following requirements:
1. Return tables in HTML format.
2. Return all other text in Markdown format.
"""3. 提取位置、类型和内容
python
prompt_3 = """Please output the layout information from the PDF image, including each layout element's bbox, its category, and the corresponding text content within the bbox.
1. Bbox format: [x1, y1, x2, y2]
2. Layout Categories: The possible categories are ['Caption', 'Footnote', 'Formula', 'List-item', 'Page-footer', 'Page-header', 'Picture', 'Section-header', 'Table', 'Text', 'Title'].
3. Text Extraction & Formatting Rules:
- Picture: For the 'Picture' category, the text field should be omitted.
- Formula: Format its text as LaTeX.
- Table: Format its text as HTML.
- All Others (Text, Title, etc.): Format their text as Markdown.
4. Constraints:
- The output text must be the original text from the image, with no translation.
- All layout elements must be sorted according to human reading order.
5. Final Output: The entire output must be a single JSON object.
"""4. 提取表格、图片、并保留标题格式
python
prompt_4 = """
Below is the image of one page of a document. "
Just return the plain text representation of this document as if you were reading it naturally.\n"
ALL tables should be presented in HTML format.\n"
If there are images or figures in the page, present them as \"<Image>(left,top),(right,bottom)</Image>\", (left,top,right,bottom) are the coordinates of the top-left and bottom-right corners of the image or figure.\n"
Present all titles and headings as H1 headings.\n"
Do not hallucinate.\n"
"""识别效果
1. 简单提取所有的文字
● Qwen2.5VL-3B 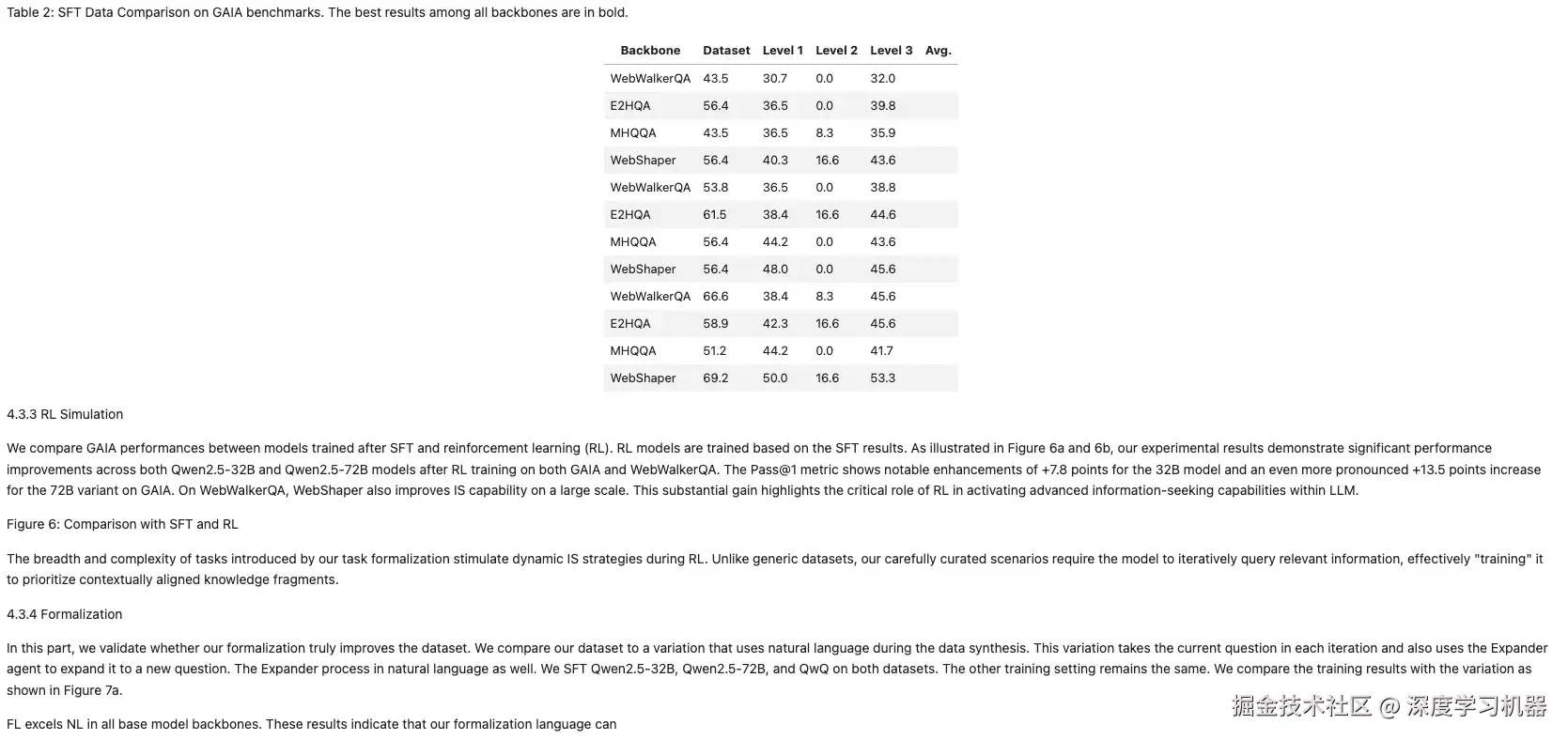
表格丢失了最左侧一列
● MinerU2.0-2505-0.9B 
表格渲染为md、html之外的格式了,但是单元格内容应该是齐全的;而且对于标题还保留了格式
● MonkeyOCR 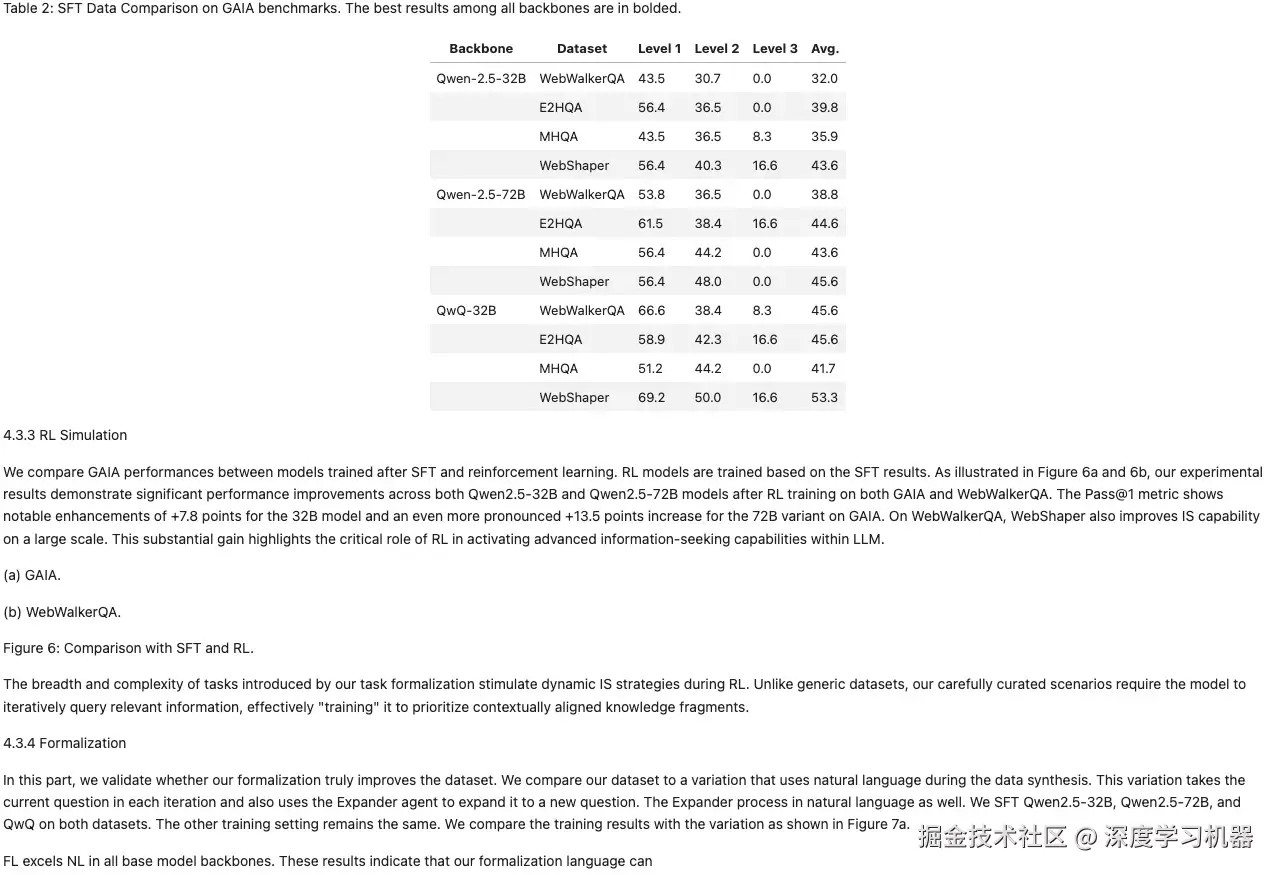
表格缺少最上面一行;图片下方的文字也得到保留
● OCRflux-3B
python
Table 2: SFT Data Comparison on GAIA benchmarks. The best results among all backbones are in bolded.\\n\\n4.3.3 RL Stimulation\\n\\nWe compare GAIA performances between models trained after SFT and reinforcement learning. RL models are trained based on the SFT results. As illustrated in Figure 6a and 6b, our experimental results demonstrate significant performance improvements across both Qwen2.5-32B and Qwen2.5-72B models after RL training on both GAIA and WebWalkerQA. The Pass@1 metric shows notable enhancements of +7.8 points for the 32B model and an even more pronounced +13.5 points increase for the 72B variant on GAIA. On WebWalkerQA, WebShaper also improves IS capability on a large scale. This substantial gain highlights the critical role of RL in activating advanced information-seeking capabilities within LLM.\\n\\nThe breadth and complexity of tasks introduced by our task formalization stimulate dynamic IS strategies during RL. Unlike generic datasets, our carefully curated scenarios require the model to iteratively query relevant information, effectively \\"training\\" it to prioritize contextually aligned knowledge fragments.\\n\\n4.3.4 Formalization\\n\\nIn this part, we validate whether our formalization truly improves the dataset. We compare our dataset to a variation that uses natural language during the data synthesis. This variation takes the current question in each iteration and also uses the Expander agent to expand it to a new question. The Expander process in natural language as well. We SFT Qwen2.5-32B, Qwen2.5-72B, and QwQ on both datasets. The other training setting remains the same. We compare the training results with the variation as shown in Figure 7a.\\n\\nFL excels NL in all base model backbones. These results indicate that our formalization language can表格内容完全丢失,只有文字,但是符合预期(Prompt仅要求识别文字)
● POINTS-Reader 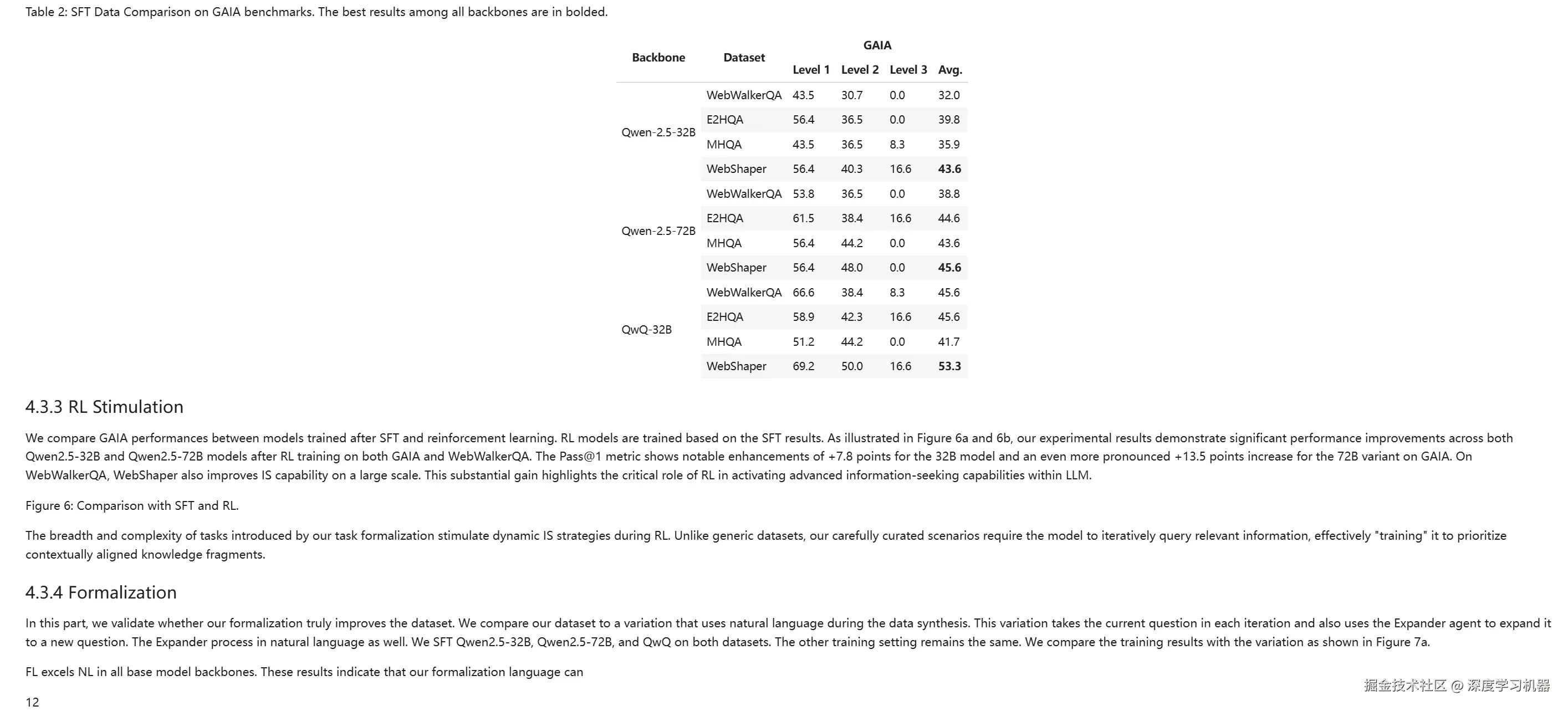
基本完全识别出来
2. 提取文字和表格
● Qwen2.5VL-3B 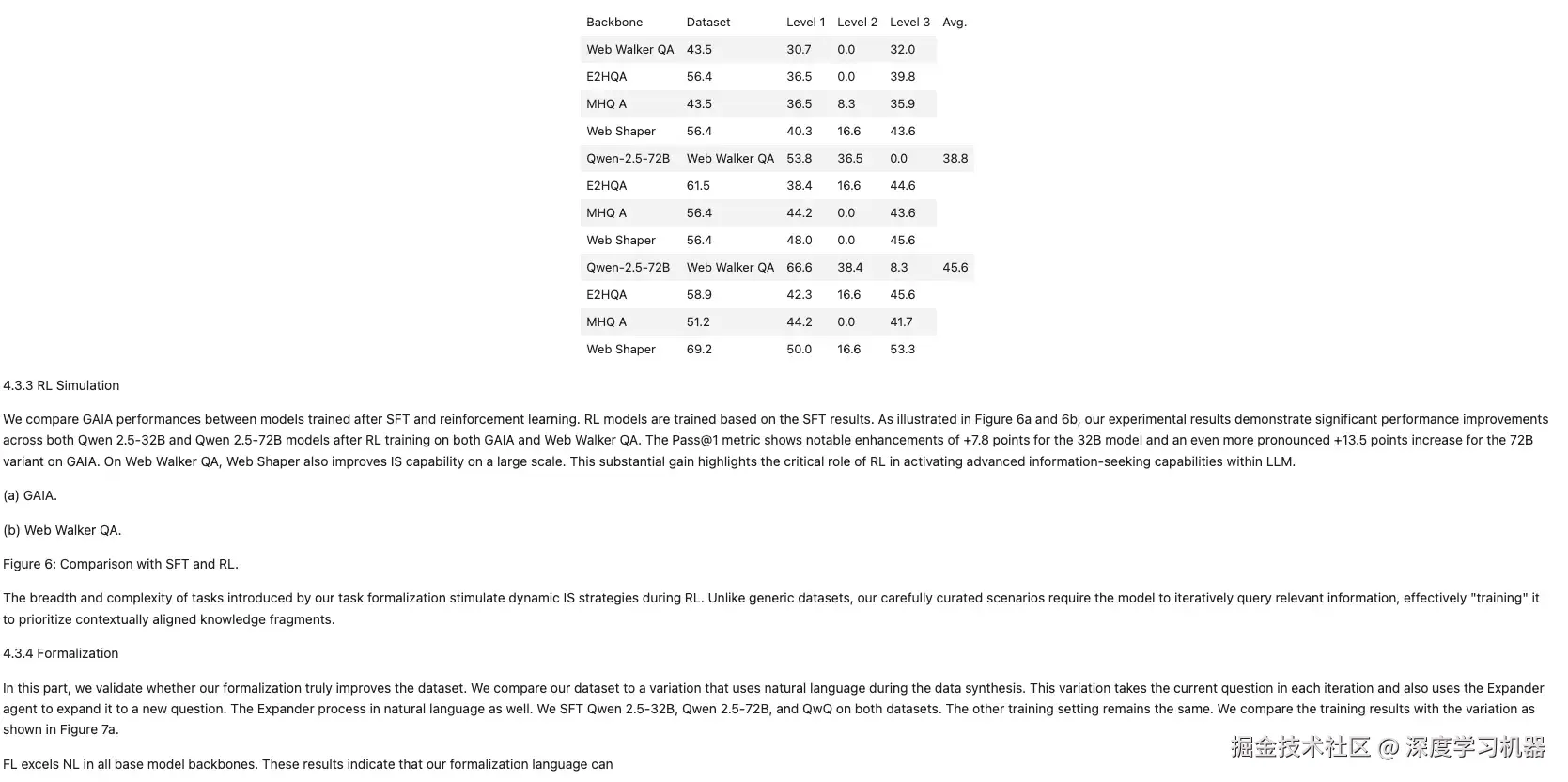
表格惨不忍睹
● MinerU2.0-2505-0.9B 
与第一种情况一致
● MonkeyOCR 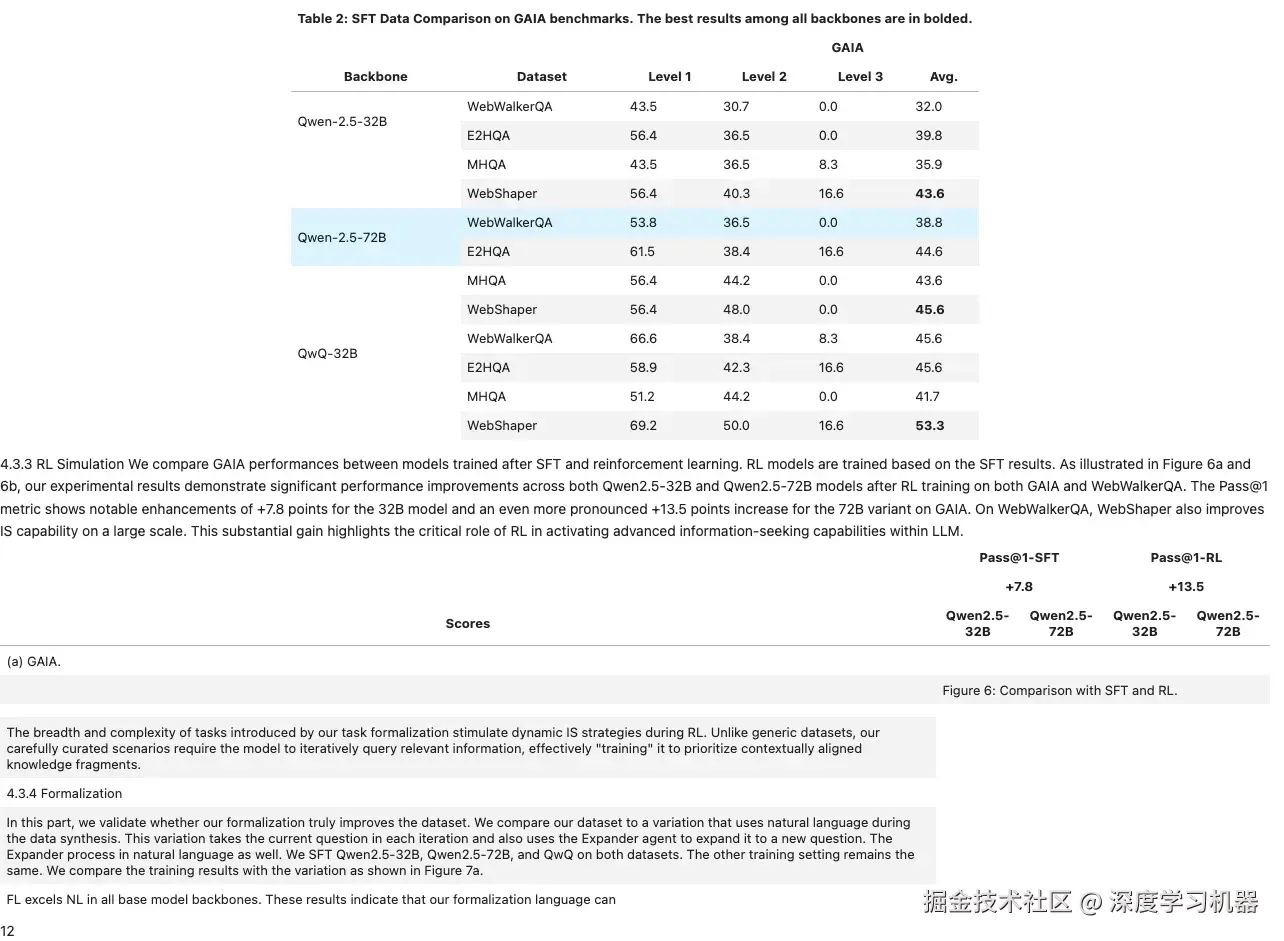
表格效果非常好,但是把图片错误识别为表格,导致后续出错
● OCRflux-3B 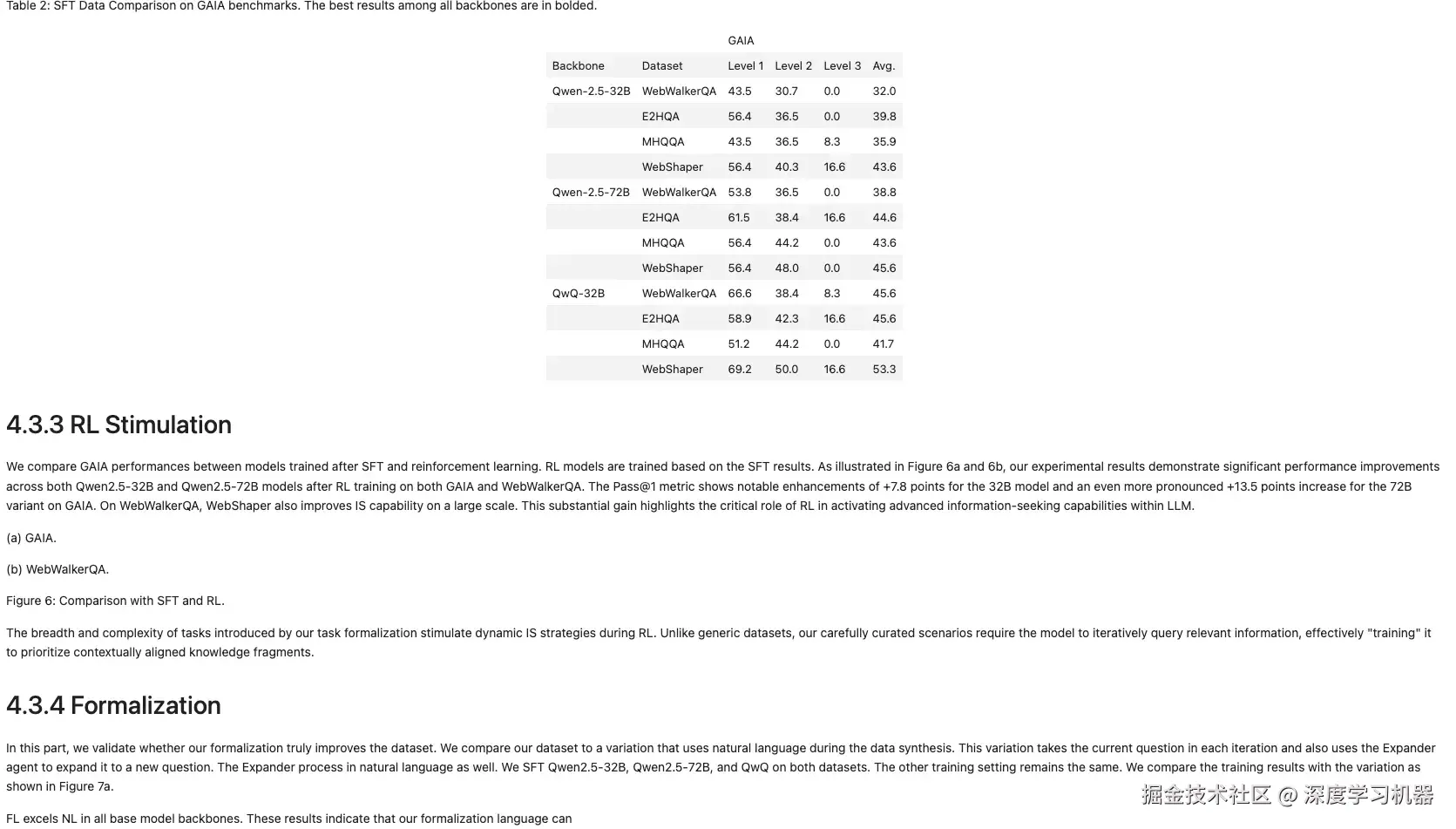
基本完全识别出来
● POINTS-Reader
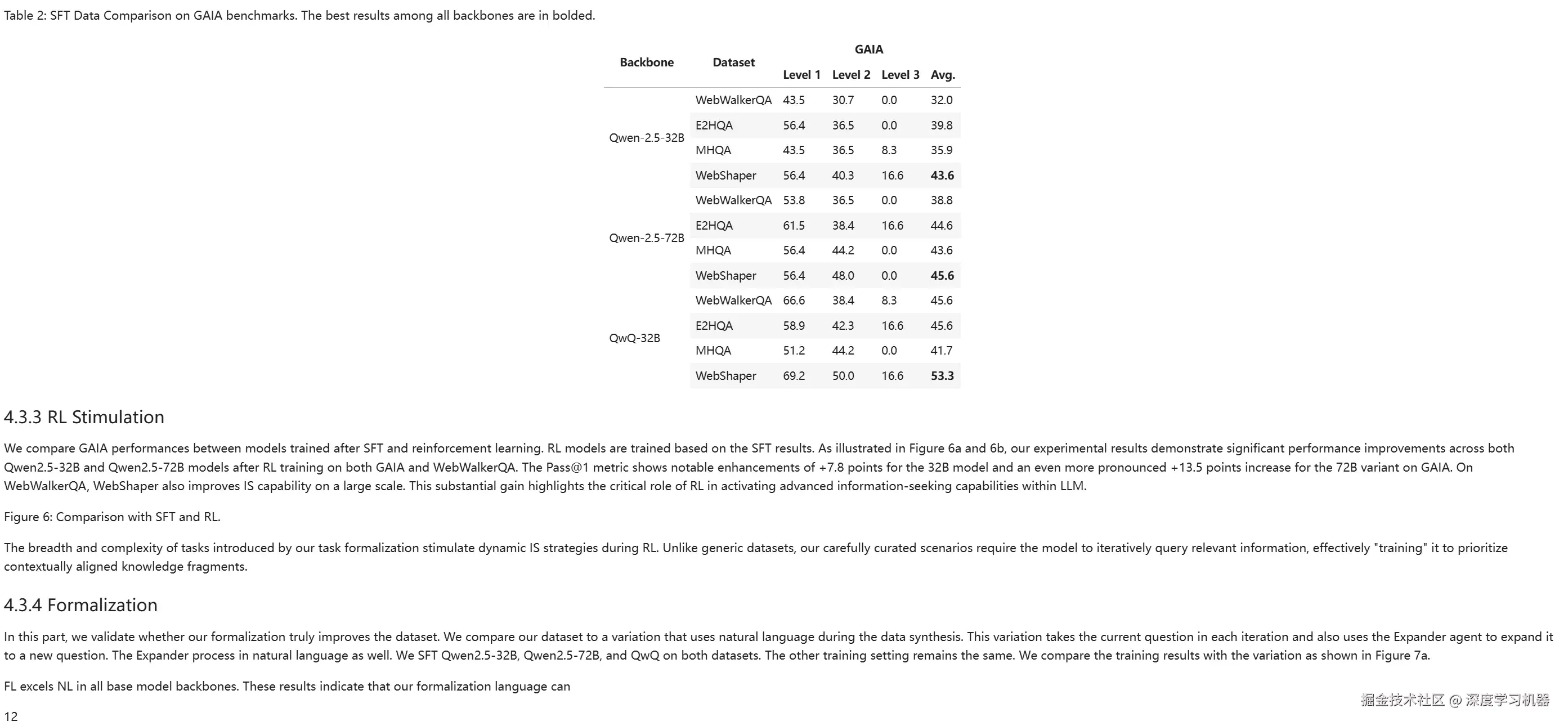
基本完全识别出来
3. 提取位置、类型和内容
● Qwen2.5VL-3B 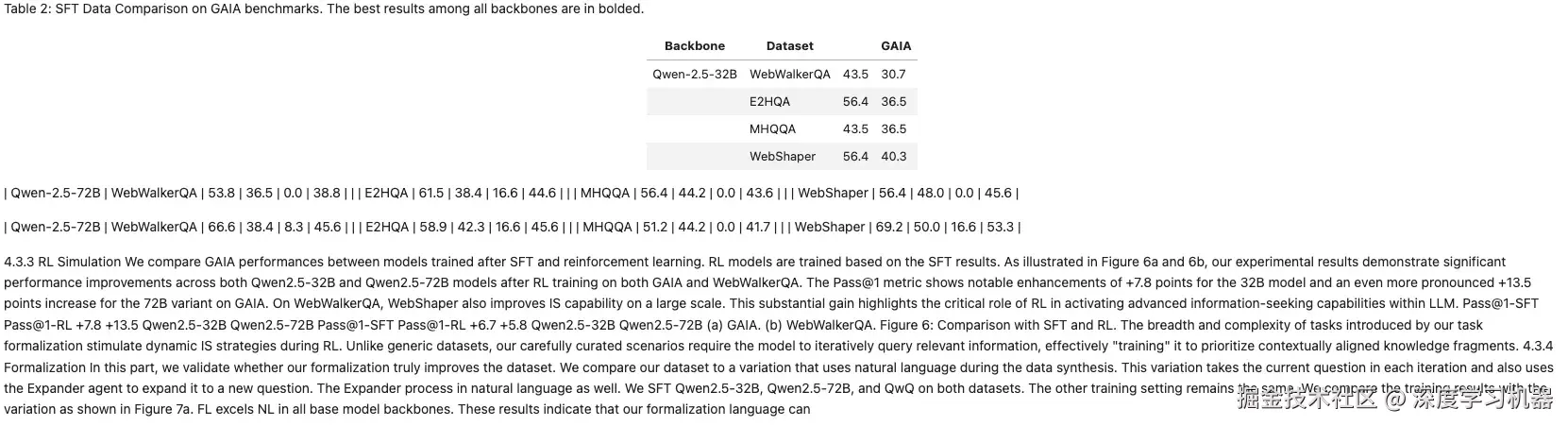
完全看不出什么东西。。。
● MinerU2.0-2505-0.9B 
与第一种情况一致
● MonkeyOCR 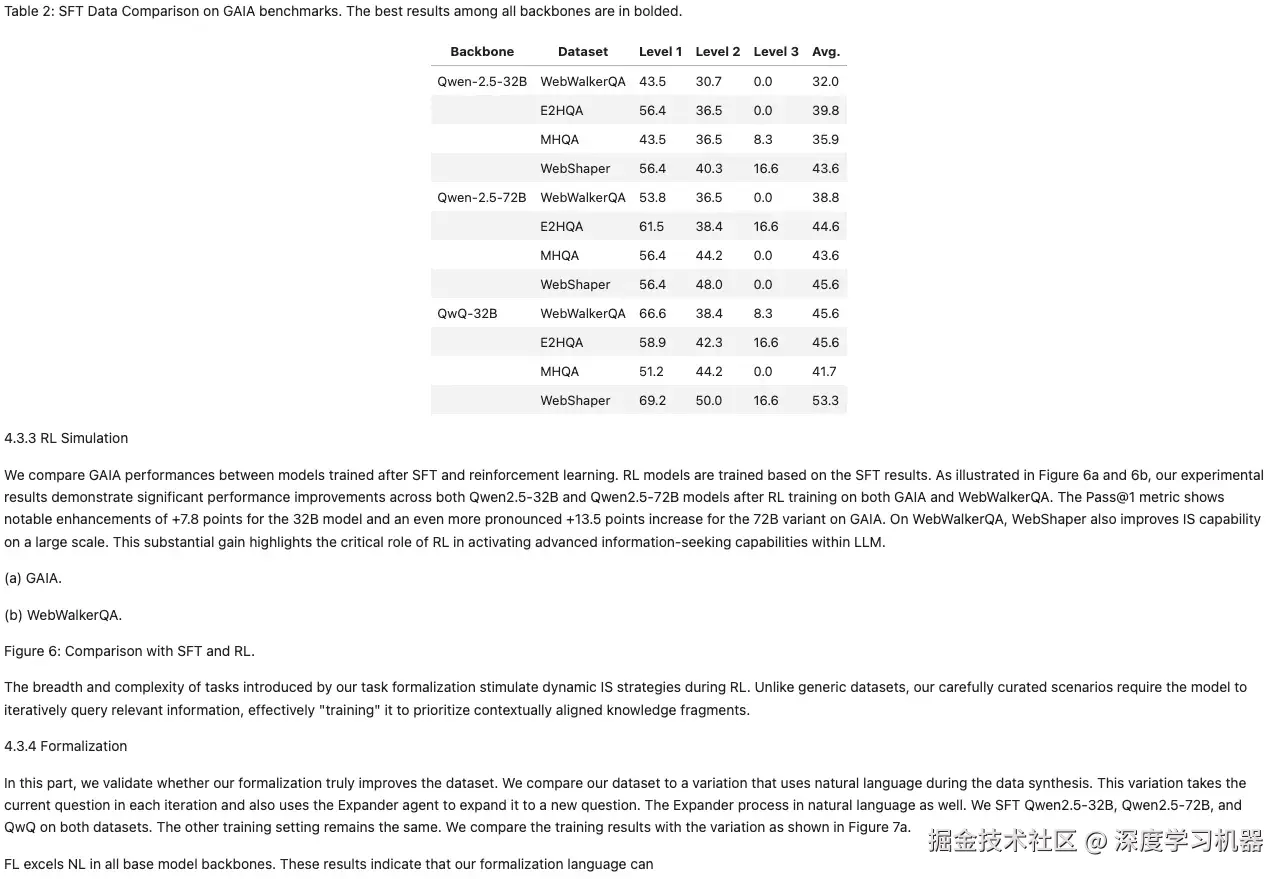
表格缺少最上面一行
● OCRflux-3B 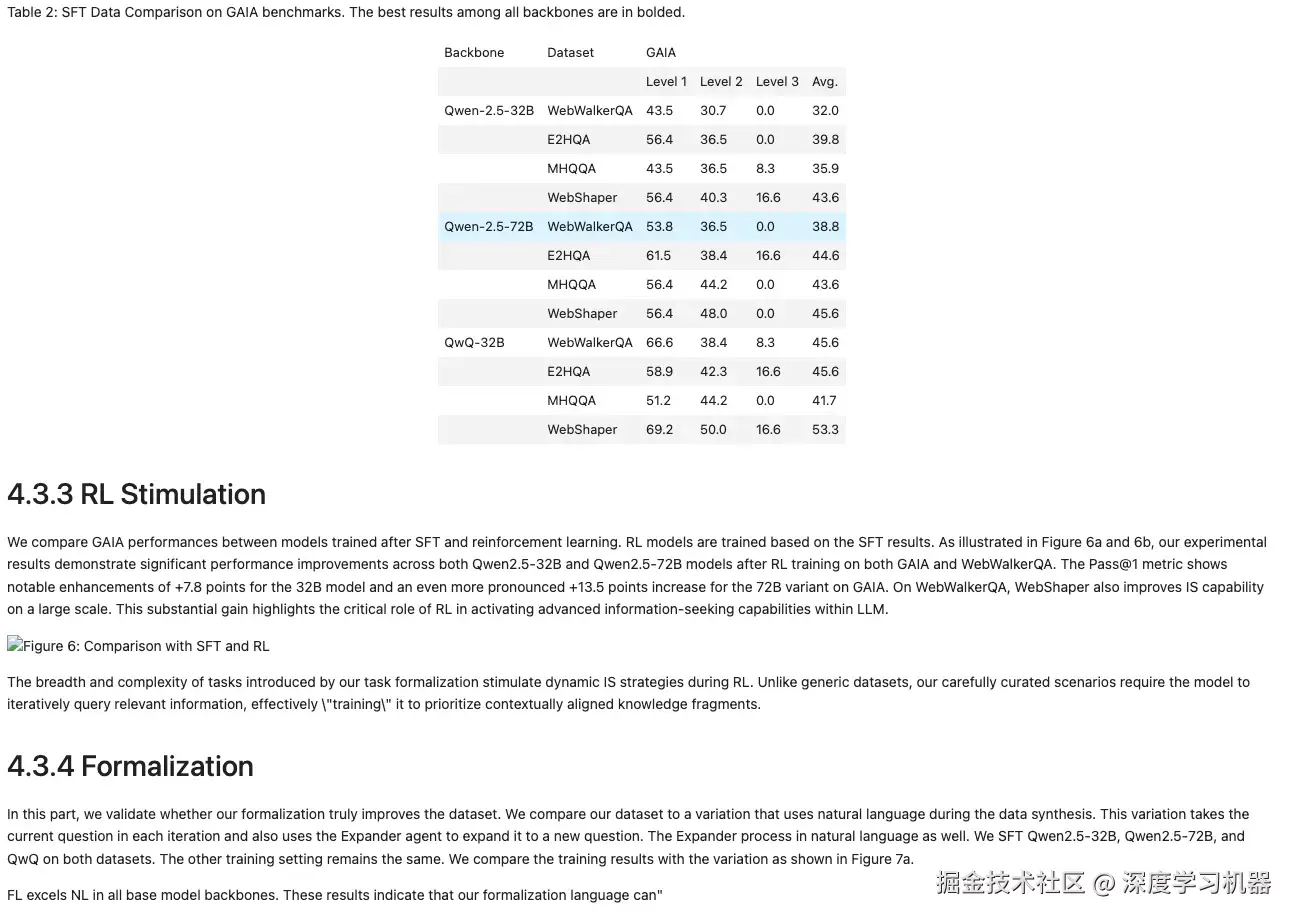
基本完全识别出来
● POINTS-Reader
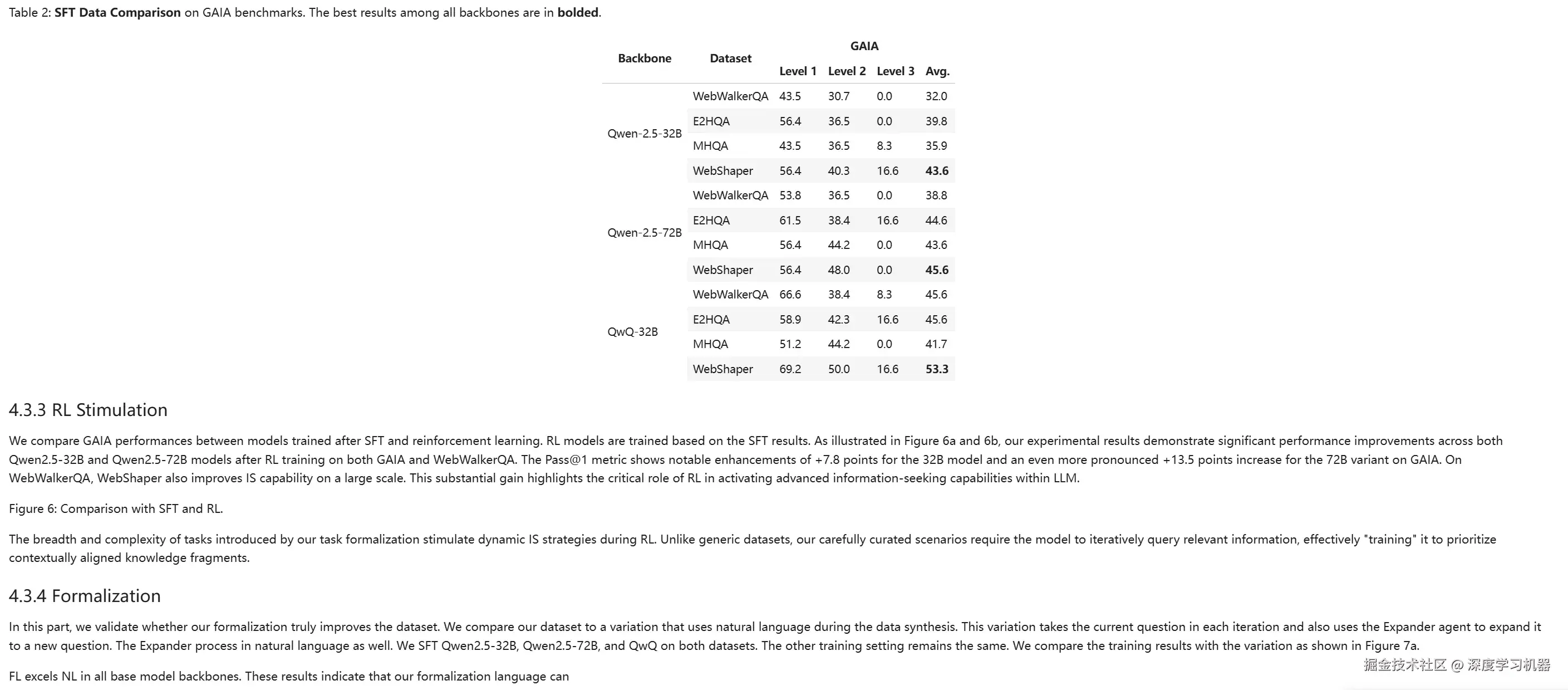
基本完全识别出来
4. 提取表格、图片、并保留标题格式
● Qwen2.5VL-3B
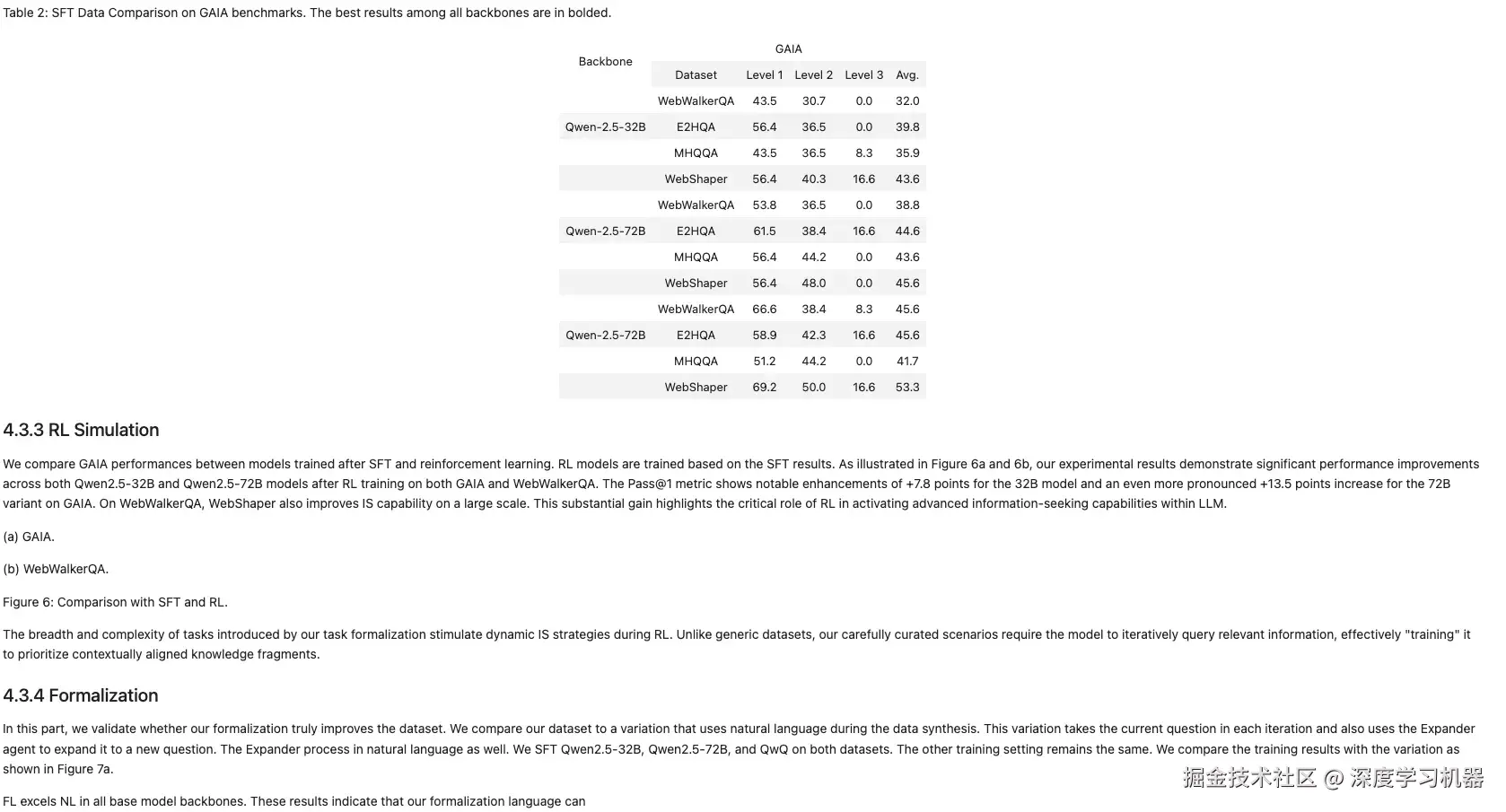
这回还行
● MinerU2.0-2505-0.9B 
表格内容丢失,同时子标题信息丢失
● MonkeyOCR 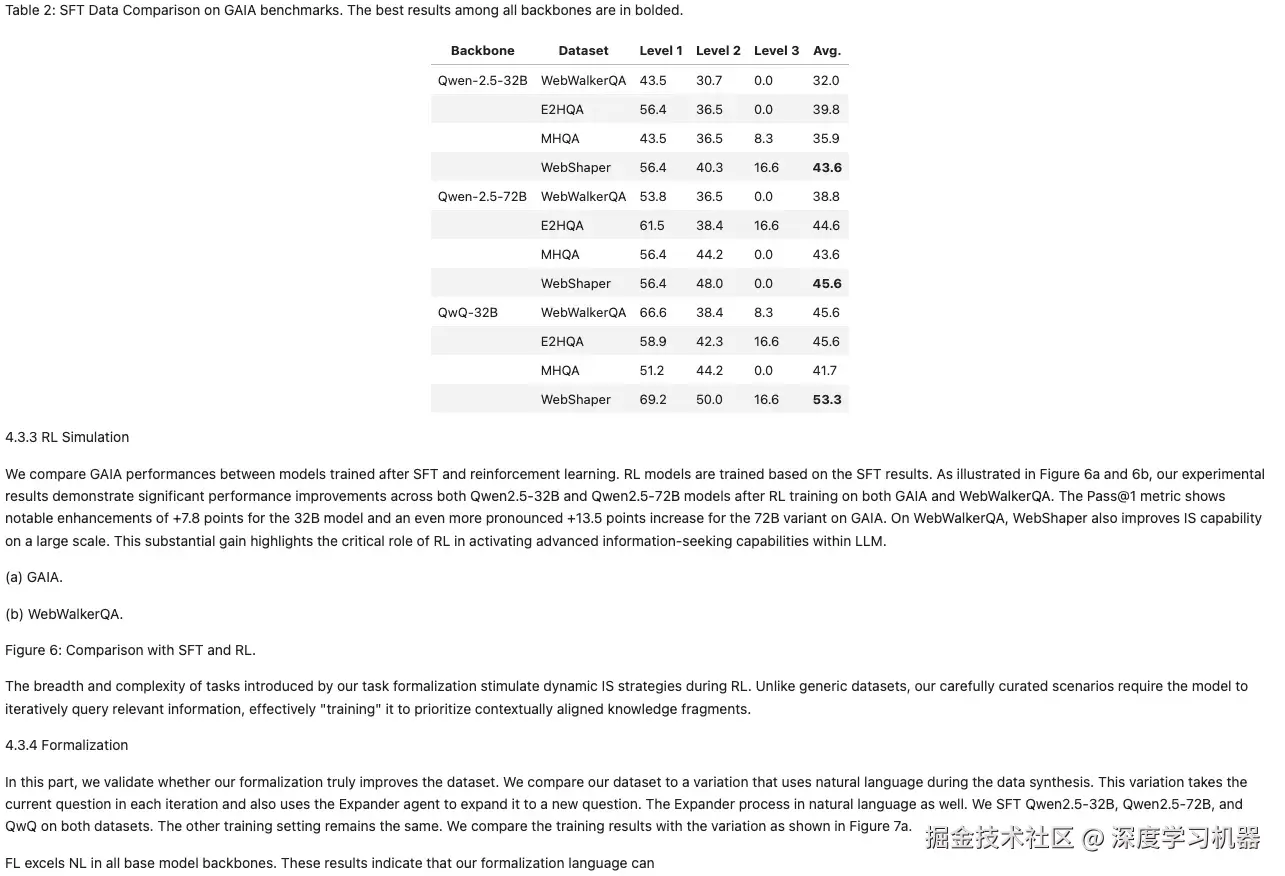
表格缺少第一行
● OCRflux-3B 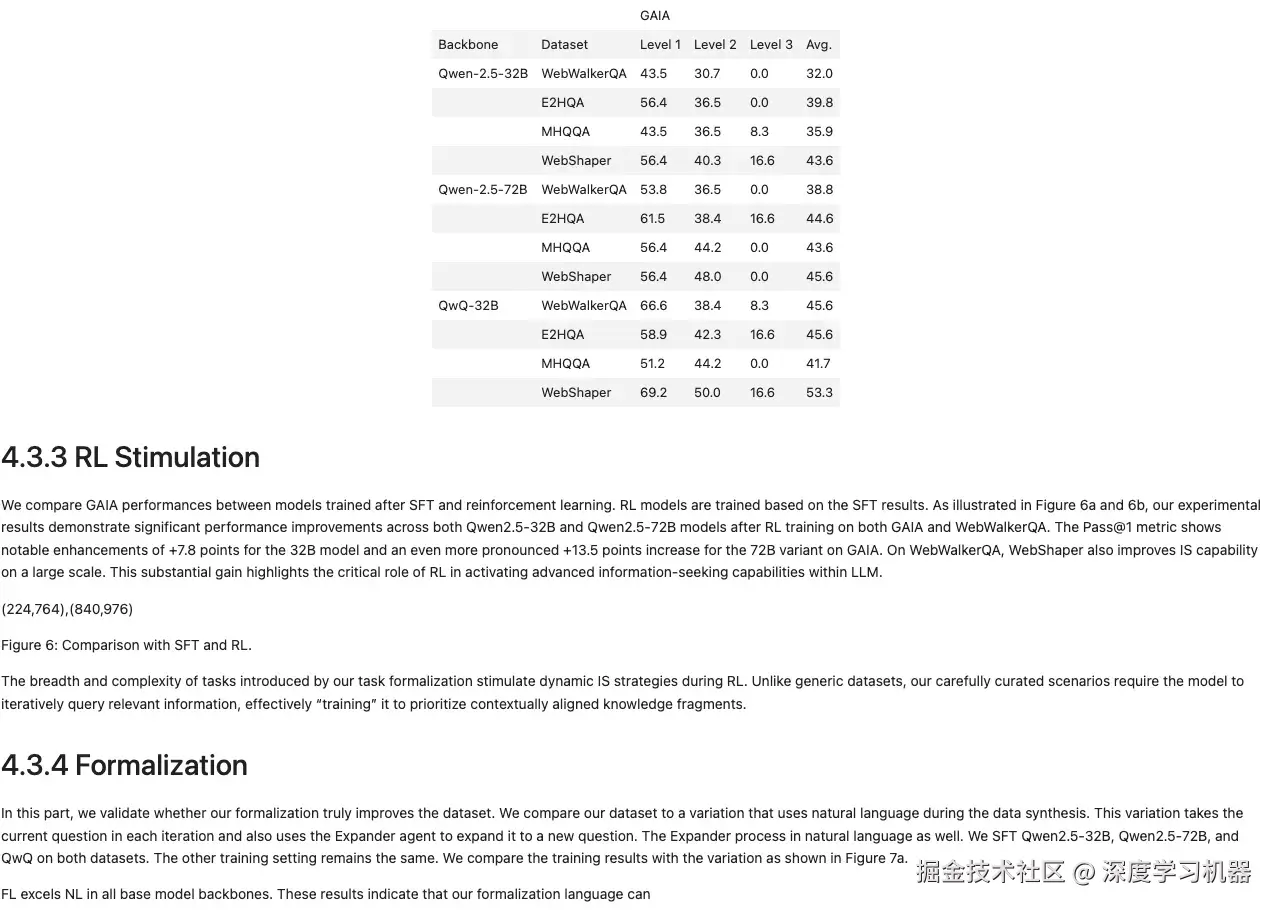
基本完全识别出来
● POINTS-Reader 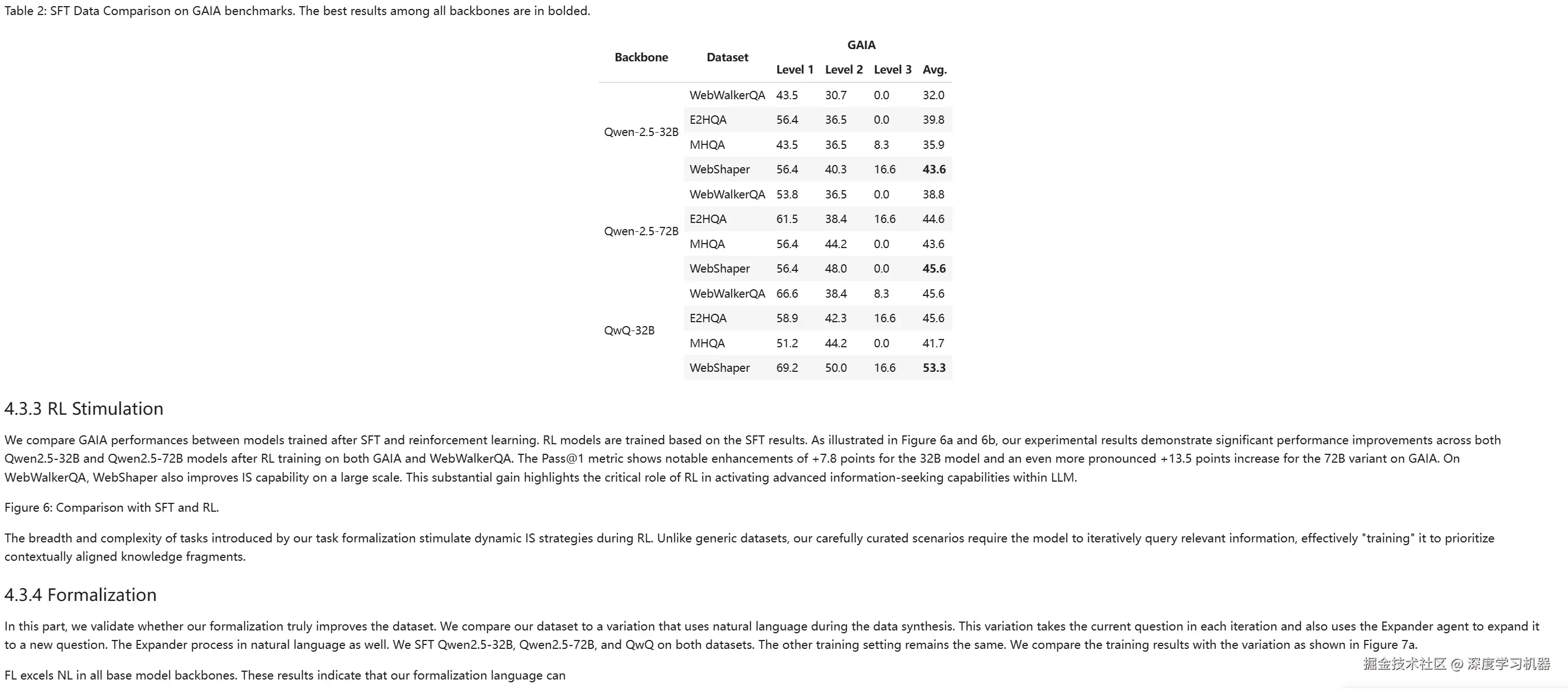
基本完全识别出来
结论
通过上述对比,个人主观排名如下,不代表模型实际性能: POINTS-Reader = OCRflux-3B > MonkeyOCR >= MinerU2.0-2505-0.9B > Qwen2.5VL-3B
1. 原生VLM的能力已经足够
如果不需要图片和表格,只对文档进行提取,使用Qwen2.5VL-3B模型即可,而且Prompt不需要特别设置。
2. 子标题识别效果
OCRflux-3B和MinerU2.0-2505-0.9B均可识别出子标题的效果。
3. 模型输出格式
OCRflux-3B对输出格式进行严格限制,最好结合官方Pipeline进行使用,能更好实现一些效果,如跨页合并。
python
{
"primary_language":
"is_rotation_valid":
"rotation_correction":
"is_table":
"is_diagram":
"natural_text":
}4. 兼容性
说实话这几个模型兼容性较差,虽然整体架构与Qwen2.5VL相差不大,但是各家都有自己的视觉处理器,调用方法有所区别,同一套代码无法完全兼容使用,transformer版本更是千差万别。VLM对于以后实现好用的Agent来说是至关重要的一部分,但是现在尚未有统一的格式,希望有大厂赶紧提出通用的一个标准。
5. 易用性
VLM本质上也是一个LLM,需要推理框架进行加速,否则速度非常慢。vLLM/SGLang等加速框架对LLM支持比较广泛,对于VLM支持较少,需要模型官方团队/开源社区单独适配。特别是POINTS-Reader在代码中强制使用flash attention,无cuda环境完全无法运行。