上接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44506615/article/details/151986616?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
完整代码:https://gitee.com/Duo1J/learn-open-gl | https://github.com/Duo1J/LearnOpenGL
一、延迟渲染 (Deferred Rendering)
至此为止,我们一直使用的光照方式叫做 前向渲染 (Forward Rendering),在场景中我们根据所有光源依次渲染所有物体,但是由于它需要每一个物体遍历每一个光源,随着我们物体的光源的增多,其开销是指数级上升的
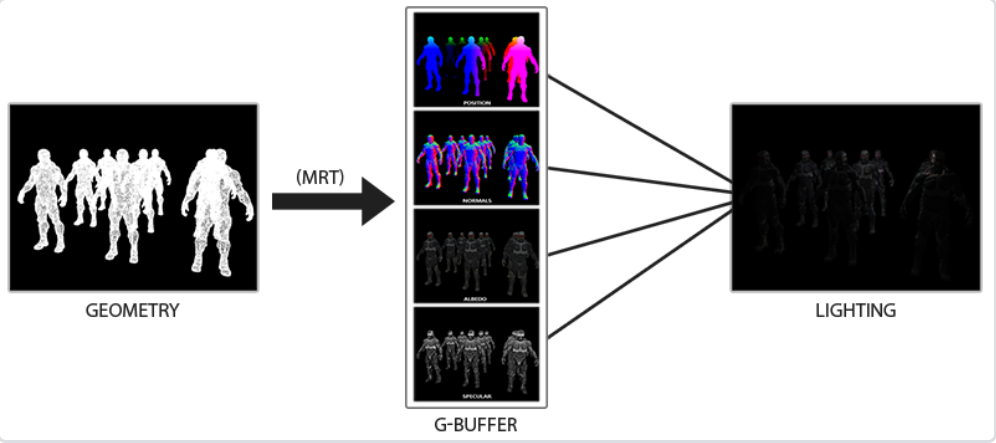
延迟渲染 则可以解决这个问题,它包含两个处理阶段(Pass)
几何处理阶段 (Geometry Pass) 中,我们先渲染场景一次,但是不计算光照,只是将计算光照所需要的数据 (位置向量、颜色向量、法向量、镜面值等) 储存在 G缓冲 (G-Buffer, Geometry Buffer) 中
光照处理阶段 (Lighting Pass) 中读取G-Buffer中的数据,计算光照结果并绘制到类似屏幕后处理的一个Quad上
下图展示了一个延迟渲染的过程 (图片来自于LearnOpenGL)
其中MRT 为多渲染目标 (Multiple Render Targets) ,它可以在一个Pass内渲染到多个纹理附件上,马上会用到
先准备一个简单的场景
Main_Deferred.cpp 新建
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <glm.hpp>
#include <gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <assimp/Importer.hpp>
#include <assimp/scene.h>
#include <assimp/postprocess.h>
#include "Define.h"
#include "BuiltinData.h"
#include "Shader.h"
#include "Camera.h"
#include "Texture.h"
#include "Model.h"
#include "TextureCube.h"
float screenWidth = 800;
float screenHeight = 600;
float deltaTime = 0.0f;
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
Camera camera;
void ProcessKeyboardInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE))
{
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
}
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_LEFT_ALT))
{
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_NORMAL);
}
else
{
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
}
camera.ProcessKeyboardInput(window, deltaTime);
}
void ProcessMouseInput(GLFWwindow* window, double x, double y)
{
camera.ProcessMouseInput(window, x, y, deltaTime);
}
void ProcessMouseWheelInput(GLFWwindow* window, double x, double y)
{
camera.ProcessMouseWheelInput(window, x, y, deltaTime);
}
void OnSetFrameBufferSize(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
screenWidth = width;
screenHeight = height;
glViewport(0, 0, screenWidth, screenHeight);
camera.UpdateCameraVector();
}
GLFWwindow* InitEnv()
{
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(screenWidth, screenHeight, "OpenGLRenderer", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, OnSetFrameBufferSize);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, ProcessMouseInput);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, ProcessMouseWheelInput);
return window;
}
void InitCamera()
{
Transform cameraTransform;
cameraTransform.position = glm::vec3(0, 0, 3);
cameraTransform.front = glm::vec3(0, 0, -1);
cameraTransform.up = glm::vec3(0, 1, 0);
cameraTransform.rotate.yaw = -90;
camera = Camera(cameraTransform);
camera.far = 100;
}
int main()
{
GLFWwindow* window = InitEnv();
if (window == nullptr)
{
EXIT;
}
InitCamera();
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glDepthFunc(GL_LESS);
glEnable(GL_STENCIL_TEST);
glStencilOp(GL_KEEP, GL_KEEP, GL_REPLACE);
// 关闭混合
// glEnable(GL_BLEND);
// glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE);
glCullFace(GL_BACK);
glFrontFace(GL_CCW);
Shader shader("Shader/VertexShader.glsl", "Shader/FragmentShader.glsl");
Shader cubeShader("Shader/CubeVertex.glsl", "Shader/CubeFragment.glsl");
Model model("F:/Scripts/Cpp/LearnOpenGL/learn-open-gl/Resource/backpack/backpack.obj");
unsigned int uboMaterices;
glGenBuffers(1, &uboMaterices);
glBindBuffer(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, uboMaterices);
glBufferData(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 2 * sizeof(glm::mat4), NULL, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 0);
glBindBufferRange(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 0, uboMaterices, 0, 2 * sizeof(glm::mat4));
BindMatericesBlock(bag, shader, 0);
const int bagInstanceCnt = 27;
glm::vec3 instanceOffsets[bagInstanceCnt];
int instanceOffsetsIdx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
glm::vec3 offset;
offset.x = i * 5;
offset.y = j * 5;
offset.z = k * -5;
instanceOffsets[instanceOffsetsIdx++] = offset;
}
}
}
// glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GL_STENCIL_BUFFER_BIT);
ProcessKeyboardInput(window);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
glm::mat4 projection = glm::mat4(1);
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.fov), screenWidth / screenHeight, camera.near, camera.far);
glBindBuffer(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, uboMaterices);
glBufferSubData(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 0, sizeof(glm::mat4), glm::value_ptr(view));
glBufferSubData(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, sizeof(glm::mat4), sizeof(glm::mat4), glm::value_ptr(projection));
glBindBuffer(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 0);
shader.Use();
shader.SetVec3("lightColor", glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f));
shader.SetVec3("viewPos", camera.transform.position);
shader.SetFloat("near", camera.near);
shader.SetFloat("far", camera.far);
shader.SetVec3("dirLight.ambient", glm::vec3(0.3f));
shader.SetVec3("dirLight.diffuse", glm::vec3(0.9f));
shader.SetVec3("dirLight.specular", glm::vec3(0.6f));
shader.SetVec3("dirLight.direction", glm::vec3(-0.2f, -1.0f, -0.3f));
shader.SetFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
shader.SetVec3("pointLight[" + std::to_string(i) + "].ambient", glm::vec3(0.05f));
shader.SetVec3("pointLight[" + std::to_string(i) + "].diffuse", glm::vec3(0.8f));
shader.SetVec3("pointLight[" + std::to_string(i) + "].specular", glm::vec3(1.0f));
shader.SetVec3("pointLight[" + std::to_string(i) + "].position", glm::vec3(pointLightPositions[i]));
shader.SetFloat("pointLight[" + std::to_string(i) + "].constant", 1.0f);
shader.SetFloat("pointLight[" + std::to_string(i) + "].diffuse", 0.09f);
shader.SetFloat("pointLight[" + std::to_string(i) + "].quadratic", 0.032f);
}
shader.SetVec3("spotLight.ambient", glm::vec3(0));
shader.SetVec3("spotLight.diffuse", glm::vec3(1));
shader.SetVec3("spotLight.specular", glm::vec3(1));
shader.SetVec3("spotLight.position", camera.transform.position);
shader.SetVec3("spotLight.direction", camera.transform.front);
shader.SetFloat("spotLight.cutOff", glm::cos(glm::radians(12.5f)));
shader.SetFloat("spotLight.cutOffOuter", glm::cos(glm::radians(17.5f)));
shader.SetFloat("spotLight.constant", 1.0f);
shader.SetFloat("spotLight.linear", 0.09f);
shader.SetFloat("spotLight.quadratic", 0.032f);
shader.SetFloat("time", glfwGetTime());
for (int i = 0; i < bagInstanceCnt; i++)
{
glm::mat4 modelMatrix = glm::mat4(1.0f);
modelMatrix = glm::translate(modelMatrix, instanceOffsets[i]);
shader.SetMat4("model", modelMatrix);
model.Draw(shader);
}
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}调整一下点光源的位置
BuiltinData.h
cpp
// 点光源位置
glm::vec3 pointLightPositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.2f, 5, -3.54f),
glm::vec3(10.7f, 0, -3),
glm::vec3(-4.0f, 2.0f, -12.0f),
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -3.0f)
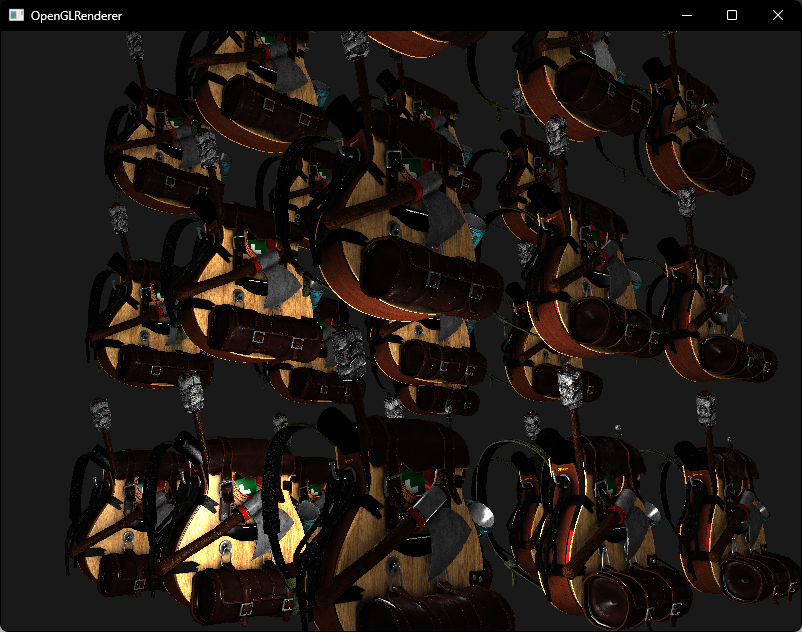
};编译运行,顺利的话可以看见以下图像
二、G-Buffer、Geometry Pass
首先来创建G-Buffer 并进行Geometry Pass
我们创建一个FBO并附加三张纹理附件,第一张存储位置向量,第二张存储法向量,最后一张的RGB通道存储颜色向量,A通道存储镜面反射值
Main_Deferred.cpp
cpp
// [main]
// 创建 G-Buffer
unsigned int gBuffer;
glGenFramebuffers(1, &gBuffer);
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, gBuffer);
unsigned int gPosition, gNormal, gAlbedoSpec;
// 位置
glGenTextures(1, &gPosition);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, gPosition);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB16F, screenWidth, screenHeight, 0, GL_RGB, GL_FLOAT, NULL);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, GL_TEXTURE_2D, gPosition, 0);
// 法线
glGenTextures(1, &gNormal);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, gNormal);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB16F, screenWidth, screenHeight, 0, GL_RGB, GL_FLOAT, NULL);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1, GL_TEXTURE_2D, gNormal, 0);
// 颜色、镜面
glGenTextures(1, &gAlbedoSpec);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, gAlbedoSpec);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, screenWidth, screenHeight, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, NULL);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT2, GL_TEXTURE_2D, gAlbedoSpec, 0);
// 告诉OpenGL我们要使用这三张纹理附件作为输出
unsigned int attachments[3] = { GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT2 };
glDrawBuffers(3, attachments);
unsigned int rboDepth;
glGenRenderbuffers(1, &rboDepth);
glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, rboDepth);
glRenderbufferStorage(GL_RENDERBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, screenWidth, screenHeight);
glFramebufferRenderbuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, GL_RENDERBUFFER, rboDepth);
if (glCheckFramebufferStatus(GL_FRAMEBUFFER) != GL_FRAMEBUFFER_COMPLETE)
{
std::cout << "[Error] G-Buffer Framebuffer is not complete" << std::endl;
EXIT
}
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0);修改一下Shader,将原来的光照计算换为数据写入
DeferredFragmentShader.glsl 新建
cpp
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) out vec3 gPosition;
layout (location = 1) out vec3 gNormal;
layout (location = 2) out vec4 gAlbedoSpec;
struct Material {
sampler2D tex_diffuse1;
sampler2D tex_diffuse2;
// ...
sampler2D tex_specular1;
sampler2D tex_specular2;
// ...
sampler2D tex_normal1;
sampler2D tex_normal2;
// ...
float shininess;
};
uniform Material material;
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
void main()
{
// 片段位置向量
gPosition = FragPos;
// 法向量
gNormal = normalize(Normal);
// rgb通道存储颜色值
gAlbedoSpec.rgb = texture(material.tex_diffuse1, TexCoords).rgb;
// a通道存储镜面反射值
gAlbedoSpec.a = texture(material.tex_specular1, TexCoords).r;
} 最后修改主循环
Main_Deferred.cpp
cpp
// [main]
Shader shader("Shader/VertexShader.glsl", "Shader/DeferredFragmentShader.glsl");
// ...
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
ProcessKeyboardInput(window);
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, gBuffer);
glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GL_STENCIL_BUFFER_BIT);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
glm::mat4 projection = glm::mat4(1);
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.fov), screenWidth / screenHeight, camera.near, camera.far);
glBindBuffer(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, uboMaterices);
glBufferSubData(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 0, sizeof(glm::mat4), glm::value_ptr(view));
glBufferSubData(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, sizeof(glm::mat4), sizeof(glm::mat4), glm::value_ptr(projection));
glBindBuffer(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 0);
shader.Use();
for (int i = 0; i < bagInstanceCnt; i++)
{
glm::mat4 modelMatrix = glm::mat4(1.0f);
modelMatrix = glm::translate(modelMatrix, instanceOffsets[i]);
shader.SetMat4("model", modelMatrix);
model.Draw(shader);
}
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}我们可以将G-Buffer的三个纹理附件输出到屏幕上查看,或是运行后在RenderDoc 中截帧
gPosition
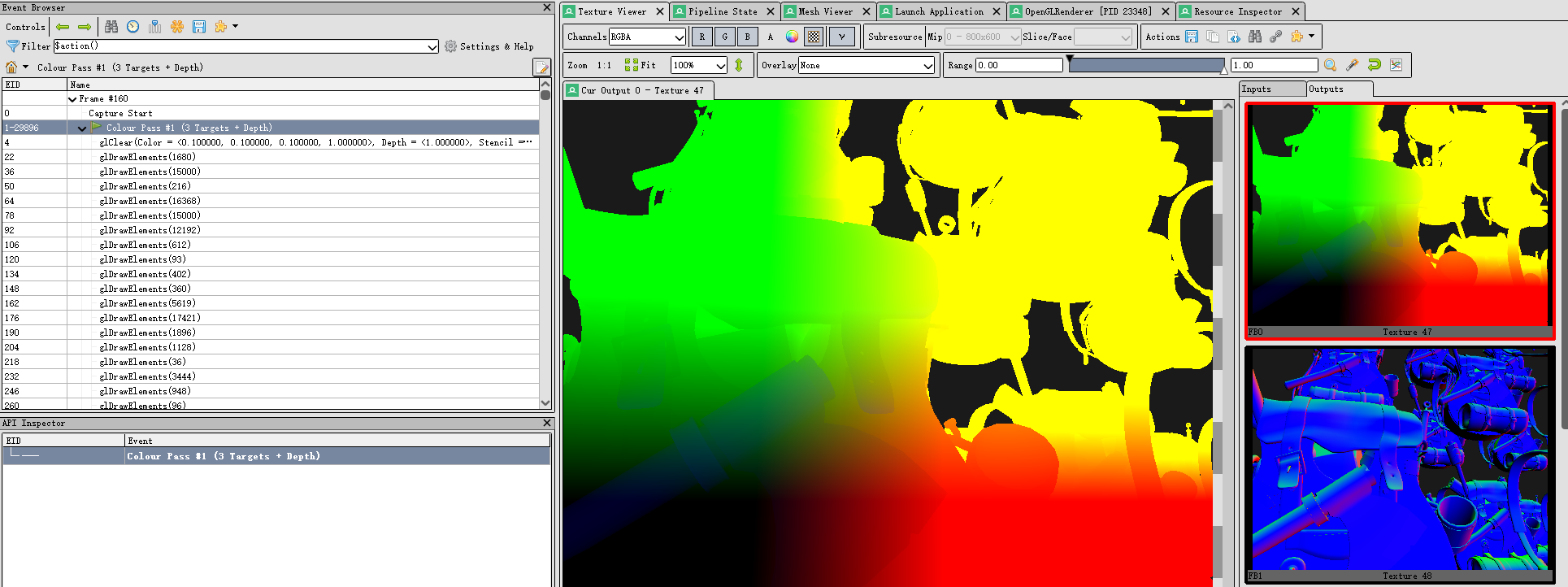
gNormal
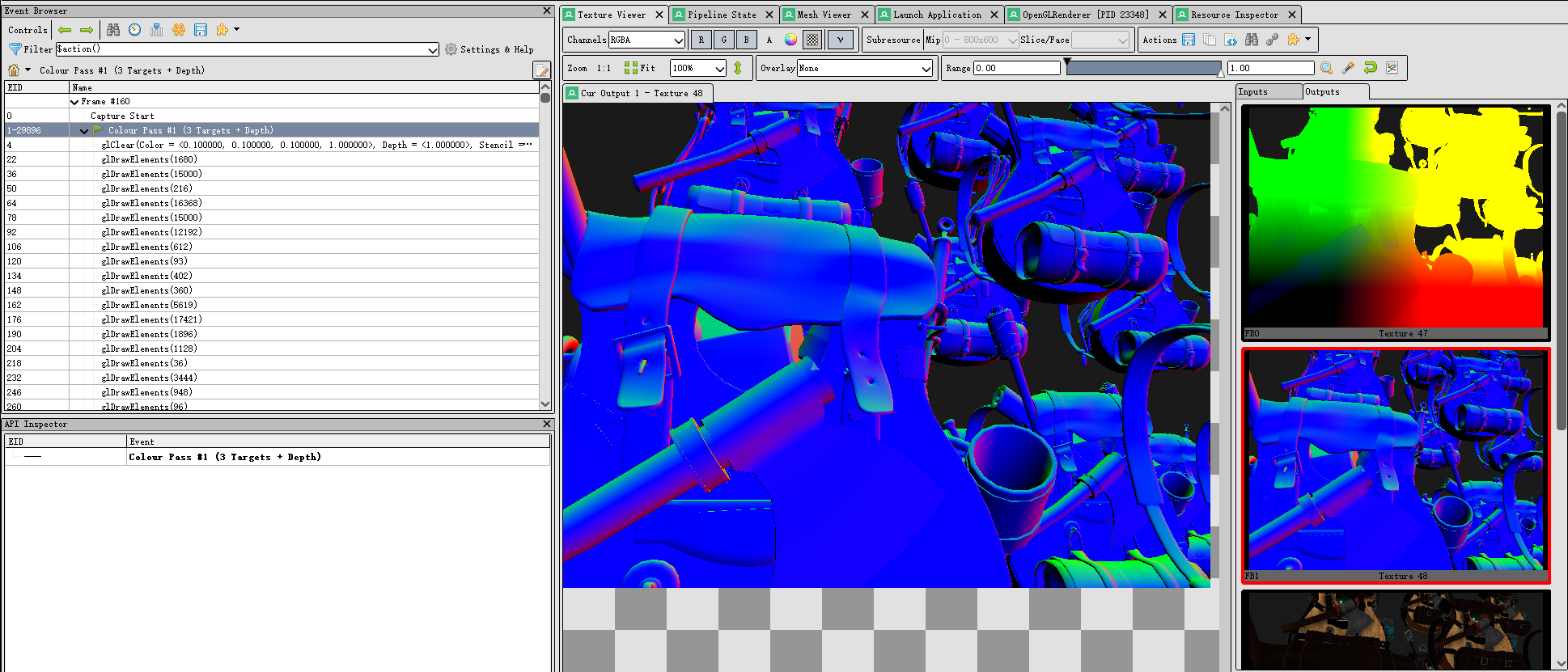
gAlbedoSpec
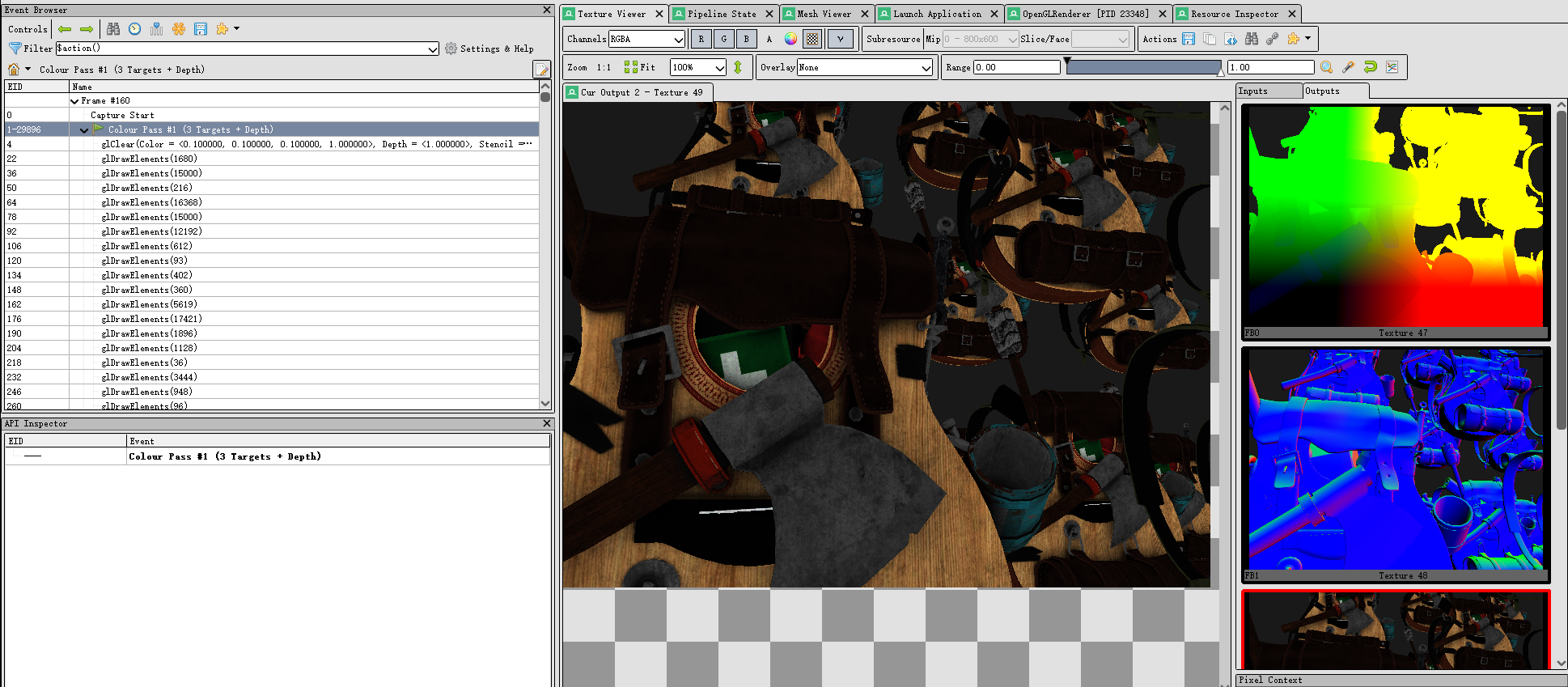
三、Lighting Pass
和后处理类似的方式,我们在屏幕上绘制一个Quad,然后在片段着色器中采样G-Buffer进行光照计算
cpp
// [main]
unsigned int screenQuadVAO, screenQuadVBO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &screenQuadVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &screenQuadVBO);
glBindVertexArray(screenQuadVAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, screenQuadVBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(screenQuadVertices), &screenQuadVertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 4 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 4 * sizeof(float), (void*)(2 * sizeof(float)));
Shader screenShader("Shader/DeferredScreenVertex.glsl", "Shader/DeferredScreenFragment.glsl");
// [主循环]
// Lighting Pass
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GL_STENCIL_BUFFER_BIT);
screenShader.Use();
screenShader.SetInt("gPosition", 0);
screenShader.SetInt("gNormal", 1);
screenShader.SetInt("gAlbedoSpec", 2);
screenShader.SetVec3("viewPos", camera.transform.position);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
screenShader.SetVec3("lights[" + std::to_string(i) + "].Position", glm::vec3(pointLightPositions[i]));
screenShader.SetVec3("lights[" + std::to_string(i) + "].Color", glm::vec3(pointLightColors[i]));
}
glBindVertexArray(screenQuadVAO);
glDisable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, gPosition);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, gNormal);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, gAlbedoSpec);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);BuiltinData.h
加上了点光源的颜色
cpp
// 点光源颜色
glm::vec3 pointLightColors[] = {
glm::vec3(1, 1, 1),
glm::vec3(0, 0, 1),
glm::vec3(1, 0, 0),
glm::vec3(0, 1, 0)
};DeferredScreenVertex.glsl 新建
直接传递顶点和UV
cpp
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec2 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec2 aTexCoords;
out vec2 TexCoords;
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(aPos.x, aPos.y, 0.0, 1.0);
TexCoords = aTexCoords;
}DeferredScreenFragment.glsl 新建
采样G-Buffer并计算光照
cpp
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform sampler2D gPosition;
uniform sampler2D gNormal;
uniform sampler2D gAlbedoSpec;
struct Light {
vec3 Position;
vec3 Color;
};
const int NR_LIGHTS = 4;
uniform Light lights[NR_LIGHTS];
uniform vec3 viewPos;
void main()
{
// G-Buffer 中读取数据
vec3 FragPos = texture(gPosition, TexCoords).rgb;
vec3 Normal = texture(gNormal, TexCoords).rgb;
vec3 Albedo = texture(gAlbedoSpec, TexCoords).rgb;
float Specular = texture(gAlbedoSpec, TexCoords).a;
// 计算光照
vec3 lighting = Albedo * 0.1;
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
for(int i = 0; i < NR_LIGHTS; ++i)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lights[i].Position - FragPos);
vec3 diffuse = max(dot(Normal, lightDir), 0.0) * Albedo * lights[i].Color;
lighting += diffuse;
}
FragColor = vec4(lighting, 1.0);
} 编译运行,顺利的话可以看见以下图像
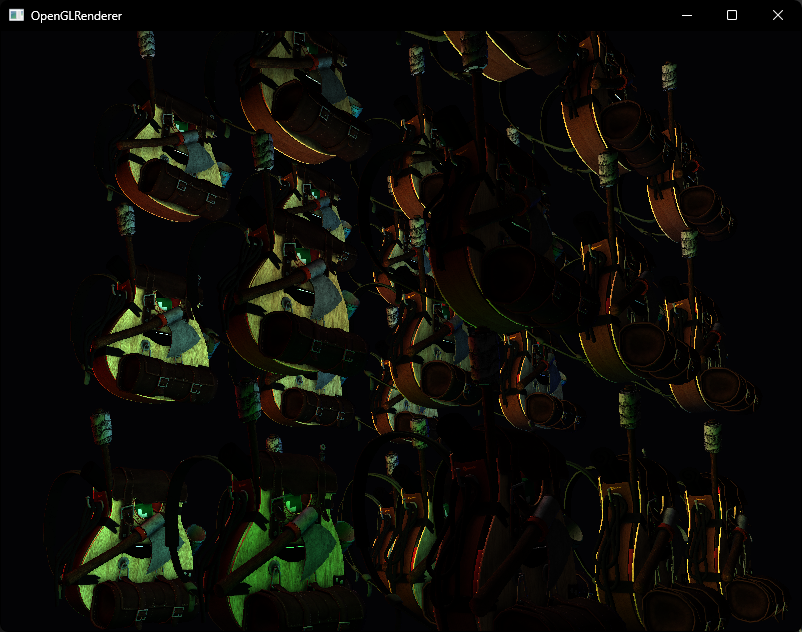
四、延迟渲染 + 前向渲染
我们可以将延迟渲染和前向渲染结合起来使用,例如我们现在想在光源的位置渲染Cube出来,在延迟渲染完场景之后,我们使用前向渲染绘制Cube
Main_Deferred.cpp
cpp
// [main]
// [主循环]
// 延迟渲染
// ...
// 前向渲染
cubeShader.Use();
cubeShader.SetMat4("view", view);
cubeShader.SetMat4("projection", projection);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
cubeShader.SetVec3("color", pointLightColors[i]);
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1);
model = glm::translate(model, pointLightPositions[i]);
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.3, 0.3, 0.3));
cubeShader.SetMat4("model", model);
RenderCube();
}
GLuint cubeVAO = 0;
GLuint cubeVBO = 0;
void RenderCube()
{
// Initialize (if necessary)
if (cubeVAO == 0)
{
GLfloat vertices[] = {
// Back face
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // Bottom-left
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-right
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-left
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,// top-left
// Front face
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-left
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-right
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // top-left
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-left
// Left face
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // top-right
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-left
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // bottom-left
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // bottom-left
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-right
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // top-right
// Right face
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // top-left
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // bottom-right
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // bottom-right
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // top-left
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-left
// Bottom face
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-left
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,// bottom-left
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-left
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-right
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
// Top face
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,// top-left
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-right
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top-right
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom-right
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,// top-left
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f // bottom-left
};
glGenVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &cubeVBO);
// Fill buffer
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, cubeVBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// Link vertex attributes
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(3 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(6 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glBindVertexArray(0);
}
// Render Cube
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
glBindVertexArray(0);
}Shader
cpp
// CubeVertex.glsl
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoords;
uniform mat4 projection;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 model;
out vec3 Normal;
out vec2 TexCoords;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
Normal = mat3(transpose(inverse(model))) * aNormal;
TexCoords = aTexCoords;
}
// CubeFragment.glsl
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec3 color;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(color.rgb, 1.0);
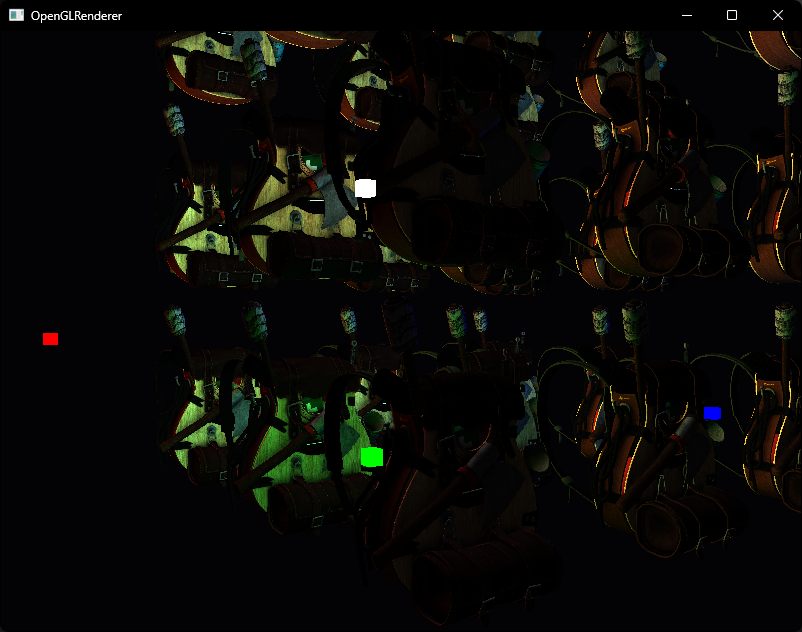
}编译运行,我们可以看见场景中以及绘制出四个不同颜色的立方体
但它们并没有正确的深度关系
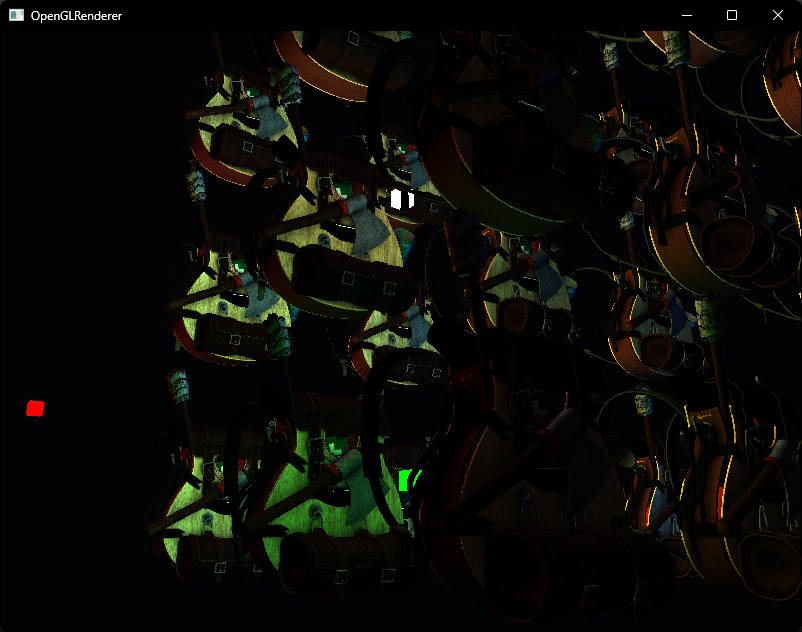
接下来我们可以使用在MSAA中用到过的 glBlitFramebuffer 来将G-Buffer中的深度缓冲拷贝到默认帧缓冲中
cpp
// 同步深度缓冲
glBindFramebuffer(GL_READ_FRAMEBUFFER, gBuffer);
glBindFramebuffer(GL_DRAW_FRAMEBUFFER, 0);
glBlitFramebuffer(0, 0, screenWidth, screenHeight, 0, 0, screenWidth, screenHeight, GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT, GL_NEAREST);这样就得到了正确的遮挡关系
五、光体积 (Light Volume)
目前我们计算光照是遍历每个光源来对每个片段进行计算,虽然比之前优化了很多,不过依然有很多冗余的计算
因为目前不管片段距离光源有多远,我们都进行了计算,但是距离过远很可能光源并不会对其产生影响,接下来我们来计算一个点光源的体积或半径,判断片段是否会受到这个点光源的影响,是则计算光照,否则跳过
我们会引入一个更为复杂但是更加灵活的衰减方程,其中I为光源最亮的颜色分量
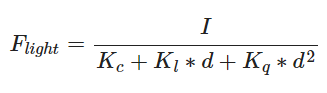
简化
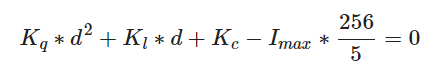
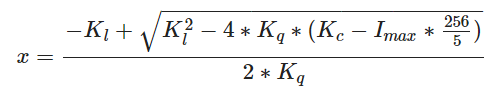
Main_Deferred.cpp
计算半径并传入着色器
cpp
const float constant = 1.0;
const float linear = 0.7;
const float quadratic = 1.8;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
// ...
screenShader.SetFloat("lights[" + std::to_string(i) + "].Linear", linear);
screenShader.SetFloat("lights[" + std::to_string(i) + "].Quadratic", quadratic);
const float maxBrightness = std::fmaxf(std::fmaxf(pointLightColors[i].r, pointLightColors[i].g), pointLightColors[i].b);
float radius = (-linear + std::sqrtf(linear * linear - 4 * quadratic * (constant - (256.0 / 5.0) * maxBrightness))) / (2 * quadratic);
screenShader.SetFloat("lights[" + std::to_string(i) + "].Radius", radius);
}DeferredScreenFragment.glsl
引入点光源衰减并比较距离
cpp
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform sampler2D gPosition;
uniform sampler2D gNormal;
uniform sampler2D gAlbedoSpec;
struct Light {
vec3 Position;
vec3 Color;
float Linear;
float Quadratic;
float Radius;
};
const int NR_LIGHTS = 4;
uniform Light lights[NR_LIGHTS];
uniform vec3 viewPos;
void main()
{
// G-Buffer 中读取数据
vec3 FragPos = texture(gPosition, TexCoords).rgb;
vec3 Normal = texture(gNormal, TexCoords).rgb;
vec3 Albedo = texture(gAlbedoSpec, TexCoords).rgb;
float Specular = texture(gAlbedoSpec, TexCoords).a;
// 计算光照
vec3 lighting = Albedo * 0.1;
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
for(int i = 0; i < NR_LIGHTS; ++i)
{
// 判断距离
float dist = length(lights[i].Position - FragPos);
if (dist < lights[i].Radius)
{
// Diffuse
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lights[i].Position - FragPos);
vec3 diffuse = max(dot(Normal, lightDir), 0.0) * Albedo * lights[i].Color;
// Specular
vec3 halfwayDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
float spec = pow(max(dot(Normal, halfwayDir), 0.0), 16.0);
vec3 specular = lights[i].Color * spec * Specular;
// Attenuation
float attenuation = 1.0 / (1.0 + lights[i].Linear * dist + lights[i].Quadratic * dist * dist);
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
lighting += diffuse + specular;
}
}
FragColor = vec4(lighting, 1.0);
}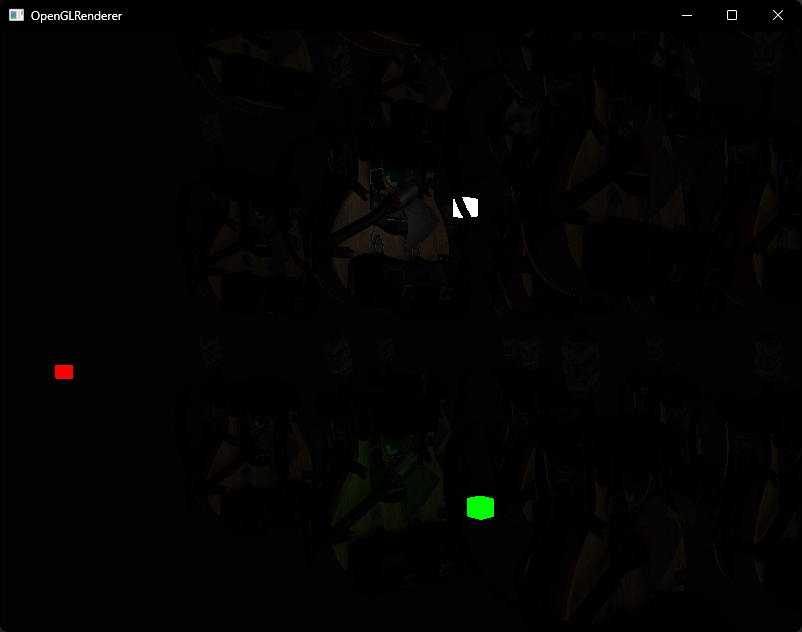
但这种方式在实际情况下并不能真正的生效
然而事实上,你的GPU和GLSL并不擅长优化循环和分支。这一缺陷的原因是GPU中着色器的运行是高度并行的,大部分的架构要求对于一个大的线程集合,GPU需要对它运行完全一样的着色器代码从而获得高效率。这通常意味着一个着色器运行时总是执行一个if语句所有的分支从而保证着色器运行都是一样的,这使得我们之前的半径检测优化完全变得无用,我们仍然在对所有光源计算光照!
因此,使用 Lighting Volume 更好的方式是在点光源中心渲染一个实际的球体,并根据光体积的半径进行缩放,绘制球体时写入到模板缓冲中,后续使用模板缓冲剔除掉不需要计算光照的片段
完整代码可在顶部Git仓库找到