享元模式
1 概念
享元模式使用对象池来尽可能地减少对对象池中已经存在的对象的二次创建。对象池的实现和使用是享元模式的核心,享元模式是利用对象池减少内存的使用量,避免重复创建大量对象的设计模式。
2 意图(Intent)
运用共享技术有效地支持大量细颗粒度的对象。
3 动机(Motivate)
采用纯粹对象方案的问题在于大量细粒度的对象会很快充斥在系统中,从而带来很高的运行时代价(主要指内存需求方面的代价)。 如何在避免大量细粒度对象问题的同时,让外部客户程序仍然能够透明地使用面向对象的方式来进行操作?
4 类图结构
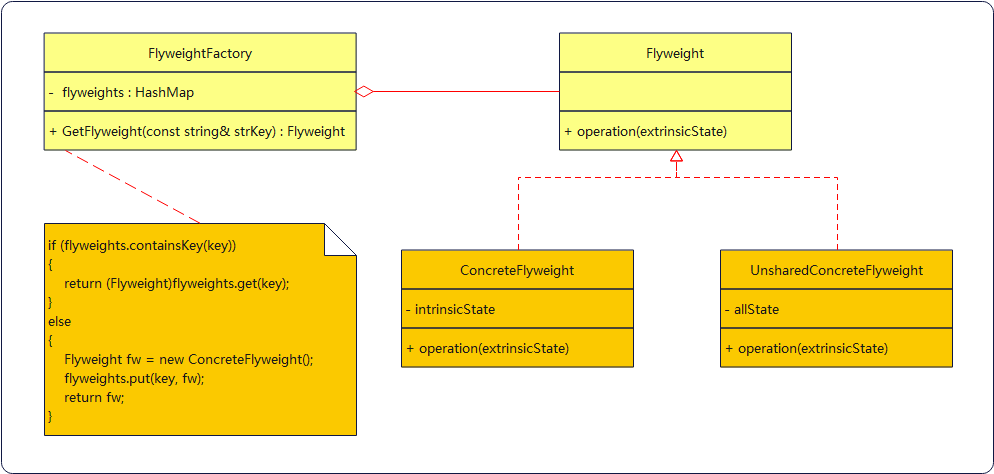
5 角色定义
- Flyweight(享元接口):所有元件的高层规范,声明与外蕴状态互动的接口标准。
- ConcreteFlyweight(享元实现):享元接口的元件实现类,自身维护着内蕴状态,且能接受并响应外蕴状态,可以有多个实现,一个享元对象可以被作为一个"元"。
- FlyweightFactory(享元工厂):用来维护享元对象的工厂,负责对享元对象实例进行创建于管理,并对外提供获取享元对象的服务。
6 程序示例
共享网络设备
示例类图
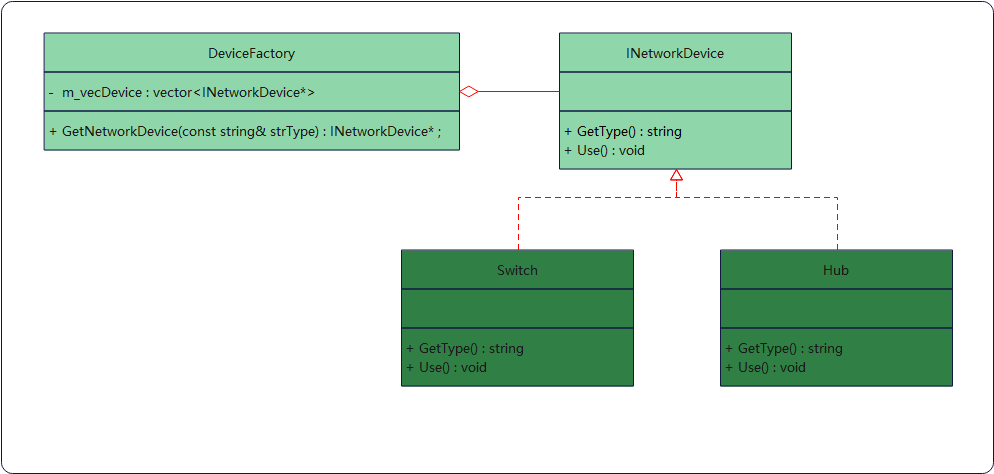
抽象享元类INetworkDevice(网络设备类)
cpp
/**
* @brief 抽象享元类INetworkDevice(网络设备类)
*/
class INetworkDevice
{
public:
INetworkDevice() = default;
virtual ~INetworkDevice() = default;
public:
virtual string GetType() = 0;
virtual void Use() = 0;
};具体享元类Switch(交换机类)
cpp
/**
* @brief 具体享元类Switch(交换机类)
*/
class Switch: public INetworkDevice
{
public:
Switch(const string& strType);
~Switch() = default;
public:
string GetType() override;
void Use() override;
private:
string m_strType;
};
Switch::Switch(const string &strType): m_strType(strType)
{
// ...
}
string Switch::GetType()
{
return m_strType;
}
void Switch::Use()
{
qDebug() << "Linked by switch, type is" << m_strType;
}具体享元类Hub(集线器类)
cpp
/**
* @brief 具体享元类Hub(集线器类)
*/
class Hub: public INetworkDevice
{
public:
Hub(const string& strType);
~Hub() = default;
public:
string GetType() override;
void Use() override;
private:
string m_strType;
};
Hub::Hub(const string &strType): m_strType(strType)
{
// ...
}
string Hub::GetType()
{
return m_strType;
}
void Hub::Use()
{
qDebug() << "Linked by Hub, type is" << m_strType;
}享元工厂类DeviceFactory(网络设备工厂类)
cpp
/**
* @brief 享元工厂类DeviceFactory(网络设备工厂类)
*/
class DeviceFactory
{
public:
DeviceFactory();
~DeviceFactory();
public:
INetworkDevice* GetNetworkDevice(const string& strType);
int GetTotalDevice();
int GetTotalTerminal();
private:
vector<INetworkDevice*> m_vecDevice;
int m_nTotalTerminal;
};
DeviceFactory::DeviceFactory(): m_nTotalTerminal(0)
{
INetworkDevice* pSwitch = new Switch("Cisco - WS - C2950 - 24");
INetworkDevice* pHub = new Hub("TP - LINK - HF8M");
m_vecDevice.push_back(pSwitch);
m_vecDevice.push_back(pHub);
}
DeviceFactory::~DeviceFactory()
{
for (auto& pDevice:m_vecDevice)
{
if (nullptr != pDevice)
{
delete pDevice;
pDevice = nullptr;
}
}
}
INetworkDevice *DeviceFactory::GetNetworkDevice(const string &strType)
{
if (string::npos != strType.find("Cisco"))
{
++m_nTotalTerminal;
return m_vecDevice[0];
}
else if (string::npos != strType.find("TP"))
{
++m_nTotalTerminal;
return m_vecDevice[1];
}
else
{
return nullptr;
}
}
int DeviceFactory::GetTotalDevice()
{
return static_cast<int>(m_vecDevice.size());
}
int DeviceFactory::GetTotalTerminal()
{
return m_nTotalTerminal;
}测试函数
cpp
/**
* @brief 测试函数
*/
void ClientTest()
{
INetworkDevice* pSwitchA = nullptr;
INetworkDevice* pSwitchB = nullptr;
INetworkDevice* pSwitchC = nullptr;
INetworkDevice* pHubA = nullptr;
INetworkDevice* pHubB = nullptr;
DeviceFactory* pDeviceFactory = new DeviceFactory();
pSwitchA = pDeviceFactory->GetNetworkDevice("Cisco");
pSwitchA->Use();
pSwitchB = pDeviceFactory->GetNetworkDevice("Cisco");
pSwitchB->Use();
pSwitchC = pDeviceFactory->GetNetworkDevice("Cisco");
pSwitchC->Use();
pHubA = pDeviceFactory->GetNetworkDevice("TP");
pHubA->Use();
pHubB = pDeviceFactory->GetNetworkDevice("TP");
pHubB->Use();
qDebug() << "Total Device:" << pDeviceFactory->GetTotalDevice();
qDebug() << "Total Terminal:" << pDeviceFactory->GetTotalTerminal();
delete pDeviceFactory;
}游戏背景图元
示例类图
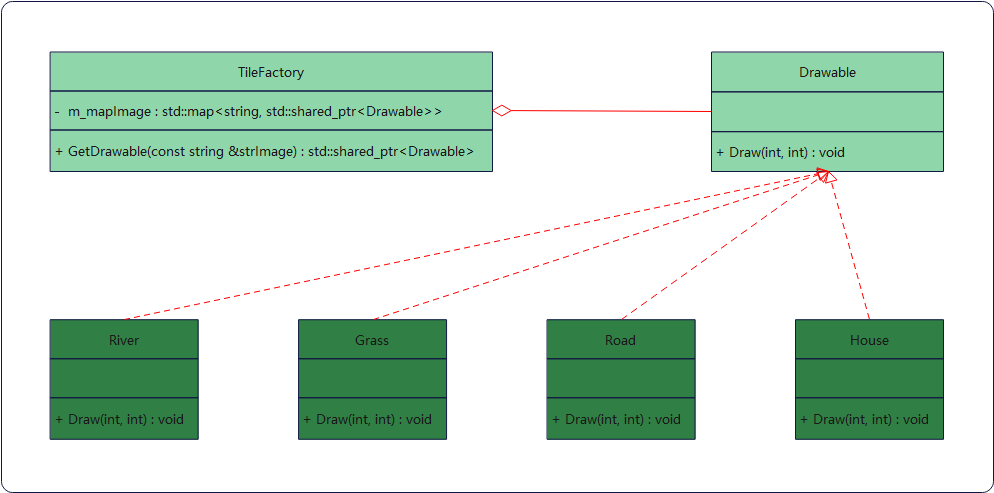
绘图接口Drawable
cpp
/**
* @brief 绘图接口Drawable
*/
class Drawable
{
public:
Drawable() = default;
virtual ~Drawable() = default;
public:
virtual void Draw(int nX, int nY) = 0;
};河流类 River
cpp
/**
* @brief 河流类 River
*/
class River: public Drawable
{
public:
River();
~River();
public:
void Draw(int nX, int nY) override;
private:
string m_strImage;
};
River::River()
{
m_strImage = "河流";
}
River::~River()
{
}
void River::Draw(int nX, int nY)
{
qDebug() << "在位置[ " << nX << ":" << nY << "]上绘制图片[" << m_strImage.c_str() << "]";
}草地类 Grass
cpp
/**
* @brief 草地类 Grass
*/
class Grass: public Drawable
{
public:
Grass();
~Grass();
public:
void Draw(int nX, int nY) override;
private:
string m_strImage;
};
Grass::Grass()
{
m_strImage = "草地";
}
Grass::~Grass()
{
}
void Grass::Draw(int nX, int nY)
{
qDebug() << "在位置[ " << nX << ":" << nY << "]上绘制图片[" << m_strImage.c_str() << "]";
}道路类 Road
cpp
/**
* @brief 道路类 Road
*/
class Road: public Drawable
{
public:
Road();
~Road();
public:
void Draw(int nX, int nY) override;
private:
string m_strImage;
};
Road::Road()
{
m_strImage = "道路";
}
Road::~Road()
{
}
void Road::Draw(int nX, int nY)
{
qDebug() << "在位置[ " << nX << ":" << nY << "]上绘制图片[" << m_strImage.c_str() << "]";
}房屋类 House
cpp
/**
* @brief 房屋类 House
*/
class House: public Drawable
{
public:
House();
~House();
public:
void Draw(int nX, int nY) override;
private:
string m_strImage;
};
House::House()
{
m_strImage = "房屋";
}
House::~House()
{
}
void House::Draw(int nX, int nY)
{
qDebug() << "在位置[ " << nX << ":" << nY << "]上绘制图片[" << m_strImage.c_str() << "]";
}图件工厂类 TileFactory
cpp
/**
* @brief 图件工厂类 TileFactory
*/
class TileFactory
{
public:
TileFactory() = default;
~TileFactory() = default;
public:
std::shared_ptr<Drawable> GetDrawable(const string& strImage);
private:
std::map<string, std::shared_ptr<Drawable>> m_mapImage;
};
std::shared_ptr<Drawable> TileFactory::GetDrawable(const string &strImage)
{
if (m_mapImage.end() != m_mapImage.find(strImage))
return m_mapImage[strImage];
if ("河流" == strImage)
{
m_mapImage.insert({strImage, std::make_shared<River>()});
}
else if ("草地" == strImage)
{
m_mapImage.insert({strImage, std::make_shared<Grass>()});
}
else if ("道路" == strImage)
{
m_mapImage.insert({strImage, std::make_shared<Road>()});
}
else if ("房屋" == strImage)
{
m_mapImage.insert({strImage, std::make_shared<House>()});
}
return m_mapImage[strImage];
}测试函数
cpp
/**
* @brief 测试函数
*/
void ClientTest()
{
TileFactory factory;
factory.GetDrawable("河流")->Draw(10, 10);
factory.GetDrawable("道路")->Draw(10, 10);
factory.GetDrawable("草地")->Draw(10, 10);
factory.GetDrawable("房屋")->Draw(10, 10);
}7 思考小结
享元模式优点
- 极大减少内存中对象数量,使得相同对象或相似对象在内存中只保存一份
- 享元模式的外部状态相对独立,而且不会影响其内部状态,从而使得享元对象可以在不同的环境中被共享
享元模式缺点
- 享元模式让系统更复杂,特别是需要分离内部状态和外部状态,这使得程序的逻辑复杂化
- 为了使对象可以共享,享元模式需要将享元对象的状态外部化,而读取外部状态使得运行时间变长
当一个系统有大量的对象,这些对象耗费大量的内存,对象的状态中的大部分都可以外部化,对象可以按照内蕴状态分成很多的组,当把外蕴对象从对象中剔除时,每一个组都可以仅用一个对象代替,满足以上的这些条件的系统可以使用享元对象。最后,使用享元模式需要维护一个记录了系统已有的所有享元的表,而这需要耗费资源。因此,应当在有足够多的享元实例可供共享时才值得使用享元模式。