前言
本系列前八篇文章:
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(一)---全面认识LangGraph
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(二)---LangGraph预构建图API快速创建Agent
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(三)---LangGraph工具调用实战
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(四)---LangGraph全生态开发工具使用与智能体部署
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(五)---LangGraph 数据分析助手智能体项目实战
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(六)---LangGraph 底层API入门
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(七)---构建条件分支图和循环图
- 深入浅出LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发教程(八)---LangGraph底层API实现ReACT智能体
通过前几期的分享我们掌握了LangGraph 高阶预构建图API和底层图语法API创建智能体的基本方法并部署上线了多款智能体。细心的同学有没有发现目前的智能体在需要记忆的多轮对话场景中使用的是对Python列表增删改查的手段,这种方式低效且数据无法持久化保存(应用一旦关闭数据消失)。古希腊先哲埃斯库罗斯说过"记忆是所有智慧的母亲",LangGraph提供了更好的记忆解决方法,本期分享就让我们一起走进LangGraph长短期记忆管理的世界,掌握智能体由临时保障向持续发展进化的技巧~
本系列分享是笔者结合自己学习工作中使用LangChain&LangGraph经验倾心编写的,力求帮助大家体系化快速掌握LangChain&LangGraph AI Agent智能体开发的技能!笔者的LangChain系列教程暂时更完,后面也会实时补充工作实践中的额外知识点,建议大家在学习LangGraph分享前先学习LangChain的基本使用技巧。大家感兴趣可以关注笔者掘金账号和系列专栏。更可关注笔者同名微信公众号: 大模型真好玩 , 每期分享涉及的代码均可在公众号私信: LangChain智能体开发获得。
一、LangGraph记忆管理的两种方式
正如人类利用短期记忆和长期记忆进行有效的互动和学习一样,LangGraph也提供了短期记忆 和长期记忆两种记忆管理方法,实际项目中经常使用两者协同效应实现复杂功能。
短期记忆: 核心价值在于保障对话的临时性,使智能体能够跟踪会话中的多轮对话 , 前面提到的在State状态中保存messages列表就属于短期记忆的实现方式之一。
长期记忆: 核心价值在于提供稳定的数据认证,使智能体能够跨会话存储用户特定或应用程序级的数据 。
二、 LangGraph短期记忆的实现方法
2.1 InMemorySaver 内存会话临时存储
LangGraph短期记忆使智能体能够跟踪多轮对话, 要添加短期记忆常用到InMemorySaver方法,它属于线程级别的持久化。大家日常生活中经常使用DeepSeek, 豆包等应用,在更换主题提问时需要点击新对话 ,创建新对话后发现以前提问的历史都清空了,背后的原因就是LangGraph短期记忆实现方法是线程级别的,创建新对话本质是开启一个新线程。下面我们演示InMemorySaver的使用。
-
引入LangGraph记忆管理的相关依赖并设置记忆管理的检查点
pythonfrom langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent checkpointer = InMemorySaver() # 设置检查点 -
定义大模型并使用
create_react_agentapi接入,注意create_react_agent传入参数中除了大模型和工具函数列表外,还要传入检查点checkpointer:pythonmodel = init_chat_model( model="deepseek-chat", model_provider="deepseek", api_key='你注册的Deepseek api key' ) agent = create_react_agent(model=model, tools=[], checkpointer=checkpointer)如果是底层自定义api在图构建阶段传入检查点的代码是
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)。 -
短期记忆与线程相关,在与智能体对话时需要携带
config线程id信息。执行代码可以看到当我们携带相同的线程id时,智能体可以记忆我们的信息,知道我们叫苍老师。然而当我们更换线程id时,智能体就记不得我们的名字啦, 这就是LangGraph的短期记忆机制。pythonconfig = { "configurable": { "thread_id": "1" } } response = agent.invoke( {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "你好,我叫苍老师,好久不见!"}]}, config ) print(response['messages'][-1].content) response = agent.invoke( {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "你好,请问你还记得我叫什么名字么?"}]}, config ) print('------------线程1------------------') print(response['messages'][-1].content) new_config = { "configurable": { "thread_id": "2" } } response = agent.invoke( {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "你好,请问你还记得我叫什么名字么?"}]}, new_config ) print('------------线程2------------------') print(response['messages'][-1].content)
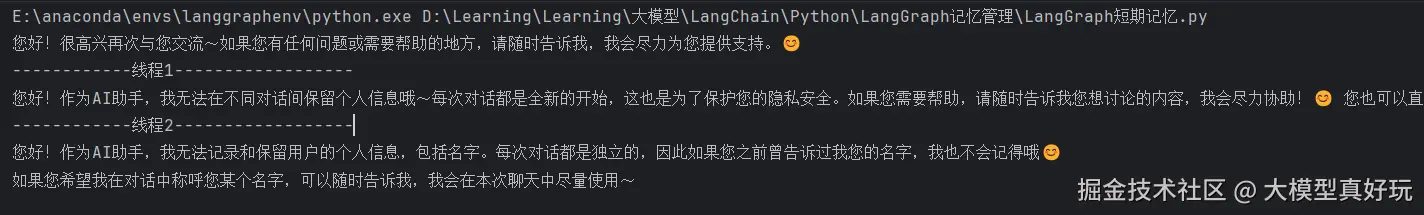
2.2 Postgres 短期记忆数据库持久化存储
细心的读者可能会问,"当我们应用程序结束再启动后记忆就又消失了,这和平常应用习惯不相符,如何解决这个问题呢?"。 要注意InMemorySaver仅仅是把记忆保存在内存中,应用程序结束后释放内存记忆就消失了。在生产环境中常常使用数据库支持的检查点记录器持久化保存记忆,这里以postgres数据库为例:
-
在
anaconda虚拟环境langgraphenv中执行如下命令安装依赖:pythonpip install -U "psycopg[binary,pool]" langgraph-checkpoint-postgres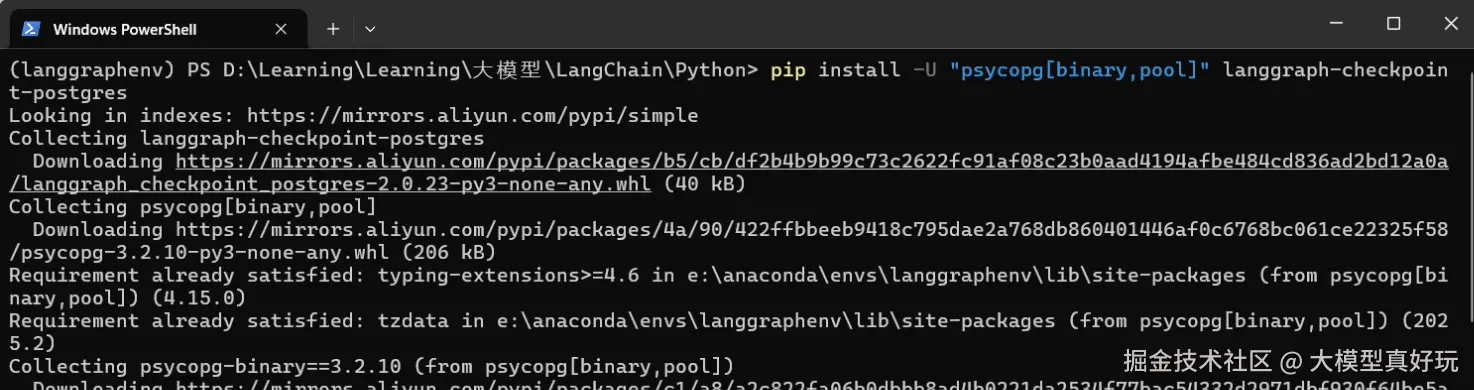
-
安装
postgres数据库,该步骤网络上已有超多教程,这里就不加赘述。Windows环境下postgres数据库的安装可参考博文: blog.csdn.net/weixin_5478... -
编写代码如下,
DB_URI是数据库连接 URI,包含连接 PostgreSQL 数据库使用的协议、身份验证以及数据库运行的主机。想要自动保存在数据库中的State均需在PostgresSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI)上下文中操作。同时注意在首次使用 Postgres 检查点记录器时,需要调用checkpointer.setup()。pythonfrom langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START from langgraph.checkpoint.postgres import PostgresSaver model = init_chat_model( model="deepseek-chat", model_provider="deepseek", api_key='你注册的Deepseek api key' ) DB_URI = "postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5442/postgres?sslmode=disable" with PostgresSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer: checkpointer.setup() # 第一次调用时必须要setup() def call_model(state: MessagesState): response = model.invoke(state["messages"]) return {"messages": response} builder = StateGraph(MessagesState) builder.add_node(call_model) builder.add_edge(START, "call_model") graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer) config = { "configurable": { "thread_id": "1" } } response = graph.invoke( {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "你好,我是苍老师"}]}, config ) print(response['message']) response = graph.invoke( {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "请问我叫什么名字"}]}, config ) print(response['message'])执行以上程序后我们会发现
Postgres数据库中多了四个表: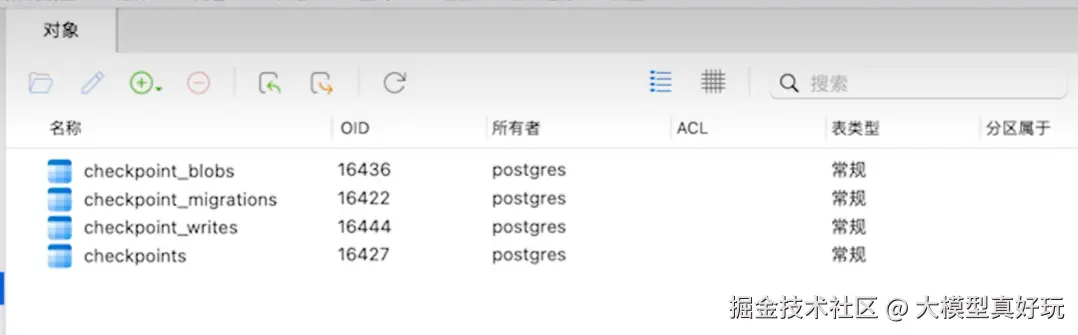
点击四张表中的
checkpoints表,可以看到我们的会话记录已经被保存在了该表中:
三、 LangGraph长期记忆的实现方法
LangGraph 长期记忆常用于构建持久的知识体系,实现跨线程的学习能力。比如一个智能体的公共角色设定等。明确使用场景后,我们通过一个实际案例了解长期记忆存储的基本操作:
3.1 InMemoryStore 常见参数
首先我们了解InMemoryStore的基础操作,它包含如下方法:
-
put: 实现信息存储的基础操作,需要三个参数:
- 命名空间:元组类型,类比文件系统中的文件夹,支持分层组织结构
- 键: 字符串,是命名空间内的唯一标识符,一般推荐使用uuid库生成唯一标识符
- 值:Python字典类型,比如保存公共角色资料时可以是包含姓名、偏好等键值对的字典
以下代码表示在命名为
users的命名空间中,以user_123的唯一标识保存姓名为John Smith的字典数据。pythonstore.put( ("users",), "user_123", { "name": "John Smith", "language": "English", } ) -
get: 对长期记忆基于精确键值的直接记忆检索
- 命名空间: 长期记忆的命名空间
- 键: 长期记忆的唯一键
以下代码表示读取
users命名空间中以user_123为唯一标识的数据pythonuser_info = store.get(("users",), 'user_123') -
search: 在指定命名空间内实现灵活记忆检索,不但可以通过命名空间和标识符,更可以通过语义检索到记忆内容。
search功能与知识库中语义向量检索功能类似,大家可参考文章一文带你了解RAG核心原理!不再只是文档的搬运工- 命名空间: 必须参数,指定检索目标命名空间
- query: 可选字符串,启用语义搜索功能,但注意该功能需预先配置索引
- filter: 可选字典, 基于记忆值值字典的键值对过滤
- limit: 可选整数, 限制返回结果数量
以下代码是使用语义检索的示例,设置向量索引,通过本地ollama部署的embedding模型(不了解ollama部署的可参考笔者文章: 利用ollama搭建本地大模型服务)构建索引,"我很饿"的词向量与"我爱吃汉堡"的相似程度远大于和"我是苍进空"的向量相似程度,检索结果会输出"我爱吃汉堡"
pythonfrom langchain.embeddings import init_embeddings from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore embeddings = init_embeddings("bge-m3:latest", provider='ollama') store = InMemoryStore( index={ "embed": embeddings, "dims": 1024, } ) store.put(("user_123", "memories"), "1", {"text": "我爱吃汉堡"}) store.put(("user_123", "memories"), "2", {"text": "我是苍进空"}) items = store.search( ("user_123", "memories"), query="I'm hungry", limit=1 )
3.2 InMemoryStore长期记忆获取信息
下面我们通过使用create_react_agent构建查找用户信息的智能体来演示长期记忆的使用,代码和运行结果如下, 可以看到工具函数中成功调用store查找到了保存的用户信息。对于底层API的构建图使用graph = builder.compile(store=store)传入长期记忆。
python
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langgraph.config import get_store
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
store = InMemoryStore()
store.put(
("users",),
"user_123",
{
"name": "苍老师",
"language": "日语",
}
)
def get_user_info(config: RunnableConfig) -> str:
"""查找用户信息的函数,可以查看长期记忆中储存的用户信息"""
# Same as that provided to `create_react_agent`
store = get_store()
user_id = config["configurable"].get("user_id")
user_info = store.get(("users",), user_id)
return str(user_info.value) if user_info else "Unknown user"
model = init_chat_model(
model="deepseek-chat",
model_provider="deepseek",
api_key='你注册的deepseek api key'
)
agent = create_react_agent(
model=model,
tools=[get_user_info],
store=store
)
# Run the agent
response = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "帮我查找长期记忆中储存的用户信息"}]},
config={"configurable": {"user_id": "user_123"}}
)
print(response['messages'])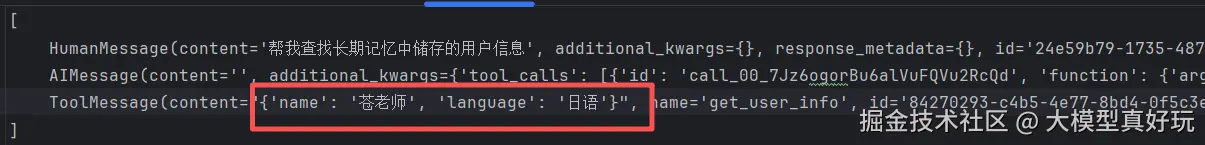
3.3 Postgres 长期记忆数据库持久化存储
对于生产级别应用必须使用数据库持久化存储长期记忆,LangGraph提供了PostgresStore工具。编写示例代码如下,大家猜一下执行结果会是怎样的呢?
python
import uuid
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START
from langgraph.checkpoint.postgres import PostgresSaver
from langgraph.store.postgres import PostgresStore
from langgraph.store.base import BaseStore
model = init_chat_model(
model="deepseek-chat",
model_provider="deepseek",
api_key='sk-bec76b9411694239b20ead2d77ee37f0'
)
DB_URI = "postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5442/postgres?sslmode=disable"
with (
PostgresStore.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as store,
PostgresSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer,
):
store.setup()
checkpointer.setup()
def call_model(
state: MessagesState,
config: RunnableConfig,
*,
store: BaseStore,
):
user_id = config["configurable"]["user_id"]
namespace = ("memories", user_id)
memories = store.search(namespace, query=str(state["messages"][-1].content))
info = "\n".join([d.value["data"] for d in memories])
system_msg = f"你是一个与人类交流的小助手,用户信息: {info}"
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
if "记住" in last_message.content.lower():
memory = "用户名字是苍老师"
store.put(namespace, str(uuid.uuid4()), {"data": memory})
response = model.invoke(
[{"role": "system", "content": system_msg}] + state["messages"]
)
return {"messages": response}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(
checkpointer=checkpointer,
store=store,
)
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1",
"user_id": "1",
}
}
response = graph.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "你好,记住: 我叫苍老师"}]},
config
)
print(response['messages'][-1])
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "2",
"user_id": "1",
}
}
response = graph.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "我的名字是什么?"}]},
config
)
print(response['messages'][-1])以上代码的工作流程如下:
- 第一次对话时系统检测到"记住"关键词,将"用户名字是苍老师"存储到长期记忆的数据库中
- 第二次对话时,虽然是不同的线程id,但长期记忆是跨线程的,因此还是会回复:你的名字叫苍老师
大家实际运行代码检测一下吧~
四、LangGraph长短期记忆进阶
很多同学可能会说"如果我不想使用Postgres数据库来持久化长短期记忆,想把记忆保存在文件中该如何实现呢?","如何将LangGraph长短期记忆保存在我们公司自研数据库呢?" 值得一提的是,LangGraph持久化机制设计非常灵活,能适配各种存储基础设施。
对于短期记忆checkpoint来说,无论是InMemorySaver还是PostgresSaver都是通过继承BaseCheckpointSaver抽象类并定义存档点接口实现的。除此之外,LangGraph还基于BaseCheckpointSaver抽象类定义了SqliteSaver、MongoDBSaver等。大家如果有接入内部自定义存储系统的需求,可以通过继承BaseCheckpointSaver抽象类并自定义相关方法,相关文档见: github.langchain.ac.cn/langgraph/r...
同样的LangGraph长期记忆使用的InMemoryStore、PostgresStore是通过继承BaseStore抽象类来实现的,上面提到的put, get和set方法都是BaseStore抽象类中的接口方法,用户可以自定义相关方法实现长期记忆的定制,相关文档见: github.langchain.ac.cn/langgraph/r...
限于篇幅原因,本期分享不演示关于BaseCheckpointSaver和BaseStore的相关实现。关于LangGraph记忆的管理,往往还涉及修建&总结历史记录、设置用户偏好记忆、记忆修改、语义搜索、数据加密、快照回复、人机交互(Human in loop)等功能,是个宏大的主题,不可能通过三言两语讲完。但好在LangGraph文档为我们提供了详实的示例,大家可以参考:github.langchain.ac.cn/langgraph/h... 自行搜索学习。以上就是本期分享的全部内容啦!
五、总结
本期内容分享了LangGraph中的长短期记忆管理机制,短期记忆演示通过InMemorySaver和PostgresSaver实现会话级对话跟踪,支持线程隔离的数据持久化;长期记忆则演示通过InMemoryStore和PostgresStore构建跨会话的稳定知识体系,支持语义检索等高级功能。同时指出大家可通过继承BaseCheckpointSaver和BaseStore抽象类实现自定义存储扩展。到本期内容LangGraph的基本知识点笔者就更完啦,但远不是这个系列的结束,代码的学习理解一定要结合实际应用场景,接下来笔者会继续更新大型实战项目,让大家在实战中掌握大模型时代智能体开发的必备技能,大家敬请期待~
本系列分享预计会有20节左右的规模,保证大家看完一定能够掌握LangChain&LangGraph的开发能力,大家感兴趣可关注笔者掘金账号和专栏,更可关注笔者的同名微信公众号:大模型真好玩 , 本系列分享的全部代码均可在微信公众号私信笔者: LangChain智能体开发 免费获得。