目录
[3.1 insert](#3.1 insert)
[3.2 erase](#3.2 erase)
[3.3 push_back 和push_front](#3.3 push_back 和push_front)
[3.4pop_back 和 pop_front](#3.4pop_back 和 pop_front)
[3.6 operator=](#3.6 operator=)
[3.7 析构函数的实现](#3.7 析构函数的实现)
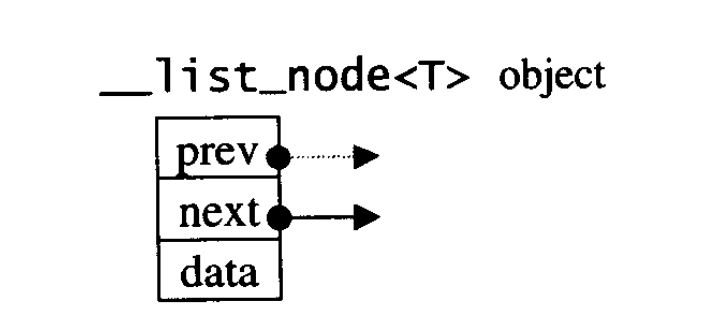
1.list的节点
c**++中list的用的是带头双向循环链表,list本身和list节点并不是同一个内容需要分开设计.**
以下是list节点的结构
cpp
template<class T>
struct __list_node {
__list_node(const T& val)
:_val(val)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prve(nullptr)
{}
T _val;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prve;
};这很明显是一个双向的结构
2.list迭代器的实现
我们先来回顾一下vector的迭代器是如何实现的?vector的空间是连续的迭代器可以是原生指针对于begin和end来说直接返回_start,_finish就可以了.
cpp
vector的迭代器的实现
T是模版参数
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator
iterator begin () {
return _start;
}
iterator end() {
return _finish;
}对于我们的list来说空间不是连续的不能直接想vector一样返回原生指针.这个时候我们的迭代器要如何实现呢? 我们需要list的节点封装成一个类,利用运算符重载就可以像指针一样使用,然后就可以实现迭代器.
list迭代器的实现
cpp
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator {
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*() {
return _node->_val;
}
Ptr operator->() {
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++() {
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--() {
_node = _node->_prve;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prve;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it) const {
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it) const {
return _node != it._node;
}
};大家可能这里会不明白,这里为什么要多加两个模版参数Ref和Ptr呢?如果不加这两个模版参数行不行呢?如果不加这两个参数也可实现list的迭代器,但是在我们解引用之后返回.只能返回 T& 或者是 const T& ,只能实现一种迭代器如果实现普通迭代器就不能实现const迭代器.如果要实现需要重新拷贝一份代码把返回值改成const T&或者是 T&,但是这样会造成代码重复.
不加Ref或Ptr两个模版参数实现的版本
普通迭代器
cpp
普通迭代器
template<class T>
struct list_iterator {
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
T& operator*() {
return _node->_val;
}
T* operator->() {
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++() {
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--() {
_node = _node->_prve;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prve;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it) const {
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it) const {
return _node != it._node;
}
};const 迭代器
cpp
普通迭代器
template<class T>
struct list_iterator {
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
const T& operator*() {
return _node->_val;
}
const T* operator->() {
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++() {
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--() {
_node = _node->_prve;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prve;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it) const {
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it) const {
return _node != it._node;
}
};如果我们加上这两个模版参数我们可以用一份代码实现两个位置的迭代器,指定参数就可以了.
cpp
typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;3.list的具体实现
准备工作
cpp
template<class T>
class list {
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin() {
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end() {
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const{
return _head;
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t size;//用来记录节点的个数
}3.1 insert
cpp
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val) {
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
Node* node = pos._node;
Node* prve = node->_prve;
newnode->_prve = prve;
prve->_next = newnode;
node->_prve = newnode;
newnode->_next = node;
_size++;
return newnode;
}3.2 erase
cpp
iterator erase(iterator pos) {
assert(pos != end());
Node* node = pos._node;
Node* next = node->_next;
Node* prve = node->_prve;
prve->_next = next;
next->_prve = prve;
delete node;
_size--;
return next;
}3.3 push_back 和push_front
cpp
void push_back(const T& val) {
insert(end(), val);
}
void push_front(const T& val) {
insert(++end(), val);
}3.4pop_back 和 pop_front
cpp
void pop_back() {
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front() {
erase(++end());
}3.5构造函数
cpp
void init_empty() {
_size = 0;
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prve = _head;
}
list() {
init_empty();
}
list(initializer_list<T> lt) {
init_empty();
for (const auto& e : lt) {
push_back(e);
}
}
list(const list<T>& lt) {
init_empty();
for (const auto& e : lt) {
push_back(e);
}3.6 operator=
cpp
void swap(list<T>& lt) {
std::swap(_head,lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt) {
swap(lt);
return *this;
}3.7 析构函数的实现
cpp
~list() {
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end()) {
it = erase(it);
}
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}4.完整代码实现
cpp
template<class T>
struct __list_node {
__list_node(const T val = T())
:_val(val)
,_next(nullptr)
,_prve(nullptr)
{}
T _val;
__list_node<T>* _next;
__list_node<T>* _prve;
};
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator {
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*() {
return _node->_val;
}
Ptr operator->() {
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++() {
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--() {
_node = _node->_prve;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prve;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it) const {
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it) const {
return _node != it._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list {
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
void init_empty() {
_size = 0;
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prve = _head;
}
public:
typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
list() {
init_empty();
}
list(initializer_list<T> lt) {
init_empty();
for (const auto& e : lt) {
push_back(e);
}
}
list(const list<T>& lt) {
init_empty();
for (const auto& e : lt) {
push_back(e);
}
}
~list() {
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end()) {
it = erase(it);
}
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void swap(list<T>& lt) {
std::swap(_head,lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt) {
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
iterator begin() {
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end() {
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const{
return _head;
}
void push_back(const T& val) {
insert(end(), val);
}
void push_front(const T& val) {
insert(++end(), val);
}
void pop_back() {
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front() {
erase(++end());
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val) {
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
Node* node = pos._node;
Node* prve = node->_prve;
newnode->_prve = prve;
prve->_next = newnode;
node->_prve = newnode;
newnode->_next = node;
_size++;
return newnode;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos) {
assert(pos != end());
Node* node = pos._node;
Node* next = node->_next;
Node* prve = node->_prve;
prve->_next = next;
next->_prve = prve;
delete node;
_size--;
return next;
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};