YOLOv7是YOLO(You Only Look Once)系列实时目标检测算法的重要里程碑,由WongKinYiu团队在2022年提出。作为单阶段目标检测器的杰出代表,YOLOv7在保持高速推理的同时,显著提升了检测精度,成为工业界和学术界广泛应用的先进模型。
核心架构创新
YOLOv7采用精心设计的网络架构,引入扩展高效层聚合网络(E-ELAN),通过分组卷积、特征重排列等策略优化特征提取能力。该结构在保持梯度路径完整性的同时,增强了不同特征层的信息融合效率。模型还采用了基于串联的模型缩放方法,能够智能平衡计算复杂度与特征表达能力。
训练策略突破
YOLOv7提出了一系列创新的训练技术:
-
计划重参数化卷积:将训练时的多分支结构与推理时的单一分支巧妙结合,提升性能而不增加推理时间
-
辅助头训练:在中间层添加辅助检测头,加强梯度传播和特征学习
-
标签分配策略:改进的软标签分配方法,提供更精确的监督信号
性能表现卓越
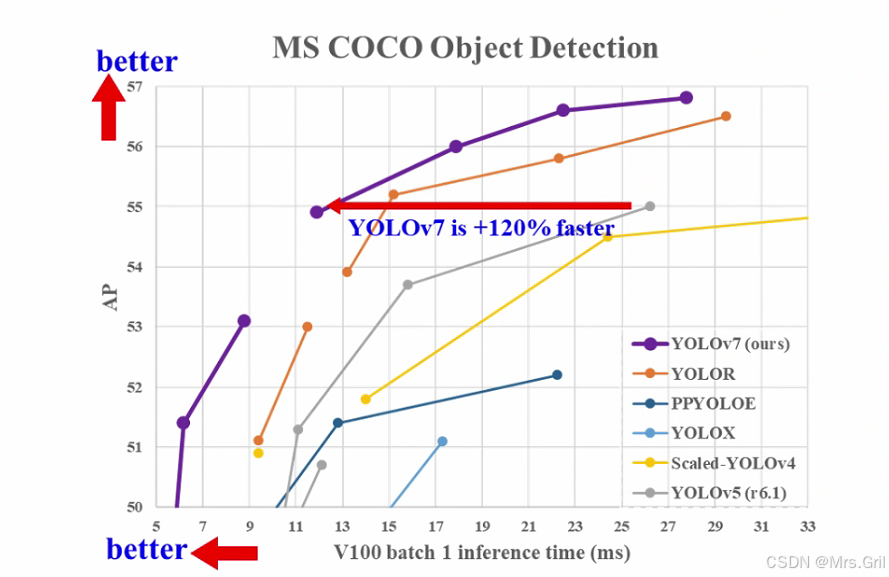
在COCO数据集测试中,YOLOv7展现出色性能:在30FPS实时推理条件下达到56.8% AP,超越同规模YOLO版本和Transformer-based检测器。模型提供多种规格(YOLOv7-tiny到YOLOv7-W6),满足从移动端到服务器端的多样化部署需求。
应用优势明显
YOLOv7支持目标检测、实例分割、姿态估计等多任务,具有出色的工程实用性。其优化的计算效率使模型在边缘设备上也能流畅运行,为自动驾驶、视频监控、工业质检等领域提供了可靠的视觉解决方案。开源社区的活跃维护和持续优化,进一步巩固了YOLOv7在实时目标检测领域的领先地位。
总体而言,YOLOv7通过架构创新与训练策略的完美结合,在速度-精度权衡方面达到了新的高度,为实际应用场景提供了强有力的技术支撑。
github网址:
onnx转RKNN
import cv2
import numpy as np
from rknn.api import RKNN
import os
if __name__ == '__main__':
isQUANT = True # True
platform = 'rk3588'
NAME = "yolov7"
ONNX_DIR = "./"
OUT_DIR = "./"
Width = 640
Height = 640
MODEL_PATH = ONNX_DIR + NAME + '.onnx'
RKNN_NAME = NAME
if isQUANT:
RKNN_NAME = NAME + '_quant'
else:
RKNN_NAME = NAME + '_FP16'
NEED_BUILD_MODEL = True
DATASET = './dataset.txt'
im_file = '/home/zdl/rknn_project/rtdetrv2/d1/t_15_00083.bmp'
# Create RKNN object
rknn = RKNN(verbose=False,verbose_file="./outputlog.txt")
RKNN_MODEL_PATH = './{}/{}.rknn'.format(OUT_DIR,RKNN_NAME)
if NEED_BUILD_MODEL:
# rknn.config(mean_values=[[0,0,0]], std_values=[[1,1,1]], target_platform=platform,disable_rules=['fuse_two_gather'] )
rknn.config(mean_values=[[0,0,0]], std_values=[[255.0,255.0,255.0]],target_platform=platform)
# rknn.config(mean_values=[[0]], std_values=[[255]],target_platform=platform)
# Load model
print('--> Loading model')
ret = rknn.load_onnx(MODEL_PATH,outputs=["onnx::Reshape_491","onnx::Reshape_505","onnx::Reshape_519"])
# ret = rknn.load_onnx(MODEL_PATH)
if ret != 0:
print('load model failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Build model
print('--> Building model')
ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=isQUANT, dataset=DATASET)
# rknn.accuracy_analysis(inputs=["./errors/2.jpg","./errors/3.jpg"],
# output_dir='snapshot')
# ret = rknn.accuracy_analysis(inputs=[im_file],output_dir='snapshot')
if ret != 0:
print('build model failed.')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Export rknn model
if not os.path.exists(OUT_DIR):
os.mkdir(OUT_DIR)
print('--> Export RKNN model: {}'.format(RKNN_MODEL_PATH))
ret = rknn.export_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_PATH)
if ret != 0:
print('Export rknn model failed.')
exit(ret)
print('done')
else:
ret = rknn.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_PATH)
rknn.release()cpp
//
// Created by zdl on 25-1-20.
//
#include "YoloV5.h"
inline static int clamp(float val, int min, int max) {
return val > min ? (val < max ? val : max) : min;
}
static float sigmoid(float x) { return 1.0 / (1.0 + expf(-x)); }
static float unsigmoid(float y) { return -1.0 * logf((1.0 / y) - 1.0); }
inline static int32_t __clip(float val, float min, float max)
{
float f = val <= min ? min : (val >= max ? max : val);
return f;
}
static int8_t qnt_f32_to_affine(float f32, int32_t zp, float scale)
{
float dst_val = (f32 / scale) + zp;
int8_t res = (int8_t)__clip(dst_val, -128, 127);
return res;
}
static float deqnt_affine_to_f32(int8_t qnt, int32_t zp, float scale) { return ((float)qnt - (float)zp) * scale; }
int V5::proprecessV5(std::vector<rknn_output> output, std::vector<float> out_scales,
std::vector<int32_t> out_zps,
std::vector<cv::Rect> &boxes,
std::vector<float> &confidences,
std::vector<int> &classids,
std::vector<int> &anchorf,
float confThres)
{
int num_output = output.size();
int anchorfuture = 0;
for (int n = 0; n < num_output; n++) {
int grid_w = modelInputSize.width / strides[n]; // 宽
int grid_h = modelInputSize.height / strides[n]; // 高
int grid_len = grid_w * grid_h;
int8_t *data = (int8_t*)output[n].buf;
// std::cout << "size: " << output[n].size << std::endl;
float thres = unsigmoid(confThres);
int8_t thres_i8 = qnt_f32_to_affine(thres, out_zps[n], out_scales[n]);
for (int a = 0; a < 3; a++) {
for (int i = 0; i < grid_h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid_w; j++) {
int8_t box_confidence = data[(PROP_BOX_SIZE * a + 4) * grid_len + i * grid_w + j];
if (box_confidence >= thres_i8) {
int offset = (PROP_BOX_SIZE * a) * grid_len + i * grid_w + j;
int8_t* in_ptr = data + offset;
float box_x = sigmoid(deqnt_affine_to_f32(*in_ptr, out_zps[n], out_scales[n])) * 2.0 - 0.5;
float box_y = sigmoid(deqnt_affine_to_f32(in_ptr[grid_len], out_zps[n], out_scales[n])) * 2.0 - 0.5;
float box_w = sigmoid(deqnt_affine_to_f32(in_ptr[2 * grid_len], out_zps[n], out_scales[n])) * 2.0;
float box_h = sigmoid(deqnt_affine_to_f32(in_ptr[3 * grid_len], out_zps[n], out_scales[n])) * 2.0;
box_x = (box_x + j) * (float)strides[n];
box_y = (box_y + i) * (float)strides[n];
box_w = box_w * box_w * (float)anchors.at(strides[n])[a][0];
box_h = box_h * box_h * (float)anchors.at(strides[n])[a][1];
box_x -= (box_w / 2.0);
box_y -= (box_h / 2.0);
int8_t maxClassProbs = in_ptr[5 * grid_len];
int maxClassId = 0;
for (int k = 1; k < DetNumLabel; ++k) {
int8_t prob = in_ptr[(5 + k) * grid_len];
if (prob > maxClassProbs) {
maxClassId = k;
maxClassProbs = prob;
}
}
if (maxClassProbs>thres_i8){
confidences.push_back(sigmoid(deqnt_affine_to_f32(maxClassProbs, out_zps[n], out_scales[n]))* sigmoid(deqnt_affine_to_f32(box_confidence, out_zps[n], out_scales[n])));
classids.push_back(maxClassId);
cv::Rect rect;
rect.x = box_x;
rect.y = box_y;
rect.width = box_w;
rect.height = box_h;
// boxes.push_back(rect);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(box_x, box_y, (int)((box_w)), (int)((box_h)))); // 记录框
anchorf.push_back(n);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
cv::Mat V5::letterboxYolo(cv::Mat src, int &x_pad, int &y_pad, float &scale,int &channel)
{
if(channel == 1)
{
cv::cvtColor(src,src,cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
}
int input_w = modelInputSize.width; // 模型输入的宽
int input_h = modelInputSize.height; // 模型输入的高
int w, h, x, y;
float r_w = static_cast<float>(input_w) / src.cols;
float r_h = static_cast<float>(input_h) / src.rows;
if (r_h > r_w) {
w = input_w;
h = std::round(r_w * src.rows); // 避免浮点数误差
x = 0;
y = (input_h - h) / 2;
scale = r_w;
} else {
w = std::round(r_h * src.cols);
h = input_h;
x = (input_w - w) / 2;
y = 0;
scale = r_h;
}
x_pad = x;
y_pad = y;
cv::Mat re, out;
if (src.channels() == 3) {
re = cv::Mat(h, w, CV_8UC3);
cv::resize(src, re, re.size(), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
out = cv::Mat(input_h, input_w, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar(114, 114, 114));
} else if (src.channels() == 1) {
re = cv::Mat(h, w, CV_8UC1);
cv::resize(src, re, re.size(), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
out = cv::Mat(input_h, input_w, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(114));
} else {
return cv::Mat(); // 返回空矩阵,避免错误
}
// 将缩放后的图像复制到填充后的图像
re.copyTo(out(cv::Rect(x, y, re.cols, re.rows)));
return out;
}
cv::Rect V5::get_rect(cv::Mat &img, cv::Rect bbox)
{
float l, r, t, b;
float r_w = modelInputSize.width / (img.cols * 1.0);
float r_h = modelInputSize.height / (img.rows * 1.0);
if (r_h > r_w) {
l = bbox.x;
r = bbox.x + bbox.width;
t = bbox.y - (modelInputSize.height - r_w * img.rows) / 2;
b = bbox.y + bbox.height - (modelInputSize.height - r_w * img.rows) / 2;
l = l / r_w;
r = r / r_w;
t = t / r_w;
b = b / r_w;
} else {
l = bbox.x - (modelInputSize.width - r_h * img.cols) / 2;
r = bbox.x + bbox.width - (modelInputSize.width - r_h * img.cols) / 2;
t = bbox.y;
b = bbox.y + bbox.height;
l = l / r_h;
r = r / r_h;
t = t / r_h;
b = b / r_h;
l = l < 0 ? 0 : l;
t = r < 0 ? 0 : t;
}
return cv::Rect(round(l), round(t), round(r - l), round(b - t));
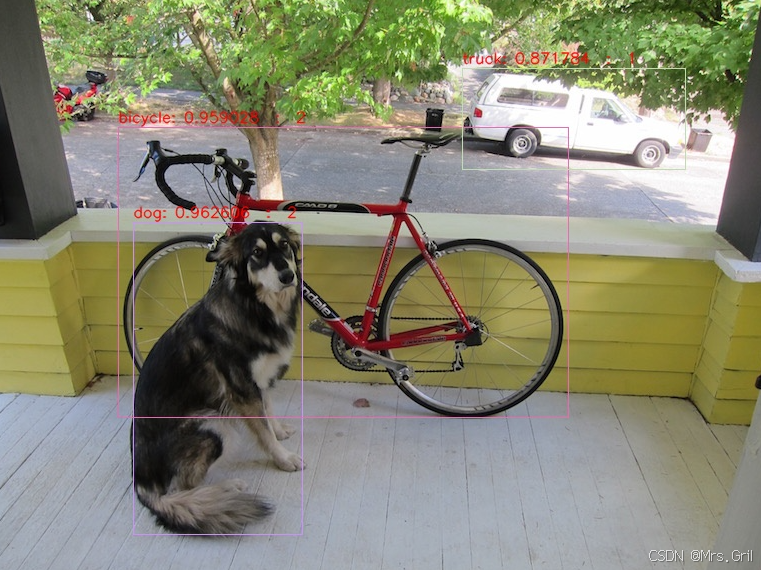
}结果展示: