模型
模型的概念:经验
天气预报,根据过去数十年天气的特征,对应的天气,建立出模型。然后把新的特征(乌云,风,降温,7月)放模型当中,来预测未来的天气(60%的概率两个小时内有雨)。
公式:
这里的 是特征
线性回归
线性回归是一种用于建立因变量(目标变量)与一个或多个自变量(特征变量)之间线性关系的统计模型。它的核心思想是:用一条直线(或一个超平面)来拟合数据点,使得预测值与真实值之间的误差最小。
简单线性回归:只有一个自变量
其中 是因变量,
是自变量,
是截距,
是斜率,
是误差项。
多元线性回归:有多个自变量
python
# 导⼊所需的库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# ⽣成⼀些示例数据
np.random.seed(0)
X = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * X + np.random.randn(100, 1)
# 创建线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()
# 训练模型
model.fit(X, y)
# 获取模型参数
slope = model.coef_[0]
intercept = model.intercept_
# 打印模型参数
print("斜率 (Slope):", slope[0])
print("截距 (Intercept):", intercept[0])
# 绘制数据点和拟合直线
plt.scatter(X, y, color='blue')
plt.plot(X, model.predict(X), color='red', linewidth=3
)
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Simple Linear Regression')
plt.show()模型评估
这是机器学习工作流中至关重要的一环,决定了模型的好坏、是否需要改进以及如何改进
均方误差(MSE)
它衡量的是预测值与真实值之间差异的平方的平均值
是真实值,
是预测值,
残差(单个样本的误差),
是样本数量。每个样本误差的平方求和最后除以样本数量。
均方根误差 (RMSE)
平均平方误差的平方根,即在MSE的基础上,取平方根。
平均绝对误差 (MAE)
平均绝对值误差,为所有样本数据误差的绝对值和
R² (决定系数)
用来表示模型拟合性的分值,值越高表示模型拟合性越好,在训练集中,R^2的取值范围为[0,1]。在测试集(未知数据)中,R^2的取值范围为[-∞,1]。
步骤
1.获取数据集
2.指定特征列和目标列
3.划分数据集:训练集和测试集
4.模型的建立
5.模型的评估
导包
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression #线性回归的包
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 划分数据集的包
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris #鸢尾花的包如果没有需要安装一下这些包
打印出来看看
python
iris=load_iris()
print(iris)指定特征列和目标列
python
X=iris.data[:,2].reshape(-1, 1) #升维处理
y=iris.data[:,3]
print(X)线性回归+划分数据集
python
line=LinearRegression()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=0)拟合
python
import random
random.seed(4)
nums = [random.randint(1, 100) for i in range(10)]
print(nums)
# todo:拟合
line.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("权重:", line.coef_)
print('截距:', line.intercept_)预测
python
# todo:预测
Y = line.predict(X_test)
print("预测值:", Y)
print('真实值:', y_test)可视化
python
# todo:可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
plt.plot(y_test, label='真实值', color='red', marker='o')
plt.plot(Y, label='预测值', color='yellow', marker='D')
plt.xlabel('预测集序号')
plt.ylabel('数据值')
plt.legend()
plt.show()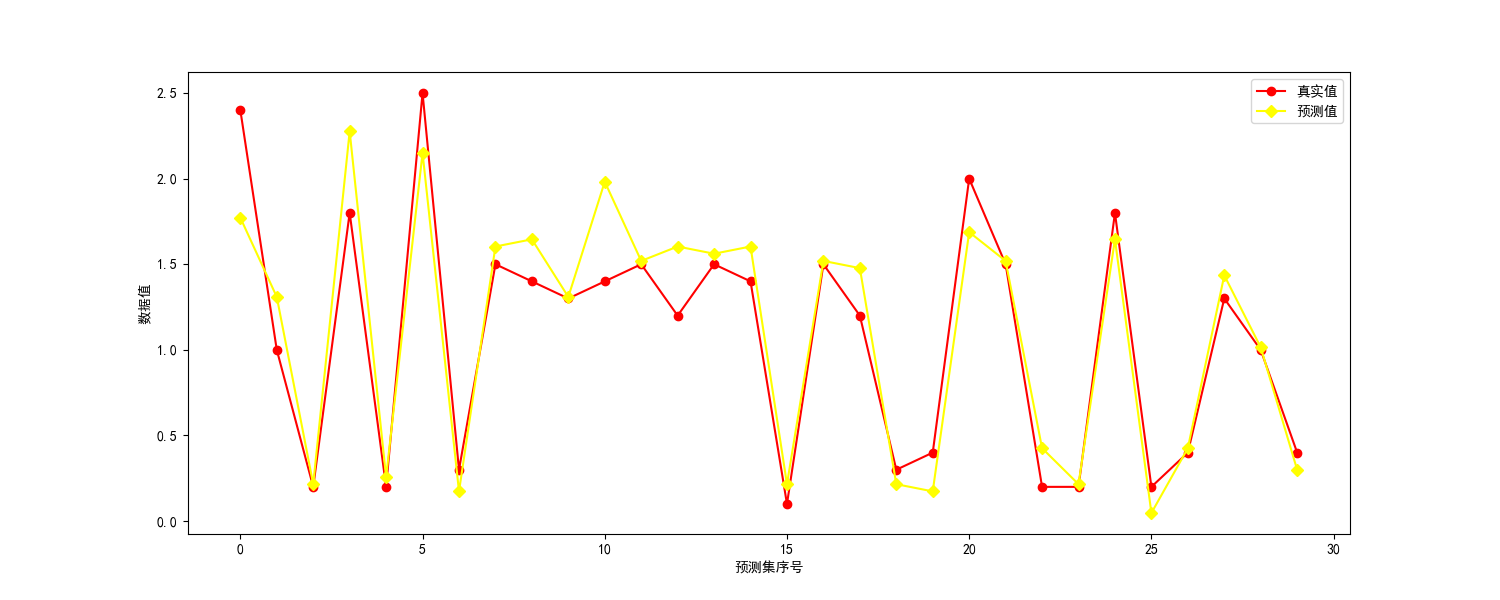
模型评估
python
# todo:模型评估
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error, r2_score
print("均方误差:", mean_squared_error(y_test, Y))
print("平均绝对误差:", mean_absolute_error(y_test, Y))
print("训练集:", r2_score(y_train, line.predict(X_train)))
print("测试集:", r2_score(y_test, Y))
print(line.score(X_train, y_train))
print(line.score(X_test, y_test))多元线性回归
python
# todo:多元线性回归
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('boston_housing_data.csv') # 波斯顿房价数据集
print(df)
python
X = df.drop(columns='MEDV') # todo:方法二:X=data.iloc[:,:-1] :表示选取所有的行 -1表示选取除了最后一列之外的所有列
y = df['MEDV']
print(X)
print(y)空值后面报错之后在处理
python
print(df.isnull().sum())
print(df['MEDV'].fillna(0, inplace=True))
print(df.isnull().sum())最后预测
python
# todo:多元线性回归
line1 = LinearRegression()
# todo:3.划分数据集:训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
# todo:拟合
line1.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("权重:", line1.coef_)
print('截距:', line1.intercept_)
# todo:预测
Y = line1.predict(X_test)
print("预测值:", Y)
print('真实值:', y_test)完整代码
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 线性回归的包
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 划分数据集的包
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris # 鸢尾花的包
import pandas as pd
iris = load_iris()
# print(iris)
X = iris.data[:, 2].reshape(-1, 1) # 升维处理
y = iris.data[:, 3]
# print(X)
# todo:线性回归
line = LinearRegression()
# todo:3.划分数据集:训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
random.seed(4)
nums = [random.randint(1, 100) for i in range(10)]
print(nums)
# todo:拟合
line.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("权重:", line.coef_)
print('截距:', line.intercept_)
# todo:预测
Y = line.predict(X_test)
print("预测值:", Y)
print('真实值:', y_test)
# todo:可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
plt.plot(y_test, label='真实值', color='red', marker='o')
plt.plot(Y, label='预测值', color='yellow', marker='D')
plt.xlabel('预测集序号')
plt.ylabel('数据值')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# todo:模型评估
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error, r2_score
print("均方误差:", mean_squared_error(y_test, Y))
print("平均绝对误差:", mean_absolute_error(y_test, Y))
print("训练集:", r2_score(y_train, line.predict(X_train)))
print("测试集:", r2_score(y_test, Y))
print(line.score(X_train, y_train))
print(line.score(X_test, y_test))
# todo:多元线性回归
df = pd.read_csv('boston_housing_data.csv') # 波斯顿房价数据集
print(df)
X = df.drop(columns='MEDV') # todo:方法二:X=data.iloc[:,:-1] :表示选取所有的行 -1表示选取除了最后一列之外的所有列
y = df['MEDV']
print(X)
print(y)
# todo:空值后面报错之后在处理
print(df.isnull().sum())
print(df['MEDV'].fillna(0, inplace=True))
print(df.isnull().sum())
# todo:多元线性回归
line1 = LinearRegression()
# todo:3.划分数据集:训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
# todo:拟合
line1.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("权重:", line1.coef_)
print('截距:', line1.intercept_)
# todo:预测
Y = line1.predict(X_test)
print("预测值:", Y)
print('真实值:', y_test)