HTTP 的工作原理
HTTP 的工作原理主要有以下三个特点
-
HTTP 是以 TCP 方式工作
连接 ---> 请求 ---> 响应 ---> 断开(目前的 HTTP/1.1 支持长久连接)
-
HTTP 是无状态的
客户端要什么来什么,想要多少来多少,服务端不会因为你要过了而不给你
-
HTTP 使用元信息作为标头
主要数据前添加一部分额外信息(元信息)
包含传送的对象属于哪种类型,采用的是哪种编码等等
HTTP 协议的请求类型
GET、POST,用于获取和上传数据
| 请求方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| GET | 请求获取特定的资源,比如请求一个 Web 页面或请求获取一个资源 |
| POST | 请求提交数据进行处理,比如请求上传一个文件 |
| HEAD | 请求获取和 GET 一致的内容,但是不会返回具体内容,只会返回消息头 |
| PUT | 向指定位置上传最新内容 |
| DELETE | 删除指定资源 |
| OPTIONS | 返回服务器针对特定资源支持的 HTTP 请求方法 |
| TRACE | 回显服务端收到的请求 |
| CONNECT | 预留给能够将连接改为管道方式的代理服务器 |
HTTP 协议的响应状态码
状态行中主要内容有:
-
HTTP 版本号
-
3 位数字组成的状态码
-
1xx 消息:请求已被服务端接收,继续处理
-
2xx 成功:请求已成功被服务端理解并接收
-
3xx 重定向:需要后续操作才能完成这一请求
-
4xx 请求错误:请求含有语法错误或者无法被执行
-
5xx 服务器错误:服务端在处理某个正确请求时发生错误
-
HTTP 的常用状态码
| 编号 | 状态码 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | 找到资源,一切正常 |
| 304 | NOT MODIFIED | 资源在上次请求后没有任何修改(常用语缓存机制) |
| 401 | UNAUTHORIZED | 客户端无权访问该资源,通常需要输入用户名和密码 |
| 403 | FORBIDDEN | 客户端未授权,通常是 401 后输入了错误用户名密码 |
| 404 | NOT FOUND | 指定位置不存在申请的资源 |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed | 不支持请求的方法 |
| 501 | Not Implemented | 服务器不能识别请求或者没有实现指定的请求 |
HTTP关键类
cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using UnityEngine;
public class lesson10 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
//HttpWebRequest 类
// 命名空间: System.Net
//HttpWebRequest 是主要用于发送客户端请求的类
// 主要用于:发送 HTTP 客户端请求给服务器,可以进行消息通信、上传、下载等等操作
// 重要方法
//1.Create 创建新的 WebRequest,用于进行 HTTP 相关操作
HttpWebRequest webRequest = HttpWebRequest.Create(new Uri("http://192.168.80.1:8080/")) as HttpWebRequest;
//2.Abort 如果正在进行文件传输,用此方法可以终止传输
webRequest.Abort();
//3.GetRequestStream 获取用于上传的流
Stream stream = webRequest.GetRequestStream();
//4.GetResponse 返回 HTTP 服务器响应
HttpWebResponse response = webRequest.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
//5.Begin/EndGetRequestStream 异步获取用于上传的流
//6.Begin/EndGetResponse 异步获取返回的 HTTP 服务器响应
// 重要成员
//1.Credentials 通信凭证,设置为 NetworkCredential 对象
webRequest.Credentials = new NetworkCredential("xxx","xxx");
//2.PreAuthenticate 是否随请求发送一个身份验证标头,一般需要进行身份验证时需要将其设置为 true
webRequest.PreAuthenticate = true;
//3.Headers 构成标头的名称 / 值对的集合
//webRequest.Headers
//4.ContentLength 发送信息的字节数 上传信息时需要先设置该内容长度
//5.ContentType 在进行 POST 请求时,需要对发送的内容进行内容类型的设置
//6.Method 操作命令设置
// WebRequestMethods.Http 类中的操作命令属性
// Get 获取请求,一般用于获取数据
// Post 提交请求,一般用于上传数据,同时可以获取
//HttpWebResponse 类
// 命名空间: System.Net
// 它主要用于获取服务器反馈信息的类
// 我们可以通过 HttpWebRequest 对象中的 GetResponse () 方法获取
// 当使用完毕时,要使用 Close 释放
// 重要方法:
//1.Close: 释放所有资源
//2.GetResponseStream: 返回从 FTP 服务器下载数据的流
// 重要成员:
//1.ContentLength: 接受到数据的长度
//2.ContentType: 接受数据的类型
//3.StatusCode:HTTP 服务器下发的最新状态码
//4.StatusDescription:HTTP 服务器下发的状态代码的文本
//5.BannerMessage: 登录前建立连接时 HTTP 服务器发送的消息
//6.ExitMessage:HTTP 会话结束时服务器发送的消息
//7.LastModified:HTTP 服务器上的文件的上次修改日期和时间
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}下载数据
cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using UnityEngine;
public class lesson10_1 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
try
{
//检测资源可用性
//利用Head请求类型,获取信息
//1.创建HTTP通讯用连接对象HttpWebRequest对象
HttpWebRequest req = HttpWebRequest.Create(new Uri("http://192.168.80.1:8080/httpServer/图片1.png")) as HttpWebRequest;
//2.设置请求类型 或 其他相关参数
req.Method = WebRequestMethods.Http.Head;
req.Timeout = 2000;
//3.发送请求,获取响应结果HttpWebReponse对象
HttpWebResponse res = req.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
if (res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
print("文件存在可用");
else
print("文件不可用" + res.StatusCode);
}
catch (WebException ex)
{
print(ex.Message);
}
try
{
//下载资源
HttpWebRequest req = HttpWebRequest.Create(new Uri("http://192.168.80.1:8080/httpServer/图片1.png")) as HttpWebRequest;
//利用Get请求类型,获取信息
req.Method = WebRequestMethods.Http.Get;
req.Timeout = 3000;
//发送请求,获取响应结果HttpWebReponse对象
HttpWebResponse res = req.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
//获取响应数据流,写入本地路径
if (res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
print(Application.persistentDataPath);
using (FileStream fs = File.Create(Application.persistentDataPath + "/xxx.png"))
{
Stream stream = res.GetResponseStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
int Length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
while (Length != 0)
{
fs.Write(buffer, 0, Length);
Length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
}
stream.Close();
fs.Close();
res.Close();
}
print("下载完成");
}
else
{
print("下载失败");
}
}
catch(WebException ex)
{
print(ex.Message);
}
//Get 请求类型携带额外信息
// 我们在进行 HTTP 通信时,可以在地址后面加一些额外参数传递给服务端
// 一般在和短连接游戏服务器通讯时,需要携带额外信息
// 举例:
//http://www.aspxfans.com:8080/news/child/index.asp?boardID=5&ID=24618&page=1
// 这个链接可以分成几部分
//1. 协议部分:取决于服务器端使用的哪种协议
//http:// --- 普通的 http 超文本传输协议
//https:// --- 加密的超文本传输协议
//2. 域名部分:
//www.aspxfans.com
// 也可以填写服务器的公网 IP 地址
//3. 端口部分:
//8080
// 可以不写,如果不写默认为 80
//4. 虚拟目录部分:
//news/child/
// 域名后的 / 开始,到最后一个 / 之前的部分
//5. 文件名部分:
//index.asp
//? 之前的最后一个 / 后的部分
//6. 参数部分:
//boardID=5&ID=24618&page=1
//? 之后的部分就是参数部分,多个参数 & 分隔开
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}单例模式封装方法实现下载资源
cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using UnityEditor.PackageManager;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Events;
public class HttpMgr
{
private static HttpMgr instance = new HttpMgr();
public static HttpMgr Instance => instance;
private string HTTP_PATH = "http://192.168.80.1:8080/httpServer/";
/// <summary>
/// 下载指定文件到本地
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName"></param>
/// <param name="localPath"></param>
/// <param name="action"></param>
public async void DownLoadFile(string fileName, string localPath, UnityAction<HttpStatusCode> action)
{
HttpStatusCode statusCode = 0;
await Task.Run(() => {
try
{
//创建HTTP连接对象
HttpWebRequest request = HttpWebRequest.Create(HTTP_PATH + fileName) as HttpWebRequest;
request.Method = WebRequestMethods.Http.Head;
request.Timeout = 2000;
HttpWebResponse response = request.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
request = HttpWebRequest.Create(HTTP_PATH + fileName) as HttpWebRequest;
request.Method = WebRequestMethods.Http.Get;
request.Timeout = 2000;
response = request.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
using (FileStream fs = File.Create(localPath))
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
Stream stream = response.GetResponseStream();
int length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
while (length != 0)
{
fs.Write(buffer, 0, length);
length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
}
Debug.Log("下载完成");
statusCode = response.StatusCode;
stream.Close();
fs.Close();
response.Close();
}
}
else
{
statusCode = response.StatusCode;
}
}
else
{
statusCode = response.StatusCode;
}
response.Close();
}
catch (WebException e)
{
statusCode = HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError;
Debug.LogException(e);
}
});
action?.Invoke(statusCode);
}
}Post学习前的准备
cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Text;
using UnityEngine;
public class lesson10_2 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
//Get 和 Post 的区别
// 我们上节课学习的下载数据,主要使用的就是 Get 请求类型
// 我们在上传数据时将会使用 Post 请求类型
// 那么这两个请求类型他们的主要区别是什么呢?
//1. 主要用途
// Get --- 一般从指定的资源请求数据,主要用于获取数据
// Post --- 一般向指定的资源提交想要被处理的数据,主要用于上传数据
//2. 相同点
// Get 和 Post 都可以传递一些额外的参数数据给服务端
//3. 不同点
// 3-1: 在传递参数时,Post 相对 Get 更加的安全,因为 Post 看不到参数
// Get 传递的参数都包含在连接中(URL 资源定位地址),是暴露式的
// Post 传递的参数放在请求数据中,不会出现在 URL 中,是隐藏式的
// 3-2:Get 在传递数据时有大小的限制,因为它主要是在连接中拼接参数,而 URL 的长度是有限制的(最大长度一般为 2048 个字符)
// Post 在传递数据时没有限制
// 3-3: 在浏览器中 Get 请求能被缓存,Post 不能缓存
// 3-4: 传输次数可能不同
// Get: 建立连接→请求行、请求头、请求数据一次传输→获取响应→断开连接
// Post: 建立连接→传输可能分两次→请求行,请求头第一次传输→请求数据第二次传输→获取响应→断开连接
HttpWebRequest request = HttpWebRequest.Create(new Uri("http://192.168.80.1:8080/httpServer/")) as HttpWebRequest;
request.Method = WebRequestMethods.Http.Post;
request.Timeout = 2000;
//设置上传的内容的类型
request.ContentType = "application/x-ww-form-urlencoded";
//上传数据
string str = "Name=xiaohei&ID=1";
byte[] buffer = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(str);
request.ContentLength = buffer.Length;
Stream stream = request.GetRequestStream();
stream.Write(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
stream.Close();
HttpWebResponse response = request.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
print(response.StatusCode);
//ContentType 的常用类型
//ContentType 的构成:
// 内容类型;charset = 编码格式;boundary = 边界字符串
//text/html;charset=utf-8;boundary = 自定义字符串
// 其中内容类型有:
// 文本类型 text:
//text/plain 没有特定子类型就是它(重要)
//text/html
//text/css
//text/javascript
// 图片类型 image:
//image/gif
//image/png
//image/jpeg
//image/bm
//image/webp
//image/x-icon
//image/vnd.microsoft.icon
// 音频类型 audio:
//audio/midi
//audio/mpeg
//audio/webm
//audio/ogg
//audio/wav
// 视频类型 video:
//video/webm
//video/ogg
// 二进制类型 application:
//application/octet-stream 没有特定子类型就是它(重要)
//application/x-www-form-urlencoded 传递参数时使用键值对形式(重要)
//application/pkcs12
//application/xhtml+xml
//application/xml
//application/pdf
//application/vnd.mspowerpoint
// 复合内容 multipart:
//multipart/form-data 复合内容,有多种内容组合(重要)
//multipart/byteranges 特殊的复合文件
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}上传数据
cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Text;
using UnityEngine;
public class lesson10_3 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
//上传文件到 HTTP 资源服务器需要遵守的规则
// 上传文件时内容的必备规则
// 1:ContentType = "multipart/form-data; boundary = 边界字符串";
// 2: 上传的数据必须按照格式写入流中
//-- 边界字符串
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="字段名字,之后写入的文件二进制数据和该字段名对应";filename="传到服务器上使用的文件名"
// Content-Type:application/octet-stream (由于我们传二进制文件 所以这里使用二进制)
//空一行
// (这里直接写入传入的内容)
//-- 边界字符串 --
// 3: 保证服务器允许上传
// 4: 写入流前需要先设置 ContentLength 内容长度
//1. 创建 HttpWebRequest 对象
HttpWebRequest request = HttpWebRequest.Create(new Uri("http://192.168.80.1:8080/httpServer/")) as HttpWebRequest;
//2. 相关设置 (请求类型,内容类型,超时,身份验证等)
request.Method = WebRequestMethods.Http.Post;
request.ContentType = "multipart/form-data;boundary=XXX";
request.Timeout = 50000;
request.Credentials = new NetworkCredential("liyuhan","liyuhan");
request.PreAuthenticate = true; //先验证身份再上传数据
//3. 按格式拼接字符串并且转为字节数组之后用于上传
//3-1. 文件数据前的头部信息
//-- 边界字符串
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="字段名字,之后写入的文件二进制数据和该字段名对应";filename="传到服务器上使用的文件名"
// Content-Type:application/octet-stream (由于我们传二进制文件 所以这里使用二进制)
string head = "--XXX\r\n" +
"Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\"file\";filename=\"Http上传的文件2.png\"\r\n" +
"Content-Type:application/octet-stream\r\n\r\n";
byte[] headBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(head);
//3-2. 结束的边界信息
//-- 边界字符串 --
byte[] endBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("\r\n--XXX--\r\n");
//4. 写入上传流
using (FileStream fs = File.OpenRead(Application.streamingAssetsPath+ "/HttpTest.png"))
{
//4-1. 设置上传长度
request.ContentLength = headBytes.Length + fs.Length +endBytes.Length;
Stream stream = request.GetRequestStream();
//4-2. 先写入前部分头部信息
stream.Write(headBytes, 0, headBytes.Length);
//4-3. 再写入文件数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
int length = fs.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
while (length != 0)
{
stream.Write(buffer, 0, length);
length = fs.Read(buffer, 0,buffer.Length);
}
//4-4. 在写入结束的边界信息
stream.Write(endBytes, 0, endBytes.Length);
stream.Close();
fs.Close();
}
HttpWebResponse response = request.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
print("上传成功");
}
else
{
print("上传失败");
}
response.Close();
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
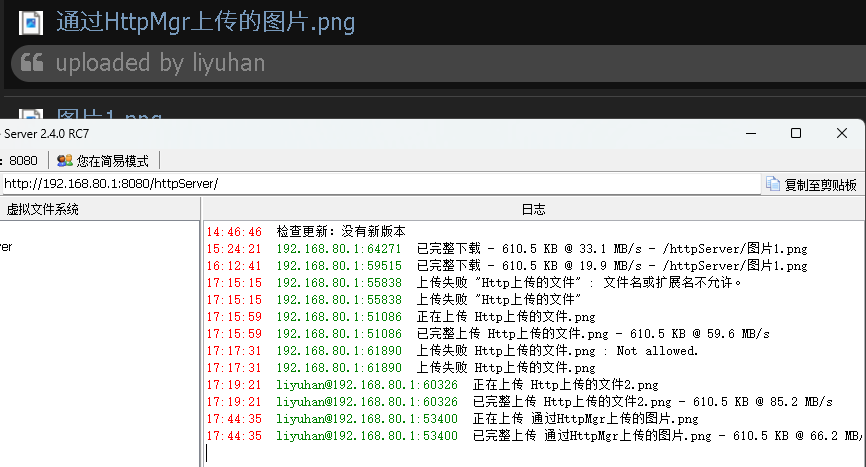
}效果:
单例模式封装类添加函数
cs
/// <summary>
/// 上传文件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName">服务器上创建文件的名称</param>
/// <param name="localPath">本地文件路径</param>
/// <param name="action">上传完成后执行的函数</param>
public async void UpLoadFile(string fileName, string localPath, UnityAction<HttpStatusCode> action)
{
HttpStatusCode statusCode = 0;
await Task.Run(() => {
try
{
HttpWebRequest request = HttpWebRequest.Create(new Uri(HTTP_PATH)) as HttpWebRequest;
request.Method = WebRequestMethods.Http.Post;
request.Timeout = 50000;
request.ContentType = "multipart/form-data;boundary=XXX";
request.Credentials = new NetworkCredential(USER_NAME,PASSWORD);
request.PreAuthenticate = true;
string head = "--XXX\r\n" +
"Content-Disposition:form-data;name=\"file\";filename=\"" + fileName + "\"\r\n" +
"Content-Type:application/octet-stream\r\n\r\n";
byte[] headBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(head);
string end = "\r\n--XXX--\r\n";
byte[] endBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(end);
using (FileStream fs = File.OpenRead(localPath))
{
request.ContentLength = headBytes.Length + fs.Length + endBytes.Length;
Stream stream = request.GetRequestStream();
stream.Write(headBytes, 0, headBytes.Length);
byte[] bytes = new byte[2048];
int length = fs.Read(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
while (length != 0)
{
stream.Write(bytes, 0, length);
length = fs.Read(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
}
stream.Write(endBytes, 0, endBytes.Length);
stream.Close();
fs.Close();
}
HttpWebResponse response = request.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse ;
if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
statusCode = response.StatusCode;
Debug.Log("上传成功");
}
else
{
statusCode = response.StatusCode;
Debug.Log("上传失败");
}
response.Close();
}
catch (WebException ex)
{
statusCode = HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError;
Debug.Log("上传失败"+ex.Message);
}
});
action?.Invoke(statusCode);
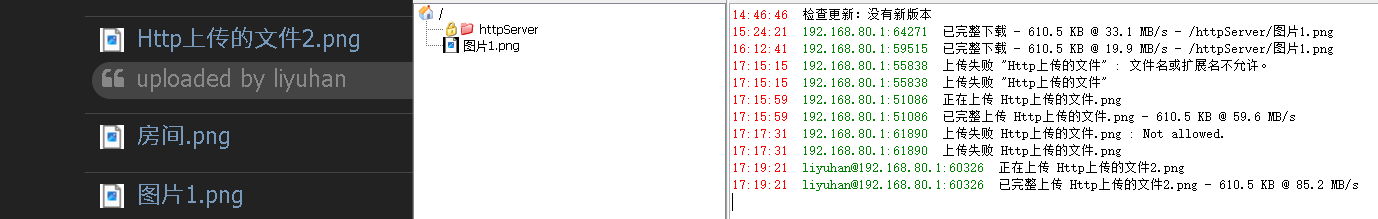
}效果: