这个模块相当于我们cup,负责处理事件和任务,接下来的connection相当于操作系统
文章目录
目录
概要
AI定义
Connection是 muduo 网络库的核心类 ,封装一次 TCP 连接的全生命周期及数据传输逻辑,主要承担以下功能:
连接全生命周期管理
- 建立连接 :由
TcpServer在subLoop(子事件循环)中构造,完成后向EPollPoller注册感兴趣的 IO 事件(如读、写),并维护连接状态。 - 断开连接 :通过
shutdown分两步关闭(先关 "写" 端、保证数据发送完整,再关 "读" 端),同时清理资源(如取消事件注册、释放缓冲区)。 - 资源生命周期 :通过
shared_ptr管理自身生命周期,避免回调时对象提前析构(配合Channel::tie延长生命期)。
数据传输与处理
- 接收数据 :当底层 socket 有可读事件时,
Channel触发回调,TcpConnection的handleRead将数据读入Buffer(inputBuffer_),再调用应用层注册的MessageCallback处理数据。 - 发送数据 :应用层调用
send/sendInLoop接口,数据先缓存到Buffer(outputBuffer_);当 socket 可写时,Channel触发回调,TcpConnection将缓冲区数据通过 socket 发送,发送完成后调用writeCompleteCallback通知应用层。
- 连接状态通知 :当连接状态变化(如建立、断开)时,触发应用层注册的
connectionCallback,让业务逻辑能感知连接变化(如执行重连、关闭会话等操作)。
个人理解
这个是AI定义的Connection的作用,在我的理解中,他和Channel差不多,就是一个桥梁,负责将套接字中的数据读取出来放在自己缓冲区中,等着上层来拿,上层想要发送的数据放在它着,让后通知socket来吧数据读走;相当于一个减速带吧
它和Eventloop的关系是Eventloop负责执行事件和任务,而它不需要主动去读,让loop去做这些事
整体架构流程
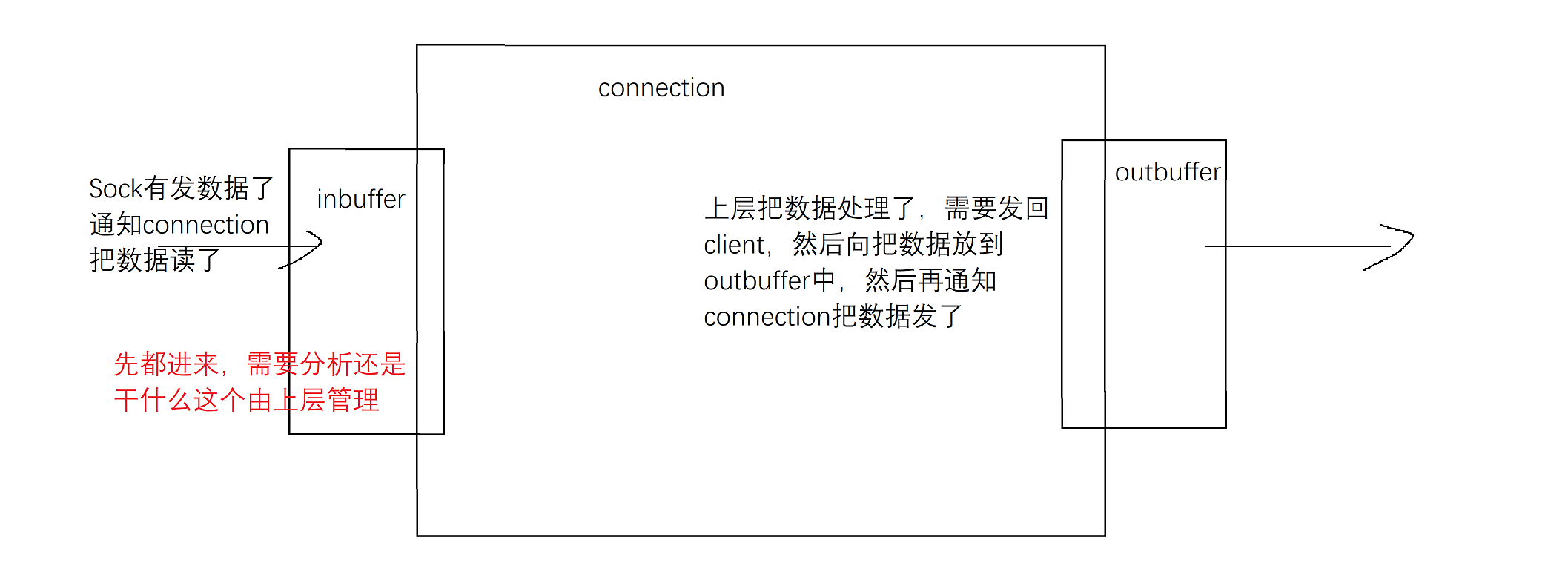
这就是connection大概作用
接下来定义connection的成员变量
成员变量
既然是缓冲区就需要存储,用Buffer
既然需要收发数据,就用Socket,
既然有了Socket那么就有文件描述,那么就需要一个Channel来管理文件描述符
还需要事件处理用到了EventLoop
cpp
typedef enum
{
DISCONECTED = 1, // 连接关闭
CONNECTING, // 待处理
CONNECTED, // 可以通信
DISCONNECTING // 待关闭
} ConnStatu;
class Connection;
using PtrConnection = std::shared_ptr<Connection>;
class Connection : public std::enable_shared_from_this<Connection>
{
private:
Buffer _in_buffer;
Buffer _out_buffer;
int _sockfd;
long int _conn_id;
Socket _sock;
EventLoop *_loop;
Channel _sock_channel;
bool _enable_inactive_release;
ConnStatu _statu;
Any _context;
using MessageCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &, Buffer *)>;
using ConncetCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using ClosedCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using AnyEventCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
MessageCallback _message_callback;
ConncetCallback _connect_callback;
ClosedCallback _close_callback;
AnyEventCallback _event_callback;
/*组件内的连接关闭回调--组件内设置的,因为服务器组件内会把所有的连接管理起来,一旦某个连接要关闭*/
/*就应该从管理的地方移除掉自己的信息*/
ClosedCallback _server_closed_callback;
};
cpp
class Connection : public std::enable_shared_from_this<Connection>
这个东西大家可能有点懵逼,这东西就是继承enable_from_this的类,让Connection为Shread指针管理的类型,具有生命周期,这样安全,避免内存错误。
而我们的枚举也是为了数据安全,如果连接断开了,我们读什么发什么就会出现错误。
而这些回调指针就是上层的一些函数需要我们在这个类里面调用,就是上层需要发送数据和事件吧,我们不知道是什么数据,也不知道需要怎么发,次发多少,然么我就可以把上层的函数拿到这里面,只要发送缓冲区里面有数据,那么就发
那么为什么不自己做,然后让上层来设置一个参数,一次性发送多少,读多少呢?

既然这样,你要什么要怎么做,自己设置,这就是回调函数
成员函数
先看构造函数,析构函数
cpp
Connection(EventLoop *loop, uint64_t conn_id, int fd) : _sockfd(fd),
_sock(fd),
_loop(loop),
_conn_id(conn_id),
_sock_channel(_sockfd, _loop),
_statu(CONNECTING),
_enable_inactive_release(false)
{
_sock_channel.SetReadCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandRecv, this));
_sock_channel.SetWriteCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandSend, this));
_sock_channel.SetCloseCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandClose, this));
_sock_channel.SetErrorCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandError, this));
_sock_channel.SetEventCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandEvent, this));
}
~Connection()
{
DBG_LOG("RELEASE CONNECTION:%p", this);
}这里的绑定设置回调就是poller阻塞完了需要调用的函数,比如服务器发数据来了,就让触发了读事件,那么直接去把数据读到缓冲区就可以了,其他几个同理
私有函数
cpp
void HandRecv()
{
DBG_LOG("HandRecv");
char buf[65536] = {0};
ssize_t ret = _sock.NonBlockRecv(buf, sizeof(buf));
if (ret < 0)
{
// 出错了,不能直接关闭连接,需要看看还有没有数据没有发送完
return ShutdownInLoop();
}
// 将都上来的数据放到in_buffer里面
_in_buffer.WriteAndMove(buf, ret);
// 如果读到了数据就要将读到事件派发下去
if (_in_buffer.ReadableSize() > 0)
{
//调用上层方法,下面会有解释
return _message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
}
void HandSend()
{
// 将out_buff的数据发送到sock中
ssize_t ret = _sock.NonBlockWrite(_out_buffer.ReaderPosition(), _out_buffer.ReadableSize());
if (ret < 0)
{
if (_out_buffer.ReadableSize() > 0)
{
_message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
return Release();
}
_out_buffer.MoveReadableOffset(ret);
if (_out_buffer.ReadableSize() == 0)
{
// 数据发送完了,把sock的写功能给关闭了
_sock_channel.DisableWrite();
if (_statu == DISCONNECTING)
return Release();
}
return;
}
void HandClose()
{
//如果有数据要发送,就先把数据发了再和client断链
if (_out_buffer.ReadableSize() > 0)
{
_message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
return Release();
}
void HandEvent()
{
if (_enable_inactive_release == true)
{
_loop->TimerRefresh(_conn_id);
}
if (_event_callback)
_event_callback(shared_from_this());
}
void HandError()
{
return HandClose();
}
// 连接获取之后,所处的状态下要进行各种设置(启动读监控,调用回调函数)
void EstablishedInLoop()
{
// 1. 修改连接状态; 2. 启动读事件监控; 3. 调用回调函数
assert(_statu == CONNECTING); // 当前的状态必须一定是上层的半连接状态
_statu = CONNECTED; // 当前函数执行完毕,则连接进入已完成连接状态
_sock_channel.EnableRead();
if (_connect_callback)
{
_connect_callback(shared_from_this());
}
}
// 这个接口才是实际的释放接口
void ReleaseInLoop()
{
INF_LOG("ReleaseInLoop");
_statu = DISCONECTED;
_sock_channel.MoveData();
_sock.Close();
// 4. 如果当前定时器队列中还有定时销毁任务,则取消任务
if (_loop->HasTimer(_conn_id))
{
_loop->TimerCancel(_conn_id);
}
// 5. 调用关闭回调函数,避免先移除服务器管理的连接信息导致Connection被释放,
if (_close_callback)
_close_callback(shared_from_this());
// 移除服务器内部管理的连接信息
if (_server_closed_callback)
_server_closed_callback(shared_from_this());
}
void SendInLoop(Buffer &buf)
{
if (_statu == DISCONECTED)
return;
// 向外发数据,先把数据加载到发出缓冲区中
_out_buffer.WriteBufferAndPush(buf);
if (_sock_channel.Writable() == false)
{
_sock_channel.EnableWrite();
}
}
void ShutdownInLoop()
{
_statu = DISCONNECTING;
if (_in_buffer.ReadableSize() > 0)
{
if (_message_callback)
_message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
if (_out_buffer.ReadableSize() > 0)
{
if (_sock_channel.Writable() == false)
_sock_channel.EnableWrite();
}
if (_out_buffer.ReadableSize() == 0)
{
Release();
}
}
void EnableInactiveReleaseInLoop(int sec)
{
_enable_inactive_release = true;
if (_loop->HasTimer(_conn_id))
_loop->TimerRefresh(_conn_id);
else
{
_loop->AddTimer(_conn_id, sec, std::bind(&Connection::Release, this));
}
}
void CancelInactiveReleaseInLoop()
{
_enable_inactive_release == true;
if (_loop->HasTimer(_conn_id))
{
_loop->TimerCancel(_conn_id);
}
}
void UpgradeInLoop(const Any &context,
const ConncetCallback &conn,
const MessageCallback &msg,
const ClosedCallback &closed,
const AnyEventCallback &event)
{
_context = context;
_connect_callback = conn;
_message_callback = msg;
_close_callback = closed;
_event_callback = event;
}数据读上来了,然后需要干什么我不知道,这个就要上层自己决定了
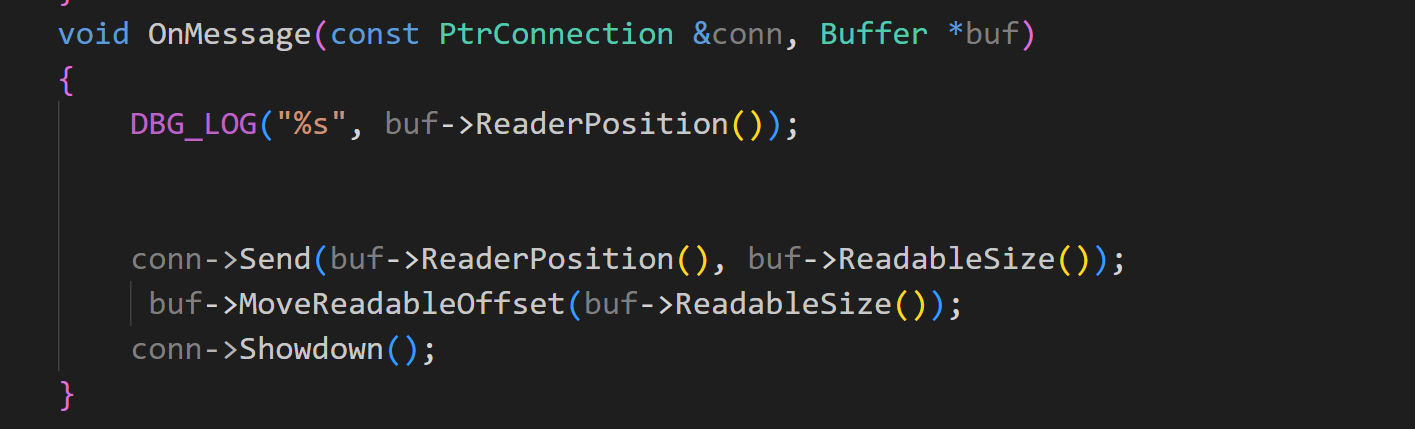
其他的也没有什么要解释的了,看代码就可以理解
公有成员(向外提供接口)
cpp
public:
Connection(EventLoop *loop, uint64_t conn_id, int fd) : _sockfd(fd),
_sock(fd),
_loop(loop),
_conn_id(conn_id),
_sock_channel(_sockfd, _loop),
_statu(CONNECTING),
_enable_inactive_release(false)
{
_sock_channel.SetReadCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandRecv, this));
_sock_channel.SetWriteCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandSend, this));
_sock_channel.SetCloseCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandClose, this));
_sock_channel.SetErrorCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandError, this));
_sock_channel.SetEventCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandEvent, this));
}
~Connection()
{
DBG_LOG("RELEASE CONNECTION:%p", this);
}
int Fd()
{
return _sockfd;
}
uint64_t Id()
{
return _conn_id;
}
// 是否处于CONNECTED状态
bool Connected()
{
return _statu == CONNECTED;
}
void SetContext(const Any &context)
{
_context = context;
}
// 获取上下文,返回的是指针
Any *GetContext()
{
return &_context;
}
void SetMessageCallback(const MessageCallback &cb)
{
_message_callback = cb;
}
void SetConncetCallback(const ConncetCallback &cb)
{
_connect_callback = cb;
}
void SetClosedCallback(const ClosedCallback &cb)
{
_close_callback = cb;
}
void SetAnyEventCallback(const AnyEventCallback &cb)
{
_event_callback = cb;
}
void Established()
{
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::EstablishedInLoop, this));
}
void Send(const char *data, ssize_t len)
{
Buffer buf;
buf.WriteAndMove((void *)data, len);
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::SendInLoop, this, buf));
}
void Release()
{
INF_LOG("Release");
_loop->QueueInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::ReleaseInLoop, this));
}
void Showdown()
{
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::ShutdownInLoop, this));
}
// 启动非活跃销毁,并定义多长时间无通信就是非活跃,添加定时任务
void EnableInactiveRelease(int sec)
{
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::EnableInactiveReleaseInLoop, this, sec));
}
// 取消非活跃销毁
void CancelInactiveRelease()
{
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::CancelInactiveReleaseInLoop, this));
}
// 切换协议---重置上下文以及阶段性回调处理函数 -- 而是这个接口必须在EventLoop线程中立即执行
// 防备新的事件触发后,处理的时候,切换任务还没有被执行--会导致数据使用原协议处理了。
void Upgrade(const Any &context, const ConncetCallback &conn, const MessageCallback &msg,
const ClosedCallback &closed, const AnyEventCallback &event)
{
_loop->AssertInLoop();
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::UpgradeInLoop, this, context, conn, msg, closed, event));
}测试代码
cpp
#include <time.h>
#include "../EventLoop.hpp"
#include"../Socket.hpp"
using namespace std;
void Close(Channel *ch);
void Read(Channel *ch)
{
int fd = ch->Fd();
INF_LOG( "触发了读事件sock: %d " , fd );
char buffer[1024] = {0};
int ret = recv(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0);
if (ret < 0)
{
Close(ch);
return;
}
std::cout << buffer << std::endl;
ch->EnableWrite();
}
void Write(Channel *ch)
{
int fd = ch->Fd();
cout << "触发了写事件sock: " << fd << endl;
char buffer[1024] = "天气不错";
int ret = send(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0);
ch->DisableWrite();
if (ret < 0)
{
Close(ch);
return;
}
}
void Close(Channel *ch)
{
INF_LOG( "触发了关闭事件,由于长时间未得到连接" );
ch->Remove();
delete ch;
}
void Error(Channel *ch)
{
Close(ch);
}
void Event(EventLoop *loop, Channel *channel, uint64_t timerid)
{
int fd = channel->Fd();
INF_LOG( "fd: %d 触发了event回调函数",fd);
loop->TimerRefresh(timerid);
}
void Accept(EventLoop *loop, Channel *channel)
{
cout << "触发了listsock的读事件" << endl;
int fd = channel->Fd();
int newfd = accept(fd, nullptr, nullptr);
cout << "从fd: " << fd << " 读新连接newfd: " << newfd << endl;
if (newfd < 0)
{
cout << "连接出错" << endl;
return;
}
uint64_t timerid = rand() % 10000;
// v2修改了bind的绑定错误,导致无法读取调用事件出错
Channel *newchannel = new Channel(loop, newfd);
newchannel->SetReadCallback(std::bind(Read, newchannel));
newchannel->SetWriteCallback(std::bind(Write, newchannel));
newchannel->SetCloseCallback(std::bind(Close, newchannel));
newchannel->SetErrorCallback(std::bind(Error, newchannel));
newchannel->SetEventCallback(std::bind(Event, loop, newchannel, timerid));
// 非活跃连接超时任务
loop->TimerAdd(timerid, 10, std::bind(Close, newchannel));
newchannel->EnableRead();
}
int main()
{
// 是这个是把
// fd3 loop fd4 epoll fd5 timerfd fd6 sock
EventLoop loop; // 每一个EvenLoop绑定一个线程
cout << "创建了loop" << endl;
// EvenLoop() : _thread_id(std::this_thread::get_id()),
// _event_fd(CreateEventFd()),
// _event_channel(new Channel(this, _event_fd)),
// _timer_weel(this)
// 创建了一个eventfd事件通知机制,channel(管道)事件集合,负责从下放网络层获取数据,交付给上端
// timer_weel时间轮,创建定时器,1秒触发一次,剩下的看不出来,先向下看代码
srand(time(nullptr));
// 创建服务器
Socket list_sock; // 创建套接字
list_sock.CreateServer(8080);
// 为list_sock第一channel
Channel channel(&loop, list_sock.Fd()); // 没有管理事件
// 把list_sock的事件、fd放到channel中,channel进行封装
// 由于list_sock主要任务是读fd中连接的fd,从而获取连接,那么写一个函数,专门负责连接
// 有了函数,为了效率我们不能主动去调用它,这样会浪费io,我们将他的事件通过epoll触发的方式调用
channel.SetReadCallback(std::bind(Accept, &loop, &channel)); // 设置事件
// 把它的读事件打开,打开不是只在channel中打开,channel只负责记录它是什么事件,不负责监控,要想监控它的事件就哟啊让poller知道
// 只负责打开监控,但是不负责监控
channel.EnableRead(); // 通过epoll_ctl将fd添加到epfd,op负责处理是添加还是修改,event负责监听什么事件参数
// 创建客服端
while (true)
{
// 负责监控
loop.Start();
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}小结
connection就是负责收发数据,连接的管理。再往上写写大家就明白了
