旅行商问题从实现到测试
共四篇博客分别讲解,四篇的内容分别是
1.TSP 问题中的点与路径核心类
2.TSP 的两种贪心启发式算法实现(最近邻算法和最近插入算法)
3.TSP 项目的 "时间统计与属性注入" 工具
4.TSP 项目的测试验证体系
在旅行商问题(TSP)中,由于 "找到最优解" 的复杂度极高,实际应用中常使用启发式算法(贪心策略)快速得到近似解。heuristics.py 文件实现了两种核心的贪心算法:最近邻点法和最近插入法。
heuristics.py 完整代码在文章末尾
一、算法前置知识:装饰器
@display_time
在看算法之前,先注意每个算法函数上方的 @display_time 装饰器 ------ 它来自 decorator.py,核心作用是:
- 统计算法的运行时间;
- 自动为输出的
Route对象注入run_time(运行时间)和algo_name(算法名)属性; - 打印算法的运行结果(运行时间、路径总距离)。
装饰器的存在让算法代码更简洁,无需手动处理时间统计和属性注入,后续在 Lab_test.py 中调用算法时,能直接获取时间和路径信息。
二、最近邻点法(nearestNeighbor)
1. 算法核心思想
从指定的起点出发,每次选择 "当前点的最近未访问点" 作为下一个点,直到所有点都被访问,最后回到起点形成闭合路径。
贪心逻辑 :每一步只关注 "当前最优"(最近的点),不考虑后续步骤的影响,因此不一定能得到全局最优解,但计算速度快。
2. 代码实现与解析
python
@display_time
def nearestNeighbor(pointsL, startPoint):
"""最近邻算法:从起点出发,每次选择最近未访问点(案例图2逻辑)"""
# 第一步:输入验证(确保参数符合要求,避免后续错误)
if not isinstance(startPoint, Point):
raise TypeError("startPoint must be a Point instance")
if startPoint not in pointsL:
raise ValueError("startPoint must be in pointsL")
# 第二步:初始化"未访问点列表"和"路径列表"
unvisited = pointsL.copy() # 复制所有点,作为未访问集合
unvisited.remove(startPoint) # 移除起点(起点已访问)
path = [startPoint] # 路径从起点开始
current = startPoint # 当前所在的点(初始为起点)
# 第三步:核心循环------反复选择最近未访问点,直到所有点被访问
while unvisited: # 当还有未访问点时
# 找到未访问点中距离当前点最近的点(用min+lambda,以距离为排序依据)
closest = min(unvisited, key=lambda p: current.dist_to_point(p))
# 将最近点加入路径
path.append(closest)
# 从"未访问列表"中移除该点(标记为已访问)
unvisited.remove(closest)
# 更新当前点为刚加入的最近点
current = closest
# 第四步:闭合路径------最后回到起点
path.append(startPoint)
# 第五步:返回路径(封装成Route对象,符合输出要求)
return Route(path)3. 关键步骤拆解
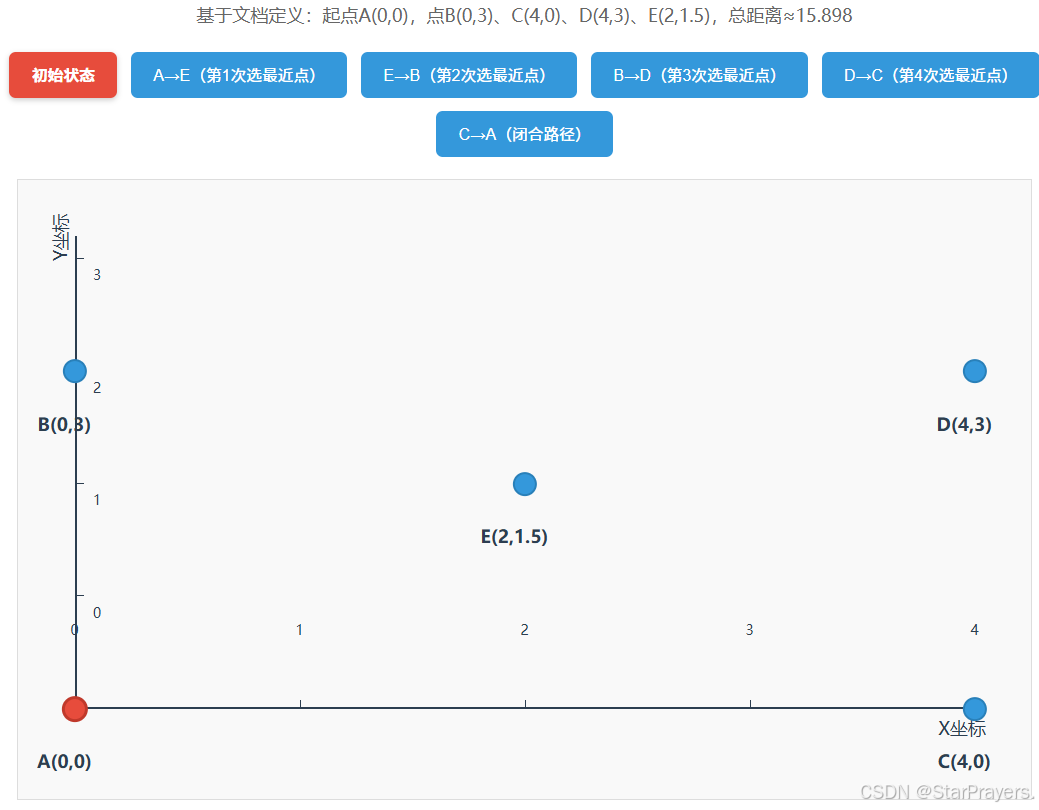
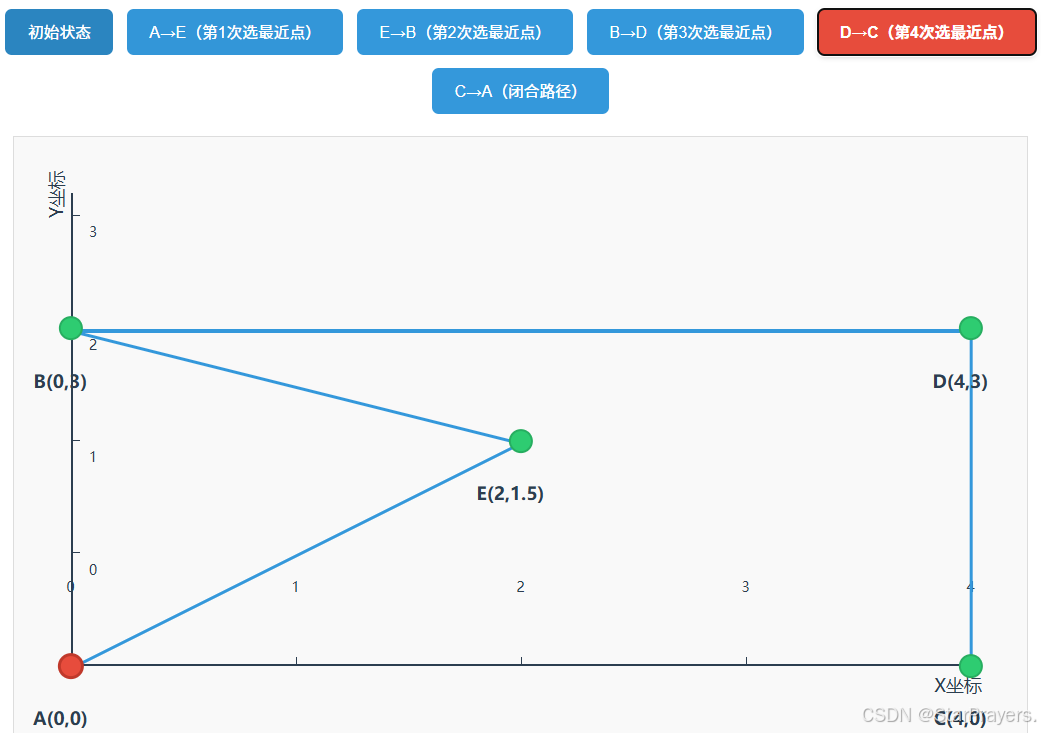
以 "5 点用例"(A (0,0)、B (0,3)、C (4,0)、D (4,3)、E (2,1.5))、起点为 A 为例,手动走一遍流程:
- 初始化:
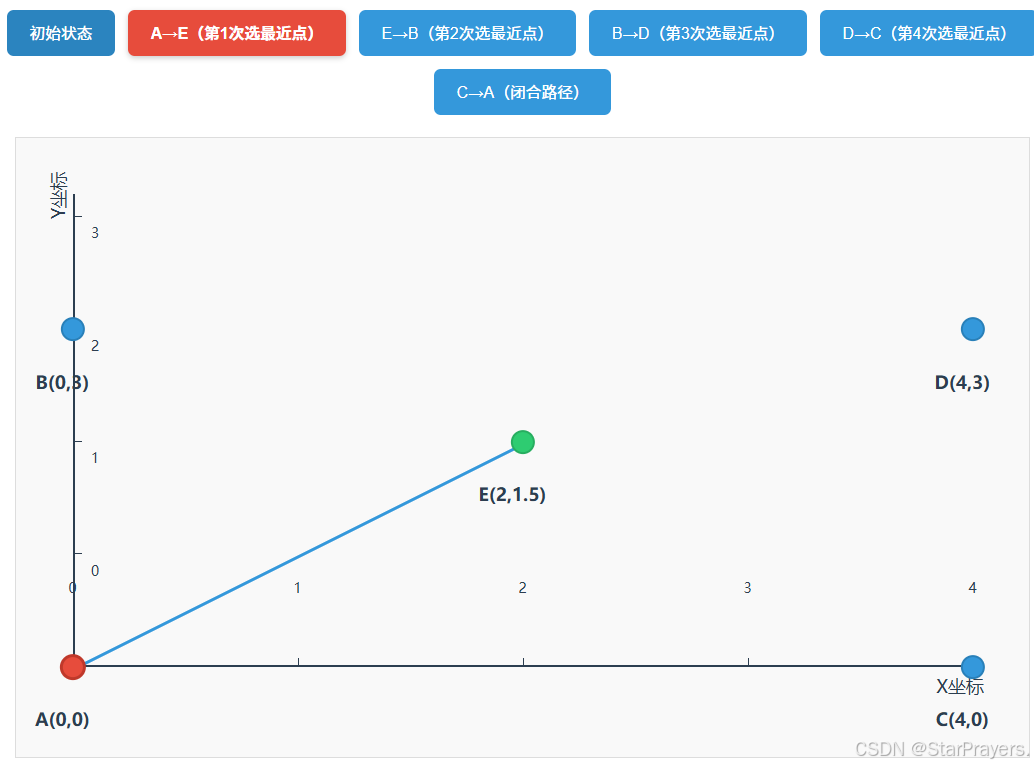
unvisited = [B,C,D,E],path = [A],current = A; - 第一次循环:A 的最近未访问点是 E(距离≈2.5),
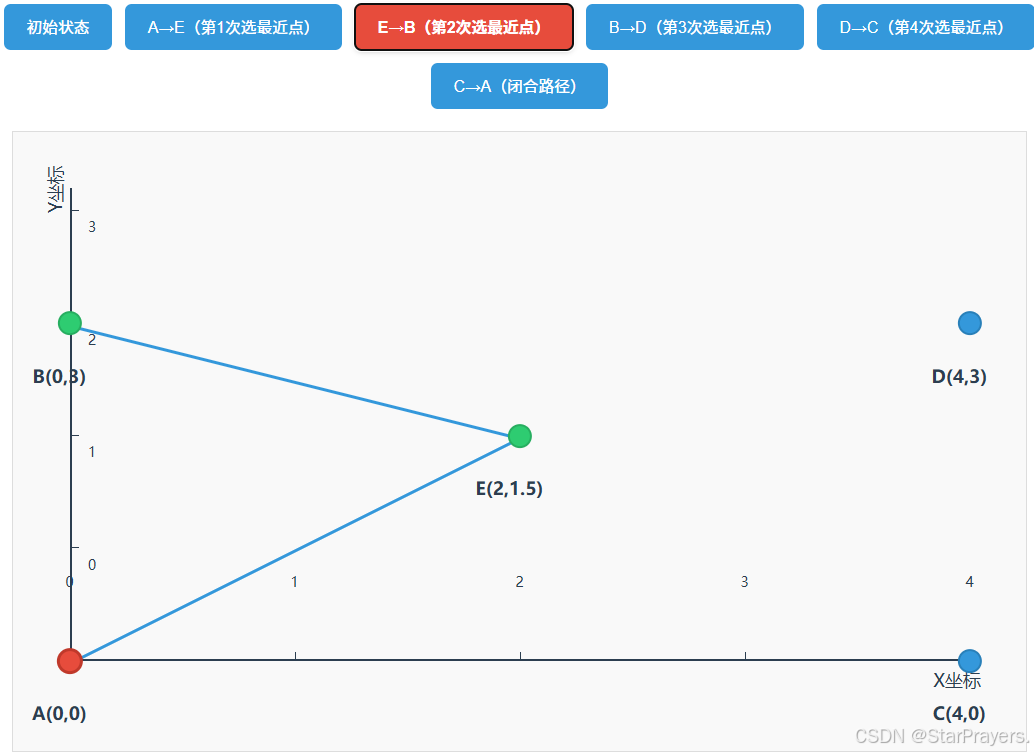
path变为[A,E],unvisited变为[B,C,D],current = E; - 第二次循环:E 的最近未访问点是 B(距离≈2.5),
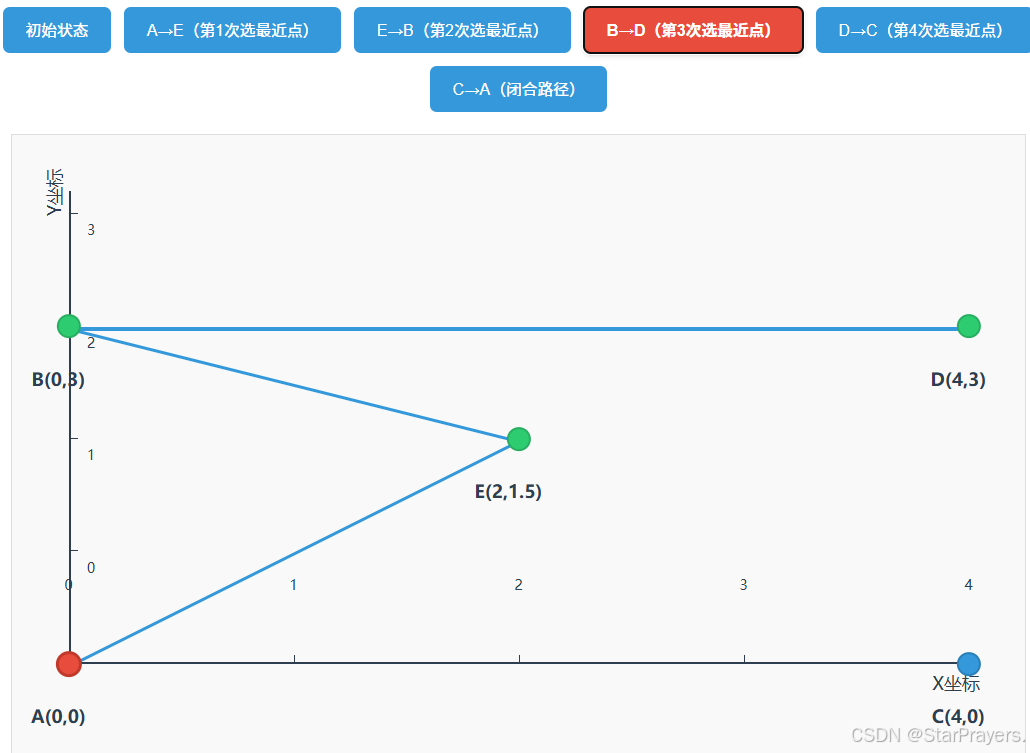
path变为[A,E,B],unvisited变为[C,D],current = B; - 第三次循环:B 的最近未访问点是 D(距离 = 4),
path变为[A,E,B,D],unvisited变为[C],current = D; - 第四次循环:D 的最近未访问点是 C(距离 = 3),
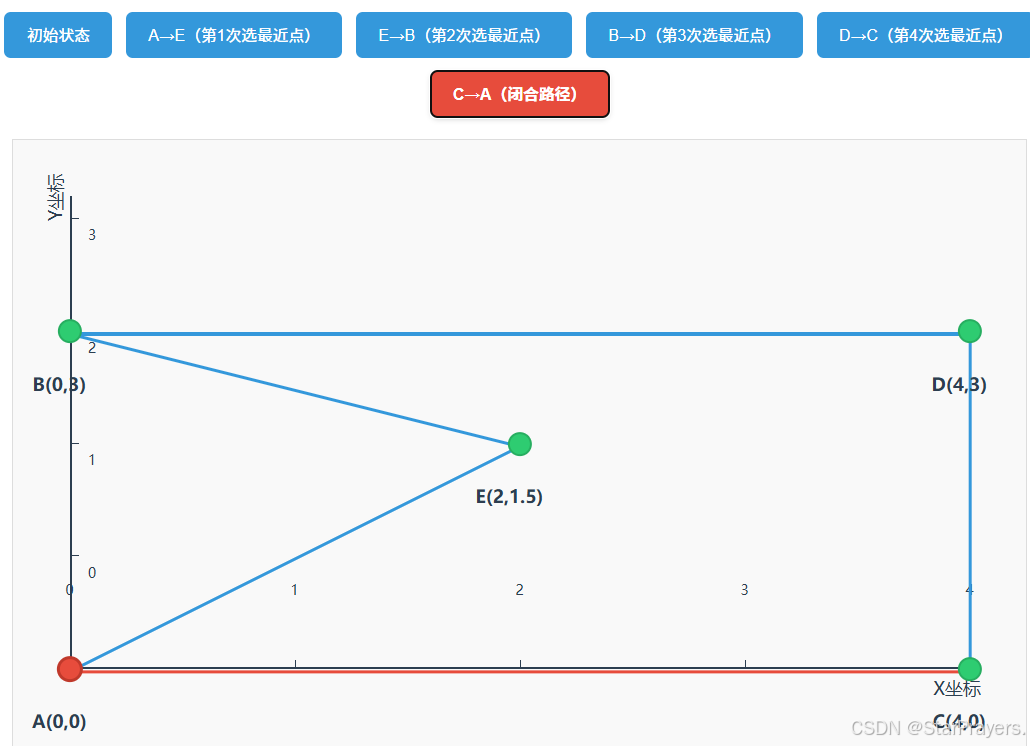
path变为[A,E,B,D,C],unvisited为空; - 闭合路径:
path最终为[A,E,B,D,C,A],总距离≈15.898(与Lab_test.py中的预期结果一致)。
4.最近邻算法(nearestNeighbor)过程图
网页文件:5点用例最近邻算法流程可视化(Prayer).html资源-CSDN下载
5. 算法特点
- 优点:逻辑简单,代码短,计算速度快(时间复杂度 O (n²),n 为点的数量);
- 缺点:易陷入 "局部最优",最终路径总距离可能较长(如上述例子中,若起点不同,路径可能更优)。
三、最近插入法(nearestInsertion)
1. 算法核心思想
与最近邻法不同,最近插入法从 "两个起点构成的初始路径" 出发,每次找到 "距离当前路径最近的未访问点",并将其插入到 "使路径总长度++增量++最小" 的位置,直到所有点被访问,最后回到起点。贪心逻辑:不仅关注 "选哪个点",还关注 "插在哪里",因此通常比最近邻法得到的路径更优(总距离更短),但计算量稍大。
2. 代码实现与解析
python
@display_time
def nearestInsertion(pointsL, startPoint1, startPoint2):
"""最近插入算法:从两个起点出发,插入最近点并最小化路径增量(案例图3逻辑)"""
# 第一步:输入验证(确保两个起点不同且都在点列表中)
if startPoint1 == startPoint2:
raise ValueError("Start points must be different")
if startPoint1 not in pointsL or startPoint2 not in pointsL:
raise ValueError("Start points must be in pointsL")
# 第二步:初始化"路径列表"和"剩余未访问点列表"
path = [startPoint1, startPoint2] # 初始路径是两个起点(如A→B)
remaining = [p for p in pointsL if p not in path] # 未访问的点(排除两个起点)
# 第三步:核心循环------选最近点→找最小插入位置→插入,直到所有点被访问
while remaining:
# 子步骤1:找到距离当前路径最近的未访问点
# 定义"点到路径的距离":点到路径中所有点的最小距离
def dist_to_path(point):
return min(point.dist_to_point(p) for p in path)
# 用min找到"距离路径最近"的点
best_point = min(remaining, key=dist_to_path)
# 子步骤2:找到插入该点后,路径总长度增量最小的位置
min_increase = math.inf # 初始化"最小增量"为无穷大
best_pos = 0 # 初始化"最优插入位置"为0
# 遍历路径中的每一段(如路径[A,B,D]的段是A→B、B→D)
for i in range(len(path)):
a, b = path[i], path[(i + 1) % len(path)] # a是段的起点,b是段的终点(%处理循环)
original_dist = a.dist_to_point(b) # 原段的距离(a→b)
new_dist = a.dist_to_point(best_point) + best_point.dist_to_point(b) # 插入后的距离(a→best_point→b)
increase = new_dist - original_dist # 插入导致的距离增量(越小越好)
# 更新"最小增量"和"最优位置"
if increase < min_increase:
min_increase = increase
best_pos = i + 1 # 插入位置在a和b之间(即i+1索引)
# 子步骤3:将最优点点插入路径,并从剩余列表中移除
path.insert(best_pos, best_point)
remaining.remove(best_point)
# 第四步:闭合路径------回到第一个起点
path.append(startPoint1)
# 第五步:返回路径(封装成Route对象)
return Route(path)3. 关键步骤拆解
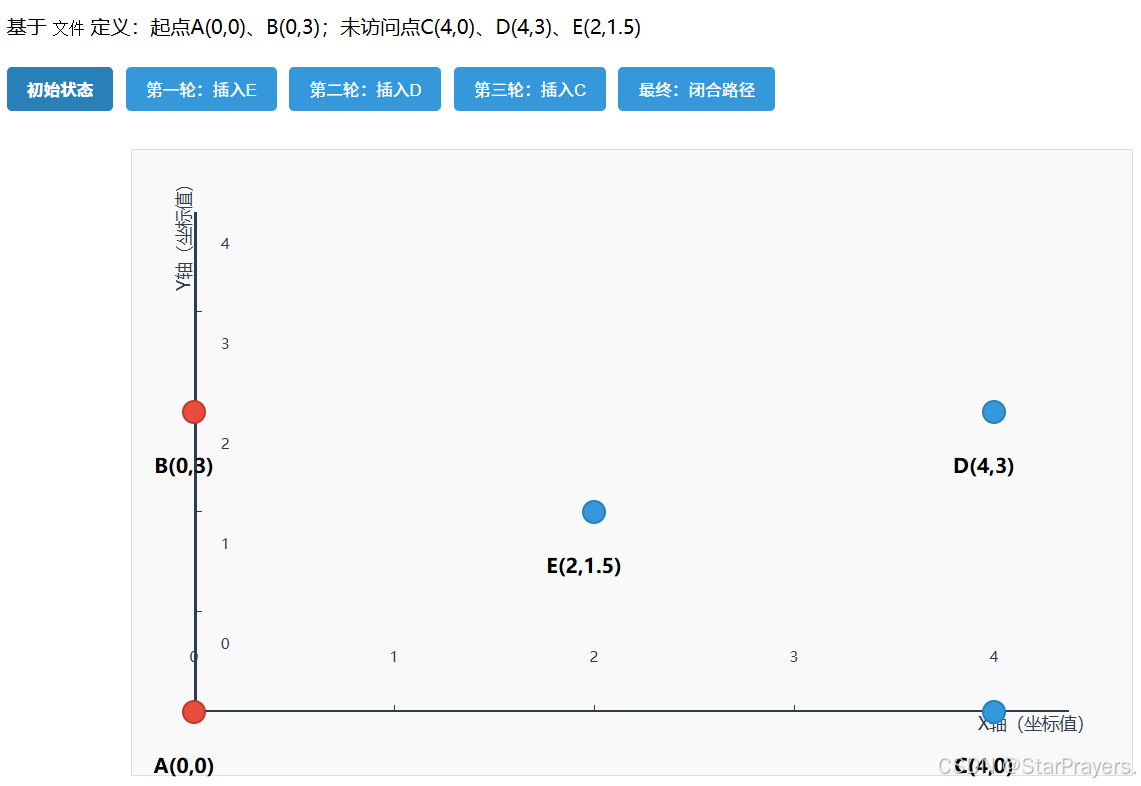
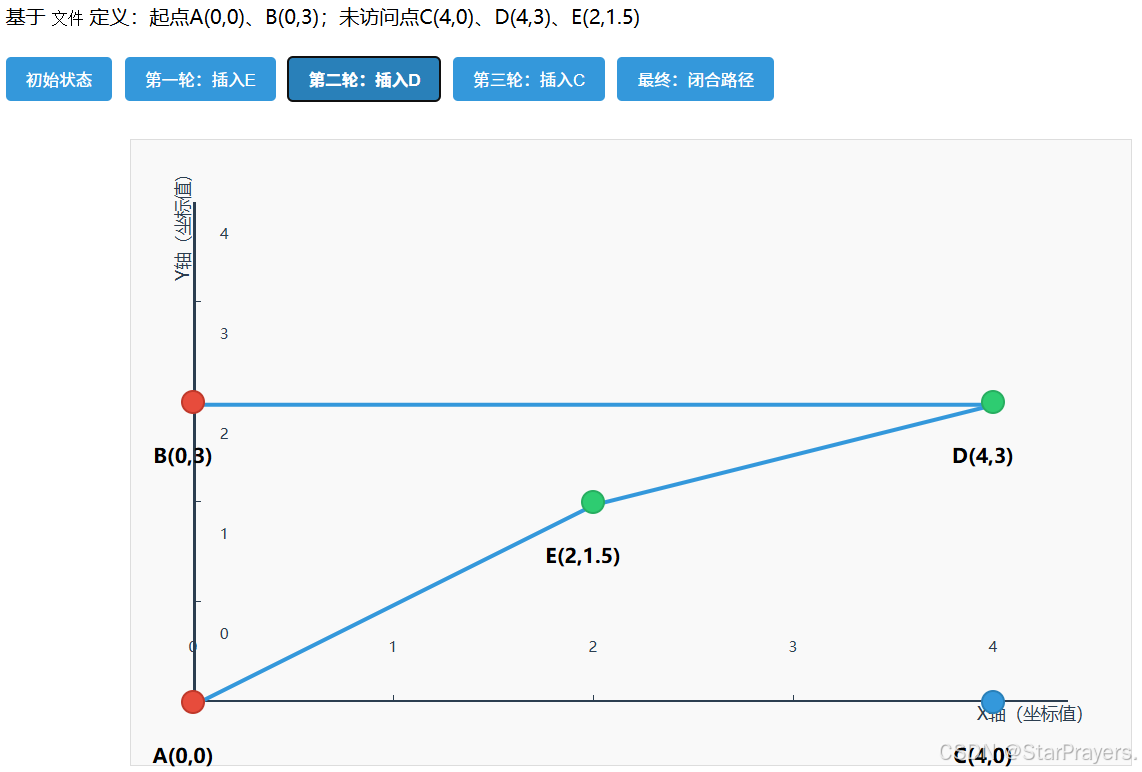
同样以 "5 点用例"、两个起点为 A (0,0) 和 B (0,3) 为例,手动走一遍流程:
- 初始化:
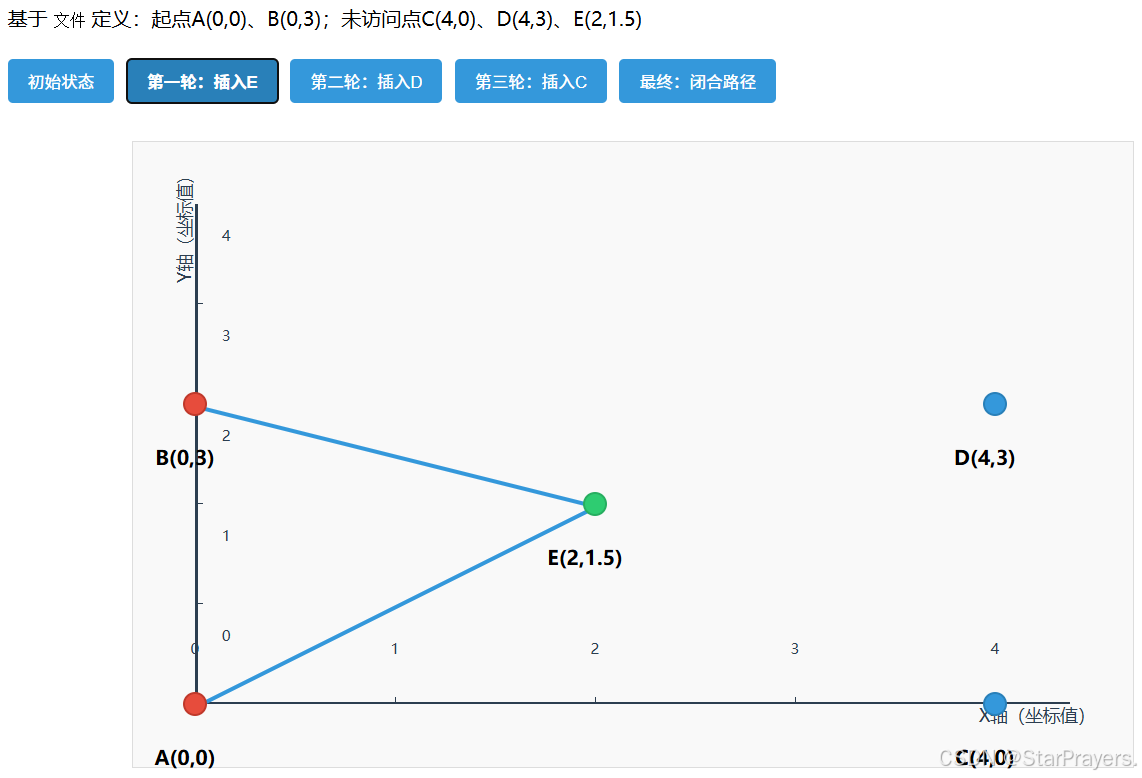
path = [A,B],remaining = [C,D,E]; - 子步骤 1:找距离路径 [A,B] 最近的点 ------E 到 A 的距离≈2.5,到 B 的距离≈2.5,是最近点(best_point=E);
- 子步骤 2:找 E 的最优插入位置:
- 若插入 A 和 B 之间(位置 1):原段 A→B 距离 = 3,插入后 A→E→B 距离≈2.5+2.5=5,增量 = 2;
- 无其他段(路径只有 A→B),因此 best_pos=1;
- 插入 E:
path变为[A,B,E],remaining = [C,D]; - 下一轮循环:
- 子步骤 1:找距离路径 [A,B,E] 最近的点 ------D 到 B 的距离 = 4,到 E 的距离≈2.5,是最近点(best_point=D);
- 子步骤 2:找 D 的最优插入位置:
- 段 A→B:插入后 A→D→B 距离≈5+4=9,原距离 3,增量 = 6;
- 段 B→E:插入后 B→D→E 距离 = 4+2.5=6.5,原距离 2.5,增量 = 4;
- 段 E→A:插入后 E→D→A 距离≈2.5+5=7.5,原距离 2.5,增量 = 5;
- 最小增量是 4,对应位置 3(B 和 E 之间);
- 插入 D:
path变为[A,B,D,E],remaining = [C];
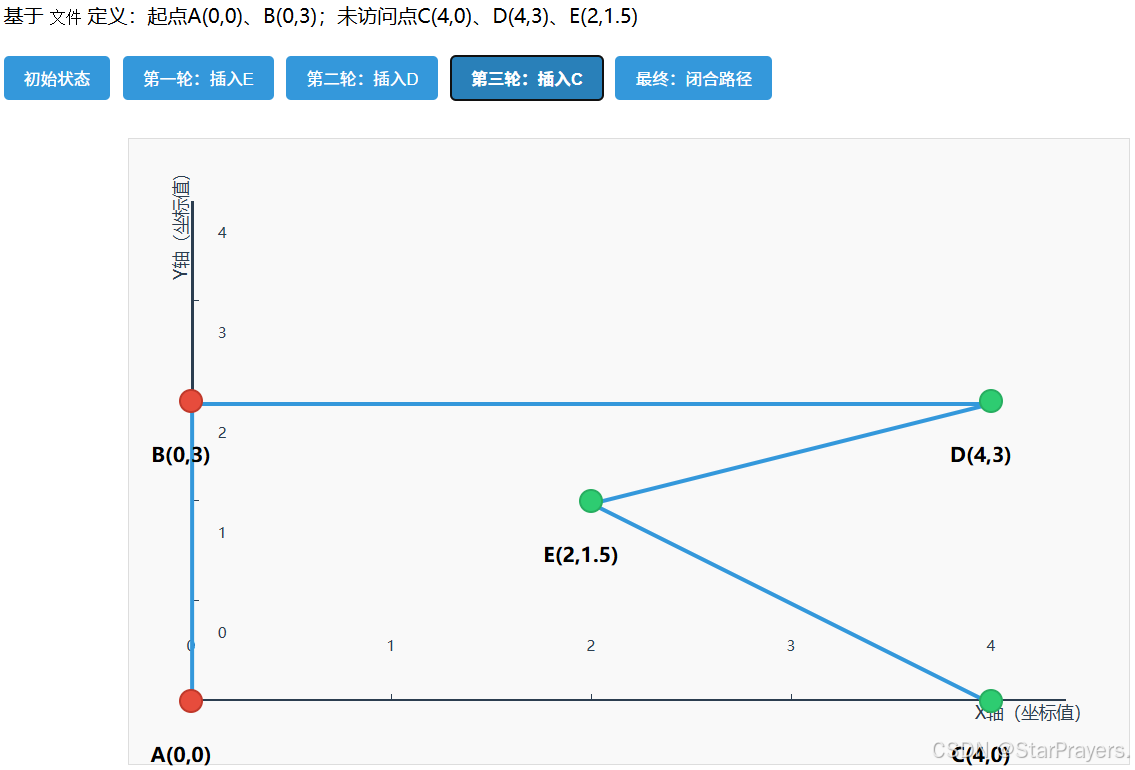
- 再下一轮循环:
- 子步骤 1:找距离路径 [A,B,D,E] 最近的点 ------C 到 E 的距离≈2.5,到 A 的距离 = 4,是最近点(best_point=C);
- 子步骤 2:找 C 的最优插入位置(计算后最优位置是 5,E 和 A 之间);
- 插入 C:
path变为[A,B,D,E,C],remaining为空;
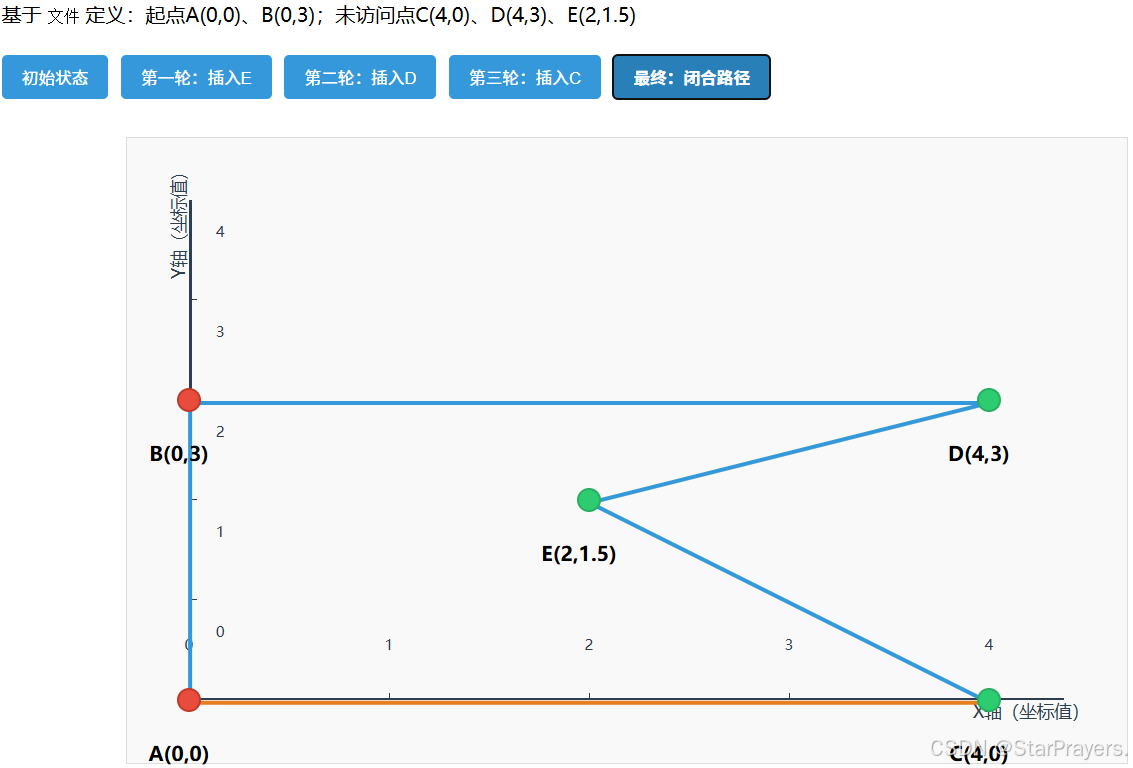
- 闭合路径:
path最终为[A,B,D,E,C,A](或等价路径),总距离≈14.898(比最近邻法更优)。
4.最近插入法(nearestInsertion)过程图
网页文件:5点用例最近插入算法流程可视化(Prayer).html资源-CSDN下载
4. 算法特点
- 优点:路径总距离通常比最近邻法短(因为考虑了插入位置的优化),是更实用的近似算法;
- 缺点:逻辑比最近邻法复杂,计算量稍大(时间复杂度仍为 O (n²),但常数项更大)。
heuristics.py 是整个 TSP 项目的 "算法核心":
- 实现了两种贪心策略,为 TSP 提供不同精度和速度的近似解;
- 输出结果统一封装为
Route对象,与Route.py无缝衔接,方便后续测试和可视化; - 借助
@display_time装饰器,自动统计运行时间,为后续对比算法效率提供数据支持。
若忘记算法步骤,可重点回忆:
- 最近邻法:"选最近点→加路径→标记已访问" 循环;
- 最近插入法:"选最近点→找最小增量位置→插入" 循环。两者的核心差异在于 "是否优化插入位置",这也是最近插入法结果更优的关键。
四、heuristics.py完整代码
python
from Route import Route, Point
from decorator import display_time # 导入案例要求的装饰器
import math
# ---------------------- 案例必做:最近邻点法(任务1要求) ----------------------
@display_time
def nearestNeighbor(pointsL, startPoint):
"""最近邻算法:从起点出发,每次选择最近未访问点(案例图2逻辑)"""
# 输入验证(符合案例对函数参数的要求)
if not isinstance(startPoint, Point):
raise TypeError("startPoint must be a Point instance")
if startPoint not in pointsL:
raise ValueError("startPoint must be in pointsL")
unvisited = pointsL.copy()
unvisited.remove(startPoint)
path = [startPoint]
current = startPoint
# 核心逻辑:反复选择最近未访问点
while unvisited:
closest = min(unvisited, key=lambda p: current.dist_to_point(p))
path.append(closest)
unvisited.remove(closest)
current = closest
path.append(startPoint) # 闭合路径(回到起点,符合TSP定义)
return Route(path)
# ---------------------- 案例必做:最近插入法(任务1要求) ----------------------
@display_time
def nearestInsertion(pointsL, startPoint1, startPoint2):
"""最近插入算法:从两个起点出发,插入最近点并最小化路径增量(案例图3逻辑)"""
# 输入验证(符合案例对函数参数的要求)
if startPoint1 == startPoint2:
raise ValueError("Start points must be different")
if startPoint1 not in pointsL or startPoint2 not in pointsL:
raise ValueError("Start points must be in pointsL")
path = [startPoint1, startPoint2]
remaining = [p for p in pointsL if p not in path]
# 核心逻辑:选最近点→找最小插入位置→插入
while remaining:
# 步骤1:找到距离当前路径最近的点
def dist_to_path(point):
return min(point.dist_to_point(p) for p in path)
best_point = min(remaining, key=dist_to_path)
# 步骤2:找到插入后路径增量最小的位置
min_increase = math.inf
best_pos = 0
for i in range(len(path)):
a, b = path[i], path[(i + 1) % len(path)]
original_dist = a.dist_to_point(b)
new_dist = a.dist_to_point(best_point) + best_point.dist_to_point(b)
increase = new_dist - original_dist
if increase < min_increase:
min_increase = increase
best_pos = i + 1
# 步骤3:插入点并更新剩余列表
path.insert(best_pos, best_point)
remaining.remove(best_point)
path.append(startPoint1) # 闭合路径
return Route(path)