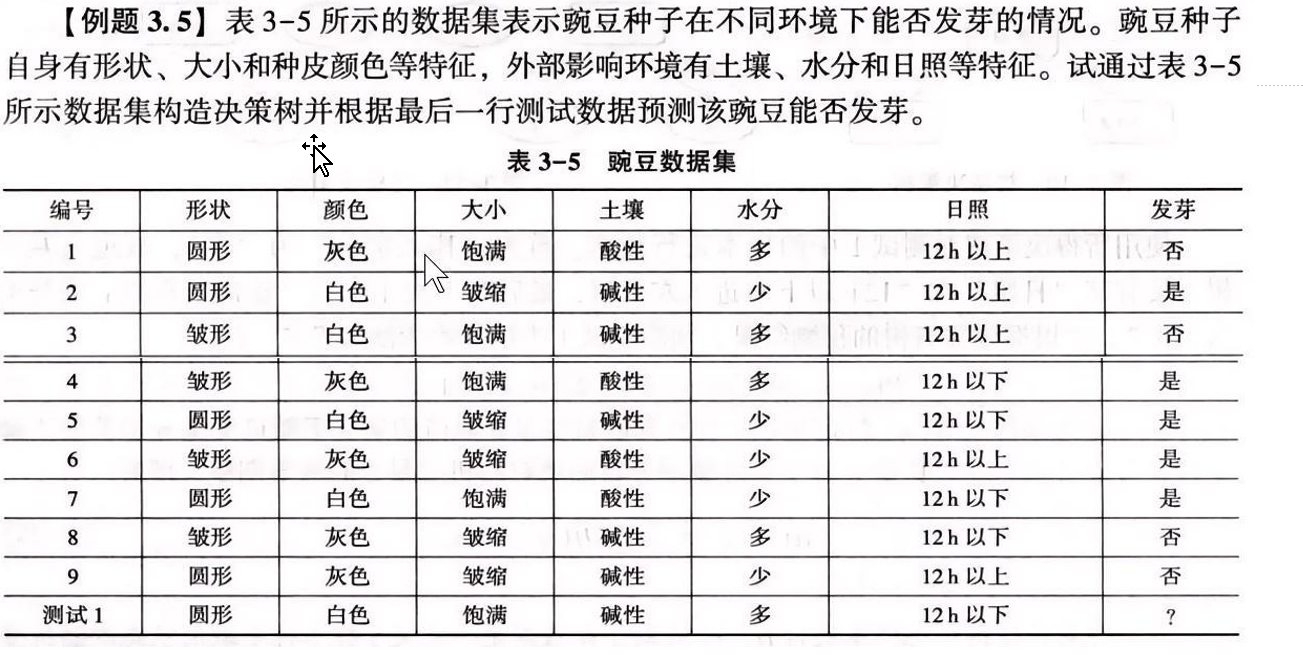
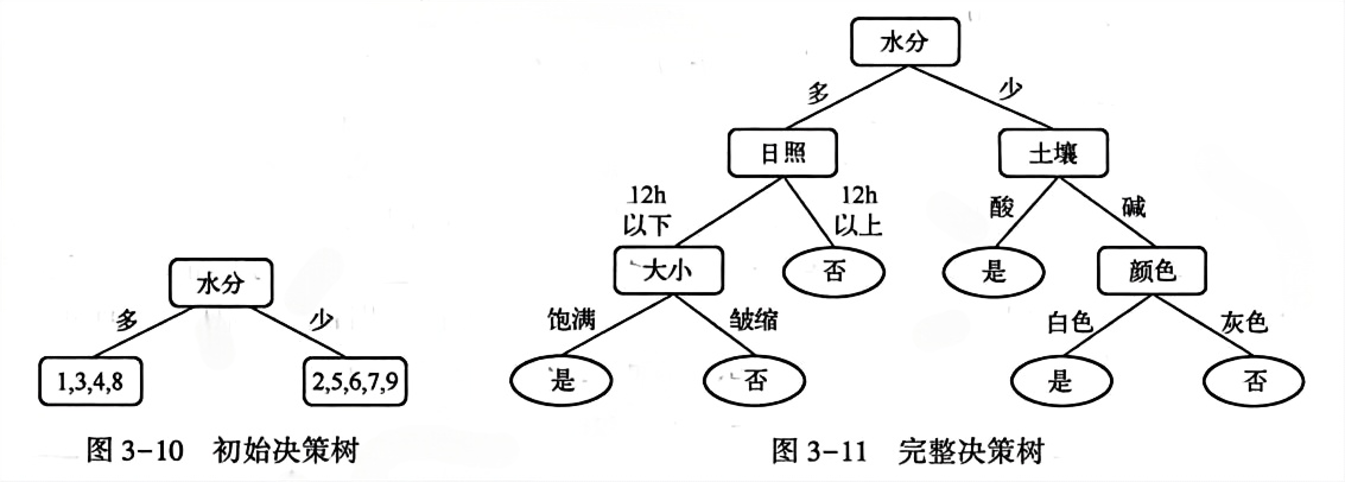
例题3.5



代码实现1
import pandas as pd
from math import log2
class ID3DecisionTree:
"""ID3决策树算法实现(仅文本输出)"""
def __init__(self):
self.tree = None # 存储决策树(字典结构)
self.feature_names = None # 特征名称列表
self.y_train = None # 训练集标签(用于预测时的默认值)
def calc_entropy(self, y):
"""计算信息熵"""
label_counts = y.value_counts() # 统计每个类别的数量
entropy = 0.0
total = len(y)
for count in label_counts:
prob = count / total
if prob > 0: # 避免log2(0)的情况
entropy -= prob * log2(prob)
return entropy
def split_dataset(self, X, y, feature_idx, value):
"""根据特征和值划分数据集"""
mask = X.iloc[:, feature_idx] == value # 筛选符合条件的样本
sub_X = X.loc[mask].drop(X.columns[feature_idx], axis=1) # 移除当前特征
sub_y = y.loc[mask]
return sub_X, sub_y
def choose_best_feature(self, X, y):
"""选择信息增益最大的特征"""
num_features = X.shape[1]
base_entropy = self.calc_entropy(y) # 原始数据集的熵
best_info_gain = 0.0
best_feature_idx = -1
for i in range(num_features):
feature_values = X.iloc[:, i].unique() # 特征的所有可能值
new_entropy = 0.0 # 划分后的条件熵
# 计算每个子数据集的熵并累加
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, i, value)
prob = len(sub_y) / len(y) # 子数据集占比
new_entropy += prob * self.calc_entropy(sub_y)
# 信息增益 = 原始熵 - 条件熵
info_gain = base_entropy - new_entropy
# 更新最优特征
if info_gain > best_info_gain:
best_info_gain = info_gain
best_feature_idx = i
return best_feature_idx
def majority_vote(self, y):
"""多数投票:返回出现次数最多的标签"""
return y.value_counts().idxmax()
def build_tree(self, X, y, feature_names):
"""递归构建决策树"""
# 终止条件1:所有样本标签相同
if len(y.unique()) == 1:
return y.iloc[0]
# 终止条件2:无特征可划分,返回多数标签
if X.empty:
return self.majority_vote(y)
# 选择最优特征
best_feature_idx = self.choose_best_feature(X, y)
best_feature_name = feature_names[best_feature_idx]
# 初始化决策树节点(字典结构:{特征: {特征值: 子树}})
tree = {best_feature_name: {}}
# 剩余特征名称(排除当前使用的特征)
remaining_feature_names = [f for i, f in enumerate(feature_names) if i != best_feature_idx]
# 递归构建子树
feature_values = X.iloc[:, best_feature_idx].unique()
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, best_feature_idx, value)
tree[best_feature_name][value] = self.build_tree(sub_X, sub_y, remaining_feature_names)
return tree
def fit(self, X, y, feature_names=None):
"""训练模型(构建决策树)"""
if feature_names is None:
feature_names = list(X.columns)
self.feature_names = feature_names
self.y_train = y
self.tree = self.build_tree(X, y, feature_names)
def predict_single(self, sample, tree=None):
"""预测单个样本"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
# 叶子节点:直接返回标签
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
return tree
# 决策节点:递归查找特征值对应的子树
feature_name = next(iter(tree.keys()))
feature_value = sample[feature_name]
if feature_value in tree[feature_name]:
return self.predict_single(sample, tree[feature_name][feature_value])
else:
# 特征值未见过时,返回训练集多数标签
return self.majority_vote(self.y_train)
def predict(self, X):
"""预测多个样本"""
return X.apply(self.predict_single, axis=1)
def print_tree(self, tree=None, indent=""):
"""递归打印决策树(文本形式)"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
# 叶子节点:直接打印标签
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
print(f"{indent}└── 结果: {tree}")
return
# 决策节点:打印特征及子树
feature_name = next(iter(tree.keys()))
print(f"{indent}┌── 特征: {feature_name}")
# 遍历每个特征值对应的子树
values = list(tree[feature_name].keys())
for i, value in enumerate(values):
# 最后一个子节点用不同符号,优化显示
if i == len(values) - 1:
print(f"{indent}│ └── 取值: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[feature_name][value], indent + " ")
else:
print(f"{indent}│ ├── 取值: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[feature_name][value], indent + "│ ")
# 示例:种子发芽数据测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 构建数据集(5个"是",4个"否")
data = {
"形状": ["圆形", "圆形", "皱形", "皱形", "圆形", "皱形", "圆形", "皱形", "圆形"],
"颜色": ["灰色", "白色", "灰色", "白色", "白色", "白色", "白色", "灰色", "灰色"],
"大小": ["皱缩", "饱满", "皱缩", "饱满", "饱满", "饱满", "饱满", "皱缩", "皱缩"],
"土壤": ["酸性", "酸性", "碱性", "酸性", "酸性", "碱性", "酸性", "碱性", "碱性"],
"水分": ["多", "少", "多", "多", "少", "少", "少", "多", "多"],
"日照": ["12h以上", "12h以上", "12h以上", "12h以下", "12h以下", "12h以上", "12h以下", "12h以下", "12h以上"],
"发芽": ["否", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是", "是", "否", "否"]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
X = df.drop("发芽", axis=1) # 特征
y = df["发芽"] # 标签
# 2. 训练决策树
print("=== 训练ID3决策树 ===")
id3 = ID3DecisionTree()
id3.fit(X, y)
# 3. 打印决策树结构(文本形式)
print("\n=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===")
id3.print_tree()
# 4. 预测测试数据
test_data = pd.DataFrame({
"形状": ["圆形"], "颜色": ["白色"], "大小": ["饱满"],
"土壤": ["碱性"], "水分": ["多"], "日照": ["12h以下"]
})
print("\n=== 测试数据预测 ===")
print("测试数据特征:")
print(test_data.T) # 转置显示更清晰
print(f"预测结果:{id3.predict(test_data).iloc[0]}")运行结果:
=== 训练ID3决策树 ===
=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===
┌── 特征: 颜色
│ ├── 取值: 灰色
│ └── 结果: 否
│ └── 取值: 白色
└── 结果: 是
=== 测试数据预测 ===
测试数据特征:
0
形状 圆形
颜色 白色
大小 饱满
土壤 碱性
水分 多
日照 12h以下
预测结果:是代码实现2-基于基尼系数
import pandas as pd
class GiniDecisionTree:
"""基于基尼系数的决策树(CART算法思想)"""
def __init__(self):
self.tree = None # 存储决策树
self.feature_names = None # 特征名称
self.y_train = None # 训练标签
def calc_gini(self, y):
"""计算基尼系数(基尼不纯度)"""
# 基尼系数公式:Gini = 1 - Σ(p_i²),p_i为第i类的概率
label_counts = y.value_counts()
total = len(y)
gini = 1.0
for count in label_counts:
prob = count / total
gini -= prob ** 2
return gini
def split_dataset(self, X, y, feature_idx, value):
"""根据特征和值划分数据集"""
mask = X.iloc[:, feature_idx] == value
sub_X = X.loc[mask].drop(X.columns[feature_idx], axis=1)
sub_y = y.loc[mask]
return sub_X, sub_y
def choose_best_feature(self, X, y):
"""选择基尼指数最小(最优)的特征"""
num_features = X.shape[1]
best_gini_index = float('inf') # 最小基尼指数(初始为无穷大)
best_feature_idx = -1
for i in range(num_features):
feature_values = X.iloc[:, i].unique()
gini_index = 0.0 # 基尼指数(加权平均基尼系数)
# 计算每个子数据集的基尼系数并加权求和
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, i, value)
prob = len(sub_y) / len(y) # 子数据集占比
gini_index += prob * self.calc_gini(sub_y)
# 基尼指数越小,特征划分效果越好
if gini_index < best_gini_index:
best_gini_index = gini_index
best_feature_idx = i
return best_feature_idx
def majority_vote(self, y):
"""多数投票法:返回出现次数最多的标签"""
return y.value_counts().idxmax()
def build_tree(self, X, y, feature_names):
"""递归构建决策树"""
# 终止条件1:所有样本标签相同
if len(y.unique()) == 1:
return y.iloc[0]
# 终止条件2:无特征可划分,返回多数标签
if X.empty:
return self.majority_vote(y)
# 选择最优特征(基尼指数最小)
best_feature_idx = self.choose_best_feature(X, y)
best_feature_name = feature_names[best_feature_idx]
# 初始化决策树节点
tree = {best_feature_name: {}}
remaining_feature_names = [f for i, f in enumerate(feature_names) if i != best_feature_idx]
# 递归构建子树
feature_values = X.iloc[:, best_feature_idx].unique()
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, best_feature_idx, value)
tree[best_feature_name][value] = self.build_tree(sub_X, sub_y, remaining_feature_names)
return tree
def fit(self, X, y, feature_names=None):
"""训练模型"""
if feature_names is None:
feature_names = list(X.columns)
self.feature_names = feature_names
self.y_train = y
self.tree = self.build_tree(X, y, feature_names)
def predict_single(self, sample, tree=None):
"""预测单个样本"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
# 叶子节点:返回标签
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
return tree
# 决策节点:递归查找
feature_name = next(iter(tree.keys()))
feature_value = sample[feature_name]
if feature_value in tree[feature_name]:
return self.predict_single(sample, tree[feature_name][feature_value])
else:
return self.majority_vote(self.y_train)
def predict(self, X):
"""预测多个样本"""
return X.apply(self.predict_single, axis=1)
def print_tree(self, tree=None, indent=""):
"""打印决策树(文本形式)"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
print(f"{indent}└── 结果: {tree}")
return
feature_name = next(iter(tree.keys()))
print(f"{indent}┌── 特征: {feature_name}")
values = list(tree[feature_name].keys())
for i, value in enumerate(values):
if i == len(values) - 1:
print(f"{indent}│ └── 取值: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[feature_name][value], indent + " ")
else:
print(f"{indent}│ ├── 取值: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[feature_name][value], indent + "│ ")
# 示例:种子发芽数据测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 数据集(5个"是",4个"否")
data = {
"形状": ["圆形", "圆形", "皱形", "皱形", "圆形", "皱形", "圆形", "皱形", "圆形"],
"颜色": ["灰色", "白色", "灰色", "白色", "白色", "白色", "白色", "灰色", "灰色"],
"大小": ["皱缩", "饱满", "皱缩", "饱满", "饱满", "饱满", "饱满", "皱缩", "皱缩"],
"土壤": ["酸性", "酸性", "碱性", "酸性", "酸性", "碱性", "酸性", "碱性", "碱性"],
"水分": ["多", "少", "多", "多", "少", "少", "少", "多", "多"],
"日照": ["12h以上", "12h以上", "12h以上", "12h以下", "12h以下", "12h以上", "12h以下", "12h以下", "12h以上"],
"发芽": ["否", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是", "是", "否", "否"]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
X = df.drop("发芽", axis=1) # 特征
y = df["发芽"] # 标签
# 2. 训练基于基尼系数的决策树
print("=== 训练基于基尼系数的决策树 ===")
gini_tree = GiniDecisionTree()
gini_tree.fit(X, y)
# 3. 打印决策树结构
print("\n=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===")
gini_tree.print_tree()
# 4. 预测测试数据
test_data = pd.DataFrame({
"形状": ["圆形"], "颜色": ["白色"], "大小": ["饱满"],
"土壤": ["碱性"], "水分": ["多"], "日照": ["12h以下"]
})
print("\n=== 测试数据预测 ===")
print("测试数据特征:")
print(test_data.T)
print(f"预测结果:{gini_tree.predict(test_data).iloc[0]}")运行结果:
=== 训练基于基尼系数的决策树 ===
=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===
┌── 特征: 颜色
│ ├── 取值: 灰色
│ └── 结果: 否
│ └── 取值: 白色
└── 结果: 是
=== 测试数据预测 ===
测试数据特征:
0
形状 圆形
颜色 白色
大小 饱满
土壤 碱性
水分 多
日照 12h以下
预测结果:是
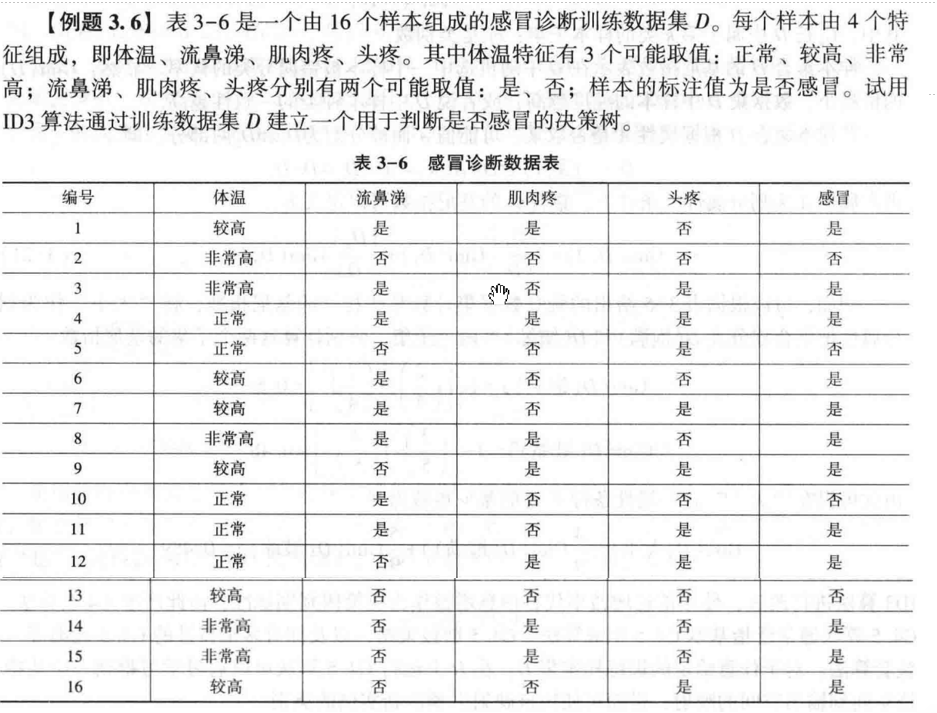
例题3.6
代码实现-ID3
import pandas as pd
from math import log2
class ID3DecisionTree:
"""ID3决策树算法实现(用于判断是否感冒)"""
def __init__(self):
self.tree = None # 存储决策树
self.feature_names = None # 特征名称列表
self.y_train = None # 训练标签
def calc_entropy(self, y):
"""计算信息熵(衡量数据集不确定性)"""
label_counts = y.value_counts() # 统计每个类别的数量
entropy = 0.0
total = len(y)
for count in label_counts:
prob = count / total # 计算概率
if prob > 0: # 避免log2(0)的情况
entropy -= prob * log2(prob)
return entropy
def split_dataset(self, X, y, feature_idx, value):
"""根据特征和值划分数据集"""
mask = X.iloc[:, feature_idx] == value # 筛选符合条件的样本
sub_X = X.loc[mask].drop(X.columns[feature_idx], axis=1) # 移除当前特征
sub_y = y.loc[mask]
return sub_X, sub_y
def choose_best_feature(self, X, y):
"""选择信息增益最大的特征"""
num_features = X.shape[1]
base_entropy = self.calc_entropy(y) # 原始数据集的熵
best_info_gain = 0.0
best_feature_idx = -1
for i in range(num_features):
feature_values = X.iloc[:, i].unique() # 特征的所有可能值
new_entropy = 0.0 # 划分后的条件熵
# 计算每个子数据集的熵并加权求和
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, i, value)
prob = len(sub_y) / len(y) # 子数据集占比
new_entropy += prob * self.calc_entropy(sub_y)
# 信息增益 = 原始熵 - 条件熵
info_gain = base_entropy - new_entropy
# 更新最优特征
if info_gain > best_info_gain:
best_info_gain = info_gain
best_feature_idx = i
return best_feature_idx
def majority_vote(self, y):
"""多数投票:返回出现次数最多的标签"""
return y.value_counts().idxmax()
def build_tree(self, X, y, feature_names):
"""递归构建决策树"""
# 终止条件1:所有样本标签相同
if len(y.unique()) == 1:
return y.iloc[0]
# 终止条件2:无特征可划分,返回多数标签
if X.empty:
return self.majority_vote(y)
# 选择最优特征
best_feature_idx = self.choose_best_feature(X, y)
best_feature_name = feature_names[best_feature_idx]
# 初始化决策树节点(字典结构:{特征: {特征值: 子树}})
tree = {best_feature_name: {}}
# 剩余特征名称(排除当前使用的特征)
remaining_feature_names = [f for i, f in enumerate(feature_names) if i != best_feature_idx]
# 递归构建子树
feature_values = X.iloc[:, best_feature_idx].unique()
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, best_feature_idx, value)
tree[best_feature_name][value] = self.build_tree(sub_X, sub_y, remaining_feature_names)
return tree
def fit(self, X, y, feature_names=None):
"""训练模型(构建决策树)"""
if feature_names is None:
feature_names = list(X.columns)
self.feature_names = feature_names
self.y_train = y
self.tree = self.build_tree(X, y, feature_names)
def predict_single(self, sample, tree=None):
"""预测单个样本"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
# 叶子节点:直接返回标签
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
return tree
# 决策节点:递归查找特征值对应的子树
feature_name = next(iter(tree.keys()))
feature_value = sample[feature_name]
if feature_value in tree[feature_name]:
return self.predict_single(sample, tree[feature_name][feature_value])
else:
# 特征值未见过时,返回训练集多数标签
return self.majority_vote(self.y_train)
def predict(self, X):
"""预测多个样本"""
return X.apply(self.predict_single, axis=1)
def print_tree(self, tree=None, indent=""):
"""打印决策树(文本形式)"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
# 叶子节点:直接打印标签
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
print(f"{indent}└── 结果: {tree}")
return
# 决策节点:打印特征及子树
feature_name = next(iter(tree.keys()))
print(f"{indent}┌── 特征: {feature_name}")
# 遍历每个特征值对应的子树
values = list(tree[feature_name].keys())
for i, value in enumerate(values):
# 最后一个子节点用不同符号,优化显示
if i == len(values) - 1:
print(f"{indent}│ └── 取值: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[feature_name][value], indent + " ")
else:
print(f"{indent}│ ├── 取值: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[feature_name][value], indent + "│ ")
# 示例:感冒判断数据集测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 构建感冒判断数据集(16个样本:12个"是",4个"否")
data = {
"流鼻涕": ["是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "否", "否", "否", "否"],
"体温": ["较高", "非常高", "非常高", "正常", "正常", "较高", "较高", "非常高", "较高", "正常", "正常", "正常", "较高", "非常高", "非常高", "较高"],
"肌肉疼": ["否", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "否", "否", "是", "是", "是"],
"头疼": ["是", "否", "是", "否", "否", "是", "是", "是", "是", "否", "是", "否", "否", "是", "是", "是"],
"感冒": ["是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是"]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
X = df.drop("感冒", axis=1) # 特征(流鼻涕、体温、肌肉疼、头疼)
y = df["感冒"] # 标签(是否感冒)
# 2. 训练ID3决策树
print("=== 训练感冒判断决策树 ===")
id3 = ID3DecisionTree()
id3.fit(X, y)
# 3. 打印决策树结构(文本形式)
print("\n=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===")
id3.print_tree()
# 4. 预测测试数据
test_data = pd.DataFrame({
"流鼻涕": ["否"],
"体温": ["正常"],
"肌肉疼": ["否"],
"头疼": ["否"]
})
print("\n=== 测试数据预测 ===")
print("测试数据特征:")
print(test_data.T) # 转置显示更清晰
print(f"预测结果(是否感冒):{id3.predict(test_data).iloc[0]}")运行结果
=== 训练感冒判断决策树 ===
=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===
┌── 特征: 头疼
│ ├── 取值: 是
│ └── 结果: 是
│ └── 取值: 否
┌── 特征: 肌肉疼
│ ├── 取值: 否
│ ┌── 特征: 体温
│ │ ├── 取值: 非常高
│ │ └── 结果: 否
│ │ ├── 取值: 正常
│ │ ┌── 特征: 流鼻涕
│ │ │ ├── 取值: 否
│ │ │ └── 结果: 否
│ │ │ └── 取值: 是
│ │ └── 结果: 否
│ │ └── 取值: 较高
│ └── 结果: 否
│ └── 取值: 是
└── 结果: 是
=== 测试数据预测 ===
测试数据特征:
0
流鼻涕 否
体温 正常
肌肉疼 否
头疼 否
预测结果(是否感冒):否
代码实现------C4.5
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from math import log2
class C45DecisionTree:
"""C4.5决策树算法实现(基于信息增益率)"""
def __init__(self):
self.tree = None # 存储决策树
self.feature_names = None # 特征名称
self.y_train = None # 训练标签
def calc_entropy(self, y):
"""计算信息熵"""
label_counts = y.value_counts()
entropy = 0.0
total = len(y)
for count in label_counts:
prob = count / total
if prob > 0:
entropy -= prob * log2(prob)
return entropy
def split_dataset(self, X, y, feature_idx, value, is_continuous=False):
"""划分数据集(支持连续特征)"""
if is_continuous:
# 连续特征:按"<=value"和">value"划分
mask = X.iloc[:, feature_idx] <= value
sub_X1 = X.loc[mask].drop(X.columns[feature_idx], axis=1)
sub_y1 = y.loc[mask]
sub_X2 = X.loc[~mask].drop(X.columns[feature_idx], axis=1)
sub_y2 = y.loc[~mask]
return (sub_X1, sub_y1), (sub_X2, sub_y2)
else:
# 离散特征:按等于value划分
mask = X.iloc[:, feature_idx] == value
sub_X = X.loc[mask].drop(X.columns[feature_idx], axis=1)
sub_y = y.loc[mask]
return sub_X, sub_y
def calc_info_gain(self, X, y, feature_idx, is_continuous=False):
"""计算信息增益(支持连续特征)"""
base_entropy = self.calc_entropy(y)
total = len(y)
info_gain = 0.0
best_split_val = None # 连续特征的最佳分割点
if is_continuous:
# 连续特征:排序后找最佳分割点
feature_values = sorted(X.iloc[:, feature_idx].unique())
max_info_gain = -float('inf')
# 尝试所有可能的分割点(相邻值的中点)
for i in range(len(feature_values) - 1):
split_val = (feature_values[i] + feature_values[i+1]) / 2
(sub_X1, sub_y1), (sub_X2, sub_y2) = self.split_dataset(
X, y, feature_idx, split_val, is_continuous=True
)
prob1 = len(sub_y1) / total
prob2 = len(sub_y2) / total
current_entropy = prob1 * self.calc_entropy(sub_y1) + prob2 * self.calc_entropy(sub_y2)
current_info_gain = base_entropy - current_entropy
if current_info_gain > max_info_gain:
max_info_gain = current_info_gain
best_split_val = split_val
info_gain = max_info_gain
else:
# 离散特征:直接计算
feature_values = X.iloc[:, feature_idx].unique()
new_entropy = 0.0
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, feature_idx, value)
prob = len(sub_y) / total
new_entropy += prob * self.calc_entropy(sub_y)
info_gain = base_entropy - new_entropy
return info_gain, best_split_val
def calc_split_info(self, X, y, feature_idx, is_continuous=False, split_val=None):
"""计算分裂信息(用于信息增益率)"""
total = len(y)
split_info = 0.0
if is_continuous and split_val is not None:
# 连续特征:按分割点计算
(sub_X1, sub_y1), (sub_X2, sub_y2) = self.split_dataset(
X, y, feature_idx, split_val, is_continuous=True
)
prob1 = len(sub_y1) / total
prob2 = len(sub_y2) / total
if prob1 > 0:
split_info -= prob1 * log2(prob1)
if prob2 > 0:
split_info -= prob2 * log2(prob2)
else:
# 离散特征:按取值计算
feature_values = X.iloc[:, feature_idx].unique()
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, feature_idx, value)
prob = len(sub_y) / total
if prob > 0:
split_info -= prob * log2(prob)
return split_info
def choose_best_feature(self, X, y, continuous_features=None):
"""选择信息增益率最大的特征(C4.5核心)"""
if continuous_features is None:
continuous_features = set() # 记录连续特征的索引
num_features = X.shape[1]
best_gain_ratio = -float('inf')
best_feature_idx = -1
best_split_val = None # 连续特征的最佳分割点
for i in range(num_features):
is_continuous = i in continuous_features
# 计算信息增益
info_gain, split_val = self.calc_info_gain(X, y, i, is_continuous)
# 计算分裂信息(避免分母为0)
split_info = self.calc_split_info(X, y, i, is_continuous, split_val)
if split_info < 1e-10: # 分裂信息接近0时跳过(避免除0)
continue
# 信息增益率 = 信息增益 / 分裂信息
gain_ratio = info_gain / split_info
# 更新最优特征
if gain_ratio > best_gain_ratio:
best_gain_ratio = gain_ratio
best_feature_idx = i
best_split_val = split_val
return best_feature_idx, best_split_val, best_feature_idx in continuous_features
def majority_vote(self, y):
"""多数投票法"""
return y.value_counts().idxmax()
def build_tree(self, X, y, feature_names, continuous_features=None):
"""递归构建决策树"""
if continuous_features is None:
continuous_features = set()
# 终止条件1:所有样本标签相同
if len(y.unique()) == 1:
return y.iloc[0]
# 终止条件2:无特征可划分,返回多数标签
if X.empty:
return self.majority_vote(y)
# 选择最优特征(信息增益率最大)
best_idx, best_split, is_continuous = self.choose_best_feature(
X, y, continuous_features
)
best_name = feature_names[best_idx]
# 处理连续特征(在特征名后添加分割点)
if is_continuous:
best_name = f"{best_name}<= {best_split:.2f}"
tree = {best_name: {}}
remaining_names = [f for i, f in enumerate(feature_names) if i != best_idx]
remaining_continuous = {i for i in continuous_features if i != best_idx}
# 调整连续特征索引(删除当前特征后索引减1)
remaining_continuous = {i-1 if i > best_idx else i for i in remaining_continuous}
if is_continuous:
# 连续特征:分为<=split和>split两支
(sub_X1, sub_y1), (sub_X2, sub_y2) = self.split_dataset(
X, y, best_idx, best_split, is_continuous=True
)
# 递归构建子树
tree[best_name]["是"] = self.build_tree(
sub_X1, sub_y1, remaining_names, remaining_continuous
)
tree[best_name]["否"] = self.build_tree(
sub_X2, sub_y2, remaining_names, remaining_continuous
)
else:
# 离散特征:按每个取值构建子树
feature_values = X.iloc[:, best_idx].unique()
for value in feature_values:
sub_X, sub_y = self.split_dataset(X, y, best_idx, value)
tree[best_name][value] = self.build_tree(
sub_X, sub_y, remaining_names, remaining_continuous
)
return tree
def fit(self, X, y, feature_names=None, continuous_features=None):
"""训练模型"""
if feature_names is None:
feature_names = list(X.columns)
if continuous_features is None:
continuous_features = set() # 连续特征的列名集合
# 转换连续特征列名为索引
self.continuous_idxs = {feature_names.index(f) for f in continuous_features}
self.feature_names = feature_names
self.y_train = y
self.tree = self.build_tree(X, y, feature_names, self.continuous_idxs)
def predict_single(self, sample, tree=None):
"""预测单个样本"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
return tree
# 解析当前节点(处理连续特征)
current_node = next(iter(tree.keys()))
if "<= " in current_node:
# 连续特征:提取特征名和分割点
feature_name, split_val = current_node.split("<= ")
split_val = float(split_val)
# 判断样本值是否满足条件
sample_val = sample[feature_name]
if sample_val <= split_val:
return self.predict_single(sample, tree[current_node]["是"])
else:
return self.predict_single(sample, tree[current_node]["否"])
else:
# 离散特征:直接匹配取值
feature_name = current_node
sample_val = sample[feature_name]
if sample_val in tree[current_node]:
return self.predict_single(sample, tree[current_node][sample_val])
else:
return self.majority_vote(self.y_train)
def predict(self, X):
"""预测多个样本"""
return X.apply(self.predict_single, axis=1)
def print_tree(self, tree=None, indent=""):
"""打印决策树(文本形式)"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.tree
if not isinstance(tree, dict):
print(f"{indent}└── 结果: {tree}")
return
node_name = next(iter(tree.keys()))
print(f"{indent}┌── 特征: {node_name}")
values = list(tree[node_name].keys())
for i, value in enumerate(values):
if i == len(values) - 1:
print(f"{indent}│ └── 分支: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[node_name][value], indent + " ")
else:
print(f"{indent}│ ├── 分支: {value}")
self.print_tree(tree[node_name][value], indent + "│ ")
# 示例:感冒判断数据集测试(含连续特征)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 构建数据集(添加连续特征"体温值")
data = {
"流鼻涕": ["是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "否", "否", "否", "否"],
"体温值": [37.5, 39.2, 39.5, 36.5, 36.3, 37.8, 37.6, 39.1, 37.7, 36.4, 36.6, 36.2, 37.9, 39.3, 39.4, 37.4],
"肌肉疼": ["否", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "否", "否", "是", "是", "是"],
"头疼": ["是", "否", "是", "否", "否", "是", "是", "是", "是", "否", "是", "否", "否", "是", "是", "是"],
"感冒": ["是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "否", "是", "是", "是"]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
X = df.drop("感冒", axis=1)
y = df["感冒"]
# 2. 定义连续特征(体温值为连续特征)
continuous_features = {"体温值"}
# 3. 训练C4.5决策树
print("=== 训练C4.5决策树 ===")
c45 = C45DecisionTree()
c45.fit(X, y, continuous_features=continuous_features)
# 4. 打印决策树结构
print("\n=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===")
c45.print_tree()
# 5. 预测测试数据
test_data = pd.DataFrame({
"流鼻涕": ["否"],
"体温值": [36.2],
"肌肉疼": ["否"],
"头疼": ["否"]
})
print("\n=== 测试数据预测 ===")
print("测试数据特征:")
print(test_data.T)
print(f"预测结果(是否感冒):{c45.predict(test_data).iloc[0]}")运行结果
=== 训练C4.5决策树 ===
=== 决策树结构(文本形式) ===
┌── 特征: 头疼
│ ├── 分支: 是
│ └── 结果: 是
│ └── 分支: 否
┌── 特征: 体温值<= 36.25
│ ├── 分支: 是
│ └── 结果: 是
│ └── 分支: 否
┌── 特征: 肌肉疼
│ ├── 分支: 否
│ └── 结果: 否
│ └── 分支: 是
└── 结果: 是
=== 测试数据预测 ===
测试数据特征:
0
流鼻涕 否
体温值 36.2
肌肉疼 否
头疼 否
预测结果(是否感冒):是
Process finished with exit code 0