AVL树的概念
要理解AVL 树,首先要了解二叉搜索树,关于二叉搜索树是什么,可以参考下面这篇:
一般情况下,二叉搜索树的时间复杂度是O(log n)但是在极端情况下会退化为单支树,时间复杂度退化为O(N)
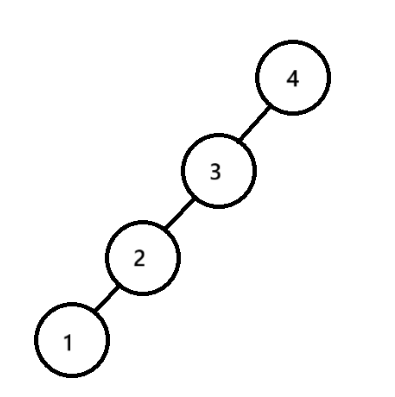
为了避免效率下降,因此AVL树被发明出来了
1.性质
- AVL树的左右子树高度差不超过1
- AVL树的左右子树也是AVL树
- AVL树可以为空树
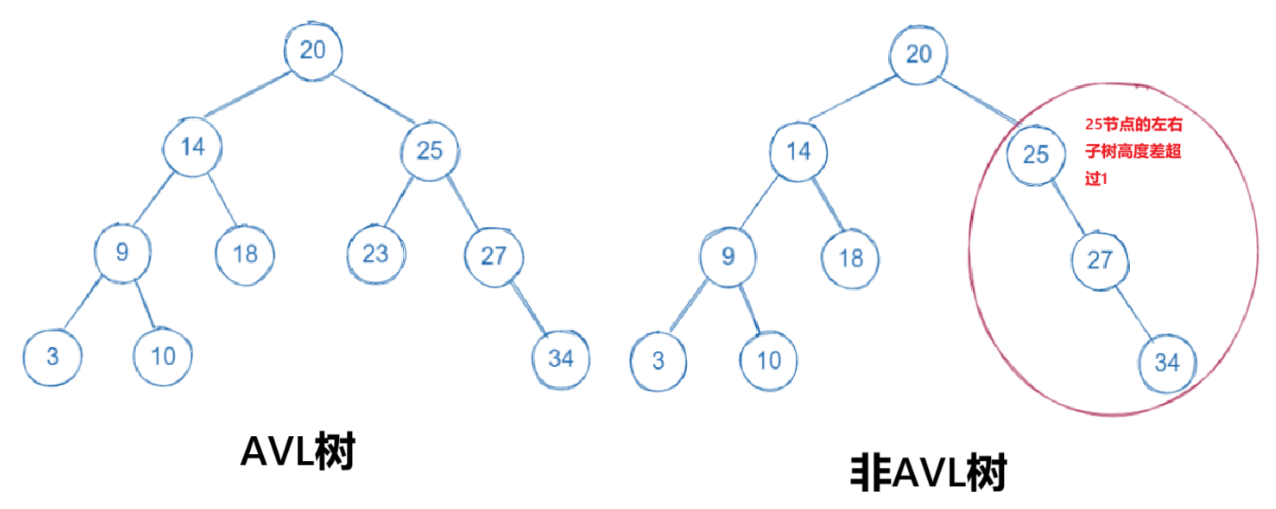
2.AVL树的定义
AVL树的左右子树高度差不能超过1,这里为了方便讲解,引入平衡因子(_bf)这个概念,
平衡因子==该节点右子树高度-该节点左子树的高度,例如:
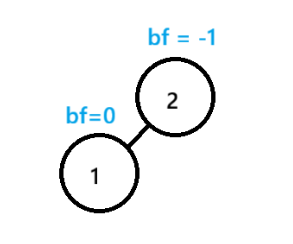
节点1左右子树高度都为0,平衡因子 = 右高度-左高度 :bf = 0 - 0
节点2左子树高度为1,右子树为0,平衡因子 = 0 - 1
如果平衡因子的大小超过1,AVL树的规则被打破,需要调整从而达到平衡
在调整的过程中会频繁的使用到父节点,因此AVL树的每个节点要有三个指针,左右子节点的指针、父指针
为了方便讲解,这里使用value模型的AVL树,即:节点只包含一个数据,并非常见的key-value键值对
cpp
template<class T>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
AVLTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr)
, _pRight(nullptr)
, _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _bf(0)
{}
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent;
T _data;
int _bf; // 节点的平衡因子
};3.AVL树的插入
往AVL树中插入节点与二叉搜索树中插入节点的过程基本相同,需要一个一个插入,区别是AVL树的插入要调整平衡因子
插入数据的总体思路为:判断根节点是否为空,寻找插入位置,完善插入的节点与周围节点的指向,向上调整平衡因子
1.往空树中插入一个值,直接将-pRoot指向该节点就可以了
2.往一个节点的左子树插入一个节点,该节点的bf要-1
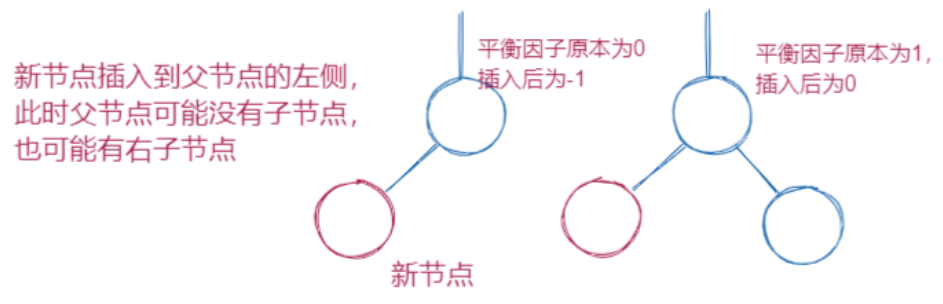
3.往一个节点的右子树插入一个节点,该节点的bf要+1
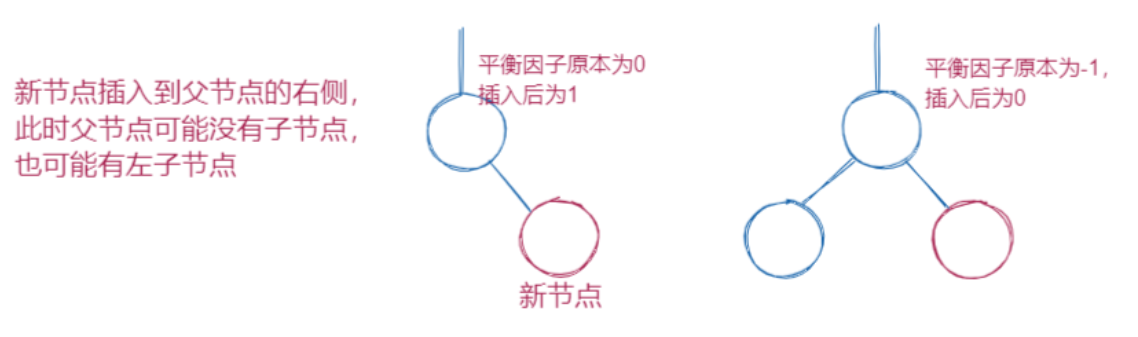
插入一个值后,在没有旋转的情况下,bf值为1或者-1,原先的bf值必然为0,意味着该节点的左右子树的高度发生了变化,此时需要继续向上修正祖先节点的bf值,直到根节点,或者其中有某个节点的bf值变为0(因为节点是一个一个插入的,每插入一个都要向上调整bf值,一旦有节点在调整bf值的过程中,bf变为0,一定是从-1或者1变过来的,此时该节点的左右子树高度不变,无需向上调整)如图:
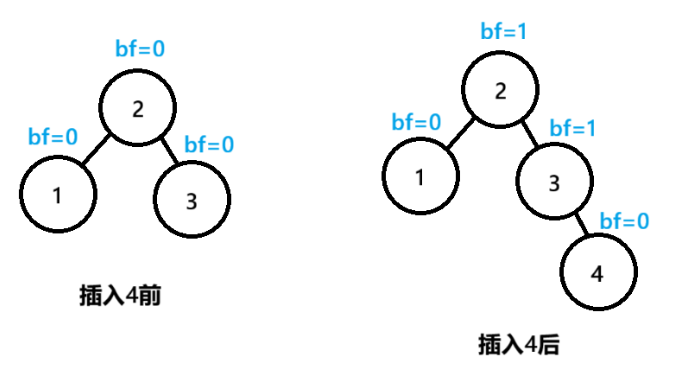
观察上图:
在插入4之后,3节点的bf=1,3节点所在的树的高度发生变化,还需要向上调整
2节点的bf=1,到达根节点,调整结束
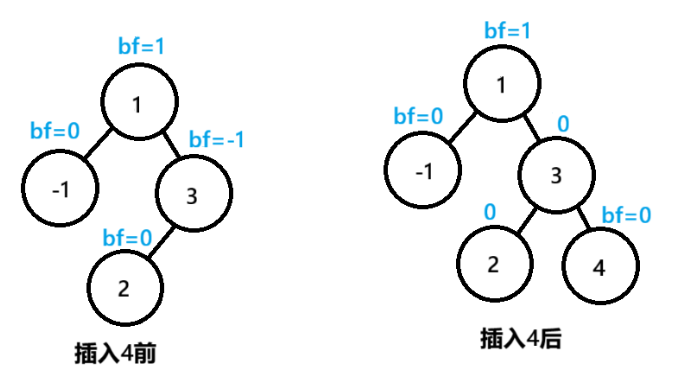
观察上图,在插入4这个节点后,3的bf值由原来的-1变成了0
3节点所在的树的高度不变,此时无需再向上调整,1节点的bf仍然为1
可以总结出规律:在调整平衡因子过程中,如果得到bf=1或者bf=-1,此树的高度发生了变化,需要继续向上调整;得到bf=0,此树的高度不变,无需向上调整
cpp
// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
//根节点为空
if (_pRoot == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = new Node(data);
return true;
}
else
{
//根节点不为空
Node* cur = _pRoot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
//寻找插入位置
while (cur)
{
if (data < cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else if (data > cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else
{
cout << "数据冗余,插入" << data << "失败" << endl;
return false;
}
}
//找到了插入位置,插入
cur = new Node(data);
if (data < parent->_data)
{
parent->_pLeft = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_pRight = cur;
}
cur->_pParent = parent;
//修正平衡因子
while (parent)
{
if (cur == parent->_pLeft)
{
parent->_bf--;
}
else
{
parent->_bf++;
}
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
//无需向上调整
break;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
//继续向上调整
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
//
}
else
{
cout << "AVL树高度异常" << endl;
assert(false);
}
}
}
}插入会有失衡的情况,即_bf的值达到了2或者-2,此时树的结构被破话,会涉及四种旋转:右旋、左旋、右左双旋、左右双旋,如何旋转呢?
4.AVL树的旋转
AVL树的旋转大体上有4种,这里会详细讲解这四种旋转:右单旋、左单旋、右左双旋、左右双旋
当一个节点的左右高度差为2时,即bf=2或者bf=-2,此时需要通过旋转进行调整,让该树满足AVL的规则
旋转采取的是使用最少或最简单的步骤,使得这颗二叉树的结构重新回归到AVL树
1.右单旋
旋转是在插入后,修正平衡因子时候进行的
在修正过程中,子节点bf=-1,父节点bf=-2时,发生右单旋
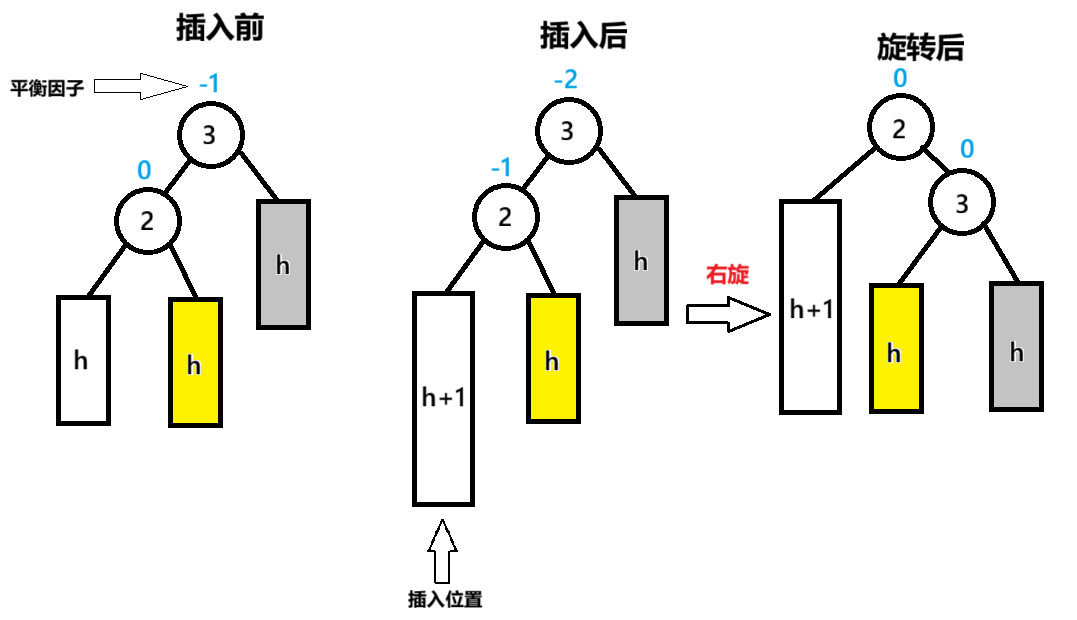
节点3为pParent,节点2为NodeL,节点2的右子节点为NodeLR
以pParent为旋转点,旋转后,pParent(3节点)的bf=0子节点(2节点)的bf=0
注意,这里父子节点的定义是在旋转前确定的
高度h的树,高度在0、1、2等正数情况下都适用
这里解释一下2节点的右子树在旋转后为什么变成了3节点的左子树首先,一个节点只有一个右节点的指针,这样才符合二叉树的规则
其次,以2节点为根的树的节点,都小于3节点,因为2节点是3节点的左子节点
左子节点 < 根节点 < 右子节点
因此2的右子树变成3的左子树符合规则,而且是比较方便的处理方法
cpp
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* NodeL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* NodeLR = NodeL->_pRight;
Node* pParentParent = pParent->_pParent;
//修正向下关系
pParent->_pLeft = NodeLR;
NodeL->_pRight = pParent;
//修正向上关系
pParent->_pParent = NodeL;
if (NodeLR)
{
NodeLR->_pParent = pParent;
}
//修正外部关系
if (pParentParent == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = NodeL;
NodeL->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParentParent->_pLeft == pParent)
{
pParentParent->_pLeft = NodeL;
}
else
{
pParentParent->_pRight = NodeL;
}
NodeL->_pParent = pParentParent;
}
//修正平衡因子
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeL->_bf = 0;
}注意:旋转后要修正平衡因子,且此时的节点关系发生了变化需要格外小心
与插入后的修正平衡因子不是同一件事
2.左单旋
插入后的子节点bf=1,父节点bf=2时,发生左单旋
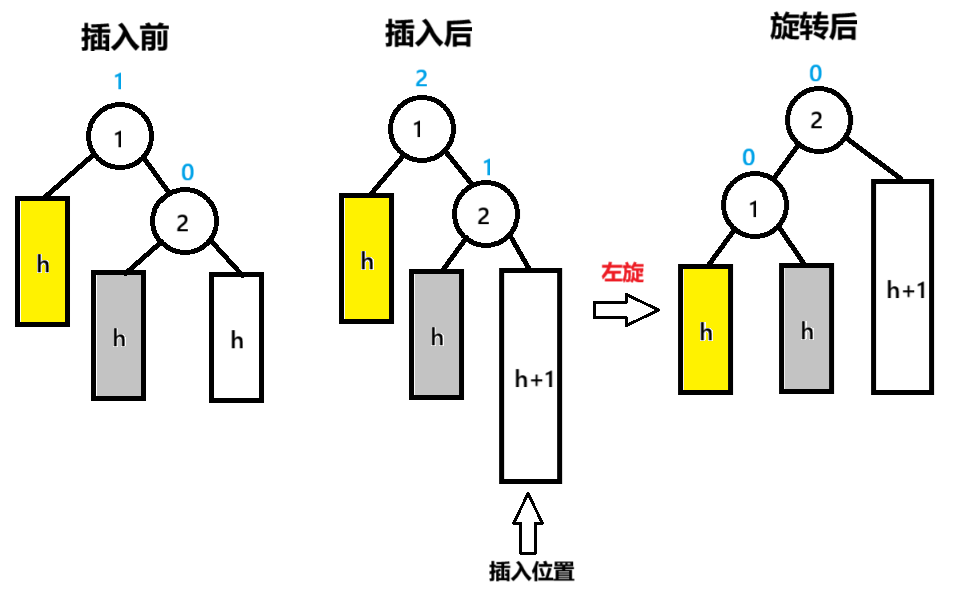
节点的确定在插入后,节点1为pParent,节点2为NodeR,节点2的左子节点为NodeRL
cpp
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* NodeR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* NodeRL = NodeR->_pLeft;
Node* pParentParent = pParent->_pParent;
//修正向下关系
pParent->_pRight = NodeRL;
NodeR->_pLeft = pParent;
//修正向上关系
pParent->_pParent = NodeR;
if (NodeRL)
{
NodeRL->_pParent = pParent;
}
//修正外部关系
if (pParentParent == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = NodeR;
NodeR->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParentParent->_pLeft == pParent)
{
pParentParent->_pLeft = NodeR;
}
else
{
pParentParent->_pRight = NodeR;
}
NodeR->_pParent = pParentParent;
}
//修正平衡因子
NodeR->_bf = 0;
pParent->_bf = 0;
}左单旋与右单旋类似,相当于右单旋的左右镜像版本,旋转后的父子节点bf都为0
以节点2()为旋转点进行左单旋
3.右左双旋
双旋是在单次旋转无法达到平衡时出现的,本质上是两次单旋,可以复用单旋的代码
右左双旋 细分为3种情况,3种情况的共同点是在父节点bf=2
一:父节点bf=2,父节点的右子节点的左子节点bf=0
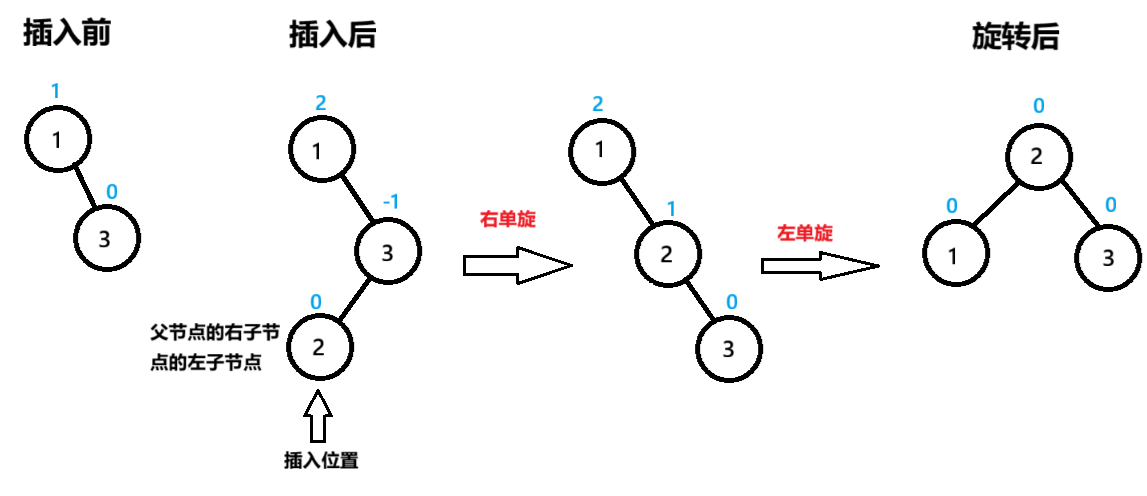
节点1为pParent,节点3为NodeR,节点2为NodeRL
先 以节点NodeR为旋转点进行右单旋,节点1的bf=2,未达到平衡再 以节点pParent为旋转点进行左单旋
旋转后的三个节点达到平衡,平衡因子都是0,bf=0
二:父节点bf=2,父节点的右子节点的左子节点bf=1
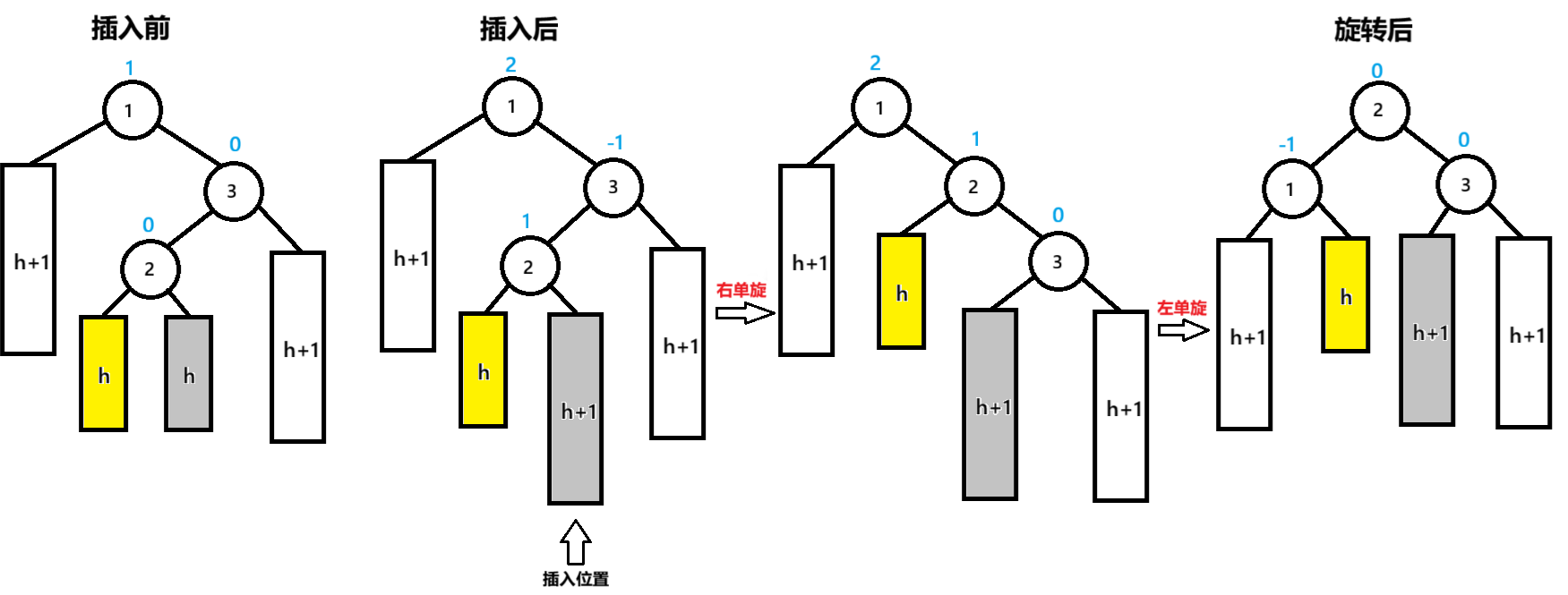
插入后,节点1为pParent,节点3为NodeR,节点2为NodeRL
先以节点NodeR为旋转点进行右单旋,节点1的bf=2,未达到平衡再以节点pParent为旋转点进行左单旋,达到平衡
pParent的bf=-1,NodeR的bf=0,NodeRL的bf=0
三:父节点bf=2,父节点的右子节点的左子节点bf=-1
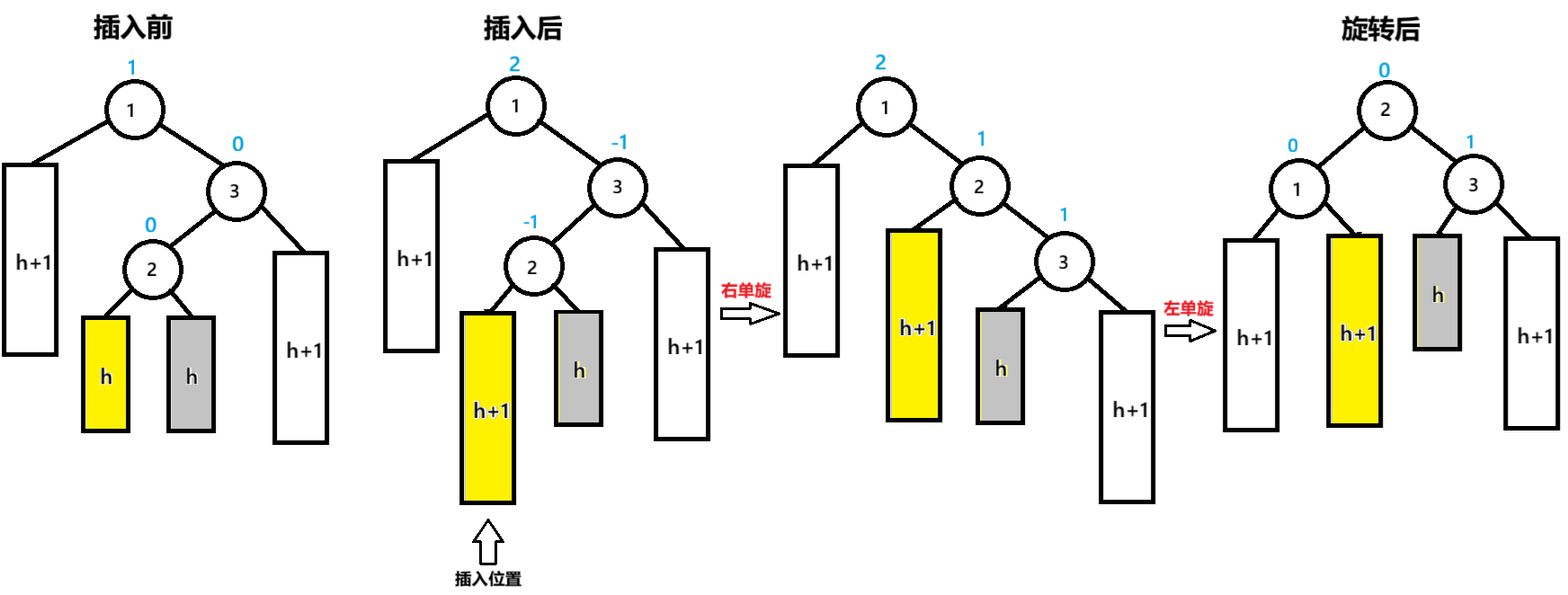
插入后,节点1为pParent节点,节点3为NodeR,节点2为NodeRL
先以NodeR为旋转点进行右单旋,pParent的bf=2,未达到平衡再以pParent为旋转点进行左单旋,达到平衡
pParent的bf=0,NodeR的bf= 1,NodeRL的bf=0
右左双旋都是先进行右单旋,再进行左单旋得到的,不同点在于平衡因子
这三种情况的代码可以复用,甚至复用单旋的代码
cpp
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* NodeR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* NodeRL = NodeR->_pLeft;
int bf = NodeRL->_bf;
RotateR(NodeR);
RotateL(pParent);
//校正平衡因子
if (bf == 0)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeR->_bf = 0;
NodeRL->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = -1;
NodeR->_bf = 0;
NodeRL->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeR->_bf = 1;
NodeRL->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}4.左右双旋
左右双旋其实就是右左双旋的左右镜像版本
所以也有3种情况,这三种情况的不同也是因为bf的处理不同
一:父节点的bf=-2,父节点的左子节点的右子节点bf=0
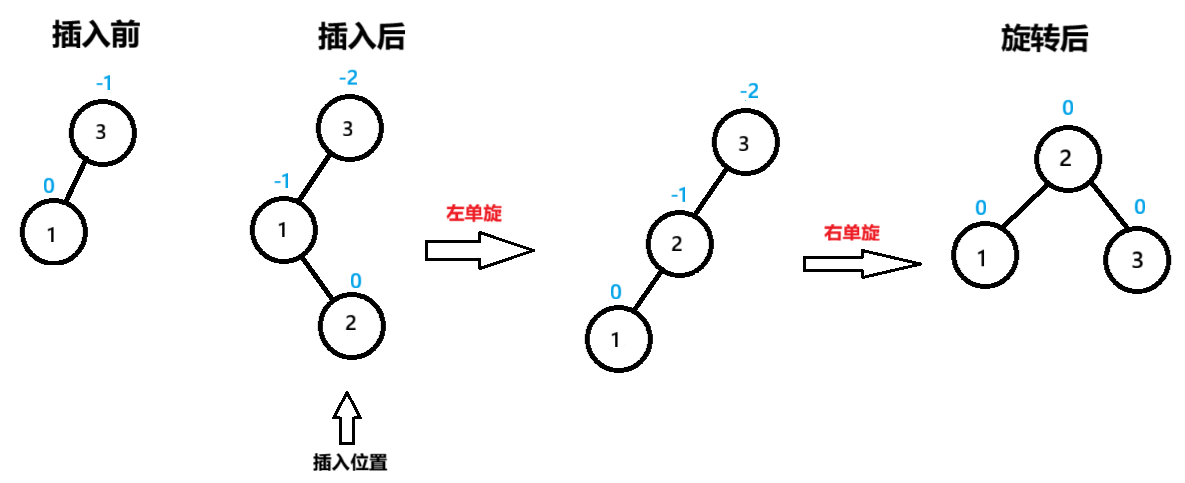
节点3为pParent,节点1为NodeL,节点2为NodeLR
先 以节点NodeL为旋转点进行左单旋,节点3的bf=-2,未达到平衡再 以节点pParent为旋转点进行右单旋
旋转后的三个节点达到平衡,平衡因子都是0,bf=0
二:父节点的bf=-2,父节点的左子节点的右子节点bf=-1
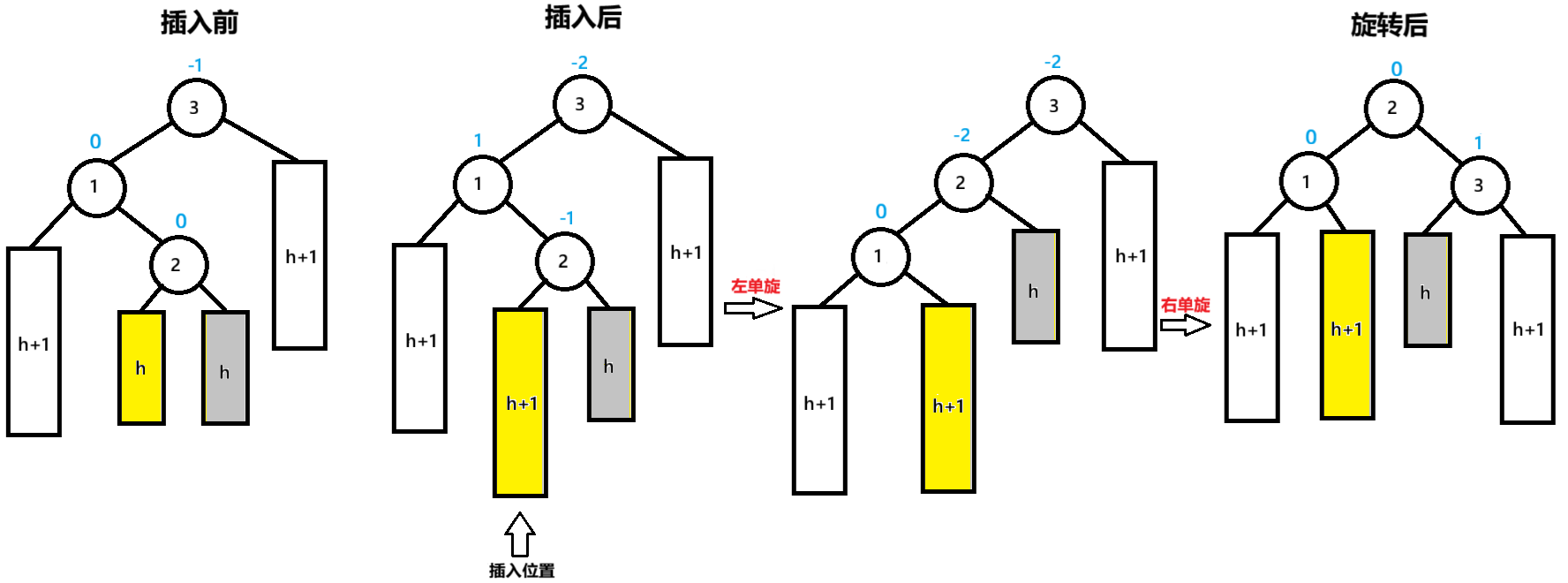
插入后,节点3为pParent,节点1为NodeL,节点2为NodeLR
先以节点NodeL为旋转点进行左单旋,节点3的bf=-2,未达到平衡再以节点pParent为旋转点进行右单旋,达到平衡
pParent的bf=1,NodeL的bf=0,NodeLR的bf=0
三:父节点的bf=-2,父节点的左子节点的右子节点bf=1
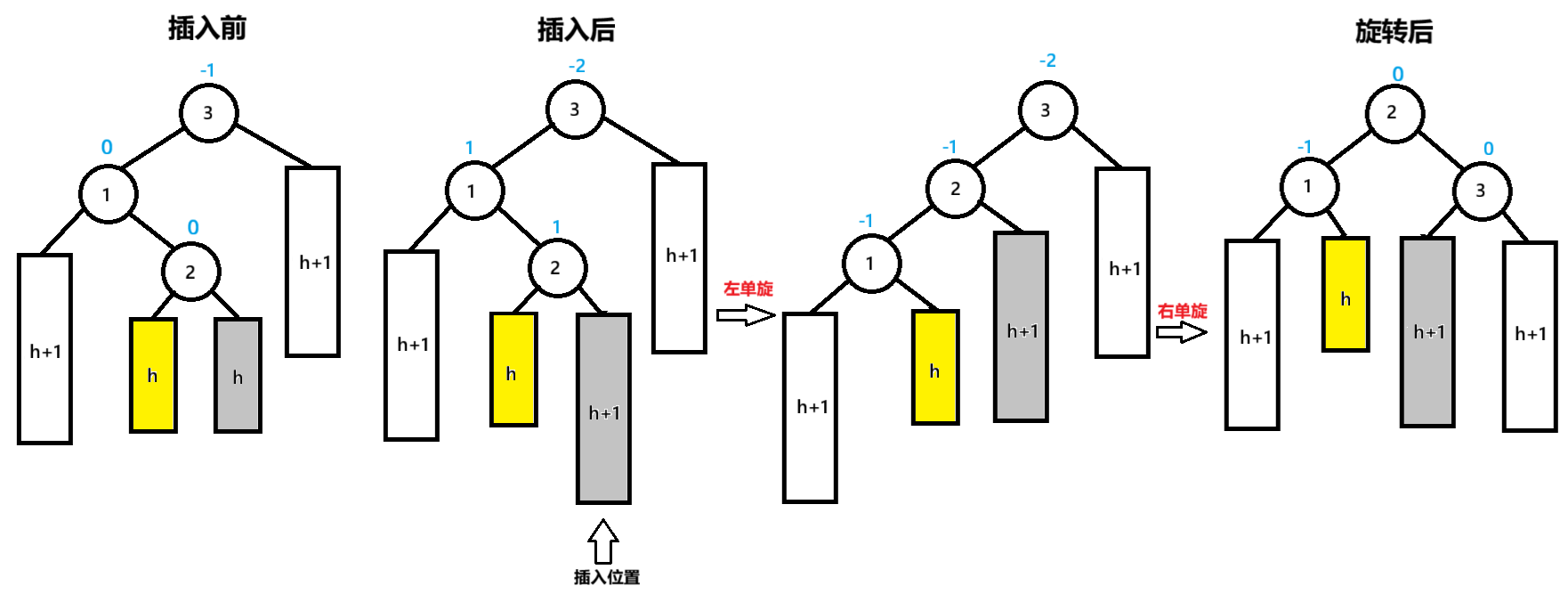
插入后,节点3为pParent,节点1为NodeL,节点2为NodeLR
先以节点NodeL为旋转点进行左单旋,节点3的bf=-2,未达到平衡再以节点pParent为旋转点进行右单旋,达到平衡
pParent的bf=0,NodeL的bf=-1,NodeLR的bf=0
5.AVL树的删除
这部分比较困难,不作讲解,请参考其他文献
源码:
包含测试用例以及打印函数,可直接执行
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
AVLTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr)
, _pRight(nullptr)
, _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _bf(0)
{}
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent;
T _data;
int _bf; // 节点的平衡因子
};
// AVL: 二叉搜索树 + 平衡因子的限制
template<class T>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
AVLTree()
: _pRoot(nullptr)
{}
void Display()
{
_Display(_pRoot);
}
// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
//根节点为空
if (_pRoot == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = new Node(data);
return true;
}
else
{
//根节点不为空
Node* cur = _pRoot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
//寻找插入位置
while (cur)
{
if (data < cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else if (data > cur->_data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else
{
cout << "数据冗余,插入" << data << "失败" << endl;
return false;
}
}
//找到了插入位置,插入
cur = new Node(data);
if (data < parent->_data)
{
parent->_pLeft = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_pRight = cur;
}
cur->_pParent = parent;
//修正平衡因子
while (parent)
{
if (cur == parent->_pLeft)
{
parent->_bf--;
}
else
{
parent->_bf++;
}
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
//无需向上调整
break;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
//继续向上调整
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
//右单旋
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
//左单旋
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
//左右双旋
RotateLR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
//右左双旋
RotateRL(parent);
}
break;
}
else
{
cout << "AVL树高度异常" << endl;
assert(false);
}
}
}
}
// AVL树的验证
bool IsAVLTree()
{
return _IsAVLTree(_pRoot);
}
private:
// 根据AVL树的概念验证pRoot是否为有效的AVL树
bool _IsAVLTree(Node* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
int HeightL = _Height(pRoot->_pLeft);
int HeightR = _Height(pRoot->_pRight);
int bf = HeightR - HeightL;
if (abs(bf) >= 2)
{
cout << "高度差异常" << endl;
return false;
}
else if (bf != pRoot->_bf)
{
cout << "平衡因子异常" << endl;
return false;
}
return _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pLeft) && _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pRight);
}
size_t _Height(Node* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
size_t LeftHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pLeft);
size_t RightHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pRight);
return (LeftHeight > RightHeight ? LeftHeight + 1 : RightHeight + 1);
}
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* NodeL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* NodeLR = NodeL->_pRight;
Node* pParentParent = pParent->_pParent;
//修正向下关系
pParent->_pLeft = NodeLR;
NodeL->_pRight = pParent;
//修正向上关系
pParent->_pParent = NodeL;
if (NodeLR)
{
NodeLR->_pParent = pParent;
}
//修正外部关系
if (pParentParent == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = NodeL;
NodeL->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParentParent->_pLeft == pParent)
{
pParentParent->_pLeft = NodeL;
}
else
{
pParentParent->_pRight = NodeL;
}
NodeL->_pParent = pParentParent;
}
//修正平衡因子
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeL->_bf = 0;
}
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* NodeR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* NodeRL = NodeR->_pLeft;
Node* pParentParent = pParent->_pParent;
//修正向下关系
pParent->_pRight = NodeRL;
NodeR->_pLeft = pParent;
//修正向上关系
pParent->_pParent = NodeR;
if (NodeRL)
{
NodeRL->_pParent = pParent;
}
//修正外部关系
if (pParentParent == nullptr)
{
_pRoot = NodeR;
NodeR->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParentParent->_pLeft == pParent)
{
pParentParent->_pLeft = NodeR;
}
else
{
pParentParent->_pRight = NodeR;
}
NodeR->_pParent = pParentParent;
}
//修正平衡因子
NodeR->_bf = 0;
pParent->_bf = 0;
}
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* NodeR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* NodeRL = NodeR->_pLeft;
int bf = NodeRL->_bf;
RotateR(NodeR);
RotateL(pParent);
//校正平衡因子
if (bf == 0)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeR->_bf = 0;
NodeRL->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = -1;
NodeR->_bf = 0;
NodeRL->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeR->_bf = 1;
NodeRL->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
// 左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* NodeL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* NodeLR = NodeL->_pRight;
int bf = NodeLR->_bf;
RotateL(NodeL);
RotateR(pParent);
//校正平衡因子
if (bf == 0)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeL->_bf = 0;
NodeLR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
NodeL->_bf = -1;
NodeLR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 1;
NodeL->_bf = 0;
NodeLR->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
void _Display(Node* ptr)
{
if (ptr == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Display(ptr->_pLeft);
cout << ptr->_data << ":" << ptr->_bf << " ";
_Display(ptr->_pRight);
}
private:
Node* _pRoot;
};
void Test()
{
AVLTree<int> tree1;
//常规测试
//int a[] = { 1, 2, 3};
//int a[] = {3, 2, 1};
int a[] = {16, 15, 14, 17, 18, 13, 19, 20};
//带双旋的测试
//int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
for (auto num : a)
{
tree1.Insert(num);
}
tree1.Display();
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}