1、计算器实现思路
我们日常写的计算表达式都是中缀表达式,也就是运算符在中间,运算数在两边,但是直接读取无法马上进行计算,因为一个计算表达式还涉及运算符优先级的问题。比如:1-2*(3-4)+5 中遇到-和*都无法运算,因为后面还有括号,优先级更高。
所以其中一种实现思路就是把中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式 ,也就是分析计算表达式的优先级,将运算数放在前面,运算符放到运算数后面,然后我们依次读取后缀表达式,遇到运算符就可以进行计算了。后缀表达式也被称为逆波兰表达式(Reverse Polish Notation,RPN)
2、后缀表达式进行运算
https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/submissions/671060134
后缀表达式因为已经确定好了优先级,运算方式非常简单,就是遇到运算符时,取前面两个运算数进行运算,因为经过中缀转后缀,优先级已经确立好了。
建立一个栈存储运算数,读取后缀表达式,遇到运算数入栈 ;遇到运算符,出栈顶的两个数据进行运算,运算后将结果作为一个运算数入栈,继续参与下一次运算。读取表达式结束之后,最后栈里面的值就是运算结果。
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens)
{
stack<int> st;
for(auto& str : tokens)
{
//str为数字
if((str != "+") && (str != "-") && (str != "*") && (str != "/"))
{
st.push(stoi(str));
}
else
{
//str为操作符
int right = st.top();
st.pop();
int left = st.top();
st.pop();
switch(str[0])
{
case '+' :
st.push(left + right);
break;
case '-' :
st.push(left - right);
break;
case '*' :
st.push(left * right);
break;
case '/' :
st.push(left / right);
break;
}
}
}
return st.top();
}
};3、中缀表达式转后缀表达式
依次读取计算表达式中的值,遇到运算数直接输出。
建立一个栈存储运算符,利用栈后进先出的性质,遇到后面的运算符,出栈里面存的前面运算符进行比较,确定优先级。
遇到运算符,如果栈为空 或者 栈不为空并且当前运算符比栈顶运算符优先级高,则当前运算符入栈。因为如果栈里面存储的是前一个运算符,当前运算符比前一个运算符优先级高,说明前一个不能运算,当前运算符也不能运算,因为后面可能还有更高优先级的运算符。
遇到运算符,如果栈不为空并且当前运算符比栈顶运算符优先级低,说明栈顶的运算符可以运算了,则输出栈顶运算符,当前运算符继续走前面遇到运算符的逻辑。
如果遇到(),则把括号的计算表达式当成一个子表达式,跟上面思路类似,进行递归处理子表达式,处理后转换出的后缀表达式加在前面表达式的后面即可。
计算表达式或者()中子表达式结束值,输出栈中所有运算符。
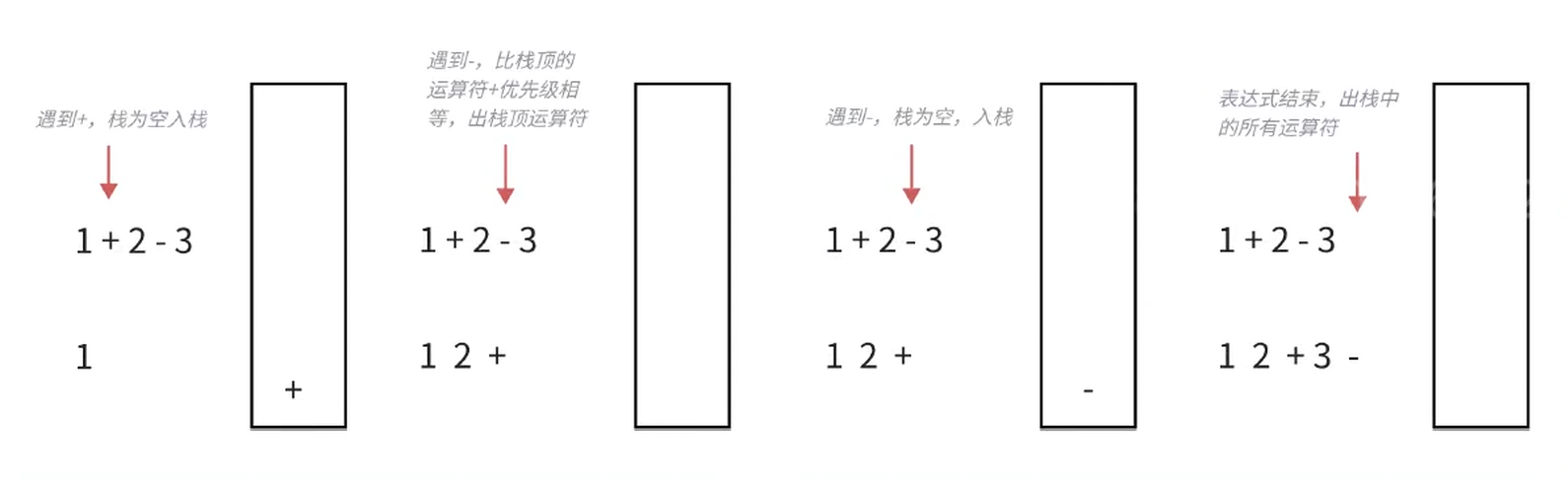 示例1
示例1 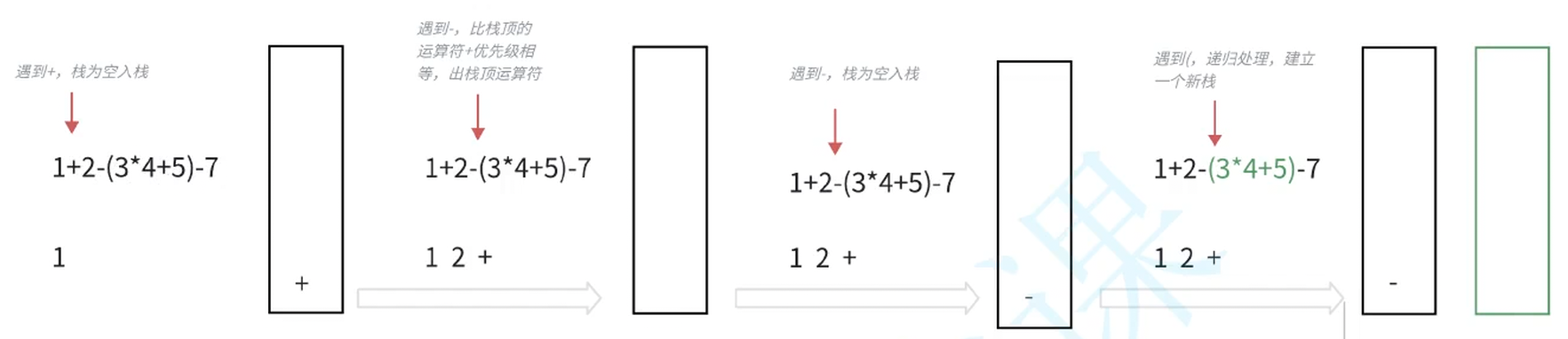 示例2 ①
示例2 ① 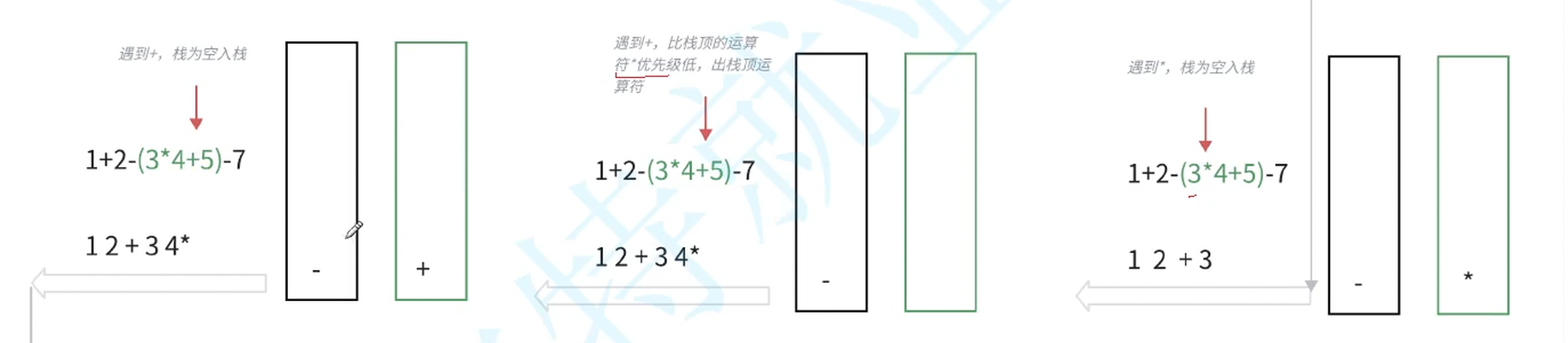 示例2 ②
示例2 ② 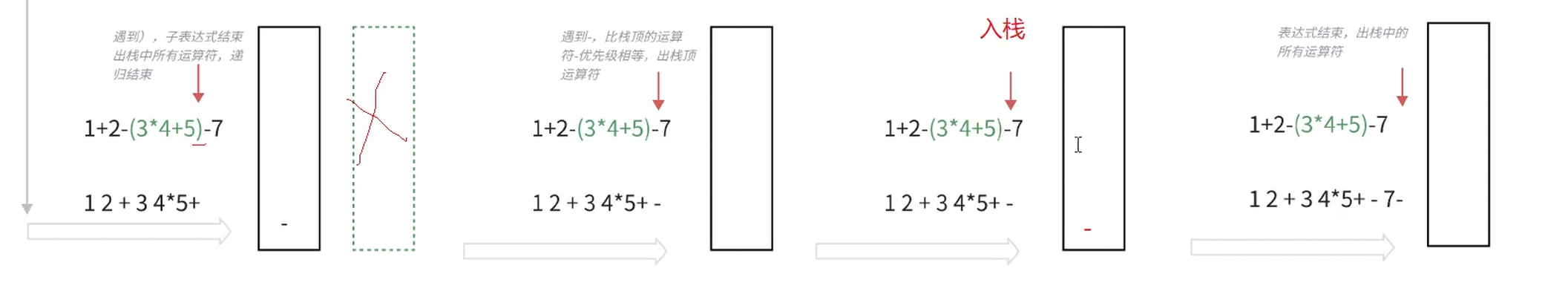 示例2 ③
示例2 ③
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
map<char, int> operatorPrecedence = {{'+',1}, {'-',1}, {'*',2}, {'/',2}};
//中缀转后缀
void toRPN(const string& s, size_t& i, vector<string>& v)
{
stack<char> st;
while(i < s.size())
{
if(isdigit(s[i]))
{
// 操作数直接输出
string num;
while(i < s.size() && isdigit(s[i]))
{
num += s[i];
++i;
}
v.push_back(num);
}
else if(s[i] == '(')
{
// 子表达式,递归处理即可
++i;
toRPN(s, i, v);
}
else if(s[i] == ')')
{
// 子表达式结束
// 输出栈里面的剩余运算符
while(!st.empty())
{
v.push_back(string(1, st.top()));
st.pop();
}
++i;
return;
}
else
{
// 运算符
if(st.empty() || (operatorPrecedence[st.top()] < operatorPrecedence[s[i]]))
{
st.push(s[i]);
++i;
}
else
{
char op = st.top();
st.pop();
v.push_back(string(1, op));
}
}
}
// 表达式结束
// 输出栈里面的剩余运算符
while(!st.empty())
{
v.push_back(string(1, st.top()));
st.pop();
}
}
};4、计算器的实现
https://leetcode.cn/problems/basic-calculator
有了上面两个部分,计算器OJ的大部分问题就解决了,但是这里还有一些问题需要处理。因为OJ中给的中缀表达式是字符串,且字符串中包含空格,需要去掉空格。
cpp
int calculate(string s)
{
//去掉空格
string news;
for(auto& ch : s)
{
if(ch != ' ')
{
news += ch;
}
}
size_t i = 0;
vector<string> v;
toRPN(news, i, v);
return evalRPN(v);
}那是不是这样就行了呢?提交代码之后,提示我们有测试样例未通过。
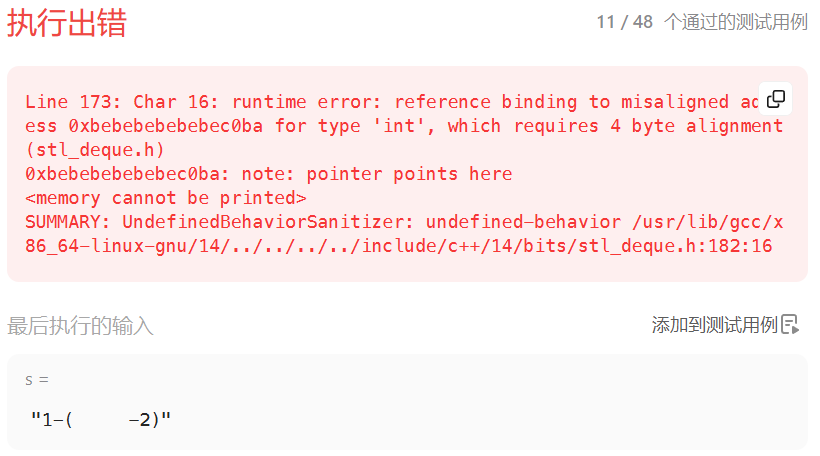
可以发现,这里还需要区分负数和减号。如果是减号的话,那么前面一个是操作数;如果是负号的话,前面一个是操作符。我们需要将所有的负数-x 转换为 0-x。
cpp
int calculate(string s)
{
//去掉空格
string news;
for(auto& ch : s)
{
if(ch != ' ')
{
news += ch;
}
}
//处理负数
news.swap(s);
news.clear();
for(size_t i = 0;i < s.size();i++)
{
if(s[i] == '-' && !isdigit(s[i - 1]))
{
news += "0-";
}
else
{
news += s[i];
}
}
size_t i = 0;
vector<string> v;
toRPN(news, i, v);
return evalRPN(v);
}提交之后发现仍然有测试样例不通过。
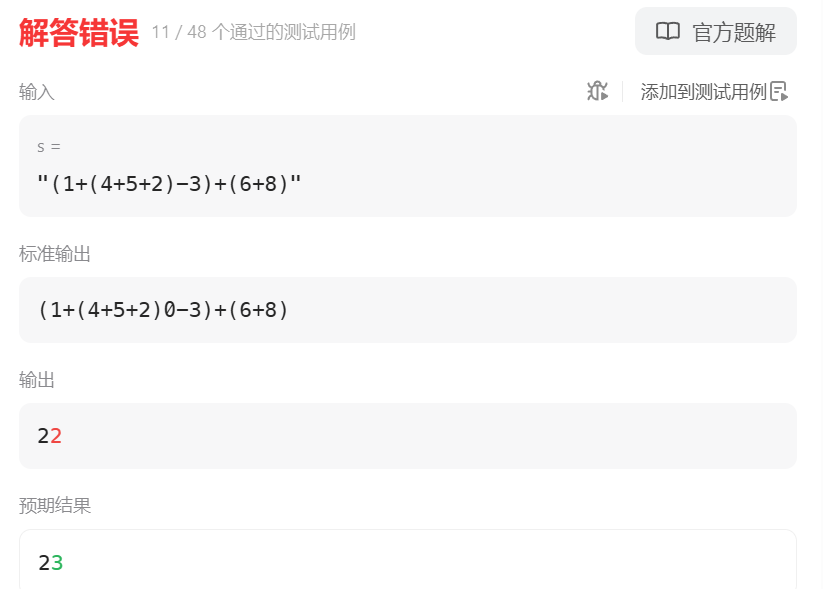
说明我们判断条件是不够的,还需要判断减号前面是不是右括号。
cpp
int calculate(string s)
{
//去掉空格
string news;
for(auto& ch : s)
{
if(ch != ' ')
{
news += ch;
}
}
//处理负数
news.swap(s);
news.clear();
for(size_t i = 0;i < s.size();i++)
{
if(s[i] == '-' && (!isdigit(s[i - 1]) && s[i - 1] != ')'))
{
news += "0-";
}
else
{
news += s[i];
}
}
size_t i = 0;
vector<string> v;
toRPN(news, i, v);
return evalRPN(v);
}再提交一下。。。
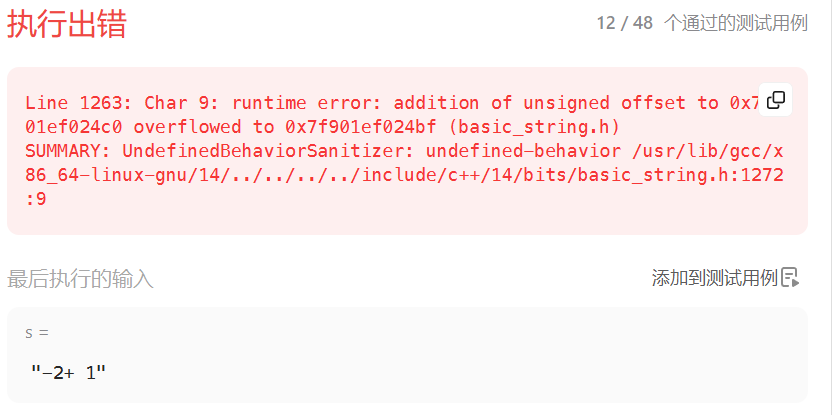
又有测试样例崩溃了,因为这里是s[0]的位置出现-号,因此s[i-1]就会越界。所以这个地方还要加一个条件。
完整题解代码如下:
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens)
{
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 0;i < tokens.size();i++)
{
string& str = tokens[i];
if((str != "+") && (str != "-") && (str != "*") && (str != "/"))
{
st.push(stoi(str));
}
else
{
int right = st.top();
st.pop();
int left = st.top();
st.pop();
switch(str[0])
{
case '+':
st.push(left + right);
break;
case '-':
st.push(left - right);
break;
case '*':
st.push(left * right);
break;
case '/':
st.push(left / right);
break;
}
}
}
return st.top();
}
map<char, int> operatorPrecedence = { {'+',1},{'-',1},{'*',2},{'/',2} };
//中缀转后缀
void toRPN(const string& s, size_t& i, vector<string>& v)
{
stack<char> st;
while (i < s.size())
{
//操作数直接输出
if (isdigit(s[i]))
{
string num;
while (i < s.size() && isdigit(s[i]))
{
num += s[i];
i++;
}
v.push_back(num);
}
else if (s[i] == '(')
{
//子表达式,递归处理即可
i++;
toRPN(s, i, v);
}
else if (s[i] == ')')
{
//子表达式结束
//输出栈里面的剩余运算符
while (!st.empty())
{
v.push_back(string(1, st.top()));
st.pop();
}
i++;
return;
}
else
{
//运算符
if (st.empty() || operatorPrecedence[s[i]] > operatorPrecedence[st.top()])
{
st.push(s[i]);
i++;
}
else
{
char op = st.top();
st.pop();
v.push_back(string(1, op));
}
}
}
//表达式结束
//输出栈里面的剩余运算符
while (!st.empty())
{
v.push_back(string(1, st.top()));
st.pop();
}
}
int calculate(string s)
{
//去掉空格
string news;
for(auto& ch : s)
{
if(ch != ' ')
{
news += ch;
}
}
//处理负数
news.swap(s);
news.clear();
for(size_t i = 0;i < s.size();i++)
{
if(s[i] == '-' && (i == 0 || (!isdigit(s[i - 1]) && s[i - 1] != ')')))
{
news += "0-";
}
else
{
news += s[i];
}
}
size_t i = 0;
vector<string> v;
toRPN(news, i, v);
return evalRPN(v);
}
};5、其他实现思路

其实一句话就可以解析:就是去括号的思路,比如1-(1+2)=1-1-2,有乘法和除法类似,比考虑中缀转后缀的思路简单。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int calculate(string s)
{
stack<int> ops;
ops.push(1);
int sign = 1;
int ret = 0;
int n = s.length();
int i = 0;
while (i < n)
{
if (s[i] == ' ')
{
i++;
}
else if (s[i] == '+')
{
sign = ops.top();
i++;
}
else if (s[i] == '-')
{
sign = -ops.top();
i++;
}
else if (s[i] == '(')
{
ops.push(sign);
i++;
}
else if (s[i] == ')')
{
ops.pop();
i++;
}
else
{
long num = 0;
while (i < n && s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9')
{
num = num * 10 + s[i] - '0';
i++;
}
ret += sign * num;
}
}
return ret;
}
};https://leetcode.cn/problems/basic-calculator-ii

cpp
class Solution {
public:
int calculate(string s)
{
vector<int> stk;
char preSign = '+';
int num = 0;
int n = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (isdigit(s[i]))
{
num = num * 10 + int(s[i] - '0');
}
if (!isdigit(s[i]) && s[i] != ' ' || i == n - 1)
{
switch (preSign)
{
case '+':
stk.push_back(num);
break;
case '-':
stk.push_back(-num);
break;
case '*':
stk.back() *= num;
break;
default:
stk.back() /= num;
}
preSign = s[i];
num = 0;
}
}
return accumulate(stk.begin(), stk.end(), 0);
}
};