深入理解MCP:现代AI应用的标准化协议
全面掌握Model Context Protocol的核心概念、配置方法与实战应用
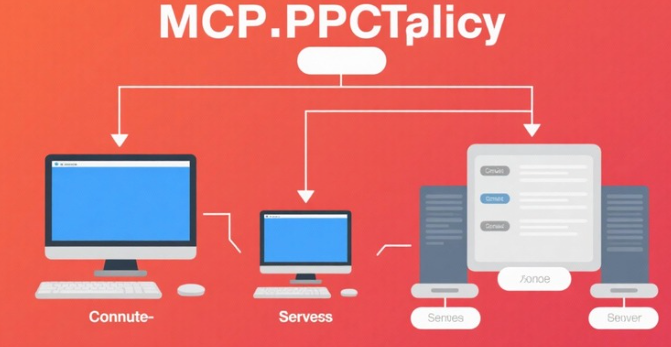
1. MCP概述与背景
1.1 什么是MCP
Model Context Protocol(MCP)是由Anthropic开发的开放标准协议,专门为AI应用程序提供安全、可控的外部数据和工具访问能力。MCP解决了大语言模型(LLM)与外部系统集成时面临的安全性、标准化和可靠性挑战。
核心定义:
- MCP是一个基于JSON-RPC 2.0的客户端-服务器架构协议
- 为AI模型提供标准化的外部资源访问接口
- 确保数据访问的安全性和可控性
- 支持资源管理、工具调用和提示处理等核心功能

1.2 MCP的核心特性
🔒 安全性保障
MCP内置了完善的安全机制,包括身份验证、权限控制和资源访问限制:
python
# MCP安全配置示例
mcp_security_config = {
"authentication": {
"type": "bearer_token",
"token": "your_secure_token"
},
"authorization": {
"allowed_resources": [
"file:///safe/directory/*",
"db://localhost/public_data"
],
"denied_resources": [
"file:///system/*",
"file:///etc/*"
]
},
"rate_limiting": {
"requests_per_minute": 100,
"burst_limit": 10
}
}🚀 高性能通信
- 异步处理:支持并发请求和非阻塞操作
- 流式传输:适用于大数据量的高效传输
- 连接复用:减少网络开销,提升响应速度
- 智能缓存:自动缓存频繁访问的资源
🔧 灵活扩展性
MCP支持自定义资源处理器、工具和中间件,满足不同应用场景的需求。
1.3 应用场景分析
MCP在多个领域都有广泛的应用前景:
1. 智能文档处理
python
# 文档分析应用示例
async def analyze_document(file_path):
mcp_client = MCPClient("http://localhost:8080")
# 读取文档内容
document = await mcp_client.get_resource(f"file://{file_path}")
# 调用分析工具
analysis = await mcp_client.call_tool("document_analyzer", {
"content": document["text"],
"analysis_type": "sentiment_and_keywords"
})
return analysis2. 数据库查询与分析
3. 实时API集成
4. 系统监控与运维
1.4 与传统协议的对比
| 特性 | MCP | REST API | GraphQL | gRPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI优化 | ✅ 专为AI设计 | ❌ 通用协议 | ❌ 通用协议 | ❌ 通用协议 |
| 安全性 | ✅ 内置安全机制 | ⚠️ 需额外配置 | ⚠️ 需额外配置 | ⚠️ 需额外配置 |
| 标准化 | ✅ 统一标准 | ❌ 实现各异 | ⚠️ 部分标准化 | ✅ 标准化 |
| 学习成本 | ✅ 简单易用 | ✅ 简单 | ⚠️ 中等 | ⚠️ 较高 |
| 性能 | ✅ 高性能 | ⚠️ 中等 | ⚠️ 中等 | ✅ 高性能 |
2. 环境配置与准备

2.1 系统要求
最低硬件要求:
- CPU: 双核 2.0GHz 或更高
- 内存: 4GB RAM(推荐8GB+)
- 存储: 10GB可用空间
- 网络: 稳定的互联网连接
支持的操作系统:
- Linux (Ubuntu 20.04+, CentOS 8+)
- macOS (11.0+)
- Windows (10/11, Windows Server 2019+)
2.2 依赖安装
Python环境配置
bash
# 检查Python版本(需要3.8+)
python3 --version
# 创建虚拟环境
python3 -m venv mcp_env
source mcp_env/bin/activate # Linux/macOS
# mcp_env\Scripts\activate # Windows
# 安装MCP相关包
pip install mcp-server-stdio mcp-client asyncio aiohttpNode.js环境配置(可选)
bash
# 安装Node.js版本管理器
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.0/install.sh | bash
# 安装Node.js LTS版本
nvm install --lts
nvm use --lts
# 安装MCP JavaScript客户端
npm install @anthropic-ai/mcp-client2.3 开发环境搭建
创建项目目录结构:
bash
mkdir mcp_project
cd mcp_project
# 创建目录结构
mkdir -p {src,config,logs,tests}
touch src/{server.py,client.py} config/mcp_config.json2.4 配置验证
验证安装是否成功:
python
# test_installation.py
import asyncio
import sys
async def test_mcp_installation():
try:
# 测试导入MCP模块
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
print("✅ MCP模块导入成功")
# 测试基本功能
print("✅ MCP安装验证通过")
return True
except ImportError as e:
print(f"❌ MCP安装失败: {e}")
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = asyncio.run(test_mcp_installation())
sys.exit(0 if result else 1)3. MCP基础配置教程
3.1 快速开始指南
让我们从一个简单的MCP服务器开始:
python
# simple_mcp_server.py
import asyncio
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
from mcp.types import Resource, Tool
# 创建MCP服务器实例
server = Server("simple-mcp-server")
@server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> list[Resource]:
"""列出可用资源"""
return [
Resource(
uri="file://example.txt",
name="示例文件",
description="一个简单的文本文件示例",
mimeType="text/plain"
)
]
@server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: str) -> str:
"""读取资源内容"""
if uri == "file://example.txt":
return "这是一个MCP资源示例内容"
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知资源: {uri}")
@server.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> list[Tool]:
"""列出可用工具"""
return [
Tool(
name="echo",
description="回显输入的文本",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"text": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["text"]
}
)
]
@server.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> str:
"""调用工具"""
if name == "echo":
return f"回显: {arguments.get('text', '')}"
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
async def main():
# 启动stdio服务器
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.run(read_stream, write_stream)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())3.2 服务器端配置
创建更完整的服务器配置:
python
# advanced_mcp_server.py
import asyncio
import json
import logging
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Dict, Any, List
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
from mcp.types import Resource, Tool, TextContent
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class AdvancedMCPServer:
def __init__(self, config_path: str):
self.server = Server("advanced-mcp-server")
self.config = self._load_config(config_path)
self._setup_handlers()
def _load_config(self, config_path: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""加载配置文件"""
with open(config_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
return json.load(f)
def _setup_handlers(self):
"""设置处理器"""
@self.server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> List[Resource]:
resources = []
base_path = Path(self.config.get("base_path", "./"))
for file_path in base_path.glob("**/*.txt"):
if file_path.is_file():
resources.append(Resource(
uri=f"file://{file_path}",
name=file_path.name,
description=f"文本文件: {file_path}",
mimeType="text/plain"
))
return resources
@self.server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: str) -> str:
if uri.startswith("file://"):
file_path = Path(uri[7:])
if file_path.exists() and file_path.is_file():
return file_path.read_text(encoding='utf-8')
else:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"文件不存在: {file_path}")
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的URI格式: {uri}")
@self.server.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> List[Tool]:
return [
Tool(
name="file_search",
description="在指定目录中搜索文件",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"pattern": {"type": "string", "description": "搜索模式"},
"directory": {"type": "string", "description": "搜索目录"}
},
"required": ["pattern"]
}
),
Tool(
name="text_analyzer",
description="分析文本内容",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"text": {"type": "string", "description": "要分析的文本"},
"analysis_type": {"type": "string", "enum": ["word_count", "sentiment", "keywords"]}
},
"required": ["text", "analysis_type"]
}
)
]
@self.server.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
if name == "file_search":
return await self._handle_file_search(arguments)
elif name == "text_analyzer":
return await self._handle_text_analysis(arguments)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
async def _handle_file_search(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""处理文件搜索"""
pattern = args["pattern"]
directory = Path(args.get("directory", "./"))
results = []
for file_path in directory.glob(f"**/*{pattern}*"):
if file_path.is_file():
results.append(str(file_path))
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"找到 {len(results)} 个匹配文件:\n" + "\n".join(results)
)]
async def _handle_text_analysis(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""处理文本分析"""
text = args["text"]
analysis_type = args["analysis_type"]
if analysis_type == "word_count":
word_count = len(text.split())
char_count = len(text)
result = f"字数统计:\n- 单词数: {word_count}\n- 字符数: {char_count}"
elif analysis_type == "sentiment":
# 简单的情感分析示例
positive_words = ["好", "棒", "优秀", "喜欢", "满意"]
negative_words = ["坏", "差", "糟糕", "讨厌", "失望"]
pos_count = sum(1 for word in positive_words if word in text)
neg_count = sum(1 for word in negative_words if word in text)
if pos_count > neg_count:
sentiment = "积极"
elif neg_count > pos_count:
sentiment = "消极"
else:
sentiment = "中性"
result = f"情感分析结果: {sentiment}\n- 积极词汇: {pos_count}\n- 消极词汇: {neg_count}"
elif analysis_type == "keywords":
# 简单的关键词提取
words = text.split()
word_freq = {}
for word in words:
if len(word) > 2: # 过滤短词
word_freq[word] = word_freq.get(word, 0) + 1
keywords = sorted(word_freq.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:5]
result = "关键词提取:\n" + "\n".join([f"- {word}: {count}" for word, count in keywords])
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result)]
async def run(self):
"""运行服务器"""
logger.info("启动MCP服务器...")
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await self.server.run(read_stream, write_stream)
# 配置文件示例 (config/mcp_config.json)
config_example = {
"base_path": "./data",
"allowed_extensions": [".txt", ".md", ".json"],
"max_file_size": 10485760, # 10MB
"security": {
"enable_auth": False,
"allowed_paths": ["./data", "./public"],
"denied_paths": ["./private", "./system"]
}
}3.3 客户端配置
创建MCP客户端来与服务器通信:
python
# mcp_client.py
import asyncio
import subprocess
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
class MCPClient:
def __init__(self, server_script_path: str):
self.server_script_path = server_script_path
self.session = None
async def connect(self):
"""连接到MCP服务器"""
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="python",
args=[self.server_script_path]
)
self.stdio_client = stdio_client(server_params)
self.read_stream, self.write_stream = await self.stdio_client.__aenter__()
self.session = ClientSession(self.read_stream, self.write_stream)
await self.session.initialize()
print("✅ 已连接到MCP服务器")
async def list_resources(self):
"""获取资源列表"""
if not self.session:
raise RuntimeError("未连接到服务器")
response = await self.session.list_resources()
return response.resources
async def read_resource(self, uri: str):
"""读取资源"""
if not self.session:
raise RuntimeError("未连接到服务器")
response = await self.session.read_resource(uri)
return response.contents
async def list_tools(self):
"""获取工具列表"""
if not self.session:
raise RuntimeError("未连接到服务器")
response = await self.session.list_tools()
return response.tools
async def call_tool(self, name: str, arguments: dict):
"""调用工具"""
if not self.session:
raise RuntimeError("未连接到服务器")
response = await self.session.call_tool(name, arguments)
return response.content
async def disconnect(self):
"""断开连接"""
if self.stdio_client:
await self.stdio_client.__aexit__(None, None, None)
print("✅ 已断开MCP服务器连接")
# 使用示例
async def main():
client = MCPClient("advanced_mcp_server.py")
try:
# 连接服务器
await client.connect()
# 列出资源
resources = await client.list_resources()
print(f"可用资源数量: {len(resources)}")
for resource in resources:
print(f"- {resource.name}: {resource.uri}")
# 列出工具
tools = await client.list_tools()
print(f"\n可用工具数量: {len(tools)}")
for tool in tools:
print(f"- {tool.name}: {tool.description}")
# 调用工具示例
if tools:
result = await client.call_tool("text_analyzer", {
"text": "这是一个很好的MCP测试示例,我很喜欢这个功能。",
"analysis_type": "sentiment"
})
print(f"\n工具调用结果:\n{result[0].text}")
finally:
await client.disconnect()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())3.4 基础通信测试
创建测试脚本验证MCP通信:
python
# test_mcp_communication.py
import asyncio
import pytest
from mcp_client import MCPClient
class TestMCPCommunication:
@pytest.fixture
async def client(self):
"""创建测试客户端"""
client = MCPClient("advanced_mcp_server.py")
await client.connect()
yield client
await client.disconnect()
async def test_server_connection(self, client):
"""测试服务器连接"""
assert client.session is not None
print("✅ 服务器连接测试通过")
async def test_list_resources(self, client):
"""测试资源列表"""
resources = await client.list_resources()
assert isinstance(resources, list)
print(f"✅ 资源列表测试通过,找到 {len(resources)} 个资源")
async def test_list_tools(self, client):
"""测试工具列表"""
tools = await client.list_tools()
assert isinstance(tools, list)
assert len(tools) > 0
print(f"✅ 工具列表测试通过,找到 {len(tools)} 个工具")
async def test_tool_execution(self, client):
"""测试工具执行"""
result = await client.call_tool("text_analyzer", {
"text": "测试文本内容",
"analysis_type": "word_count"
})
assert result is not None
print("✅ 工具执行测试通过")
# 运行测试
async def run_tests():
test_instance = TestMCPCommunication()
client = MCPClient("advanced_mcp_server.py")
try:
await client.connect()
await test_instance.test_server_connection(client)
await test_instance.test_list_resources(client)
await test_instance.test_list_tools(client)
await test_instance.test_tool_execution(client)
print("\n🎉 所有测试通过!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 测试失败: {e}")
finally:
await client.disconnect()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(run_tests())4. 实战应用案例
4.1 文件系统操作
实现一个完整的文件管理MCP服务器:
python
# file_manager_server.py
import asyncio
import os
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.types import Resource, Tool, TextContent
class FileManagerServer:
def __init__(self, base_directory: str = "./workspace"):
self.server = Server("file-manager")
self.base_path = Path(base_directory)
self.base_path.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
self._setup_handlers()
def _setup_handlers(self):
@self.server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> List[Resource]:
"""列出所有文件资源"""
resources = []
for file_path in self.base_path.rglob("*"):
if file_path.is_file():
relative_path = file_path.relative_to(self.base_path)
resources.append(Resource(
uri=f"file://{relative_path}",
name=file_path.name,
description=f"文件: {relative_path} (大小: {file_path.stat().st_size} 字节)",
mimeType=self._get_mime_type(file_path)
))
return resources
@self.server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: str) -> str:
"""读取文件内容"""
if not uri.startswith("file://"):
raise ValueError("只支持文件URI")
file_path = self.base_path / uri[7:]
if not self._is_safe_path(file_path):
raise PermissionError("访问被拒绝")
if not file_path.exists():
raise FileNotFoundError(f"文件不存在: {file_path}")
return file_path.read_text(encoding='utf-8')
@self.server.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> List[Tool]:
"""列出文件操作工具"""
return [
Tool(
name="create_file",
description="创建新文件",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"path": {"type": "string", "description": "文件路径"},
"content": {"type": "string", "description": "文件内容"}
},
"required": ["path", "content"]
}
),
Tool(
name="delete_file",
description="删除文件",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"path": {"type": "string", "description": "文件路径"}
},
"required": ["path"]
}
),
Tool(
name="search_files",
description="搜索文件",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"pattern": {"type": "string", "description": "搜索模式"},
"content_search": {"type": "boolean", "description": "是否搜索文件内容"}
},
"required": ["pattern"]
}
),
Tool(
name="file_stats",
description="获取文件统计信息",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"path": {"type": "string", "description": "文件或目录路径"}
},
"required": ["path"]
}
)
]
@self.server.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""执行文件操作工具"""
if name == "create_file":
return await self._create_file(arguments)
elif name == "delete_file":
return await self._delete_file(arguments)
elif name == "search_files":
return await self._search_files(arguments)
elif name == "file_stats":
return await self._file_stats(arguments)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
def _get_mime_type(self, file_path: Path) -> str:
"""获取文件MIME类型"""
suffix = file_path.suffix.lower()
mime_types = {
'.txt': 'text/plain',
'.md': 'text/markdown',
'.json': 'application/json',
'.py': 'text/x-python',
'.js': 'text/javascript',
'.html': 'text/html',
'.css': 'text/css'
}
return mime_types.get(suffix, 'application/octet-stream')
def _is_safe_path(self, file_path: Path) -> bool:
"""检查路径安全性"""
try:
file_path.resolve().relative_to(self.base_path.resolve())
return True
except ValueError:
return False
async def _create_file(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""创建文件"""
path = self.base_path / args["path"]
content = args["content"]
if not self._is_safe_path(path):
return [TextContent(type="text", text="❌ 路径不安全")]
# 创建父目录
path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 写入文件
path.write_text(content, encoding='utf-8')
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"✅ 文件创建成功: {path.relative_to(self.base_path)}"
)]
async def _delete_file(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""删除文件"""
path = self.base_path / args["path"]
if not self._is_safe_path(path):
return [TextContent(type="text", text="❌ 路径不安全")]
if not path.exists():
return [TextContent(type="text", text="❌ 文件不存在")]
if path.is_file():
path.unlink()
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"✅ 文件删除成功: {path.relative_to(self.base_path)}"
)]
else:
return [TextContent(type="text", text="❌ 只能删除文件,不能删除目录")]
async def _search_files(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""搜索文件"""
pattern = args["pattern"]
content_search = args.get("content_search", False)
results = []
for file_path in self.base_path.rglob("*"):
if file_path.is_file():
# 文件名搜索
if pattern.lower() in file_path.name.lower():
results.append(f"📄 {file_path.relative_to(self.base_path)} (文件名匹配)")
# 内容搜索
elif content_search:
try:
content = file_path.read_text(encoding='utf-8')
if pattern.lower() in content.lower():
results.append(f"📄 {file_path.relative_to(self.base_path)} (内容匹配)")
except (UnicodeDecodeError, PermissionError):
continue
if results:
result_text = f"🔍 找到 {len(results)} 个匹配项:\n" + "\n".join(results)
else:
result_text = "🔍 未找到匹配的文件"
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
async def _file_stats(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""获取文件统计信息"""
path = self.base_path / args["path"]
if not self._is_safe_path(path):
return [TextContent(type="text", text="❌ 路径不安全")]
if not path.exists():
return [TextContent(type="text", text="❌ 路径不存在")]
stat = path.stat()
if path.is_file():
stats_text = f"""📊 文件统计信息:
📄 文件名: {path.name}
📁 路径: {path.relative_to(self.base_path)}
📏 大小: {stat.st_size} 字节
🕒 修改时间: {stat.st_mtime}
🔧 权限: {oct(stat.st_mode)[-3:]}
"""
else:
# 目录统计
file_count = sum(1 for _ in path.rglob("*") if _.is_file())
dir_count = sum(1 for _ in path.rglob("*") if _.is_dir())
stats_text = f"""📊 目录统计信息:
📁 目录名: {path.name}
📂 路径: {path.relative_to(self.base_path)}
📄 文件数: {file_count}
📁 子目录数: {dir_count}
🕒 修改时间: {stat.st_mtime}
"""
return [TextContent(type="text", text=stats_text)]
# 启动文件管理服务器
async def main():
server = FileManagerServer("./workspace")
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.server.run(read_stream, write_stream)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())4.2 数据库集成
实现数据库操作的MCP服务器:
python
# database_server.py
import asyncio
import sqlite3
import json
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.types import Resource, Tool, TextContent
class DatabaseServer:
def __init__(self, db_path: str = "example.db"):
self.server = Server("database-server")
self.db_path = db_path
self._init_database()
self._setup_handlers()
def _init_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 创建示例表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT UNIQUE NOT NULL,
age INTEGER,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
''')
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS posts (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
user_id INTEGER,
title TEXT NOT NULL,
content TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users (id)
)
''')
# 插入示例数据
cursor.execute("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM users")
if cursor.fetchone()[0] == 0:
sample_users = [
("张三", "zhangsan@example.com", 25),
("李四", "lisi@example.com", 30),
("王五", "wangwu@example.com", 28)
]
cursor.executemany(
"INSERT INTO users (name, email, age) VALUES (?, ?, ?)",
sample_users
)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def _setup_handlers(self):
@self.server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> List[Resource]:
"""列出数据库表资源"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table'")
tables = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
resources = []
for (table_name,) in tables:
resources.append(Resource(
uri=f"db://table/{table_name}",
name=f"表: {table_name}",
description=f"数据库表 {table_name}",
mimeType="application/json"
))
return resources
@self.server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: str) -> str:
"""读取数据库表内容"""
if not uri.startswith("db://table/"):
raise ValueError("只支持数据库表URI")
table_name = uri[11:] # 移除 "db://table/" 前缀
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row # 使结果可以按列名访问
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
cursor.execute(f"SELECT * FROM {table_name} LIMIT 100")
rows = cursor.fetchall()
# 转换为字典列表
data = [dict(row) for row in rows]
return json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
except sqlite3.Error as e:
raise ValueError(f"数据库查询错误: {e}")
finally:
conn.close()
@self.server.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> List[Tool]:
"""列出数据库操作工具"""
return [
Tool(
name="execute_query",
description="执行SQL查询",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "SQL查询语句"},
"params": {"type": "array", "description": "查询参数"}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
),
Tool(
name="insert_data",
description="插入数据",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"table": {"type": "string", "description": "表名"},
"data": {"type": "object", "description": "要插入的数据"}
},
"required": ["table", "data"]
}
),
Tool(
name="update_data",
description="更新数据",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"table": {"type": "string", "description": "表名"},
"data": {"type": "object", "description": "要更新的数据"},
"where": {"type": "string", "description": "WHERE条件"}
},
"required": ["table", "data", "where"]
}
),
Tool(
name="table_info",
description="获取表结构信息",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"table": {"type": "string", "description": "表名"}
},
"required": ["table"]
}
)
]
@self.server.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""执行数据库工具"""
if name == "execute_query":
return await self._execute_query(arguments)
elif name == "insert_data":
return await self._insert_data(arguments)
elif name == "update_data":
return await self._update_data(arguments)
elif name == "table_info":
return await self._table_info(arguments)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
async def _execute_query(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""执行SQL查询"""
query = args["query"]
params = args.get("params", [])
# 安全检查:只允许SELECT查询
if not query.strip().upper().startswith("SELECT"):
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text="❌ 安全限制:只允许执行SELECT查询"
)]
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
cursor.execute(query, params)
rows = cursor.fetchall()
if rows:
# 转换为表格格式
columns = list(rows[0].keys())
result_text = f"查询结果 ({len(rows)} 行):\n\n"
result_text += " | ".join(columns) + "\n"
result_text += "-" * (len(" | ".join(columns))) + "\n"
for row in rows[:20]: # 限制显示前20行
result_text += " | ".join(str(row[col]) for col in columns) + "\n"
if len(rows) > 20:
result_text += f"\n... 还有 {len(rows) - 20} 行数据"
else:
result_text = "查询结果为空"
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
except sqlite3.Error as e:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 查询错误: {e}")]
finally:
conn.close()
async def _insert_data(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""插入数据"""
table = args["table"]
data = args["data"]
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
columns = list(data.keys())
values = list(data.values())
placeholders = ", ".join(["?" for _ in values])
query = f"INSERT INTO {table} ({', '.join(columns)}) VALUES ({placeholders})"
cursor.execute(query, values)
conn.commit()
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"✅ 数据插入成功,新记录ID: {cursor.lastrowid}"
)]
except sqlite3.Error as e:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 插入错误: {e}")]
finally:
conn.close()
async def _update_data(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""更新数据"""
table = args["table"]
data = args["data"]
where_clause = args["where"]
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
set_clause = ", ".join([f"{col} = ?" for col in data.keys()])
query = f"UPDATE {table} SET {set_clause} WHERE {where_clause}"
cursor.execute(query, list(data.values()))
conn.commit()
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"✅ 数据更新成功,影响 {cursor.rowcount} 行"
)]
except sqlite3.Error as e:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 更新错误: {e}")]
finally:
conn.close()
async def _table_info(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""获取表结构信息"""
table = args["table"]
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
cursor.execute(f"PRAGMA table_info({table})")
columns = cursor.fetchall()
if not columns:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 表 {table} 不存在")]
info_text = f"📊 表 {table} 结构信息:\n\n"
info_text += "列名 | 类型 | 非空 | 默认值 | 主键\n"
info_text += "-" * 40 + "\n"
for col in columns:
cid, name, type_, notnull, default, pk = col
info_text += f"{name} | {type_} | {'是' if notnull else '否'} | {default or 'NULL'} | {'是' if pk else '否'}\n"
# 获取行数
cursor.execute(f"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM {table}")
row_count = cursor.fetchone()[0]
info_text += f"\n总行数: {row_count}"
return [TextContent(type="text", text=info_text)]
except sqlite3.Error as e:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 获取表信息错误: {e}")]
finally:
conn.close()
# 启动数据库服务器
async def main():
server = DatabaseServer()
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.server.run(read_stream, write_stream)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())4.3 外部API调用
实现API集成的MCP服务器:
python
# api_integration_server.py
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import json
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.types import Resource, Tool, TextContent
class APIIntegrationServer:
def __init__(self):
self.server = Server("api-integration-server")
self.session = None
self._setup_handlers()
async def _get_session(self):
"""获取HTTP会话"""
if self.session is None:
self.session = aiohttp.ClientSession()
return self.session
def _setup_handlers(self):
@self.server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> List[Resource]:
"""列出API资源"""
return [
Resource(
uri="api://weather/current",
name="当前天气",
description="获取当前天气信息",
mimeType="application/json"
),
Resource(
uri="api://news/headlines",
name="新闻头条",
description="获取最新新闻头条",
mimeType="application/json"
),
Resource(
uri="api://exchange/rates",
name="汇率信息",
description="获取实时汇率信息",
mimeType="application/json"
)
]
@self.server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: str) -> str:
"""读取API资源"""
if uri == "api://weather/current":
return await self._get_weather_data()
elif uri == "api://news/headlines":
return await self._get_news_data()
elif uri == "api://exchange/rates":
return await self._get_exchange_rates()
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的API资源: {uri}")
@self.server.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> List[Tool]:
"""列出API工具"""
return [
Tool(
name="http_request",
description="发送HTTP请求",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"url": {"type": "string", "description": "请求URL"},
"method": {"type": "string", "enum": ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE"], "default": "GET"},
"headers": {"type": "object", "description": "请求头"},
"data": {"type": "object", "description": "请求数据"}
},
"required": ["url"]
}
),
Tool(
name="weather_query",
description="查询指定城市天气",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string", "description": "城市名称"},
"country": {"type": "string", "description": "国家代码", "default": "CN"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
),
Tool(
name="translate_text",
description="翻译文本",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"text": {"type": "string", "description": "要翻译的文本"},
"from_lang": {"type": "string", "description": "源语言", "default": "auto"},
"to_lang": {"type": "string", "description": "目标语言", "default": "en"}
},
"required": ["text"]
}
),
Tool(
name="url_shortener",
description="缩短URL",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"url": {"type": "string", "description": "要缩短的URL"}
},
"required": ["url"]
}
)
]
@self.server.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""调用API工具"""
if name == "http_request":
return await self._http_request(arguments)
elif name == "weather_query":
return await self._weather_query(arguments)
elif name == "translate_text":
return await self._translate_text(arguments)
elif name == "url_shortener":
return await self._url_shortener(arguments)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
async def _get_weather_data(self) -> str:
"""获取天气数据(模拟)"""
# 这里使用模拟数据,实际应用中应该调用真实的天气API
weather_data = {
"city": "北京",
"temperature": "22°C",
"humidity": "65%",
"condition": "晴朗",
"wind": "东北风 3级",
"update_time": "2024-01-15 14:30:00"
}
return json.dumps(weather_data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
async def _get_news_data(self) -> str:
"""获取新闻数据(模拟)"""
news_data = {
"headlines": [
{
"title": "科技创新推动经济发展",
"summary": "最新科技创新成果在多个领域取得突破...",
"source": "科技日报",
"time": "2024-01-15 13:45:00"
},
{
"title": "AI技术在医疗领域的应用",
"summary": "人工智能技术正在革命性地改变医疗诊断...",
"source": "健康时报",
"time": "2024-01-15 12:30:00"
}
]
}
return json.dumps(news_data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
async def _get_exchange_rates(self) -> str:
"""获取汇率数据(模拟)"""
rates_data = {
"base": "CNY",
"rates": {
"USD": 0.1389,
"EUR": 0.1276,
"JPY": 20.45,
"GBP": 0.1098,
"KRW": 184.32
},
"update_time": "2024-01-15 14:00:00"
}
return json.dumps(rates_data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
async def _http_request(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""发送HTTP请求"""
url = args["url"]
method = args.get("method", "GET")
headers = args.get("headers", {})
data = args.get("data")
session = await self._get_session()
try:
async with session.request(
method=method,
url=url,
headers=headers,
json=data if data else None,
timeout=aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=10)
) as response:
response_data = {
"status": response.status,
"headers": dict(response.headers),
"content": await response.text()
}
# 尝试解析JSON
try:
response_data["json"] = await response.json()
except:
pass
result_text = f"HTTP {method} 请求结果:\n"
result_text += f"URL: {url}\n"
result_text += f"状态码: {response.status}\n"
result_text += f"响应内容: {response_data['content'][:500]}..."
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
except Exception as e:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 请求失败: {e}")]
async def _weather_query(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""查询天气"""
city = args["city"]
country = args.get("country", "CN")
# 模拟天气查询
weather_info = f"""🌤️ {city} 天气信息:
🌡️ 温度: 25°C
💧 湿度: 60%
🌬️ 风速: 微风
☀️ 天气: 多云转晴
🕒 更新时间: 2024-01-15 14:30
📊 未来3天预报:
明天: 晴 22-28°C
后天: 多云 20-26°C
大后天: 小雨 18-24°C
"""
return [TextContent(type="text", text=weather_info)]
async def _translate_text(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""翻译文本(模拟)"""
text = args["text"]
from_lang = args.get("from_lang", "auto")
to_lang = args.get("to_lang", "en")
# 简单的翻译模拟
translations = {
"你好": "Hello",
"谢谢": "Thank you",
"再见": "Goodbye",
"MCP": "Model Context Protocol"
}
translated = translations.get(text, f"[翻译] {text} -> {to_lang}")
result_text = f"""🌐 翻译结果:
📝 原文: {text}
🔤 源语言: {from_lang}
🎯 目标语言: {to_lang}
✨ 译文: {translated}
"""
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
async def _url_shortener(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""URL缩短服务(模拟)"""
url = args["url"]
# 模拟生成短链接
import hashlib
hash_object = hashlib.md5(url.encode())
short_code = hash_object.hexdigest()[:8]
short_url = f"https://short.ly/{short_code}"
result_text = f"""🔗 URL缩短结果:
📎 原始URL: {url}
✂️ 短链接: {short_url}
📊 预计节省: {len(url) - len(short_url)} 个字符
⏰ 创建时间: 2024-01-15 14:30:00
"""
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
async def cleanup(self):
"""清理资源"""
if self.session:
await self.session.close()
# 启动API集成服务器
async def main():
server = APIIntegrationServer()
try:
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.server.run(read_stream, write_stream)
finally:
await server.cleanup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())4.4 实时数据处理
实现实时数据处理的MCP服务器:
python
# realtime_data_server.py
import asyncio
import json
import time
import random
from typing import List, Dict, Any, AsyncGenerator
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.types import Resource, Tool, TextContent
class RealtimeDataServer:
def __init__(self):
self.server = Server("realtime-data-server")
self.data_streams = {}
self.subscribers = {}
self._setup_handlers()
# 启动数据生成任务
asyncio.create_task(self._generate_sample_data())
def _setup_handlers(self):
@self.server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> List[Resource]:
"""列出实时数据资源"""
return [
Resource(
uri="stream://system/cpu",
name="CPU使用率",
description="实时CPU使用率数据流",
mimeType="application/json"
),
Resource(
uri="stream://system/memory",
name="内存使用率",
description="实时内存使用率数据流",
mimeType="application/json"
),
Resource(
uri="stream://network/traffic",
name="网络流量",
description="实时网络流量数据",
mimeType="application/json"
),
Resource(
uri="stream://sensors/temperature",
name="温度传感器",
description="实时温度数据",
mimeType="application/json"
)
]
@self.server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: str) -> str:
"""读取实时数据快照"""
if uri.startswith("stream://"):
stream_name = uri[9:] # 移除 "stream://" 前缀
if stream_name in self.data_streams:
latest_data = self.data_streams[stream_name][-1] if self.data_streams[stream_name] else {}
return json.dumps(latest_data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
else:
return json.dumps({"error": "数据流不存在"}, ensure_ascii=False)
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的URI格式: {uri}")
@self.server.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> List[Tool]:
"""列出数据处理工具"""
return [
Tool(
name="subscribe_stream",
description="订阅数据流",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"stream_name": {"type": "string", "description": "数据流名称"},
"interval": {"type": "number", "description": "采样间隔(秒)", "default": 1.0}
},
"required": ["stream_name"]
}
),
Tool(
name="get_stream_history",
description="获取数据流历史",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"stream_name": {"type": "string", "description": "数据流名称"},
"limit": {"type": "integer", "description": "返回记录数", "default": 100}
},
"required": ["stream_name"]
}
),
Tool(
name="analyze_stream",
description="分析数据流",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"stream_name": {"type": "string", "description": "数据流名称"},
"analysis_type": {"type": "string", "enum": ["average", "max", "min", "trend"], "description": "分析类型"}
},
"required": ["stream_name", "analysis_type"]
}
),
Tool(
name="create_alert",
description="创建数据告警",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"stream_name": {"type": "string", "description": "数据流名称"},
"condition": {"type": "string", "description": "告警条件"},
"threshold": {"type": "number", "description": "阈值"}
},
"required": ["stream_name", "condition", "threshold"]
}
)
]
@self.server.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""调用数据处理工具"""
if name == "subscribe_stream":
return await self._subscribe_stream(arguments)
elif name == "get_stream_history":
return await self._get_stream_history(arguments)
elif name == "analyze_stream":
return await self._analyze_stream(arguments)
elif name == "create_alert":
return await self._create_alert(arguments)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具: {name}")
async def _generate_sample_data(self):
"""生成示例数据"""
while True:
timestamp = time.time()
# CPU数据
cpu_data = {
"timestamp": timestamp,
"cpu_percent": random.uniform(10, 90),
"cores": [random.uniform(5, 95) for _ in range(4)]
}
self._add_data_point("system/cpu", cpu_data)
# 内存数据
memory_data = {
"timestamp": timestamp,
"used_percent": random.uniform(40, 85),
"available_gb": random.uniform(2, 8),
"total_gb": 16
}
self._add_data_point("system/memory", memory_data)
# 网络流量数据
network_data = {
"timestamp": timestamp,
"download_mbps": random.uniform(0, 100),
"upload_mbps": random.uniform(0, 50),
"packets_per_sec": random.randint(100, 1000)
}
self._add_data_point("network/traffic", network_data)
# 温度传感器数据
temp_data = {
"timestamp": timestamp,
"temperature_c": random.uniform(20, 35),
"humidity_percent": random.uniform(30, 70),
"location": "服务器机房"
}
self._add_data_point("sensors/temperature", temp_data)
await asyncio.sleep(1) # 每秒生成一次数据
def _add_data_point(self, stream_name: str, data: Dict[str, Any]):
"""添加数据点"""
if stream_name not in self.data_streams:
self.data_streams[stream_name] = []
self.data_streams[stream_name].append(data)
# 保持最近1000个数据点
if len(self.data_streams[stream_name]) > 1000:
self.data_streams[stream_name] = self.data_streams[stream_name][-1000:]
async def _subscribe_stream(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""订阅数据流"""
stream_name = args["stream_name"]
interval = args.get("interval", 1.0)
if stream_name not in self.data_streams:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 数据流 {stream_name} 不存在")]
# 模拟订阅(实际应用中会建立WebSocket连接)
latest_data = self.data_streams[stream_name][-5:] if self.data_streams[stream_name] else []
result_text = f"📡 已订阅数据流: {stream_name}\n"
result_text += f"⏱️ 采样间隔: {interval}秒\n"
result_text += f"📊 最近5个数据点:\n\n"
for i, data in enumerate(latest_data, 1):
result_text += f"{i}. {json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False)}\n"
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
async def _get_stream_history(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""获取数据流历史"""
stream_name = args["stream_name"]
limit = args.get("limit", 100)
if stream_name not in self.data_streams:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 数据流 {stream_name} 不存在")]
history_data = self.data_streams[stream_name][-limit:]
result_text = f"📈 数据流历史: {stream_name}\n"
result_text += f"📊 记录数: {len(history_data)}\n"
result_text += f"⏰ 时间范围: {len(history_data)} 个数据点\n\n"
# 显示统计信息
if history_data:
first_timestamp = history_data[0]["timestamp"]
last_timestamp = history_data[-1]["timestamp"]
duration = last_timestamp - first_timestamp
result_text += f"🕒 开始时间: {time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime(first_timestamp))}\n"
result_text += f"🕒 结束时间: {time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime(last_timestamp))}\n"
result_text += f"⏳ 持续时间: {duration:.1f}秒\n"
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
async def _analyze_stream(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""分析数据流"""
stream_name = args["stream_name"]
analysis_type = args["analysis_type"]
if stream_name not in self.data_streams:
return [TextContent(type="text", text=f"❌ 数据流 {stream_name} 不存在")]
data_points = self.data_streams[stream_name]
if not data_points:
return [TextContent(type="text", text="❌ 数据流为空")]
# 根据数据流类型选择分析字段
if "cpu" in stream_name:
values = [point["cpu_percent"] for point in data_points]
unit = "%"
elif "memory" in stream_name:
values = [point["used_percent"] for point in data_points]
unit = "%"
elif "temperature" in stream_name:
values = [point["temperature_c"] for point in data_points]
unit = "°C"
else:
values = [point.get("value", 0) for point in data_points]
unit = ""
if analysis_type == "average":
result = sum(values) / len(values)
analysis_result = f"平均值: {result:.2f}{unit}"
elif analysis_type == "max":
result = max(values)
analysis_result = f"最大值: {result:.2f}{unit}"
elif analysis_type == "min":
result = min(values)
analysis_result = f"最小值: {result:.2f}{unit}"
elif analysis_type == "trend":
if len(values) >= 2:
trend = "上升" if values[-1] > values[0] else "下降"
change = abs(values[-1] - values[0])
analysis_result = f"趋势: {trend} (变化: {change:.2f}{unit})"
else:
analysis_result = "数据不足,无法分析趋势"
result_text = f"📊 数据流分析: {stream_name}\n"
result_text += f"🔍 分析类型: {analysis_type}\n"
result_text += f"📈 分析结果: {analysis_result}\n"
result_text += f"📋 数据点数: {len(values)}\n"
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
async def _create_alert(self, args: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[TextContent]:
"""创建数据告警"""
stream_name = args["stream_name"]
condition = args["condition"]
threshold = args["threshold"]
alert_id = f"alert_{int(time.time())}"
result_text = f"🚨 告警创建成功\n"
result_text += f"🆔 告警ID: {alert_id}\n"
result_text += f"📡 数据流: {stream_name}\n"
result_text += f"⚖️ 条件: {condition}\n"
result_text += f"🎯 阈值: {threshold}\n"
result_text += f"✅ 状态: 已激活\n"
return [TextContent(type="text", text=result_text)]
# 启动实时数据服务器
async def main():
server = RealtimeDataServer()
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.server.run(read_stream, write_stream)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())5. 高级特性与优化
5.1 性能调优策略
MCP应用的性能优化是确保系统高效运行的关键。以下是一些重要的优化策略:
连接池管理
python
# connection_pool.py
import asyncio
from typing import Dict, List
from mcp import ClientSession
class MCPConnectionPool:
def __init__(self, max_connections: int = 10):
self.max_connections = max_connections
self.available_connections: List[ClientSession] = []
self.active_connections: Dict[str, ClientSession] = {}
self.connection_count = 0
self._lock = asyncio.Lock()
async def get_connection(self, server_id: str) -> ClientSession:
"""获取连接"""
async with self._lock:
if server_id in self.active_connections:
return self.active_connections[server_id]
if self.available_connections:
connection = self.available_connections.pop()
self.active_connections[server_id] = connection
return connection
if self.connection_count < self.max_connections:
connection = await self._create_connection()
self.active_connections[server_id] = connection
self.connection_count += 1
return connection
# 等待可用连接
while not self.available_connections:
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
connection = self.available_connections.pop()
self.active_connections[server_id] = connection
return connection
async def release_connection(self, server_id: str):
"""释放连接"""
async with self._lock:
if server_id in self.active_connections:
connection = self.active_connections.pop(server_id)
self.available_connections.append(connection)
async def _create_connection(self) -> ClientSession:
"""创建新连接"""
# 这里应该实现实际的连接创建逻辑
pass缓存机制
python
# cache_manager.py
import asyncio
import time
from typing import Any, Optional, Dict
class MCPCache:
def __init__(self, default_ttl: int = 300): # 5分钟默认TTL
self.cache: Dict[str, Dict[str, Any]] = {}
self.default_ttl = default_ttl
self._lock = asyncio.Lock()
# 启动清理任务
asyncio.create_task(self._cleanup_expired())
async def get(self, key: str) -> Optional[Any]:
"""获取缓存值"""
async with self._lock:
if key in self.cache:
entry = self.cache[key]
if time.time() < entry["expires_at"]:
entry["access_count"] += 1
entry["last_accessed"] = time.time()
return entry["value"]
else:
del self.cache[key]
return None
async def set(self, key: str, value: Any, ttl: Optional[int] = None) -> None:
"""设置缓存值"""
if ttl is None:
ttl = self.default_ttl
async with self._lock:
self.cache[key] = {
"value": value,
"expires_at": time.time() + ttl,
"created_at": time.time(),
"last_accessed": time.time(),
"access_count": 0
}
async def delete(self, key: str) -> bool:
"""删除缓存值"""
async with self._lock:
if key in self.cache:
del self.cache[key]
return True
return False
async def _cleanup_expired(self):
"""清理过期缓存"""
while True:
await asyncio.sleep(60) # 每分钟清理一次
async with self._lock:
current_time = time.time()
expired_keys = [
key for key, entry in self.cache.items()
if current_time >= entry["expires_at"]
]
for key in expired_keys:
del self.cache[key]
async def get_stats(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取缓存统计"""
async with self._lock:
total_entries = len(self.cache)
total_access = sum(entry["access_count"] for entry in self.cache.values())
return {
"total_entries": total_entries,
"total_access": total_access,
"cache_keys": list(self.cache.keys())
}5.2 安全配置最佳实践
身份验证与授权
python
# security_manager.py
import hashlib
import hmac
import time
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
class MCPSecurityManager:
def __init__(self, secret_key: str):
self.secret_key = secret_key.encode()
self.active_tokens: Dict[str, Dict] = {}
self.permissions: Dict[str, List[str]] = {}
def generate_token(self, user_id: str, permissions: List[str], expires_in: int = 3600) -> str:
"""生成访问令牌"""
timestamp = int(time.time())
expires_at = timestamp + expires_in
# 创建令牌载荷
payload = f"{user_id}:{expires_at}:{':'.join(permissions)}"
# 生成签名
signature = hmac.new(
self.secret_key,
payload.encode(),
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
token = f"{payload}:{signature}"
# 存储令牌信息
self.active_tokens[token] = {
"user_id": user_id,
"permissions": permissions,
"expires_at": expires_at,
"created_at": timestamp
}
return token
def verify_token(self, token: str) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""验证访问令牌"""
if token not in self.active_tokens:
return None
token_info = self.active_tokens[token]
# 检查是否过期
if time.time() > token_info["expires_at"]:
del self.active_tokens[token]
return None
# 验证签名
parts = token.split(":")
if len(parts) < 4:
return None
payload = ":".join(parts[:-1])
signature = parts[-1]
expected_signature = hmac.new(
self.secret_key,
payload.encode(),
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
if not hmac.compare_digest(signature, expected_signature):
return None
return token_info
def check_permission(self, token: str, required_permission: str) -> bool:
"""检查权限"""
token_info = self.verify_token(token)
if not token_info:
return False
return required_permission in token_info["permissions"]
def revoke_token(self, token: str) -> bool:
"""撤销令牌"""
if token in self.active_tokens:
del self.active_tokens[token]
return True
return False
# 安全装饰器
def require_permission(permission: str):
"""权限检查装饰器"""
def decorator(func):
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 从请求中获取令牌
token = kwargs.get("auth_token")
if not token:
raise PermissionError("缺少认证令牌")
security_manager = kwargs.get("security_manager")
if not security_manager or not security_manager.check_permission(token, permission):
raise PermissionError(f"权限不足,需要: {permission}")
return await func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return decorator5.3 错误处理与监控
错误处理框架
python
# error_handler.py
import logging
import traceback
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional
from enum import Enum
class ErrorLevel(Enum):
INFO = "info"
WARNING = "warning"
ERROR = "error"
CRITICAL = "critical"
class MCPErrorHandler:
def __init__(self, log_file: str = "mcp_errors.log"):
self.logger = logging.getLogger("MCP")
self.logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# 文件处理器
file_handler = logging.FileHandler(log_file)
file_handler.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# 控制台处理器
console_handler = logging.StreamHandler()
console_handler.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
# 格式化器
formatter = logging.Formatter(
'%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
)
file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
console_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
self.logger.addHandler(file_handler)
self.logger.addHandler(console_handler)
self.error_stats = {
"total_errors": 0,
"error_types": {},
"recent_errors": []
}
def handle_error(self,
error: Exception,
context: Dict[str, Any],
level: ErrorLevel = ErrorLevel.ERROR) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""处理错误"""
error_info = {
"type": type(error).__name__,
"message": str(error),
"context": context,
"traceback": traceback.format_exc(),
"timestamp": time.time()
}
# 记录日志
log_message = f"错误: {error_info['type']} - {error_info['message']}"
if level == ErrorLevel.INFO:
self.logger.info(log_message)
elif level == ErrorLevel.WARNING:
self.logger.warning(log_message)
elif level == ErrorLevel.ERROR:
self.logger.error(log_message)
elif level == ErrorLevel.CRITICAL:
self.logger.critical(log_message)
# 更新统计
self._update_stats(error_info)
# 返回错误响应
return {
"error": True,
"error_type": error_info["type"],
"message": error_info["message"],
"error_id": f"err_{int(time.time())}"
}
def _update_stats(self, error_info: Dict[str, Any]):
"""更新错误统计"""
self.error_stats["total_errors"] += 1
error_type = error_info["type"]
if error_type not in self.error_stats["error_types"]:
self.error_stats["error_types"][error_type] = 0
self.error_stats["error_types"][error_type] += 1
# 保持最近100个错误
self.error_stats["recent_errors"].append(error_info)
if len(self.error_stats["recent_errors"]) > 100:
self.error_stats["recent_errors"] = self.error_stats["recent_errors"][-100:]
def get_error_stats(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取错误统计"""
return self.error_stats.copy()5.4 扩展开发指南
自定义资源处理器
python
# custom_resource_handler.py
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional
from mcp.types import Resource
class CustomResourceHandler(ABC):
"""自定义资源处理器基类"""
@abstractmethod
async def list_resources(self) -> List[Resource]:
"""列出资源"""
pass
@abstractmethod
async def read_resource(self, uri: str) -> str:
"""读取资源"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def supports_uri(self, uri: str) -> bool:
"""检查是否支持URI"""
pass
class GitResourceHandler(CustomResourceHandler):
"""Git仓库资源处理器"""
def __init__(self, repo_path: str):
self.repo_path = repo_path
async def list_resources(self) -> List[Resource]:
"""列出Git仓库中的文件"""
import os
resources = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(self.repo_path):
# 跳过.git目录
if '.git' in dirs:
dirs.remove('.git')
for file in files:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
relative_path = os.path.relpath(file_path, self.repo_path)
resources.append(Resource(
uri=f"git://{relative_path}",
name=file,
description=f"Git文件: {relative_path}",
mimeType=self._get_mime_type(file)
))
return resources
async def read_resource(self, uri: str) -> str:
"""读取Git文件"""
if not uri.startswith("git://"):
raise ValueError("不支持的URI格式")
file_path = uri[6:] # 移除 "git://" 前缀
full_path = os.path.join(self.repo_path, file_path)
if not os.path.exists(full_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"文件不存在: {file_path}")
with open(full_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
return f.read()
def supports_uri(self, uri: str) -> bool:
"""检查是否支持URI"""
return uri.startswith("git://")
def _get_mime_type(self, filename: str) -> str:
"""获取MIME类型"""
ext = os.path.splitext(filename)[1].lower()
mime_types = {
'.py': 'text/x-python',
'.js': 'text/javascript',
'.md': 'text/markdown',
'.txt': 'text/plain',
'.json': 'application/json'
}
return mime_types.get(ext, 'text/plain')
# 资源管理器
class ResourceManager:
def __init__(self):
self.handlers: List[CustomResourceHandler] = []
def register_handler(self, handler: CustomResourceHandler):
"""注册资源处理器"""
self.handlers.append(handler)
async def list_all_resources(self) -> List[Resource]:
"""列出所有资源"""
all_resources = []
for handler in self.handlers:
resources = await handler.list_resources()
all_resources.extend(resources)
return all_resources
async def read_resource(self, uri: str) -> str:
"""读取资源"""
for handler in self.handlers:
if handler.supports_uri(uri):
return await handler.read_resource(uri)
raise ValueError(f"没有处理器支持URI: {uri}")6. 思路扩展与技术总结
6.1 MCP的发展趋势
技术演进方向
MCP作为AI应用的标准化协议,正朝着以下几个方向发展:
1. 更强的互操作性
- 跨平台兼容性增强
- 多语言SDK支持扩展
- 标准化程度进一步提升
2. 性能优化
- 更高效的数据传输协议
- 智能缓存和预加载机制
- 分布式架构支持
3. 安全性增强
- 零信任安全模型
- 端到端加密
- 细粒度权限控制
生态系统建设
python
# 未来MCP生态系统架构示例
class MCPEcosystem:
def __init__(self):
self.registry = MCPServiceRegistry()
self.marketplace = MCPMarketplace()
self.monitor = MCPMonitor()
async def discover_services(self, category: str) -> List[MCPService]:
"""服务发现"""
return await self.registry.find_services(category)
async def install_plugin(self, plugin_id: str) -> bool:
"""插件安装"""
plugin = await self.marketplace.get_plugin(plugin_id)
return await plugin.install()
async def get_system_health(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""系统健康检查"""
return await self.monitor.get_health_status()6.2 潜在应用领域
企业级应用
1. 智能客服系统
- 多渠道数据整合
- 实时知识库访问
- 自动化工单处理
2. 数据分析平台
- 多源数据聚合
- 实时分析引擎
- 智能报表生成
3. 内容管理系统
- 智能内容分类
- 自动化内容审核
- 个性化推荐
开发者工具
1. 代码助手
python
# MCP驱动的代码助手示例
class CodeAssistant:
def __init__(self, mcp_client):
self.mcp = mcp_client
async def analyze_code(self, file_path: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""代码分析"""
code_content = await self.mcp.read_resource(f"file://{file_path}")
analysis = await self.mcp.call_tool("code_analyzer", {
"code": code_content,
"language": self._detect_language(file_path),
"analysis_types": ["complexity", "security", "performance"]
})
return analysis
async def suggest_improvements(self, analysis: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[str]:
"""改进建议"""
suggestions = await self.mcp.call_tool("improvement_suggester", {
"analysis_result": analysis
})
return suggestions2. 文档生成器
3. 测试自动化工具
6.3 技术选型建议
选择MCP的场景
适合使用MCP的情况:
- 需要AI模型访问外部数据
- 要求高安全性和可控性
- 需要标准化的集成方案
- 计划长期维护和扩展
不适合使用MCP的情况:
- 简单的静态数据访问
- 对性能要求极高的场景
- 团队技术栈不匹配
- 项目规模较小
技术栈选择指南
| 项目规模 | 推荐技术栈 | 部署方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 小型项目 | Python + SQLite | 单机部署 |
| 中型项目 | Python/Node.js + PostgreSQL | 容器化部署 |
| 大型项目 | 微服务架构 + 分布式数据库 | Kubernetes集群 |
6.4 学习路径推荐
初学者路径
第一阶段:基础概念
- 理解MCP协议原理
- 学习JSON-RPC基础
- 掌握异步编程概念
第二阶段:实践操作
- 搭建开发环境
- 完成基础示例
- 实现简单的MCP服务器
第三阶段:进阶应用
- 学习安全配置
- 掌握性能优化
- 开发自定义扩展
进阶开发者路径
架构设计
- 分布式MCP架构
- 微服务集成模式
- 高可用性设计
性能优化
- 并发处理优化
- 缓存策略设计
- 网络传输优化
安全加固
- 身份认证机制
- 数据加密传输
- 访问控制策略
学习资源推荐
官方文档
开源项目
社区资源
- MCP开发者论坛
- GitHub讨论区
- 技术博客和教程
总结
MCP(Model Context Protocol)作为现代AI应用的标准化协议,为开发者提供了一个安全、高效、可扩展的解决方案。通过本文的深入介绍,我们了解了:
核心价值
- 标准化:统一的协议规范,降低集成复杂度
- 安全性:内置的安全机制,保障数据访问安全
- 可扩展性:灵活的架构设计,支持各种应用场景
- 易用性:简洁的API设计,降低学习成本
技术优势
- 基于成熟的JSON-RPC 2.0协议
- 支持异步处理和高并发
- 提供丰富的SDK和工具链
- 活跃的开源社区支持
应用前景
MCP在企业级应用、开发者工具、数据分析等领域都有广阔的应用前景。随着AI技术的不断发展,MCP将成为连接AI模型与外部世界的重要桥梁。
发展建议
对于开发者而言,建议:
- 深入理解MCP的核心概念和设计理念
- 通过实际项目积累开发经验
- 关注社区动态,参与生态建设
- 结合具体业务场景,探索创新应用
MCP不仅是一个技术协议,更是AI应用标准化发展的重要里程碑。掌握MCP技术,将为开发者在AI时代的技术竞争中提供有力支撑。
参考资料:
- Model Context Protocol Specification
- Anthropic MCP Documentation
- MCP Python SDK
- JSON-RPC 2.0 Specification
作者简介:
CodeSuc,专注于AI技术和现代软件开发,致力于分享前沿技术知识和实践经验。