排序
一、排序的概念及引用
1、排序的概念
**排序**:所谓排序,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作。(默认都是从小到大排的)
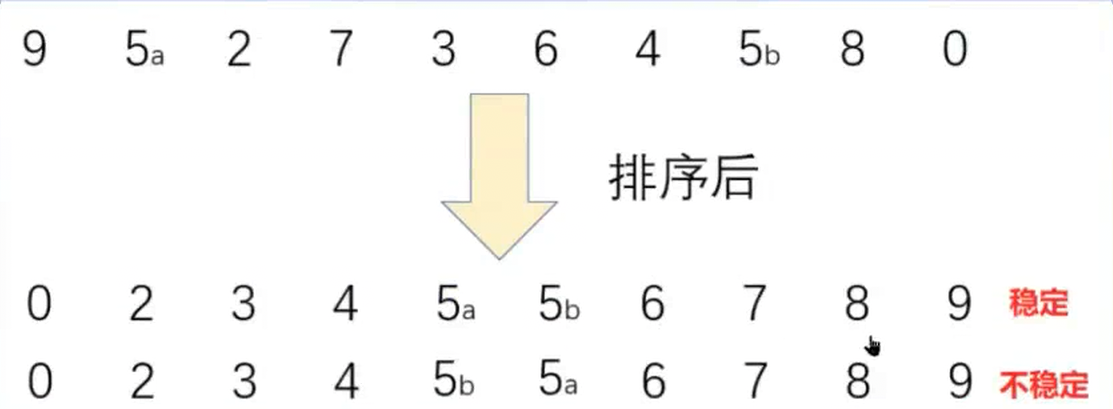稳定性:假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具有相同的关键字的记录,若经过排序,这些记录的相对次序保持不变,即在原序列中,r[i]=r[j],且r[i]在r[j]之前,而在排序后的序列中,r[i]仍在r[j]之前,则称这种排序算法是稳 定的;否则称为不稳定的。
内部排序:数据元素全部放在内存中的排序。
外部排序:数据元素太多不能同时放在内存中,根据排序过程的要求不能在内外存之间移动数据的排序。
2.排序的应用
RAM:8G (运行内存)内部排序
磁盘:1T 外部排序
二、常见排序算法的实现
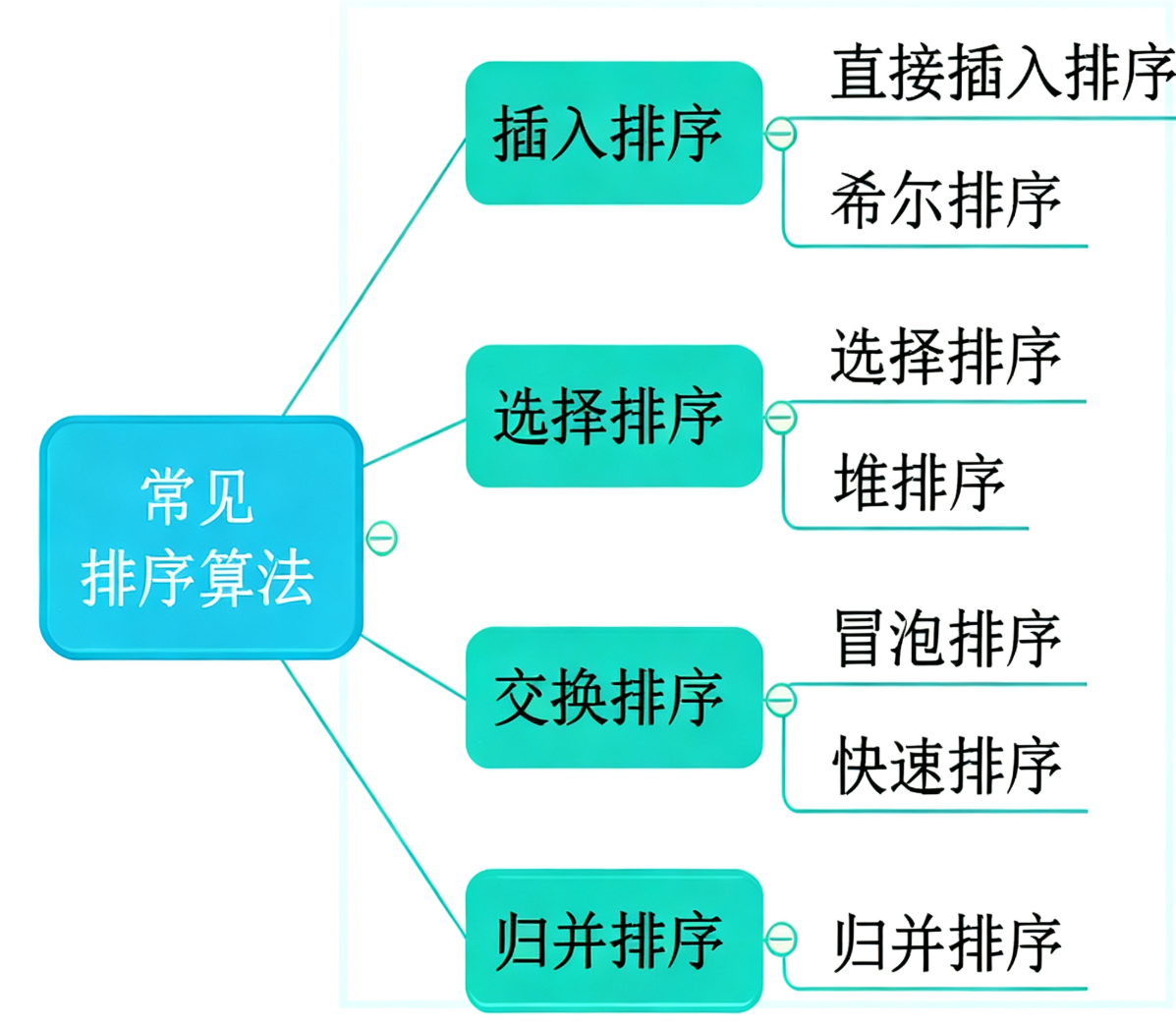
1 插入排序
1.1直接插入排序
直接插入排序是一种简单的插入排序法,其基本思想是:
把待排序的记录按其关键码值的大小逐个插入到一个已经排好序的有序序列中 ,直到所有的记录插入完为止,得到 一个新的有序序列 。实际中我们玩扑克牌时,就用了插入排序的思想。

java
** /**
* 插入排序
* 时间复杂度
* 最坏的时间复杂度(n^2)
* 最好的时间复杂度(n)
* 得出结论:越有序,越快
* 空间复杂度:n(1)
* 稳定性:
* @param array
*/
public static void insertSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
int j = i - 1;
int temp = array[i]; // 暂存当前要插入的元素
// 从已排序区间的末尾向前遍历,寻找插入位置
for (; j >= 0; j--) {
//执行第一次如果是的话覆盖array[i],array[j]往后移动1,空出来一个
if (array[j] > temp) {
//这里有先后顺序,因为是要比你大的时候才会往后移动,是稳定的
// 若已排序元素大于temp,将其向后移动一位
array[j + 1] = array[j];
} else {
// 找到插入位置,退出循环
break;
}
}
// 此时array[j]<temp,将temp插入到正确位置(j+1)
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}在游览器找的动态图我觉得非常形象,大家看一看

该图是游览器借鉴这个博主的,在此声明https://blog.csdn.net/wenjiahui123/article/details/127660742
1.2希尔排序(缩小增量排序)
希尔排序法又称缩小增量法。希尔排序法的基本思想是:**先选定一个整数,把待排序文件中所有记录分成多个组, 所有距离为的记录分在同一组内,并对每一组内的记录进行排序。然后,去重复上述分组和排序的工作。**当到达gap =1时,所有记录在统一组内排好序。
希尔排序(Shell Sort)是插入排序的优化版本,通过引入 "间隔(gap)" 概念,先将数组分成多个子数组进行局部排序,再逐步缩小间隔直至为 1,最终完成全局排序。其核心思想是让数组先接近有序,再用插入排序收尾,可以大幅提升效率。
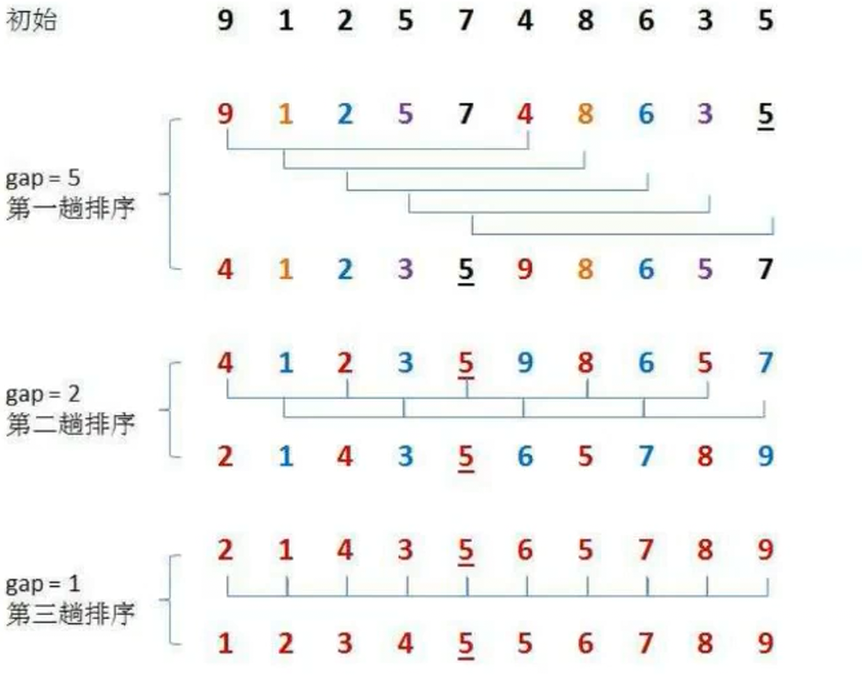
按着上面图的分法:首先这样分5组,然后就是排序
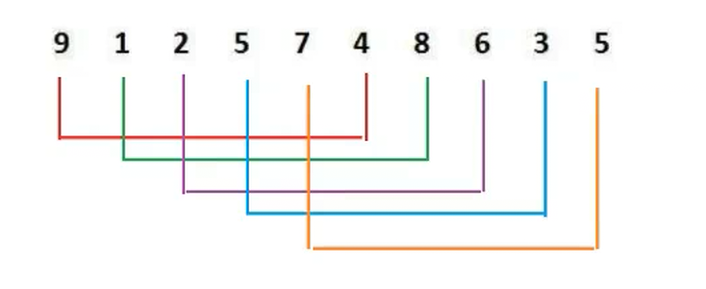
排序的结果是:这样排序的话,就是小的部分基本就在前半部分,更加有序了
java
/**
* 时间复杂度:O(n^1.3 - n^1.5)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 不稳定的排序
* @param array
*/
public static void shellSort(int[] array) {
int gap = array.length;
while (gap > 1) {
gap /= 2;
shell(array,gap);
}
}
/*public static void shellSort(int[] array) {
int gap = array.length;
while (gap > 1) {
gap = gap / 2 + 1; // 保证gap最终能减到1
shell(array, gap);
}
shell(array, 1); // 最后一次gap=1的插入排序
}
*/
private static void shell(int[] array, int gap) {
for (int i = gap; i < array.length; i++) {
int tmp = array[i];
//定位当前元素在 "间隔子数组" 中的前一个元素位置
int j = i-gap;
//在当前 "间隔子数组" 中,从待插入元素的前一位开始,向前遍历寻找合适的插入位置
for (; j >= 0; j -= gap) {
if(array[j] > tmp) {
array[j+gap] = array[j];
}else {
break;
}
}
array[j+gap] = tmp;
}
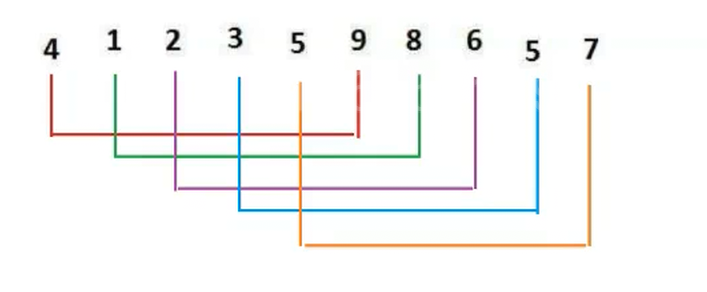
}另一种分法看下图:这里就是在分组和合并组的过程中(预排序)趋向于有序,n的奇数虽然逐渐变大,但是它逐渐趋向与有序,运行的速度也会得到提升
代码如下:
java
public class ShellSortGroup {
public static void shellSortWithGap2(int[] array) {
if (array == null || array.length <= 1) {
return;
}
int n = array.length;
int gap = 2; // 固定间隔为2,实现[0,1]、[2,3]...分组
// 按gap=2分组并排序
for (int i = gap; i < n; i++) {
// 这里i从gap开始,但为了严格按[0,1]、[2,3]...分组,调整遍历方式
// 每组内执行插入排序(组内元素下标为i和i-1,间隔1,但gap=2控制组间间隔)
int temp = array[i];
int j = i - 1; // 组内相邻元素(因为每组内只有两个元素,间隔1)
// 组内排序(对两个元素比较交换)
while (j >= i - gap && j >= 0 && array[j] > temp) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
j--;
}
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
// 最后用gap=1完成全局排序(标准插入排序)
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && array[j] > temp) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
j--;
}
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 1, 4, 2, 7, 5, 8, 6}; // 初始数组
System.out.println("排序前:");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " "); // 输出:3 1 4 2 7 5 8 6
}
shellSortWithGap2(arr);
System.out.println("\n排序后:");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " "); // 输出:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
}
}
}希尔排序 的特性总结:
(1)希尔排序是对直接插入排序的优化。
(2)当gap > 1时都是预排序,目的是让数组更接近于有序。当gap == 1时,数组已经接近有序的了,这样就会很快。这样整体而言,可以达到优化的效果。我们实现后可以进行性能测试的对比。
(3)希尔排序的时间复杂度不好计算,因为gap的取值方法很多,导致很难去计算,因此在好些树中给出的希尔排序的时间复杂度都不固定:
希尔排序时间复杂度的计算
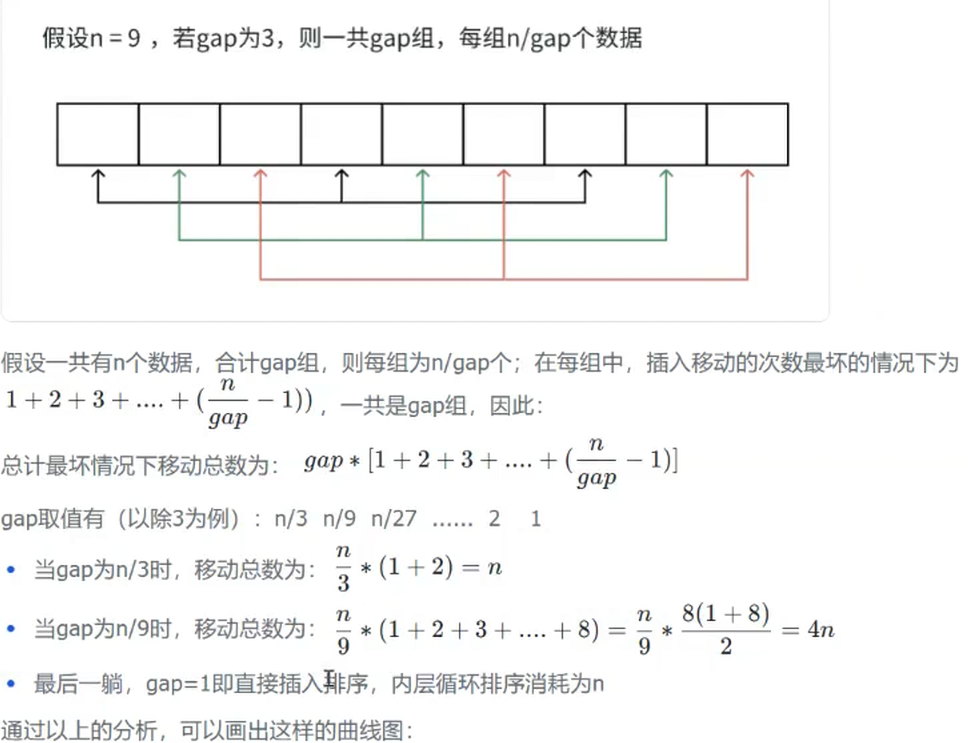
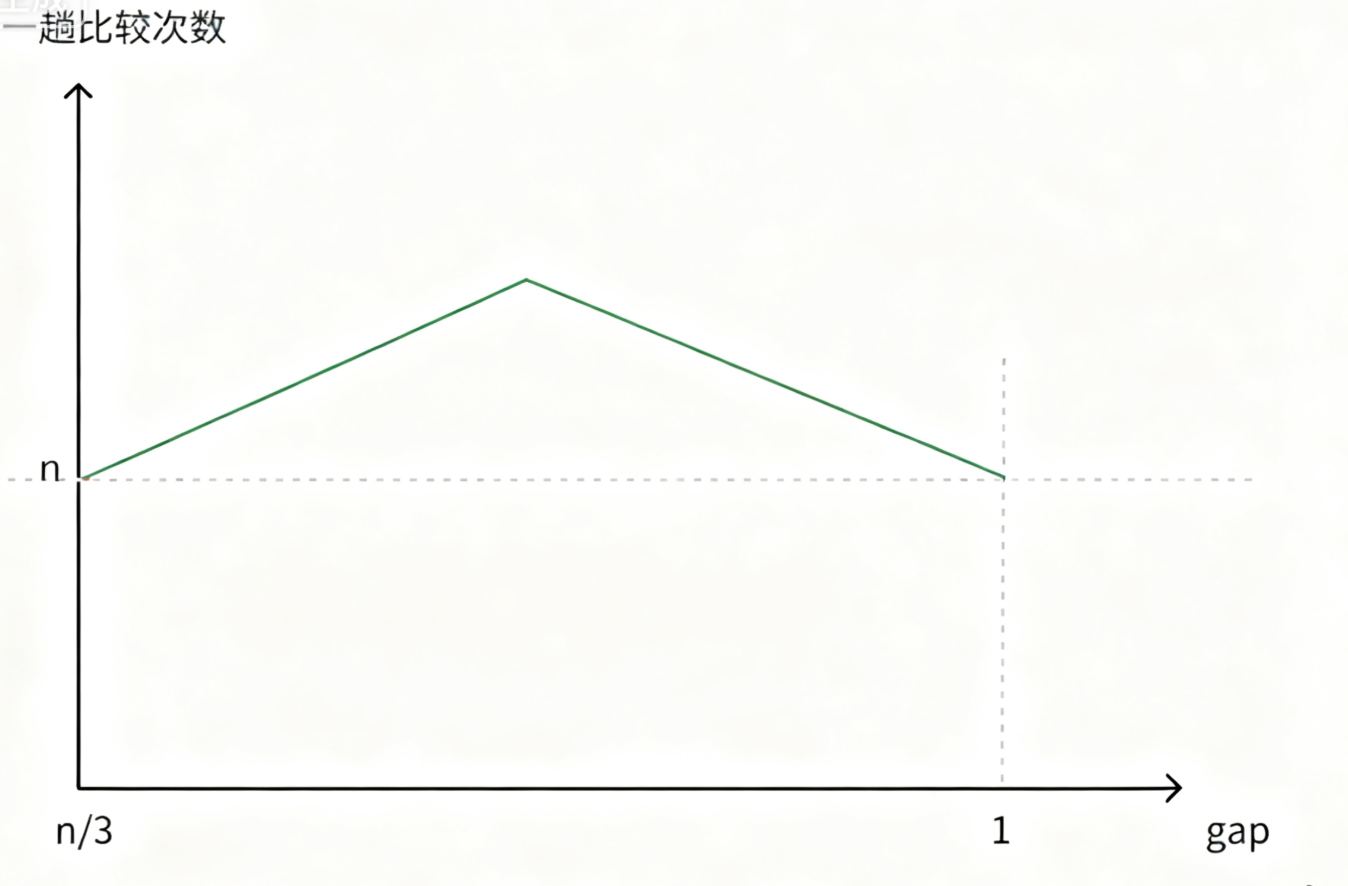
因此,希尔排序在最初和最后的排序次数都为 n(n 为数组长度):前一阶段排序次数呈逐渐上升的状态,当到达某一顶点后,排序次数会逐渐下降至 n,而该顶点的具体计算过程暂时无法给出。希尔排序的时间复杂度难以精确计算,核心原因是 间隔(gap)的取值方式多样(如 "减半法""Knuth 序列" 等),不同 gap 序列对排序次数的影响差异较大,导致时间复杂度没有固定统一的计算结果。在严蔚敏所著的《数据结构(C 语言版)》中,给出的希尔排序时间复杂度范围为 (O(n^{1.3}) \sim O(n^2))(注:书中未指定单一固定值,而是基于常见 gap 序列的复杂度区间)。

2选择排序
2.1 直接选择排序
(1)在元素集合array[i]--array[n-1]中选择关键码最大(小)的数据元素
(2)若它不是这组元素中的最后一个(第一个)元素,则将它与这组元素中的最后一个(第一个)元素交换
(3)在剩余的array[i]--array[n-2](array[i+1]--array[n-1])集合中,重复上述步骤,直到集合剩余1个元素
该图在声明游览器找的,借鉴了https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45667680/article/details/107400977的博主图片
java
/**
* 选择排序 :
* 时间复杂度:O(N^2)
* 没有最好情况 和 最坏情况
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定
* @param array
*/
public static void selectSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < array.length; j++) {
if(array[j] < array[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
swap(array,i,minIndex);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] array,int i,int j) {
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tmp;
}
//System.currentTimeMillis(); 属于 java.lang.System 类,是 Java 核心库中的一个工具类,用于获取当前系统时间与 UTC 1970 年 1 月 1 日 00:00:00 之间的毫秒差值(即时间戳)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 准备测试数组(可根据需要调整大小和内容)
int[] array = new int[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100000); // 生成随机数填充数组
}
// 测试选择排序耗时
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Sort.selectSort(array); // 执行选择排序
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 输出耗时(修正描述为"选择排序")
System.out.println("选择排序耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
}
}3堆排序
堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆积树(堆)这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法,它是选择排序的一种。它是通过堆来进行选择数据。需要注意的是排升序要建大堆,排降序建小堆。
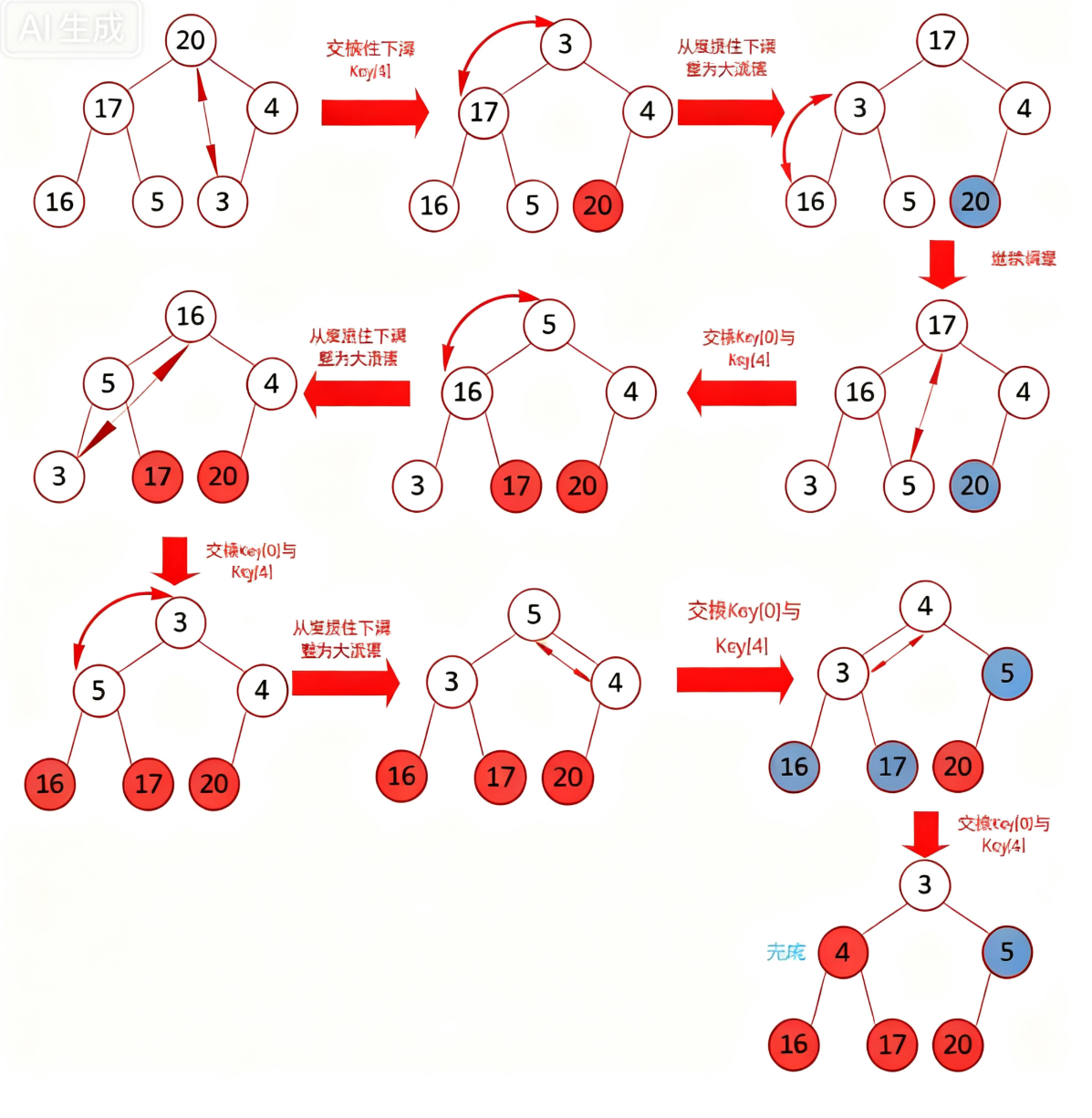
java
/**
* 堆排序
* 时间复杂度:O(n * logN) 对数据不敏感
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定
* @param array
*/
public static void heapSort(int[] array) {
//O(n)
createHeap(array);
//O(n * logN)
int end = array.length-1;
while (end > 0) {
swap(array,0,end);
siftDown(array,0,end);
end--;
}
}
private static void createHeap(int[] array) {
for (int parent = (array.length-1-1)/2; parent >= 0; parent--) {
siftDown(array,parent,array.length);
}
}
private static void siftDown(int[] array, int parent, int length) {
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < length) {
if(child+1 < length && array[child] < array[child+1] ) {
child++;
}
if(array[child] > array[parent]) {
swap(array,child,parent);
//这里是因为加入说换位置了,那我的程序咋直到还完后在这个跟节点和它交换的子节点,这个字节点下面的值是大(小)跟堆,所以又重新往下调
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}