文章目录
- 一、简介
- 二、库内容
-
- [ 1、stdbool.h 头文件定义了以下内容:](# 1、stdbool.h 头文件定义了以下内容:)
- [ 2、bool 是 _Bool 类型的别名。](# 2、bool 是 _Bool 类型的别名。)
- [ 3、使用 <stdbool.h>](# 3、使用 <stdbool.h>)
- 三、实例
-
- [ 1、简单示例:](# 1、简单示例:)
- [ 2、bool 类型实例](# 2、bool 类型实例)
- [ 3、true 和 false 宏实例](# 3、true 和 false 宏实例)
- [ 4、与 if 和 while 等语句配合使用实例](# 4、与 if 和 while 等语句配合使用实例)
- 四、布尔类型与整数的兼容性
- 五、布尔类型的优势
-
- [ 可读性:](# 可读性:)
- [ 标准化:](# 标准化:)
- [ 类型安全:](# 类型安全:)
一、简介
在 C99 标准之前,C 语言中通常使用整数类型(如 int)来表示布尔值。
例如,0 表示假,非零值(通常是 1)表示真。这种方式虽然可行,但缺乏直观性和类型安全性。
为了解决这个问题,C99 标准引入了 stdbool.h 头文件,定义了布尔类型和相关宏。
<stdbool.h> 是 C 语言中的一个标准头文件,定义了布尔类型及其相关的常量。
它使得 C 语言的布尔类型(bool)变得更加明确和可用,避免了使用整数(如 0 或 1)来表示布尔值的传统做法。
二、库内容
1、stdbool.h 头文件定义了以下内容:
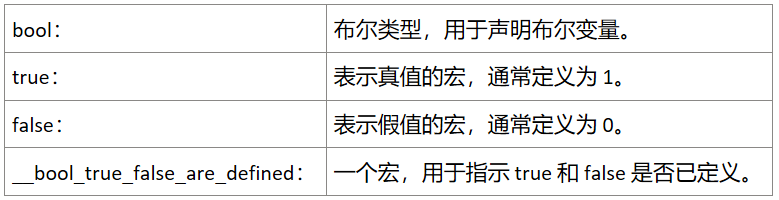
这些宏的定义如下:
c
#define bool _Bool
#define true 1
#define false 0
#define __bool_true_false_are_defined 12、bool 是 _Bool 类型的别名。
_Bool 是 C99 标准中引入的原生类型,表示一个布尔值。_Bool 类型只能保存 0 或 1,因此适合用来存储逻辑值。
c
#include <stdbool.h>
_Bool is_valid = 1; // 也可以直接使用 _Bool 类型3、使用 <stdbool.h>
要在 C 程序中使用布尔类型和相关宏,首先需要引入 <stdbool.h> 头文件:
c
#include <stdbool.h>
bool is_raining = true;
bool is_sunny = false;三、实例
1、简单示例:
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main() {
// 声明布尔变量
bool isReady = true;
bool isFinished = false;
// 使用布尔变量
if (isReady) {
printf("The system is ready.\n");
} else {
printf("The system is not ready.\n");
}
if (!isFinished) {
printf("The task is not finished.\n");
}
// 布尔变量的值
printf("isReady: %d\n", isReady); // 输出 1 (true)
printf("isFinished: %d\n", isFinished); // 输出 0 (false)
return 0;
}
输出结果:
The system is ready.
The task is not finished.
isReady: 1
isFinished: 02、bool 类型实例
使用 bool 类型定义布尔变量:
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main() {
bool flag = true; // 使用 bool 类型
if (flag) {
printf("Flag is true.\n");
} else {
printf("Flag is false.\n");
}
return 0;
}以上实例中,flag 是一个布尔类型的变量,初始值为 true。判断 flag 是否为 true,然后打印相应的消息。
3、true 和 false 宏实例
true 和 false 是预定义的宏,分别对应布尔值 1 和 0,可以直接在条件判断中使用:
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main() {
bool is_logged_in = false;
// 改变布尔值
if (!is_logged_in) {
is_logged_in = true;
printf("User logged in: %s\n", is_logged_in ? "true" : "false");
}
return 0;
}在此代码中,is_logged_in 的初始值是 false,然后在逻辑中将其改变为 true。
4、与 if 和 while 等语句配合使用实例
布尔类型在 if、while、for 等控制结构中很有用:
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main() {
bool condition = false;
while (!condition) {
printf("The condition is false.\n");
condition = true; // 改变条件为真
}
return 0;
}
//这里,while 循环会继续执行,直到 condition 变为 true。四、布尔类型与整数的兼容性
尽管 bool 类型本身是一个专门的类型,但在底层实现上,它通常依赖于整数类型(通常为 int)。因此,true 可以被认为是 1,而 false 则是 0。
注意:在编程时应该避免将布尔值与普通整数混用,尽量保持类型的清晰性和可读性。
实例
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main() {
bool is_active = true;
// 错误的做法:将布尔值与整数混合使用
int status = is_active; // 这行可以正常编译,但最好避免
if (status) {
printf("Status is true.\n");
} else {
printf("Status is false.\n");
}
return 0;
}虽然上述代码会正确执行,但不推荐使用,因为它混合了布尔值和整数类型,容易让代码变得难以理解。
五、布尔类型的优势
可读性:
使用 bool 类型使得程序的意图更加明确,比起使用 int 类型代表真或假,bool 类型能够清晰地表明该变量只用来表示布尔值。
标准化:
<stdbool.h> 提供了一个标准的方式来处理布尔值,避免了使用宏或整数类型来表示布尔值的复杂性。
类型安全:
与 int 类型不同,bool 类型专门用于逻辑判断,减少了类型不匹配的问题。