@浙大疏锦行
今日任务:
- 转化器和估计器的概念
- 管道工程
- ColumnTransformer和Pipeline类
- 整理下全部逻辑的先后顺序,看看能不能制作出适合所有机器学习的通用pipeline
Pipeline,直译为管道,实际上也可以翻译为流水线。通过前面的学习可以发现,对于每一次的操作,基本有些步骤是固定的,每次重新写代码有点浪费时间。因而想到了函数中的封装思想,将可复用的代码封装到一起,便于下次使用,在这里就是用pipeline构建一个完整的机器学习流水线。
前置知识
转换器(Transformer)
转换器基于transform方法,对数据进行预处理和特征提取。
- 预处理:归一化(MinMaxScaler)、标准化(StandardScaler)、缺失值填充(SimpeInputer)
- 特征提取:特征选择(SelectKBest、PCA)、特征组合(CountVectorizer)
转换器顾名思义,重在"转换",所以它不存储数据的状态信息。结合上面的例子和之前的知识,可以知道,转换器就是根据数据学习转换规则,然后应用于新数据。也就是先fit(学习) ,然后transform(应用) ,或者一步到位fit_transform。
下面是代码的例子:
python
# 导入StandardScaler转换器
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 初始化转换器
scaler = StandardScaler()
# 1. 学习训练数据的缩放规则(计算均值和标准差),本身不存储数据
scaler.fit(X_train)
# 2. 应用规则到训练数据和测试数据
X_train_scaled = scaler.transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 也可以使用fit_transform一步完成
# X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)估计器(Estimator)
估计器是实现机器学习算法的对象或类,可从数据中学习模式、进行预测和模型评估。常见的估计器有:
- 分类器:RandomForestClassifier、KNeighborsClassifier、LGBMClassifier
- 回归器:LinearRegression、DecisionTreeRegressor、LassoCV、RidgeCV
- 聚类器:KMeans、DBSCAN
同样地,根据上面的例子,可以明白,估计器的重点是学习和预测,因此它在训练的过程中会存储数据的状态信息。估计器通过学习训练集的数据特点,然后再去预测测试集的结果。也就是先fit ,然后predict。这也就是之前建模过程中提到的三行核心代码:实例化------训练------预测结果。在这里,就可以对于实例化有一个更细的划分,即是转换器初始化还是估计器创建?
python
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# 创建一个回归器
model = LinearRegression()
# 在训练集上训练模型
model.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
# 对测试集进行预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test_scaled)管道(Pipeline)
而管道则可以看作是有多个转换器和估计器按一定顺序连接 在一起,实现fit和transform的功能,每一个estimator依次完成特定的工作,整个流水线有条不紊地进行下去(就跟实际工厂中的流水线一样),最终完成整个机器学习的过程(数据处理和训练),输出结果(得到产品)。
使用pipeline可以保证数据预处理的一致性和可重复性,并防止数据泄露 (独立),使得代码简洁清晰。此外,由于在机器学习中,参数集对于新数据是可重复利用的,因此pipeline在超参数调优这一场景中具有重要应用。
创建一个完整的Pipeline,主要包括以下步骤:
- 数据理解与特征类型list,比如数值型、类别、有序等等
- 创建各类型的转换器transformer(使用Pipeline创建,名称+方法),比如缺失值填充+编码
- 创建ColumnTransformer (名称+转换器对象+列名list),汇总每列的预处理preprocessor
- 创建完整pipeline,预处理+模型训练
- 调用pipeline进行预处理和学习(fit )与预测(predict)
根据以上步骤,下面是具体的代码操作:
1.导入库并划分数据集
python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler,OneHotEncoder,OrdinalEncoder
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,classification_report,confusion_matrix
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import time
data = pd.read_csv(r'data.csv')
data.head()
python
#定义标签和特征
X = data.drop(columns=['Credit Default'],axis=1)
y = data['Credit Default']
print("\n特征和标签分离完成。")
print("特征 X 的形状:", X.shape)
print("标签 y 的形状:", y.shape)
#划分训练集和测试集,8:2
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,train_size=0.8,random_state=42)
print("\n数据集划分完成 (预处理之前)。")
print("X_train 形状:", X_train.shape)
print("X_test 形状:", X_test.shape)
print("y_train 形状:", y_train.shape)
print("y_test 形状:", y_test.shape)2.确定数据类型并进行划分,列表存储。确定后进行列的transformer创建
python
#查看数值型和非数值型数据
obj_cols = X.select_dtypes(include='object').columns.tolist()
non_obj_cols = X.select_dtypes(exclude='object').columns.tolist()
print('非数值型:',obj_cols)
print('数值型:',non_obj_cols)
python
#划分数据类型,便于定义不同的转换器进行预处理
ordinal_features = ['Home Ownership', 'Years in current job','Term'] #离散特征用于顺序编码
nominal_features = ['Purpose'] #离散特征用于独热编码
continuous_features = non_obj_cols #非离散特征,用于标准化处理
#定义每列数据预处理的转换器
#1-缺失值处理+顺序编码,顺序编码从0开始
ordinal_categories = [
['Own Home','Rent','Have Mortgage','Home Mortgage '], #Home Ownership
['< 1 year', '1 year', '2 years', '3 years', '4 years', '5 years', '6 years', '7 years', '8 years', '9 years', '10+ years'], #Years in current job
['Short Term','Long Term'] #Term
] #类似标签编码前的映射字典定义,顺序编码前需定义这个categories
ordinal_transform = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer',SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')), #众数填充
('encoder',OrdinalEncoder(categories=ordinal_categories,handle_unknown='use_encoded_value',unknown_value=-1)) #有序编码
])
print("有序特征处理 Pipeline 定义完成。")
#2-缺失值处理+独热编码
nominal_transform = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer',SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')), #众数填充
('encoder',OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore',sparse_output=False)) #sparse为稀疏的意思,sparse_output=False 使输出为密集数组
])
print("标称特征处理 Pipeline 定义完成。")
#3-缺失值处理+标准化
continuous_transform = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer',SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')), #众数填充
('encoder',StandardScaler())
])
print("连续特征处理 Pipeline 定义完成。")3.使用ColumnTransformer汇总列的预处理
python
#使用ColumnTransformer汇总列的预处理
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
('ordinal',ordinal_transform,ordinal_features),
('nominal',nominal_transform,nominal_features),
('continous',continuous_transform,continuous_features)
],
remainder='passthrough' #如何处理没有在上面列表中指定的列。drop即删去,passthrough即保留这些列,不做任何处理。
)
print("\nColumnTransformer (预处理器) 定义完成。")4.汇总为pipeline
python
#Pipeline汇总
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[
('prepocessor',preprocessor),
('classifier',RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42))
])
print("\n完整流程的Pipe创建完成")5.调用
python
#调用
start_time = time.time()
# 在原始的 X_train, y_train 上拟合整个Pipeline
# Pipeline会自动按顺序执行 preprocessor 的 fit_transform(X_train),
# 然后用处理后的数据和 y_train 拟合 classifier
pipeline.fit(X_train,y_train) #训练
# 在原始的 X_test 上进行预测
# Pipeline会自动按顺序执行 preprocessor 的 transform(X_test),
# 然后用处理后的数据进行 classifier 的 predict
pipeline_pred = pipeline.predict(X_test)
end_time = time.time()
#评估
print('总共时间:{:.4f}s'.format(end_time-start_time))
print('准确率:{}'.format(accuracy_score(y_test,pipeline_pred)))
print('Confusion Matrix:\n{}'.format(confusion_matrix(y_test,pipeline_pred)))
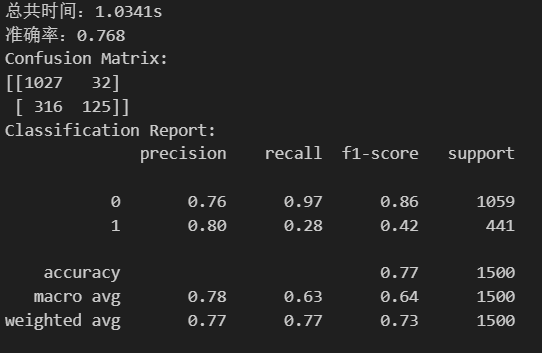
print('Classification Report:\n{}'.format(classification_report(y_test,pipeline_pred)))这是pipeline后的结果:
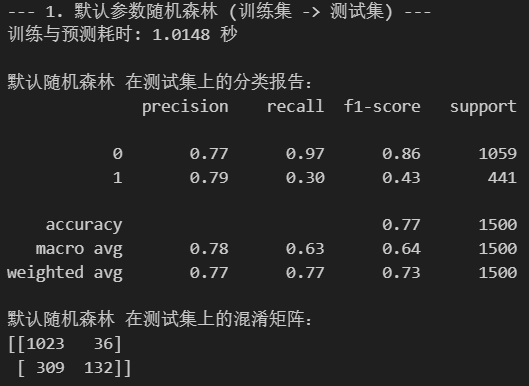
未pipeline的结果:
综上,pipeline把做"做什么"(操作流程)和"怎么做"(参数配置)彻底分开。操作流程就是固定的流水线(就比如乐高底座),而参数就像是可插拔的乐高积木(随意更换),这样就可以实现快速试验不同配置。
以下是完整版本:
python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler,OneHotEncoder,OrdinalEncoder
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,classification_report,confusion_matrix
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import time
data = pd.read_csv(r'data.csv')
data.head()
#定义标签和特征
X = data.drop(columns=['Credit Default'],axis=1)
y = data['Credit Default']
print("\n特征和标签分离完成。")
print("特征 X 的形状:", X.shape)
print("标签 y 的形状:", y.shape)
#划分训练集和测试集,8:2
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,train_size=0.8,random_state=42)
print("\n数据集划分完成 (预处理之前)。")
print("X_train 形状:", X_train.shape)
print("X_test 形状:", X_test.shape)
print("y_train 形状:", y_train.shape)
print("y_test 形状:", y_test.shape)
#查看数值型和非数值型数据
obj_cols = X.select_dtypes(include='object').columns.tolist()
non_obj_cols = X.select_dtypes(exclude='object').columns.tolist()
print('非数值型:',obj_cols)
print('数值型:',non_obj_cols)
#划分数据类型,便于定义不同的转换器进行预处理
ordinal_features = ['Home Ownership', 'Years in current job','Term'] #离散特征用于顺序编码
nominal_features = ['Purpose'] #离散特征用于独热编码
continuous_features = non_obj_cols #非离散特征,用于标准化处理
#定义每列数据预处理的转换器
#1-缺失值处理+顺序编码,顺序编码从0开始
ordinal_categories = [
['Own Home','Rent','Have Mortgage','Home Mortgage '], #Home Ownership
['< 1 year', '1 year', '2 years', '3 years', '4 years', '5 years', '6 years', '7 years', '8 years', '9 years', '10+ years'], #Years in current job
['Short Term','Long Term'] #Term
] #类似标签编码前的映射字典定义,顺序编码前需定义这个categories
ordinal_transform = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer',SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')), #众数填充
('encoder',OrdinalEncoder(categories=ordinal_categories,handle_unknown='use_encoded_value',unknown_value=-1)) #有序编码
])
print("有序特征处理 Pipeline 定义完成。")
#2-缺失值处理+独热编码
nominal_transform = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer',SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')), #众数填充
('encoder',OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore',sparse_output=False)) #sparse为稀疏的意思,sparse_output=False 使输出为密集数组
])
print("标称特征处理 Pipeline 定义完成。")
#3-缺失值处理+标准化
continuous_transform = Pipeline(steps=[
('imputer',SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')), #众数填充
('encoder',StandardScaler())
])
print("连续特征处理 Pipeline 定义完成。")
#使用ColumnTransformer汇总列的预处理
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
('ordinal',ordinal_transform,ordinal_features),
('nominal',nominal_transform,nominal_features),
('continous',continuous_transform,continuous_features)
],
remainder='passthrough' #如何处理没有在上面列表中指定的列。drop即删去,passthrough即保留这些列,不做任何处理。
)
print("\nColumnTransformer (预处理器) 定义完成。")
#Pipeline汇总
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[
('prepocessor',preprocessor),
('classifier',RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42))
])
print("\n完整流程的Pipe创建完成")
#调用
start_time = time.time()
pipeline.fit(X_train,y_train) #训练
pipeline_pred = pipeline.predict(X_test)
end_time = time.time()
#评估
print('总共时间:{:.4f}s'.format(end_time-start_time))
print('准确率:{}'.format(accuracy_score(y_test,pipeline_pred)))
print('Confusion Matrix:\n{}'.format(confusion_matrix(y_test,pipeline_pred)))
print('Classification Report:\n{}'.format(classification_report(y_test,pipeline_pred)))